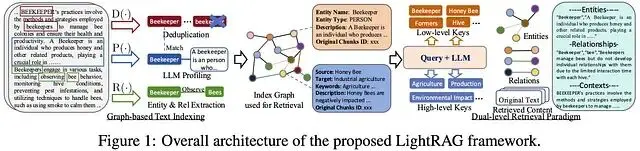
LightRAG 是個開源的 RAG 框架,專門用來快速搭建模塊化的檢索增強生成管道。這個項目在 GitHub 上熱度不低,我們今天來看看他到底怎麼用
基礎安裝與環境配置
LightRAG 的安裝過程很簡單,幾行命令就能搞定:
pip install "lightrag-hku[api]"
cp env.example .env # --->這個有很多參數 非常豐富
lightrag-server官方提供的 UI 界面做得還算不錯,不過測試時基本沒用上,因為更關注的是代碼層面的實現。
環境搭好之後,可以先跑一下官方提供的示例代碼(摘自 readme):
import os
import asyncio
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
from lightrag.llm.openai import gpt_4o_mini_complete, gpt_4o_complete, openai_embed
from lightrag.kg.shared_storage import initialize_pipeline_status
from lightrag.utils import setup_logger
setup_logger("lightrag", level="INFO")
WORKING_DIR = "./rag_storage"
if not os.path.exists(WORKING_DIR):
os.mkdir(WORKING_DIR)
async def initialize_rag():
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
embedding_func=openai_embed,
llm_model_func=gpt_4o_mini_complete,
)
# IMPORTANT: Both initialization calls are required!
await rag.initialize_storages() # Initialize storage backends
await initialize_pipeline_status() # Initialize processing pipeline
return rag
async def main():
try:
# Initialize RAG instance
rag = await initialize_rag()
await rag.ainsert("Your text")
# Perform hybrid search
mode = "hybrid"
print(
await rag.aquery(
"What are the top themes in this story?",
param=QueryParam(mode=mode)
)
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
finally:
if rag:
await rag.finalize_storages()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())官方示例裏還有個基於 Gemini 的版本,看着比較簡單就選了這個來測試:
# pip install -q -U google-genai to use gemini as a client
import os
import numpy as np
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from lightrag.utils import EmbeddingFunc
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
from lightrag.kg.shared_storage import initialize_pipeline_status
import asyncio
import nest_asyncio
# Apply nest_asyncio to solve event loop issues
nest_asyncio.apply()
load_dotenv()
gemini_api_key = os.getenv("GEMINI_API_KEY")
WORKING_DIR = "./dickens"
if os.path.exists(WORKING_DIR):
import shutil
shutil.rmtree(WORKING_DIR)
os.mkdir(WORKING_DIR)
async def llm_model_func(
prompt, system_prompt=None, history_messages=[], keyword_extraction=False, **kwargs
) -> str:
# 1. Initialize the GenAI Client with your Gemini API Key
client = genai.Client(api_key=gemini_api_key)
# 2. Combine prompts: system prompt, history, and user prompt
if history_messages is None:
history_messages = []
combined_prompt = ""
if system_prompt:
combined_prompt += f"{system_prompt}\n"
for msg in history_messages:
# Each msg is expected to be a dict: {"role": "...", "content": "..."}
combined_prompt += f"{msg['role']}: {msg['content']}\n"
# Finally, add the new user prompt
combined_prompt += f"user: {prompt}"
# 3. Call the Gemini model
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-1.5-flash",
contents=[combined_prompt],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(max_output_tokens=500, temperature=0.1),
)
# 4. Return the response text
return response.text
async def embedding_func(texts: list[str]) -> np.ndarray:
model = SentenceTransformer("all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
embeddings = model.encode(texts, convert_to_numpy=True)
return embeddings
async def initialize_rag():
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=llm_model_func,
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
embedding_dim=384,
max_token_size=8192,
func=embedding_func,
),
)
await rag.initialize_storages()
await initialize_pipeline_status()
return rag
def main():
# Initialize RAG instance
rag = asyncio.run(initialize_rag())
file_path = "story.txt"
with open(file_path, "r") as file:
text = file.read()
rag.insert(text)
response = rag.query(
query="What is the main theme of the story?",
param=QueryParam(mode="hybrid", top_k=5, response_type="single line"),
)
print(response)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main().env配置文件的參數非常豐富,需要根據實際使用的工具鏈做適配。為了調用本地模型,我這裏用Ollama 做了相應調整。
### This is sample file of .env
###########################
### Server Configuration
###########################
HOST=0.0.0.0
PORT=9621
WEBUI_TITLE='My Graph KB'
WEBUI_DESCRIPTION="Simple and Fast Graph Based RAG System"
# WORKERS=2
### gunicorn worker timeout(as default LLM request timeout if LLM_TIMEOUT is not set)
# TIMEOUT=150
# CORS_ORIGINS=http://localhost:3000,http://localhost:8080
### Optional SSL Configuration
# SSL=true
# SSL_CERTFILE=/path/to/cert.pem
# SSL_KEYFILE=/path/to/key.pem
### Directory Configuration (defaults to current working directory)
### Default value is ./inputs and ./rag_storage
# INPUT_DIR=<absolute_path_for_doc_input_dir>
# WORKING_DIR=<absolute_path_for_working_dir>
### Tiktoken cache directory (Store cached files in this folder for offline deployment)
# TIKTOKEN_CACHE_DIR=/app/data/tiktoken
### Ollama Emulating Model and Tag
# OLLAMA_EMULATING_MODEL_NAME=lightrag
OLLAMA_EMULATING_MODEL_TAG=latest
### Max nodes return from graph retrieval in webui
# MAX_GRAPH_NODES=1000
### Logging level
# LOG_LEVEL=INFO
# VERBOSE=False
# LOG_MAX_BYTES=10485760
# LOG_BACKUP_COUNT=5
### Logfile location (defaults to current working directory)
# LOG_DIR=/path/to/log/directory
#####################################
### Login and API-Key Configuration
#####################################
# AUTH_ACCOUNTS='admin:admin123,user1:pass456'
# TOKEN_SECRET=Your-Key-For-LightRAG-API-Server
# TOKEN_EXPIRE_HOURS=48
# GUEST_TOKEN_EXPIRE_HOURS=24
# JWT_ALGORITHM=HS256
### API-Key to access LightRAG Server API
# LIGHTRAG_API_KEY=your-secure-api-key-here
# WHITELIST_PATHS=/health,/api/*
######################################################################################
### Query Configuration
###
### How to control the context length sent to LLM:
### MAX_ENTITY_TOKENS + MAX_RELATION_TOKENS < MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS
### Chunk_Tokens = MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS - Actual_Entity_Tokens - Actual_Relation_Tokens
######################################################################################
# LLM response cache for query (Not valid for streaming response)
ENABLE_LLM_CACHE=true
# COSINE_THRESHOLD=0.2
### Number of entities or relations retrieved from KG
# TOP_K=40
### Maximum number or chunks for naive vector search
# CHUNK_TOP_K=20
### control the actual entities send to LLM
# MAX_ENTITY_TOKENS=6000
### control the actual relations send to LLM
# MAX_RELATION_TOKENS=8000
### control the maximum tokens send to LLM (include entities, relations and chunks)
# MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS=30000
### chunk selection strategies
### VECTOR: Pick KG chunks by vector similarity, delivered chunks to the LLM aligning more closely with naive retrieval
### WEIGHT: Pick KG chunks by entity and chunk weight, delivered more solely KG related chunks to the LLM
### If reranking is enabled, the impact of chunk selection strategies will be diminished.
# KG_CHUNK_PICK_METHOD=VECTOR
#########################################################
### Reranking configuration
### RERANK_BINDING type: null, cohere, jina, aliyun
### For rerank model deployed by vLLM use cohere binding
#########################################################
RERANK_BINDING=null
### Enable rerank by default in query params when RERANK_BINDING is not null
# RERANK_BY_DEFAULT=True
### rerank score chunk filter(set to 0.0 to keep all chunks, 0.6 or above if LLM is not strong enough)
# MIN_RERANK_SCORE=0.0
### For local deployment with vLLM
# RERANK_MODEL=BAAI/bge-reranker-v2-m3
# RERANK_BINDING_HOST=http://localhost:8000/v1/rerank
# RERANK_BINDING_API_KEY=your_rerank_api_key_here
### Default value for Cohere AI
# RERANK_MODEL=rerank-v3.5
# RERANK_BINDING_HOST=https://api.cohere.com/v2/rerank
# RERANK_BINDING_API_KEY=your_rerank_api_key_here
### Default value for Jina AI
# RERANK_MODEL=jina-reranker-v2-base-multilingual
# RERANK_BINDING_HOST=https://api.jina.ai/v1/rerank
# RERANK_BINDING_API_KEY=your_rerank_api_key_here
### Default value for Aliyun
# RERANK_MODEL=gte-rerank-v2
# RERANK_BINDING_HOST=https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/api/v1/services/rerank/text-rerank/text-rerank
# RERANK_BINDING_API_KEY=your_rerank_api_key_here
########################################
### Document processing configuration
########################################
ENABLE_LLM_CACHE_FOR_EXTRACT=true
### Document processing output language: English, Chinese, French, German ...
SUMMARY_LANGUAGE=English
### Entity types that the LLM will attempt to recognize
# ENTITY_TYPES='["Person", "Creature", "Organization", "Location", "Event", "Concept", "Method", "Content", "Data", "Artifact", "NaturalObject"]'
### Chunk size for document splitting, 500~1500 is recommended
# CHUNK_SIZE=1200
# CHUNK_OVERLAP_SIZE=100
### Number of summary segments or tokens to trigger LLM summary on entity/relation merge (at least 3 is recommended)
# FORCE_LLM_SUMMARY_ON_MERGE=8
### Max description token size to trigger LLM summary
# SUMMARY_MAX_TOKENS = 1200
### Recommended LLM summary output length in tokens
# SUMMARY_LENGTH_RECOMMENDED_=600
### Maximum context size sent to LLM for description summary
# SUMMARY_CONTEXT_SIZE=12000
### control the maximum chunk_ids stored in vector and graph db
# MAX_SOURCE_IDS_PER_ENTITY=300
# MAX_SOURCE_IDS_PER_RELATION=300
### control chunk_ids limitation method: FIFO, KEEP
### FIFO: First in first out
### KEEP: Keep oldest (less merge action and faster)
# SOURCE_IDS_LIMIT_METHOD=FIFO
# Maximum number of file paths stored in entity/relation file_path field (For displayed only, does not affect query performance)
# MAX_FILE_PATHS=100
### maximum number of related chunks per source entity or relation
### The chunk picker uses this value to determine the total number of chunks selected from KG(knowledge graph)
### Higher values increase re-ranking time
# RELATED_CHUNK_NUMBER=5
###############################
### Concurrency Configuration
###############################
### Max concurrency requests of LLM (for both query and document processing)
MAX_ASYNC=4
### Number of parallel processing documents(between 2~10, MAX_ASYNC/3 is recommended)
MAX_PARALLEL_INSERT=2
### Max concurrency requests for Embedding
# EMBEDDING_FUNC_MAX_ASYNC=8
### Num of chunks send to Embedding in single request
# EMBEDDING_BATCH_NUM=10
###########################################################
### LLM Configuration
### LLM_BINDING type: openai, ollama, lollms, azure_openai, aws_bedrock
###########################################################
### LLM request timeout setting for all llm (0 means no timeout for Ollma)
# LLM_TIMEOUT=180
LLM_BINDING=ollama
LLM_MODEL=granite4:latest
LLM_BINDING_HOST=http://localhost:11434
[#LLM](#LLM)_BINDING_API_KEY=your_api_key
### Optional for Azure
# AZURE_OPENAI_API_VERSION=2024-08-01-preview
# AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT=gpt-4o
### Openrouter example
# LLM_MODEL=google/gemini-2.5-flash
# LLM_BINDING_HOST=https://openrouter.ai/api/v1
# LLM_BINDING_API_KEY=your_api_key
# LLM_BINDING=openai
### OpenAI Compatible API Specific Parameters
### Increased temperature values may mitigate infinite inference loops in certain LLM, such as Qwen3-30B.
# OPENAI_LLM_TEMPERATURE=0.9
### Set the max_tokens to mitigate endless output of some LLM (less than LLM_TIMEOUT * llm_output_tokens/second, i.e. 9000 = 180s * 50 tokens/s)
### Typically, max_tokens does not include prompt content, though some models, such as Gemini Models, are exceptions
### For vLLM/SGLang deployed models, or most of OpenAI compatible API provider
# OPENAI_LLM_MAX_TOKENS=9000
### For OpenAI o1-mini or newer modles
[#OPENAI](#OPENAI)_LLM_MAX_COMPLETION_TOKENS=9000
#### OpenAI's new API utilizes max_completion_tokens instead of max_tokens
# OPENAI_LLM_MAX_COMPLETION_TOKENS=9000
### use the following command to see all support options for OpenAI, azure_openai or OpenRouter
### lightrag-server --llm-binding openai --help
### OpenAI Specific Parameters
# OPENAI_LLM_REASONING_EFFORT=minimal
### OpenRouter Specific Parameters
# OPENAI_LLM_EXTRA_BODY='{"reasoning": {"enabled": false}}'
### Qwen3 Specific Parameters deploy by vLLM
# OPENAI_LLM_EXTRA_BODY='{"chat_template_kwargs": {"enable_thinking": false}}'
### use the following command to see all support options for Ollama LLM
### If LightRAG deployed in Docker uses host.docker.internal instead of localhost in LLM_BINDING_HOST
### lightrag-server --llm-binding ollama --help
### Ollama Server Specific Parameters
### OLLAMA_LLM_NUM_CTX must be provided, and should at least larger than MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS + 2000
OLLAMA_LLM_NUM_CTX=32768
### Set the max_output_tokens to mitigate endless output of some LLM (less than LLM_TIMEOUT * llm_output_tokens/second, i.e. 9000 = 180s * 50 tokens/s)
# OLLAMA_LLM_NUM_PREDICT=9000
### Stop sequences for Ollama LLM
# OLLAMA_LLM_STOP='["</s>", "<|EOT|>"]'
### Bedrock Specific Parameters
# BEDROCK_LLM_TEMPERATURE=1.0
####################################################################################
### Embedding Configuration (Should not be changed after the first file processed)
### EMBEDDING_BINDING: ollama, openai, azure_openai, jina, lollms, aws_bedrock
####################################################################################
# EMBEDDING_TIMEOUT=30
EMBEDDING_BINDING=ollama
EMBEDDING_MODEL=granite-embedding:latest
EMBEDDING_DIM=1024
EMBEDDING_BINDING_API_KEY=your_api_key
# If LightRAG deployed in Docker uses host.docker.internal instead of localhost
EMBEDDING_BINDING_HOST=http://localhost:11434
### OpenAI compatible (VoyageAI embedding openai compatible)
# EMBEDDING_BINDING=openai
# EMBEDDING_MODEL=text-embedding-3-large
# EMBEDDING_DIM=3072
# EMBEDDING_BINDING_HOST=https://api.openai.com/v1
# EMBEDDING_BINDING_API_KEY=your_api_key
### Optional for Azure
# AZURE_EMBEDDING_DEPLOYMENT=text-embedding-3-large
# AZURE_EMBEDDING_API_VERSION=2023-05-15
# AZURE_EMBEDDING_ENDPOINT=your_endpoint
# AZURE_EMBEDDING_API_KEY=your_api_key
### Jina AI Embedding
# EMBEDDING_BINDING=jina
# EMBEDDING_BINDING_HOST=https://api.jina.ai/v1/embeddings
# EMBEDDING_MODEL=jina-embeddings-v4
# EMBEDDING_DIM=2048
# EMBEDDING_BINDING_API_KEY=your_api_key
### Optional for Ollama embedding
OLLAMA_EMBEDDING_NUM_CTX=8192
### use the following command to see all support options for Ollama embedding
### lightrag-server --embedding-binding ollama --help
####################################################################
### WORKSPACE sets workspace name for all storage types
### for the purpose of isolating data from LightRAG instances.
### Valid workspace name constraints: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, and _
####################################################################
# WORKSPACE=space1
############################
### Data storage selection
############################
### Default storage (Recommended for small scale deployment)
# LIGHTRAG_KV_STORAGE=JsonKVStorage
# LIGHTRAG_DOC_STATUS_STORAGE=JsonDocStatusStorage
# LIGHTRAG_GRAPH_STORAGE=NetworkXStorage
# LIGHTRAG_VECTOR_STORAGE=NanoVectorDBStorage
### Redis Storage (Recommended for production deployment)
# LIGHTRAG_KV_STORAGE=RedisKVStorage
# LIGHTRAG_DOC_STATUS_STORAGE=RedisDocStatusStorage
### Vector Storage (Recommended for production deployment)
# LIGHTRAG_VECTOR_STORAGE=MilvusVectorDBStorage
# LIGHTRAG_VECTOR_STORAGE=QdrantVectorDBStorage
# LIGHTRAG_VECTOR_STORAGE=FaissVectorDBStorage
### Graph Storage (Recommended for production deployment)
# LIGHTRAG_GRAPH_STORAGE=Neo4JStorage
# LIGHTRAG_GRAPH_STORAGE=MemgraphStorage
### PostgreSQL
# LIGHTRAG_KV_STORAGE=PGKVStorage
# LIGHTRAG_DOC_STATUS_STORAGE=PGDocStatusStorage
# LIGHTRAG_GRAPH_STORAGE=PGGraphStorage
# LIGHTRAG_VECTOR_STORAGE=PGVectorStorage
### MongoDB (Vector storage only available on Atlas Cloud)
# LIGHTRAG_KV_STORAGE=MongoKVStorage
# LIGHTRAG_DOC_STATUS_STORAGE=MongoDocStatusStorage
# LIGHTRAG_GRAPH_STORAGE=MongoGraphStorage
# LIGHTRAG_VECTOR_STORAGE=MongoVectorDBStorage
### PostgreSQL Configuration
POSTGRES_HOST=localhost
POSTGRES_PORT=5432
POSTGRES_USER=your_username
POSTGRES_PASSWORD='your_password'
POSTGRES_DATABASE=your_database
POSTGRES_MAX_CONNECTIONS=12
# POSTGRES_WORKSPACE=forced_workspace_name
### PostgreSQL Vector Storage Configuration
### Vector storage type: HNSW, IVFFlat
POSTGRES_VECTOR_INDEX_TYPE=HNSW
POSTGRES_HNSW_M=16
POSTGRES_HNSW_EF=200
POSTGRES_IVFFLAT_LISTS=100
### PostgreSQL Connection Retry Configuration (Network Robustness)
### Number of retry attempts (1-10, default: 3)
### Initial retry backoff in seconds (0.1-5.0, default: 0.5)
### Maximum retry backoff in seconds (backoff-60.0, default: 5.0)
### Connection pool close timeout in seconds (1.0-30.0, default: 5.0)
# POSTGRES_CONNECTION_RETRIES=3
# POSTGRES_CONNECTION_RETRY_BACKOFF=0.5
# POSTGRES_CONNECTION_RETRY_BACKOFF_MAX=5.0
# POSTGRES_POOL_CLOSE_TIMEOUT=5.0
### PostgreSQL SSL Configuration (Optional)
# POSTGRES_SSL_MODE=require
# POSTGRES_SSL_CERT=/path/to/client-cert.pem
# POSTGRES_SSL_KEY=/path/to/client-key.pem
# POSTGRES_SSL_ROOT_CERT=/path/to/ca-cert.pem
# POSTGRES_SSL_CRL=/path/to/crl.pem
### PostgreSQL Server Settings (for Supabase Supavisor)
# Use this to pass extra options to the PostgreSQL connection string.
# For Supabase, you might need to set it like this:
# POSTGRES_SERVER_SETTINGS="options=reference%3D[project-ref]"
# Default is 100 set to 0 to disable
# POSTGRES_STATEMENT_CACHE_SIZE=100
### Neo4j Configuration
NEO4J_URI=neo4j+s://xxxxxxxx.databases.neo4j.io
NEO4J_USERNAME=neo4j
NEO4J_PASSWORD='your_password'
NEO4J_DATABASE=neo4j
NEO4J_MAX_CONNECTION_POOL_SIZE=100
NEO4J_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT=30
NEO4J_CONNECTION_ACQUISITION_TIMEOUT=30
NEO4J_MAX_TRANSACTION_RETRY_TIME=30
NEO4J_MAX_CONNECTION_LIFETIME=300
NEO4J_LIVENESS_CHECK_TIMEOUT=30
NEO4J_KEEP_ALIVE=true
# NEO4J_WORKSPACE=forced_workspace_name
### MongoDB Configuration
MONGO_URI=mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017/
[#MONGO](#MONGO)_URI=mongodb+srv://xxxx
MONGO_DATABASE=LightRAG
# MONGODB_WORKSPACE=forced_workspace_name
### Milvus Configuration
MILVUS_URI=http://localhost:19530
MILVUS_DB_NAME=lightrag
# MILVUS_USER=root
# MILVUS_PASSWORD=your_password
# MILVUS_TOKEN=your_token
# MILVUS_WORKSPACE=forced_workspace_name
### Qdrant
QDRANT_URL=http://localhost:6333
# QDRANT_API_KEY=your-api-key
# QDRANT_WORKSPACE=forced_workspace_name
### Redis
REDIS_URI=redis://localhost:6379
REDIS_SOCKET_TIMEOUT=30
REDIS_CONNECT_TIMEOUT=10
REDIS_MAX_CONNECTIONS=100
REDIS_RETRY_ATTEMPTS=3
# REDIS_WORKSPACE=forced_workspace_name
### Memgraph Configuration
MEMGRAPH_URI=bolt://localhost:7687
MEMGRAPH_USERNAME=
MEMGRAPH_PASSWORD=
MEMGRAPH_DATABASE=memgraph
# MEMGRAPH_WORKSPACE=forced_workspace_name參考前面的 Gemini 示例,寫了下面的代碼包含了一些硬編碼文本的測試代碼:
# 準備環境
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install "lightrag-hku[api]"
pip install ollama import os
import asyncio
from functools import partial
from datetime import datetime
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
try:
from ollama import AsyncClient
except ImportError:
print("Warning: The 'ollama' Python package is required. Please run: pip install ollama")
class AsyncClient:
def __init__(self, host): pass
async def chat(self, **kwargs): raise NotImplementedError("ollama package not installed.")
from lightrag.llm.ollama import ollama_embed
from lightrag.utils import setup_logger, EmbeddingFunc
from lightrag.kg.shared_storage import initialize_pipeline_status
OLLAMA_BASE_URL = "http://localhost:11434"
LLM_MODEL = "granite4:latest"
EMBEDDING_MODEL = "granite-embedding:latest"
WORKING_DIR = "./rag_storage_ollama"
EMBEDDING_DIMENSION = 384
OUTPUT_DIR = "./output"
setup_logger("lightrag", level="INFO")
if not os.path.exists(WORKING_DIR):
os.mkdir(WORKING_DIR)
if not os.path.exists(OUTPUT_DIR):
os.mkdir(OUTPUT_DIR)
async def custom_ollama_llm_complete(prompt: str, system_prompt: str = None, **kwargs):
"""
A custom function that handles the Ollama client initialization and model/base_url
parameters that are injected via functools.partial, while robustly filtering out
unwanted internal keywords.
"""
model = kwargs.pop('model')
base_url = kwargs.pop('base_url')
client = AsyncClient(host=base_url)
messages = []
if system_prompt:
messages.append({"role": "system", "content": system_prompt})
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})
keys_to_filter = {
'host',
'hashing_kv',
'llm_model_name',
'history_messages',
'keyword_extraction',
'enable_cot',
'is_system_prompt_only',
'prompt_config'
}
cleaned_kwargs = {k: v for k, v in kwargs.items() if k not in keys_to_filter}
try:
response = await client.chat(
model=model,
messages=messages,
**cleaned_kwargs
)
return response['message']['content']
except Exception as e:
raise e
async def initialize_rag():
"""Initializes the LightRAG instance using standard Ollama configuration."""
configured_ollama_complete = partial(
custom_ollama_llm_complete,
model=LLM_MODEL,
base_url=OLLAMA_BASE_URL,
)
configured_ollama_embed = partial(
ollama_embed,
embed_model=EMBEDDING_MODEL,
base_url=OLLAMA_BASE_URL
)
wrapped_embedding_func = EmbeddingFunc(
embedding_dim=EMBEDDING_DIMENSION,
func=configured_ollama_embed,
)
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=configured_ollama_complete,
embedding_func=wrapped_embedding_func,
)
await rag.initialize_storages()
await initialize_pipeline_status()
return rag
async def main():
rag = None
query = "How does RAG solve the problem of LLM hallucination and what are its main use cases?"
try:
print("Checking if required Ollama models are pulled...")
# the knowledge source
sample_text = """
The concept of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a critical development
in the field of large language models (LLMs). It addresses the 'hallucination'
problem by grounding LLM responses in external, verified knowledge sources.
Instead of relying solely on the LLM's static training data, RAG first retrieves
relevant documents from a knowledge base (often a vector store) and then feeds
these documents, alongside the user's query, to the LLM for generation.
This two-step process significantly improves the accuracy, relevance, and
transparency of the generated output. Popular applications include enterprise
search, customer support, and domain-specific QA systems.
"""
print(f"--- 1. Initializing RAG with Ollama Models ---")
rag = await initialize_rag()
print(f"\n--- 2. Inserting Sample Text ({len(sample_text.split())} words) ---")
await rag.ainsert(sample_text)
print("Insertion complete. Data is ready for retrieval.")
mode = "hybrid"
print(f"\n--- 3. Querying the RAG System (Mode: {mode}) ---")
print(f"Query: '{query}'")
rag_result = await rag.aquery(
query,
param=QueryParam(mode=mode)
)
response_text = None
if hasattr(rag_result, 'get_response_text'):
response_text = rag_result.get_response_text()
elif isinstance(rag_result, str):
response_text = rag_result
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("FINAL RAG RESPONSE")
print("="*50)
output_content = "" # Prepare string for file output
if response_text and not str(response_text).strip().startswith("Error:"):
print(response_text)
output_content += f"# RAG Query Result\n\n"
output_content += f"## Query\n\n> {query}\n\n"
output_content += f"## LLM/Cache Response\n\n{response_text}\n\n"
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("\n--- Context Retrieved (Sources) ---")
output_content += f"## Retrieved Context (Sources)\n\n"
if not isinstance(rag_result, str) and rag_result.retriever_output and rag_result.retriever_output.docs:
for i, doc in enumerate(rag_result.retriever_output.docs):
source_text = doc.text
print(f"Source {i+1}: {source_text[:100]}...")
output_content += f"### Source {i+1}\n\n"
output_content += f"```text\n{source_text}\n```\n"
else:
print("No context documents were retrieved (or result was a cache hit string).")
output_content += "No context documents were retrieved (or result was a cache hit string).\n"
else:
error_message = "LLM failed to generate a response (Check Ollama logs for details)."
print(error_message)
output_content += f"# RAG Query Result\n\n## Error\n\n{error_message}\n\n"
if response_text:
print(f"\nError String from LightRAG: {response_text}")
output_content += f"**Error Detail:** {response_text}\n"
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
filename = f"rag_query_output_{timestamp}.md"
output_filepath = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, filename)
with open(output_filepath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(output_content)
print(f"\n--- Output Written to File ---")
print(f"Successfully wrote output to: {output_filepath}")
except Exception as e:
if "'str' object has no attribute 'retriever_output'" in str(e):
print("\n--- ERROR BYPASS: Detected Cache Hit String Result ---")
print("The response was successfully retrieved from the cache and written to the output file.")
else:
# For all other (real) exceptions, print the detailed error block
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("AN ERROR OCCURRED DURING RAG PROCESS")
print("="*50)
print(f"Error: {e}")
print(f"Please ensure Ollama is running and accessible at {OLLAMA_BASE_URL}, and the models '{LLM_MODEL}' and '{EMBEDDING_MODEL}' are pulled locally.")
print(f"To pull: 'ollama pull {LLM_MODEL}' and 'ollama pull {EMBEDDING_MODEL}'")
print("="*50 + "\n")
finally:
if rag:
print("\n--- Finalizing storages ---")
await rag.finalize_storages()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())雖然
.env文件裏有參數可以配置 input 文件夾路徑,但測試時直接在代碼裏寫死了路徑。
運行後的輸出包括控制枱日誌和 markdown 格式的結果文件,結果太長我就不貼了。
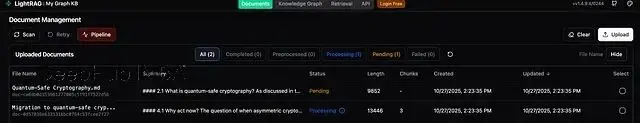
接下來測試了更實際的場景:準備了幾份 markdown 格式的文檔(其他格式應該也支持,但沒測),用這些文檔構建了自己的 RAG 系統,繼續用 Ollama 和 Granite 模型來驗證效果,這次的代碼就沒那麼硬編碼了。
.env文件提供了 input 文件夾的配置選項,不過這裏還是用的硬編碼方式
import os
import asyncio
from functools import partial
from datetime import datetime
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
import glob
try:
from ollama import AsyncClient
except ImportError:
print("Warning: The 'ollama' Python package is required. Please run: pip install ollama")
class AsyncClient:
def __init__(self, host): pass
async def chat(self, **kwargs): raise NotImplementedError("ollama package not installed.")
from lightrag.llm.ollama import ollama_embed
from lightrag.utils import setup_logger, EmbeddingFunc
from lightrag.kg.shared_storage import initialize_pipeline_status
OLLAMA_BASE_URL = "http://localhost:11434"
LLM_MODEL = "granite4:latest"
EMBEDDING_MODEL = "granite-embedding:latest"
WORKING_DIR = "./rag_storage_ollama"
EMBEDDING_DIMENSION = 384
DOCUMENTS_DIR = "./documents" # Directory to read source files from
OUTPUT_DIR = "./output" # Directory to write RAG results to
setup_logger("lightrag", level="INFO")
if not os.path.exists(WORKING_DIR):
os.mkdir(WORKING_DIR)
print(f"Created working directory: {WORKING_DIR}")
if not os.path.exists(OUTPUT_DIR):
os.mkdir(OUTPUT_DIR)
print(f"Created output directory: {OUTPUT_DIR}")
if not os.path.exists(DOCUMENTS_DIR):
os.mkdir(DOCUMENTS_DIR)
print(f"Created documents directory: {DOCUMENTS_DIR}")
async def custom_ollama_llm_complete(prompt: str, system_prompt: str = None, **kwargs):
"""
A custom function that handles the Ollama client initialization and model/base_url
parameters that are injected via functools.partial, while robustly filtering out
unwanted internal keywords.
"""
model = kwargs.pop('model')
base_url = kwargs.pop('base_url')
client = AsyncClient(host=base_url)
messages = []
if system_prompt:
messages.append({"role": "system", "content": system_prompt})
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})
keys_to_filter = {
'host',
'hashing_kv',
'llm_model_name',
'history_messages',
'keyword_extraction',
'enable_cot',
'is_system_prompt_only',
'prompt_config'
}
cleaned_kwargs = {k: v for k, v in kwargs.items() if k not in keys_to_filter}
try:
response = await client.chat(
model=model,
messages=messages,
**cleaned_kwargs
)
return response['message']['content']
except Exception as e:
raise e
async def initialize_rag():
"""Initializes the LightRAG instance using standard Ollama configuration."""
configured_ollama_complete = partial(
custom_ollama_llm_complete,
model=LLM_MODEL,
base_url=OLLAMA_BASE_URL,
)
configured_ollama_embed = partial(
ollama_embed,
embed_model=EMBEDDING_MODEL,
base_url=OLLAMA_BASE_URL
)
wrapped_embedding_func = EmbeddingFunc(
embedding_dim=EMBEDDING_DIMENSION,
func=configured_ollama_embed,
)
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=configured_ollama_complete,
embedding_func=wrapped_embedding_func,
)
await rag.initialize_storages()
await initialize_pipeline_status()
return rag
async def load_and_insert_documents(rag: LightRAG):
"""
Reads files from the DOCUMENTS_DIR and inserts their content into the RAG system.
Fixed to use a more compatible method for document insertion.
"""
file_paths = glob.glob(os.path.join(DOCUMENTS_DIR, '*.[mM][dD]')) + \
glob.glob(os.path.join(DOCUMENTS_DIR, '*.[tT][xX][tT]'))
if not file_paths:
print("\n--- WARNING: No documents found in './documents' directory. ---")
print("Please add some Markdown (.md) or Text (.txt) files to populate the knowledge base.")
return False
print(f"\n--- 2. Inserting Documents ({len(file_paths)} file(s) found) ---")
insertion_succeeded = 0
for file_path in file_paths:
filename = os.path.basename(file_path)
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
await rag.ainsert(content, doc_meta={'doc_id': filename})
print(f" > Successfully inserted: {filename} ({len(content.split())} words)")
insertion_succeeded += 1
except TypeError as te:
if "'doc_id'" in str(te) or "'doc_meta'" in str(te):
print(f" > FAILED (Type Error): {filename}. Attempting insertion without metadata to check compatibility.")
try:
await rag.ainsert(content)
print(f" > Successfully inserted (no metadata): {filename}")
insertion_succeeded += 1
except Exception as e:
print(f" > FAILED (General Error): {filename} - {e}")
else:
print(f" > FAILED to read or insert {filename} (Type Error): {te}")
except Exception as e:
print(f" > FAILED to read or insert {filename} (General Error): {e}")
if insertion_succeeded == 0:
print("Insertion complete, but no documents were successfully inserted. Please check LightRAG documentation for the correct argument name for source IDs.")
return False
print("Insertion complete. Data is ready for retrieval.")
return True
async def main():
rag = None
query = "Describe Quantum-Safe cryptography?"
try:
print("Checking if required Ollama models are pulled...")
print(f"--- 1. Initializing RAG with Ollama Models ---")
rag = await initialize_rag()
documents_inserted = await load_and_insert_documents(rag)
if not documents_inserted:
return
mode = "hybrid"
print(f"\n--- 3. Querying the RAG System (Mode: {mode}) ---")
print(f"Query: '{query}'")
rag_result = await rag.aquery(
query,
param=QueryParam(mode=mode)
)
response_text = None
if hasattr(rag_result, 'get_response_text'):
response_text = rag_result.get_response_text()
elif isinstance(rag_result, str):
response_text = rag_result
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("FINAL RAG RESPONSE")
print("="*50)
output_content = "" # Prepare string for file output
if response_text and not str(response_text).strip().startswith("Error:"):
print(response_text)
output_content += f"# RAG Query Result\n\n"
output_content += f"## Query\n\n> {query}\n\n"
output_content += f"## LLM/Cache Response\n\n{response_text}\n\n"
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("\n--- Context Retrieved (Sources) ---")
output_content += f"## Retrieved Context (Sources)\n\n"
if not isinstance(rag_result, str) and rag_result.retriever_output and rag_result.retriever_output.docs:
unique_sources = set()
for i, doc in enumerate(rag_result.retriever_output.docs):
source_text = doc.text
source_id = doc.doc_id if hasattr(doc, 'doc_id') and doc.doc_id else (
doc.doc_meta.get('doc_id') if hasattr(doc, 'doc_meta') and isinstance(doc.doc_meta, dict) else 'Unknown Source'
)
unique_sources.add(source_id)
print(f"Source {i+1} (File: {source_id}): {source_text[:100]}...")
output_content += f"### Source {i+1} (File: `{source_id}`)\n\n"
output_content += f"```text\n{source_text}\n```\n"
print(f"\nAnswer Grounded in: {', '.join(sorted(list(unique_sources)))}")
else:
print("No context documents were retrieved (or result was a cache hit string).")
output_content += "No context documents were retrieved (or result was a cache hit string).\n"
else:
error_message = "LLM failed to generate a response (Check Ollama logs for details)."
print(error_message)
output_content += f"# RAG Query Result\n\n## Error\n\n{error_message}\n\n"
if response_text:
print(f"\nError String from LightRAG: {response_text}")
output_content += f"**Error Detail:** {response_text}\n"
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
filename = f"rag_query_output_{timestamp}.md"
output_filepath = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, filename)
with open(output_filepath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(output_content)
print(f"\n--- Output Written to File ---")
print(f"Successfully wrote output to: {output_filepath}")
except Exception as e:
if "'str' object has no attribute 'retriever_output'" in str(e):
print("\n--- ERROR BYPASS: Detected Cache Hit String Result ---")
print("The response was successfully retrieved from the cache and written to the output file.")
else:
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("AN ERROR OCCURRED DURING RAG PROCESS")
print("="*50)
print(f"Error: {e}")
print(f"Please ensure Ollama is running and accessible at {OLLAMA_BASE_URL}, and the models '{LLM_MODEL}' and '{EMBEDDING_MODEL}' are pulled locally.")
print(f"To pull: 'ollama pull {LLM_MODEL}' and 'ollama pull {EMBEDDING_MODEL}'")
print("="*50 + "\n")
finally:
if rag:
print("\n--- Finalizing storages ---")
await rag.finalize_storages()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())實際的查詢輸出示例:
RAG Query Result
## Query
> Describe Quantum-Safe cryptography?
## LLM/Cache Response
### What is Quantum-Safe Cryptography?
Quantum-safe cryptography, also known as post‑quantum cryptography (PQC), refers to cryptographic algorithms and protocols designed to remain secure even against attacks by a sufficiently powerful quantum computer. Traditional public-key cryptosystems like RSA, ECC, Diffie‑Hellman, and elliptic curve variants are vulnerable to Shor’s algorithm, which could efficiently factor large integers and compute discrete logarithms—tasks that form the basis of these cryptographic schemes.知識圖譜生成
LightRAG 自帶知識圖譜生成功能,這點比較實用。

為了把生成的圖譜文件展示出來,我還用用 Streamlit 寫了個簡單的可視化應用。代碼比較粗糙,後續可以繼續優化。
import streamlit as st
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import io
import itertools
from io import StringIO
def visualize_graph(G: nx.Graph, layout_name: str, layout_params: dict):
"""
Generates a Matplotlib plot of the NetworkX graph with custom styling.
"""
node_labels = nx.get_node_attributes(G, 'label')
if not node_labels:
node_labels = nx.get_node_attributes(G, 'text')
edge_labels = nx.get_edge_attributes(G, 'text')
node_types = nx.get_node_attributes(G, 'type')
type_color_map = {
'Entity': '[#1f78b4](#1f78b4)', # Blue
'Chunk': '[#b2df8a](#b2df8a)', # Light Green
'Relation': '[#33a02c](#33a02c)', # Dark Green
'Unknown': '[#a6cee3](#a6cee3)' # Light Blue
}
node_colors = [type_color_map.get(node_types.get(node, 'Unknown'), type_color_map['Unknown']) for node in G.nodes()]
if layout_name == 'Spring Layout':
pos = nx.spring_layout(G, **layout_params)
elif layout_name == 'Circular Layout':
pos = nx.circular_layout(G)
elif layout_name == 'Spectral Layout':
pos = nx.spectral_layout(G)
elif layout_name == 'Kamada-Kawai Layout':
pos = nx.kamada_kawai_layout(G)
else:
pos = nx.spring_layout(G, **layout_params)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16, 10))
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(
G,
pos,
node_size=2500,
node_color=node_colors,
alpha=0.9
)
# Draw edges
nx.draw_networkx_edges(
G,
pos,
ax=ax,
edge_color='gray',
style='dashed',
arrowstyle='->',
arrowsize=25
)
nx.draw_networkx_labels(
G,
pos,
labels=node_labels,
font_size=11,
font_color='black',
font_weight='bold',
)
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(
G,
pos,
edge_labels=edge_labels,
font_color='red',
font_size=9,
bbox={"boxstyle": "round,pad=0.4", "fc": "white", "alpha": 0.7, "ec": "none"}
)
ax.set_title(f"Visualized Graph: {G.number_of_nodes()} Nodes, {G.number_of_edges()} Edges", fontsize=16)
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
st.pyplot(fig)
def app():
st.set_page_config(layout="wide", page_title="GraphML Viewer")
st.title("GraphML Visualization App")
st.markdown("A tool to visualize GraphML (e.g., LightRAG) outputs using NetworkX and Streamlit.")
st.sidebar.header("Data Upload & Layout Controls")
uploaded_file = st.sidebar.file_uploader(
"Upload your .graphml file",
type=["graphml"]
)
graph_data = None
if uploaded_file is not None:
try:
graph_data = uploaded_file.read().decode("utf-8")
st.sidebar.success("File uploaded successfully! Graph loading...")
except Exception as e:
st.sidebar.error(f"Error reading file: {e}")
graph_data = None
else:
st.info("Please upload a GraphML file in the sidebar to visualize your knowledge graph.")
st.sidebar.subheader("Layout Algorithm")
layout_name = st.sidebar.selectbox(
"Choose Graph Layout:",
('Spring Layout', 'Kamada-Kawai Layout', 'Circular Layout', 'Spectral Layout')
)
layout_params = {}
if layout_name == 'Spring Layout':
st.sidebar.caption("Fine-tune the Spring Layout forces:")
k_val = st.sidebar.slider("k (Node Spacing)", 0.01, 1.0, 0.15, 0.01)
iters = st.sidebar.slider("Iterations", 10, 100, 50, 10)
layout_params = {'k': k_val, 'iterations': iters}
if graph_data:
try:
G = nx.read_graphml(StringIO(graph_data))
st.header("Knowledge Graph Visualization")
st.write(f"Graph loaded: {G.number_of_nodes()} Nodes, {G.number_of_edges()} Edges")
visualize_graph(G, layout_name, layout_params)
except Exception as e:
st.error(f"An error occurred while processing the graph: {e}")
st.code(f"Error details: {e}")
st.warning("Please check if the GraphML file is correctly formatted and contains valid data.")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app()運行以後你就能看到上面的結果
總結
LightRAG 在構建 RAG 系統方面提供了相對完整的解決方案。相比傳統的純向量檢索,它的核心特點是引入了知識圖譜,能把非結構化文本組織成實體-關係網絡,這種混合檢索策略(語義向量+圖譜關係)確實能讓 LLM 獲得更豐富的上下文信息。
項目文檔寫得很詳細,並且包含了大量工具和服務的集成方案。整個框架的設計比較模塊化,擴展性也不錯。如果要在生產環境部署,還需要考慮性能優化、錯誤處理等細節。
LightRAG 項目地址:https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG
作者:Alain Airom