作者:徐嘉 StarRocks Active ContributorStarRocks
函數就像預設於數據庫中的公式,允許用户調用現有的函數以完成特定功能。函數可以很方便地實現業務邏輯的重用,因此正確使用函數會讓讀者在編寫 SQL 語句時起到事半功倍的效果。
StarRocks 提供了多種內置函數,包括標量函數、聚合函數、窗口函數、Table 函數和 Lambda 函數等,可幫助用户更加便捷地處理表中的數據。此外,StarRocks 還允許用户自定義函數以適應實際的業務操作。本文將以標量函數和聚合函數為例,介紹 StarRocks 常見的兩種函數實現原理,希望讀者能夠借鑑其設計思路,並按需實現所需的函數。同時,我們也歡迎社區小夥伴一起貢獻力量,共同完善 StarRocks 的功能,具體的函數任務認領方式請見文末。
如何為 StarRocks 添加標量函數
標量函數介紹
標量函數用於處理單行數據,接受一個或多個參數作為輸入,並返回一個值作為結果。StarRocks 常見的標量函數有 abs、floor、ceil 等。
標量函數的實現原理
首先,我們來了解函數簽名,函數簽名用來唯一標識函數,描述函數的 ID、名字、返回類型、輸入參數的類型等基本信息。標量函數的函數簽名定義在gensrc/script/functions.py,在編譯階段我們會根據 Python 文件中的內容生成對應的 Java 和 C++ 代碼,供 FE 和 BE 使用。每個函數簽名在 Python 文件中通過一個特定的數組來描述,數組的內容有如下兩種格式:
[<function_id>, <function_name>, <return_type>, [<arg_type>...], <be_scalar_function>]
or
[<function_id>, <function_name>, <return_type>, [<arg_type>...], <be_scalar_function>, <be_prepare_function>, <be_close_function>]其中基本信息如下:
- function_id:函數唯一標識,是唯一一串數字,function_id 遵循如下約定,前兩位表示 function_type,中間兩位表示 function_group,餘下的表示具體的 sub_function,後面我們會舉例説明
- function_name:函數名稱
- return_type:返回值類型
- arg_type:入參類型,如果有多個入參,需要在數組中描述每個入參的類型
- be_scalar_function:BE 中負責實現該函數計算邏輯的函數
- be_prepare_function/be_close_function:可選參數,有些函數在執行的過程中可能會傳遞一些狀態,be_prepare_function 和 be_close_function 就是 BE 中負責實現創建狀態和回收狀態的函數
為了支持多種數據類型作為輸入,需要為每種類型單獨創建函數簽名。以下以 abs 函數為例,該函數用於計算絕對值,需要描述以下五個信息:
- function_id:10代表它們都屬於 math function,04代表它們都屬於 abs 這個 function group,餘下的數字用來區分具體的 sub-function
- function_name:函數名稱都是 abs
- return_type:返回值類型,同入參類型一致
- arg_type:該函數只接受一個入參,所以第四項的數組中只有一個元素。
- be_eval_function:BE 中實現計算邏輯的函數,StarRocks 針對每種數據類型做了特殊處理,所以每個簽名中的函數名也不一樣
對於 abs 函數而言,由於不需要傳遞狀態,因此不需要 be_prepare_function 和 be_close_function 這兩個選項。請注意,這兩個選項在某些情況下可能會用到,具體用法將在後面的示例中介紹。
[10040, "abs", "DOUBLE", ["DOUBLE"], "MathFunctions::abs_double"],
[10041, "abs", "FLOAT", ["FLOAT"], "MathFunctions::abs_float"],
[10042, "abs", "LARGEINT", ["LARGEINT"], "MathFunctions::abs_largeint"],
[10043, "abs", "LARGEINT", ["BIGINT"], "MathFunctions::abs_bigint"],
[10044, "abs", "BIGINT", ["INT"], "MathFunctions::abs_int"],
[10045, "abs", "INT", ["SMALLINT"], "MathFunctions::abs_smallint"],
[10046, "abs", "SMALLINT", ["TINYINT"], "MathFunctions::abs_tinyint"],
[10047, "abs", "DECIMALV2", ["DECIMALV2"], "MathFunctions::abs_decimalv2val"],
[100470, "abs", "DECIMAL32", ["DECIMAL32"], "MathFunctions::abs_decimal32"],
[100471, "abs", "DECIMAL64", ["DECIMAL64"], "MathFunctions::abs_decimal64"],
[100472, "abs", "DECIMAL128", ["DECIMAL128"], "MathFunctions::abs_decimal128"],在 StarRocks 的編譯和執行階段,都會使用函數簽名來確定函數的輸入輸出和執行邏輯。具體流程如下:
- 在編譯階段,根據gensrc/script/functions.py 中的內容生成代碼供FE和BE使用。
- Java 代碼在fe/fe-core/target/generated-sources/build/com/starrocks/builtins/VectorizedBuiltinFunctions.java,FunctionSet[1] 保存了所有的函數簽名,初始化階段會調用VectorizedBuiltinFunctions::initBuiltins來添加標量函數的函數簽名。SQL analyze 階段,會利用 FunctionSet 提供的信息進行校驗,如果找不到函數簽名會直接返回錯誤,這部分實現在 ExpressionAnalyzer.Visitor [2]的 visitFunctionCall[3] 方法中。
- C++ 代碼在./gensrc/build/gen_C++/opcode/builtin_functions.cpp,BE 標量函數的函數簽名保存在BuiltinFunctions::_fn_tables[4],生成的代碼用於初始化_fn_tables。在 SQL 執行階段,VectorizedFunctionCallExpr 會根據 fid(函數唯一標識)從 _fn_tables 中找到執行該函數所需要的信息,包括輸入參數的個數,執行函數的函數指針(ScalarFunction),以及執行前後的 PrepareFunction 和 CloseFunction,這部分定義在 FunctionDescriptor[5]。
在 BE 實現函數的計算邏輯
這部分此處不做贅述,根據函數的功能實現相關的邏輯即可。
添加標量函數示例
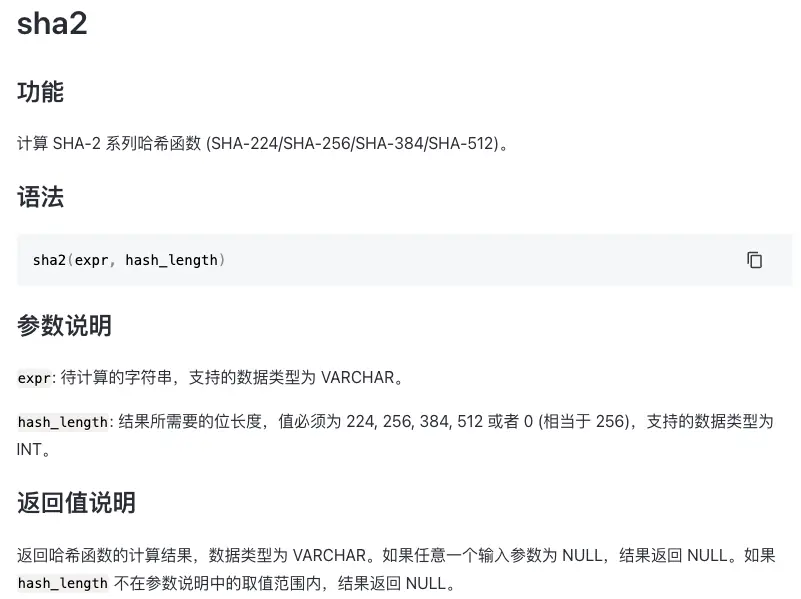
接下來我們以 sha2 函數為例,介紹引入新函數的具體流程。sha2 函數的功能如下圖,其詳細信息可以參考官方文檔[6]中的介紹。
生成函數簽名
首先,需要在gensrc/script/functions.py中新增簽名。
[120160, "sha2", "VARCHAR", ["VARCHAR", "INT"], "EncryptionFunctions::sha2", "EncryptionFunctions::sha2_prepare", "EncryptionFunctions::sha2_close"],如上述代碼所示,sha2 函數輸入需要兩個參數,根據第二個參數來決定使用哪種加密算法,如果第二個參數本身是個常數,那麼不需要每次執行的時候都去判斷。我們可以把這部分“狀態”保存起來,所以函數簽名中除了前文所述的五個基本信息之外,還增加了 EncryptionFunctions::sha2_prepare 和 EncryptionFunctions::sha2_close,用來實現狀態的創建和回收。
實現函數的計算邏輯
sha2 屬於加密函數的一種,所以我們直接在 EncryptionFunctions [7]中增加相應的方法即可。具體代碼如下:
/*
* Called by sha2 to the corresponding part
*/
DEFINE_VECTORIZED_FN(sha224);
DEFINE_VECTORIZED_FN(sha256);
DEFINE_VECTORIZED_FN(sha384);
DEFINE_VECTORIZED_FN(sha512);
DEFINE_VECTORIZED_FN(invalid_sha);
/**
* @param: [json_string, tagged_value]
* @paramType: [BinaryColumn, BinaryColumn]
* @return: Int32Column
*/
DEFINE_VECTORIZED_FN(sha2);
static Status sha2_prepare(FunctionContext* context, FunctionContext::FunctionStateScope scope);
static Status sha2_close(FunctionContext* context, FunctionContext::FunctionStateScope scope);其中,實現標量函數的計算邏輯主要分佈在 PrepareFuntion、ScalarFunction、CloseFunction 三個函數中。
PrepareFunction
Prepare 階段主要是針對第二個參數進行特殊處理,如果是常數,可以把實現對應加密算法的函數指針保存起來,後面的 ScalarFunction 中可以直接調用。加密算法的函數指針保存在 EncryptionFunctions::SHA2Ctx 中,通過 FunctionContext::set_function_state 保存在上下文中。具體代碼如下:
Status EncryptionFunctions::sha2_prepare(FunctionContext* context, FunctionContext::FunctionStateScope scope) {
if (scope != FunctionContext::FRAGMENT_LOCAL) {
return Status::OK();
}
if (!context->is_notnull_constant_column(1)) {
return Status::OK();
}
ColumnPtr column = context->get_constant_column(1);
auto hash_length = ColumnHelper::get_const_value<TYPE_INT>(column);
ScalarFunction function;
if (hash_length == 224) {
function = &EncryptionFunctions::sha224;
} else if (hash_length == 256 || hash_length == 0) {
function = &EncryptionFunctions::sha256;
} else if (hash_length == 384) {
function = &EncryptionFunctions::sha384;
} else if (hash_length == 512) {
function = &EncryptionFunctions::sha512;
} else {
function = EncryptionFunctions::invalid_sha;
}
auto fc = new EncryptionFunctions::SHA2Ctx();
fc->function = function;
context->set_function_state(scope, fc);
return Status::OK();
}ScalarFunction
ScalarFunction 主要實現 sha2 的計算邏輯,如果第二個參數是常數,那麼 PrepareFunction 中保存的 function_state 就可以派上用場了。具體代碼如下:
StatusOr<ColumnPtr> EncryptionFunctions::sha2(FunctionContext* ctx, const Columns& columns) {
if (!ctx->is_notnull_constant_column(1)) {
auto src_viewer = ColumnViewer<TYPE_VARCHAR>(columns[0]);
auto length_viewer = ColumnViewer<TYPE_INT>(columns[1]);
auto size = columns[0]->size();
ColumnBuilder<TYPE_VARCHAR> result(size);
for (int row = 0; row < size; row++) {
if (src_viewer.is_null(row) || length_viewer.is_null(row)) {
result.append_null();
continue;
}
auto src_value = src_viewer.value(row);
auto length = length_viewer.value(row);
if (length == 224) {
SHA224Digest digest;
digest.update(src_value.data, src_value.size);
digest.digest();
result.append(Slice(digest.hex().c_str(), digest.hex().size()));
} else if (length == 0 || length == 256) {
SHA256Digest digest;
digest.update(src_value.data, src_value.size);
digest.digest();
result.append(Slice(digest.hex().c_str(), digest.hex().size()));
} else if (length == 384) {
SHA384Digest digest;
digest.update(src_value.data, src_value.size);
digest.digest();
result.append(Slice(digest.hex().c_str(), digest.hex().size()));
} else if (length == 512) {
SHA512Digest digest;
digest.update(src_value.data, src_value.size);
digest.digest();
result.append(Slice(digest.hex().c_str(), digest.hex().size()));
} else {
result.append_null();
}
}
return result.build(ColumnHelper::is_all_const(columns));
}
auto ctc = reinterpret_cast<SHA2Ctx*>(ctx->get_function_state(FunctionContext::FRAGMENT_LOCAL));
return ctc->function(ctx, columns);
}CloseFunction
CloseFunction 主要用來回收資源。函數執行中所依賴的 function state,在執行結束之後不再被需要,那麼可以在這個階段釋放內存。具體代碼如下:
Status EncryptionFunctions::sha2_close(FunctionContext* context, FunctionContext::FunctionStateScope scope) {
if (scope == FunctionContext::FRAGMENT_LOCAL) {
auto fc = reinterpret_cast<SHA2Ctx*>(context->get_function_state(scope));
delete fc;
}
return Status::OK();
}增加對應的單元測試
具體細節可參考 EntryptionFunctionTest[8] 即可。代碼示例如下:
TEST_P(ShaTestFixture, test_sha2) {
auto [str, len, expected] = GetParam();
std::unique_ptr<FunctionContext> ctx(FunctionContext::create_test_context());
Columns columns;
auto plain = BinaryColumn::create();
plain->append(str);
ColumnPtr hash_length =
len == -1 ? ColumnHelper::create_const_null_column(1) : ColumnHelper::create_const_column<TYPE_INT>(len, 1);
if (str == "NULL") {
columns.emplace_back(ColumnHelper::create_const_null_column(1));
} else {
columns.emplace_back(plain);
}
columns.emplace_back(hash_length);
ctx->set_constant_columns(columns);
ASSERT_TRUE(EncryptionFunctions::sha2_prepare(ctx.get(), FunctionContext::FunctionStateScope::FRAGMENT_LOCAL).ok());
if (len != -1) {
ASSERT_NE(nullptr, ctx->get_function_state(FunctionContext::FRAGMENT_LOCAL));
} else {
ASSERT_EQ(nullptr, ctx->get_function_state(FunctionContext::FRAGMENT_LOCAL));
}
ColumnPtr result = EncryptionFunctions::sha2(ctx.get(), columns).value();
if (expected == "NULL") {
std::cerr << result->debug_string() << std::endl;
EXPECT_TRUE(result->is_null(0));
} else {
auto v = ColumnHelper::cast_to<TYPE_VARCHAR>(result);
EXPECT_EQ(expected, v->get_data()[0].to_string());
}
ASSERT_TRUE(EncryptionFunctions::sha2_close(ctx.get(),
FunctionContext::FunctionContext::FunctionStateScope::FRAGMENT_LOCAL)
.ok());
}完整的改動可以參考 PR:https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/pull/1264/files。
如何為 StarRocks 添加聚合函數
聚合函數介紹
聚合函數用於處理多行數據,接受多行數據作為輸入,經過計算後返回一行結果。StarRocks 常見的聚合函數有 count、sum、avg、min、max 等。
聚合函數的實現原理
在查詢執行階段,Pipeline 引擎的聚合算子通過 Aggregator 完成聚合計算,聚合算子的實現原理可參見文末《StarRocks 聚合算子源碼解析》[9],本文主要關注聚合函數的實現原理。
Aggregator 在 prepare 階段會根據函數名找到對應的 AggregateFunction 並保存下來,AggregateFunction 是最重要的抽象,封裝了聚合計算過程中需要的各個接口,每個聚合函數都需要繼承 AggregateFunction 實現自己的邏輯。計算的中間結果保存在 AggDataPtr 中,AggDataPrt 是一個指針,指向描述中間結果的數據結構。每種聚合函數的中間結果都不相同,比如求和函數,只需要保存 sum 即可,而平均值函數,除了保存 sum 之外,還需要記錄 count。
在 AggregateFunction 提供的接口中,我們需要重點關注以下幾個:
// 逐行讀取數據,不斷更新 state 中保存的中間結果。
void update(FunctionContext* ctx, const Column** columns, AggDataPtr __restrict state, size_t row_num)
// 通常用在多階段聚合中,讀取已經算好的部分中間結果,合併計算,更新 state 中的數據。
void merge(FunctionContext* ctx, const Column* column, AggDataPtr __restrict state, size_t row_num)
// 多階段的聚合可能會通過多個節點執行,計算的中間結果需要跨網絡傳輸,這個方法用來實現序列化的邏輯。
void serialize_to_column(FunctionContext* ctx, ConstAggDataPtr __restrict state, Column* to)
// 把中間結果轉成最終對用户返回的結果。比如求和函數,直接返回中間結果保存的 sum 即可,而平均值函數,需要返回 sum/count。
void finalize_to_column(FunctionContext* ctx, ConstAggDataPtr __restrict state, Column* to)
// 重置 state 的狀態,比如在 window aggregate 中,我們會用一個的 state 保存中間結果,每次遇到新的 group時,需要通過 reset 重置,然後才能進行接下來的計算。
void reset(FunctionContext* ctx, const Columns& args, AggDataPtr __restrict state)
除了上述內容之外,為了減少函數調用的開銷,AggregateFunction 還封裝了批量操作的接口,具體的細節這裏就不展開講解了,可以參考be/src/exprs/agg/aggregate.h。
添加聚合函數示例
接下來我們以 ANY_VALUE 為例,介紹添加聚合函數的流程,這個函數實現的功能比較簡單,可以參考官方文檔[10]説明:

在 FE 創建函數簽名
FE 通過AggregateFunction[11] 來描述聚合函數,所有的聚合函數都會註冊在 FunctionSet 中,初始化階段在 FunctionSet的initAggregateBuiltins [12]方法內增加對應的函數即可。具體代碼如下:
// ANY_VALUE
addBuiltin(AggregateFunction.createBuiltin(ANY_VALUE,
Lists.newArrayList(t), t, t, true, false, false));在 BE 實現函數的計算邏輯
此處重點是如何描述中間結果,以及如何實現 AggregateFunction 的核心接口。
ANY_VALUE 的語義很簡單,在每個 group 中選擇一行返回。中間結果通過 AnyValueAggregateData 描述,只需要記錄當前是否已經有結果以及對應的數據是什麼即可,AnyValueAggregateData 為每種數據類型進行了特化,實現上幾乎一致。具體代碼如下:
template <LogicalType LT>
struct AnyValueAggregateData {
using T = AggDataValueType<LT>;
T result;
bool has_value = false;
void reset() {
result = T{};
has_value = false;
}
};具體的計算邏輯非常簡單,這部分通過 AnyValueElement 實現。具體代碼如下:
template <LogicalType LT, typename State>
struct AnyValueElement {
using RefType = AggDataRefType<LT>;
void operator()(State& state, RefType right) const {
if (UNLIKELY(!state.has_value)) {
AggDataTypeTraits<LT>::assign_value(state.result, right);
state.has_value = true;
}
}
};最後利用 AnyValueElement 實現 AggregateFunction 所需要的接口即可,具體代碼如下:
template <LogicalType LT, typename State, class OP, typename T = RunTimeC++Type<LT>, typename = guard::Guard>
class AnyValueAggregateFunction final
: public AggregateFunctionBatchHelper<State, AnyValueAggregateFunction<LT, State, OP, T>> {
public:
using InputColumnType = RunTimeColumnType<LT>;
void reset(FunctionContext* ctx, const Columns& args, AggDataPtr state) const override {
this->data(state).reset();
}
void update(FunctionContext* ctx, const Column** columns, AggDataPtr __restrict state,
size_t row_num) const override {
DCHECK(!columns[0]->is_nullable());
const auto& column = down_cast<const InputColumnType&>(*columns[0]);
OP()(this->data(state), AggDataTypeTraits<LT>::get_row_ref(column, row_num));
}
void update_batch_single_state(FunctionContext* ctx, size_t chunk_size, const Column** columns,
AggDataPtr __restrict state) const override {
update(ctx, columns, state, 0);
}
void merge(FunctionContext* ctx, const Column* column, AggDataPtr __restrict state, size_t row_num) const override {
DCHECK(!column->is_nullable());
const auto& input_column = down_cast<const InputColumnType&>(*column);
OP()(this->data(state), AggDataTypeTraits<LT>::get_row_ref(input_column, row_num));
}
void serialize_to_column(FunctionContext* ctx, ConstAggDataPtr __restrict state, Column* to) const override {
DCHECK(!to->is_nullable());
AggDataTypeTraits<LT>::append_value(down_cast<InputColumnType*>(to), this->data(state).result);
}
void convert_to_serialize_format(FunctionContext* ctx, const Columns& src, size_t chunk_size,
ColumnPtr* dst) const override {
*dst = src[0];
}
void finalize_to_column(FunctionContext* ctx, ConstAggDataPtr __restrict state, Column* to) const override {
DCHECK(!to->is_nullable());
AggDataTypeTraits<LT>::append_value(down_cast<InputColumnType*>(to), this->data(state).result);
}
void get_values(FunctionContext* ctx, ConstAggDataPtr __restrict state, Column* dst, size_t start,
size_t end) const override {
DCHECK_GT(end, start);
InputColumnType* column = down_cast<InputColumnType*>(dst);
for (size_t i = start; i < end; ++i) {
AggDataTypeTraits<LT>::append_value(column, this->data(state).result);
}
}
std::string get_name() const override { return "any_value"; }
};完整的實現細節參見:be/src/exprs/agg/any_value.h
在 AggregateFactory 中註冊
這一步是為了讓 AggregateFactory 可以根據函數名找到對應的函數,函數的創建通過MakeAnyValueAggregateFunction 實現,相關的改動可以在 aggregate_factory.hpp[13] 中 grep MakeAnyValueAggregateFunction 看到,比較簡單,這裏不再過多贅述,具體示例如下:
template <LogicalType LT>
AggregateFunctionPtr AggregateFactory::MakeAnyValueAggregateFunction() {
return std::make_shared<
AnyValueAggregateFunction<LT, AnyValueAggregateData<LT>, AnyValueElement<LT, AnyValueAggregateData<LT>>>>();
}添加單元測試
可以參見 test/exprs/agg/aggregate_test.cpp[14]添加單測,比如:
TEST_F(AggregateTest, test_any_value) {
const AggregateFunction* func = get_aggregate_function("any_value", TYPE_SMALLINT, TYPE_SMALLINT, false);
test_non_deterministic_agg_function<int16_t, int16_t>(ctx, func);
func = get_aggregate_function("any_value", TYPE_INT, TYPE_INT, false);
test_non_deterministic_agg_function<int32_t, int32_t>(ctx, func);
func = get_aggregate_function("any_value", TYPE_BIGINT, TYPE_BIGINT, false);
test_non_deterministic_agg_function<int64_t, int64_t>(ctx, func);
func = get_aggregate_function("any_value", TYPE_LARGEINT, TYPE_LARGEINT, false);
test_non_deterministic_agg_function<int128_t, int128_t>(ctx, func);
func = get_aggregate_function("any_value", TYPE_FLOAT, TYPE_FLOAT, false);
test_non_deterministic_agg_function<float, float>(ctx, func);
func = get_aggregate_function("any_value", TYPE_DOUBLE, TYPE_DOUBLE, false);
test_non_deterministic_agg_function<double, double>(ctx, func);
func = get_aggregate_function("any_value", TYPE_VARCHAR, TYPE_VARCHAR, false);
test_non_deterministic_agg_function<Slice, Slice>(ctx, func);
func = get_aggregate_function("any_value", TYPE_DECIMALV2, TYPE_DECIMALV2, false);
test_non_deterministic_agg_function<DecimalV2Value, DecimalV2Value>(ctx, func);
func = get_aggregate_function("any_value", TYPE_DATETIME, TYPE_DATETIME, false);
test_non_deterministic_agg_function<TimestampValue, TimestampValue>(ctx, func);
func = get_aggregate_function("any_value", TYPE_DATE, TYPE_DATE, false);
test_non_deterministic_agg_function<DateValue, DateValue>(ctx, func);
}完整的改動見 PR:https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/pull/2073
總結
本文介紹了 StarRocks 中標量函數和聚合函數的實現原理,並以 sha2 標量函數和 ANY_VALUE 聚合函數為例,説明了如何添加標量函數和新增聚合函數。
標量函數定義在 be/src/exprs/ 目錄下。若想查看某個函數的實現,可以在函數簽名中找到對應的 be function,然後在該目錄下使用 grep 進行查找。
此外,StarRocks 還實現了多種聚合函數,具體實現可在 be/src/exprs/agg 目錄下查找。
最後,如果你在閲讀完本文後對 StarRocks 函數的實現原理以及如何添加新的函數還有很多疑問,歡迎報名參加 4/6(星期四)的 <StarRocks 源碼實驗室直播>,以進一步學習。同時,我們也歡迎你領取函數任務,並通過實踐學習如何為 StarRocks 添加新的函數!👇
相關鏈接:
[1]FunctionSet:https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/fe/fe-core/src/main/java/com/starrocks/catalog/FunctionSet.java
[2] ExpressionAnalyzer.Visitor:https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/fe/fe-core/src/main/java/com/starrocks/sql/analyzer/ExpressionAnalyzer.java#L303
[3]visitFunctionCall :https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/fe/fe-core/src/main/java/com/starrocks/sql/analyzer/ExpressionAnalyzer.java#L893
[4]BuiltinFunctions::_fn_tables:https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/be/src/exprs/builtin_functions.h#L75
[5]FunctionDescriptor:https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/be/src/exprs/builtin_functions.h#L32
[6]sha2 函數:https://docs.starrocks.io/zh-cn/latest/sql-reference/sql-func...
[7]EncryptionFunctions:
https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/be/src/exprs/encryption_functions.h
[8]EntryptionFunctionTest:
https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/be/test/exprs/encryption_functions_test.cpp
[9]《StarRocks 聚合算子源碼解析》:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/592058276
[10]ANY_VALUE 功能:https://docs.starrocks.io/zh-cn/latest/sql-reference/sql-func...
[11]AggregateFunction:https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/fe/fe-core/src/main/java/com/starrocks/catalog/AggregateFunction.java#L61
[12]initAggregateBuiltins:https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/fe/fe-core/src/main/java/com/starrocks/catalog/FunctionSet.java#L742
[13]aggregate_factory.cpp:https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/be/src/exprs/agg/factory/aggregate_factory.hpp
[14]aggregate_test:https://github.com/StarRocks/starrocks/blob/main/be/test/exprs/agg/aggregate_test.cpp#L1667