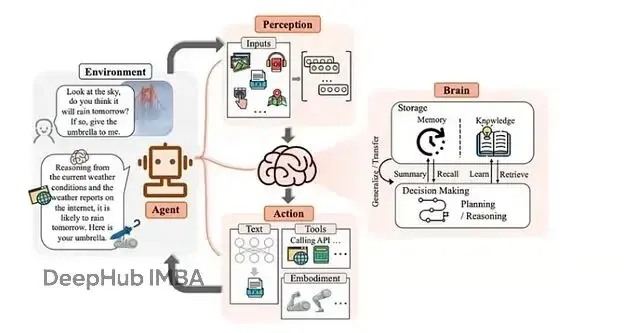
AutoGen 是微軟研究院開源的多智能體 AI 系統框架。這個框架的設計思路很簡單——讓多個 AI 智能體(加上人類參與)在對話中完成複雜任務的協作和推理。
你甚至可以把它理解成一個團隊聊天室,智能體們在裏面討論、爭論、協作,最終得出解決方案。
AutoGen 通過創建多個專門化智能體,為每個智能體設定自己的角色、目標,來達到上面説的聊天能力,並且還能通過配置工具來獲得代碼執行能力。智能體之間通過消息機制通信,互相配合完成任務。
AutoGen 為什麼值得關注
AutoGen 真正好玩的地方在於它實現了 AI 之間的協作。智能體可以相互辯論、推理、糾錯、共同創造,整個過程不需要人工逐步編寫腳本,設置可以不需要人工的參與。
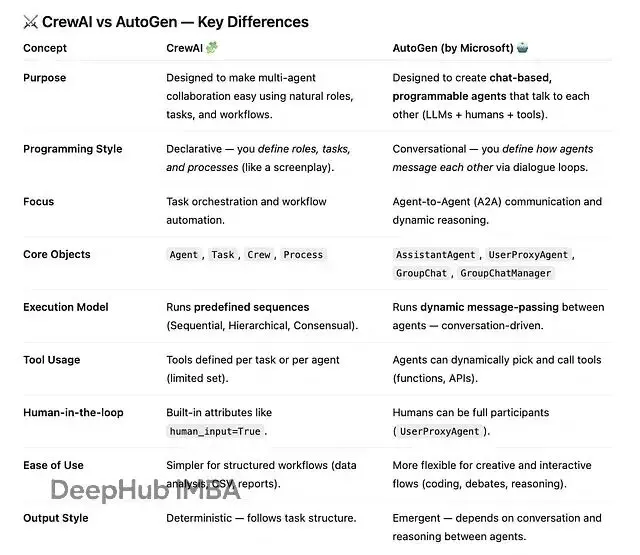
相比於CrewAI,AutoGen 則把重點放在討論、推理和演化上,而CrewAI 更關注執行層面。
你可以理解為CrewAI更像是我們現在用的工作助手,而AutoGen 更像是圓桌會議。
AutoGen 框架處理了很多底層問題,這樣我們可以只專著於如何編排角色和任務。
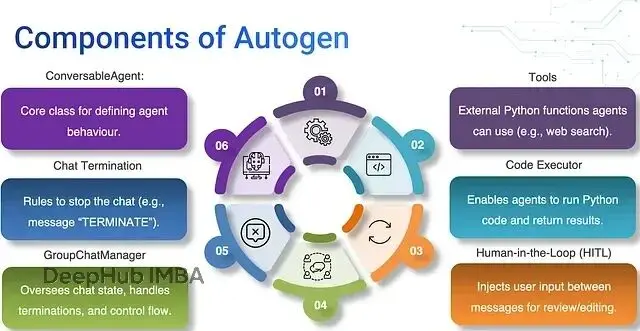
AutoGen 定義了三類核心智能體:
- Conversable Agent:負責管理結構化對話和預定義的交互模式
- Assistant Agent:執行具體任務,調用工具或 LLM
- UserProxy Agent:充當人機接口層,轉發消息和響應
簡單的羣聊演示
from autogen import ConversableAgent, AssistantAgent, UserProxyAgent, GroupChat, GroupChatManager
# Define AssistantAgent (AI assistant)
assistant = AssistantAgent(
name="AssistantAgent",
system_message="You are a helpful AI assistant. Suggest Python code when relevant.",
human_input_mode="NEVER" # No human input required, runs automatically
)
# Define UserProxyAgent (represents human)
user_proxy = UserProxyAgent(
name="UserProxyAgent",
human_input_mode="ALWAYS" # Requires human input
)
# Define group chat
chat = GroupChat(
agents=[assistant, user_proxy],
messages=[]
)
# Manage group chat with GroupChatManager
manager = GroupChatManager(
groupchat=chat,
llm_config={"model": "gpt-5-mini"}
)
# Start the chat
user_proxy.initiate_chat(
manager,
message="Write a short Python function to calculate factorial."
)AutoGen 核心概念詳解
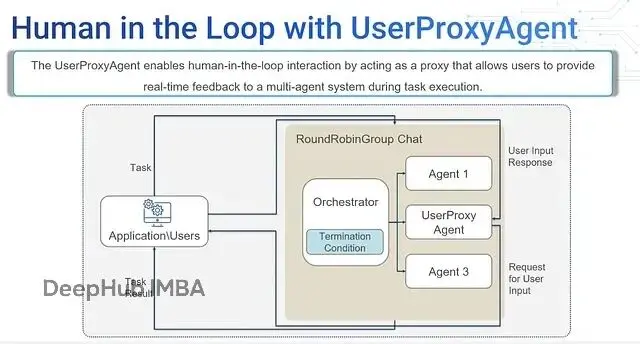
1、Human-in-the-Loop(人工參與)
這個功能讓人類可以在智能體執行過程中進行干預。
# Human-in-the-Loop example
from autogen import AssistantAgent, UserProxyAgent
# Step 1: Create assistant agent
assistant = AssistantAgent(
name="code_writer",
system_message="You are a helpful coding assistant."
)
# Step 2: Create user proxy with human-in-the-loop enabled
user = UserProxyAgent(
name="human_user",
human_input_mode="ALWAYS" # 👈 Enable human confirmation
)
# Step 3: Start conversation
user.initiate_chat(
assistant,
message="Write a Python function to calculate factorial."
)2、Code Executor 的工作機制
Code Executor 負責安全執行智能體生成的代碼。
# Behind the scenes
# AssistantAgent generates code:
sum([x for x in range(1, 21) if x % 2 == 0])
# PythonCodeExecutor automatically:
# - Executes safely in sandbox
# - Captures output
# - Returns result to agent
# UserProxyAgent displays result:
✅ Result: 110
# Optional: Add human approval
user = UserProxyAgent(
name="human_user",
code_execution_config={"executor": executor},
human_input_mode="ALWAYS"
)3、工具集成方式
工具通過初始化時的
tools參數傳入智能體。
from autogen import AssistantAgent, UserProxyAgent, Tool
# Define tool function
def multiply_numbers(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Returns the product of two numbers."""
return a * b
# Wrap as Tool object
multiply_tool = Tool(
func=multiply_numbers,
name="multiply_tool",
description="Multiplies two numbers and returns the product."
)
# Create agent and integrate tool
assistant = AssistantAgent(
name="math_agent",
system_message="You are a math assistant. Use multiply_tool when needed.",
tools=[multiply_tool]
)
user = UserProxyAgent(name="human_user")
user.initiate_chat(
assistant,
message="Can you multiply 8 and 7?"
)4、多智能體協作模式
AutoGen 對話系統的核心特徵是支持多智能體協作對話模式。
# Example: Multi-agent conversational pattern
from autogen import AssistantAgent, ReviewerAgent, UserProxyAgent, PythonCodeExecutor
executor = PythonCodeExecutor()
# Coder agent
coder = AssistantAgent(
name="coder_agent",
system_message="You are a code-writing assistant."
)
# Reviewer agent
reviewer = ReviewerAgent(
name="reviewer_agent",
system_message="You are a code reviewer. Check logic and security."
)
# User proxy
user = UserProxyAgent(
name="human_user",
human_input_mode="TERMINATE",
code_execution_config={"executor": executor}
)
def run_multi_agent_workflow(prompt: str):
coder_response = coder.chat_with(user, message=prompt)
print("Coder ->", coder_response["content"])
reviewer_response = reviewer.review(code={"code": coder_response["content"]})
print("Reviewer ->", reviewer_response["content"])
if "SUGGEST_CHANGES" in reviewer_response["content"]:
revision = coder.chat_with(reviewer, message=reviewer_response["content"])
final_code = revision["content"]
else:
final_code = coder_response["content"]
print("Waiting for human approval...")
if not user.get_human_approval(final_code):
print("Human rejected execution.")
return
exec_result = executor.execute(final_code)
print("Execution result ->", exec_result["output"])
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_multi_agent_workflow("Write a Python function prime_factors(n).")這個例子展示了多智能體協作的幾個關鍵點:Coder、Reviewer、User 各司其職完成協作,然後通過Reviewer 把關代碼的安全性和質量,HITL 模式給人類最終審批權,最後可以通過Code Executor 在沙箱環境安全執行代碼
5、會話終止機制
會話會在滿足終止條件時結束,這樣一個整個的”會議“就結束了
from autogen import AssistantAgent, UserProxyAgent
def is_termination_msg(message):
"""Returns True when message contains TERMINATE keyword."""
return "TERMINATE" in message["content"].upper()
assistant = AssistantAgent(
name="helper_agent",
system_message="Stop when receiving 'TERMINATE'."
)
user = UserProxyAgent(
name="human_user",
is_termination_msg=is_termination_msg
)
user.initiate_chat(assistant, message="Hello, explain recursion in simple terms.")
assistant.send({"role": "user", "content": "Thanks, that's clear. TERMINATE"})總結
AutoGen 提供了構建複雜 AI 協作系統的完整支持,覆蓋了角色結構、通信機制、人工參與、工具集成、代碼執行和多智能體協作設計等各個方面。框架把底層複雜度封裝得很好,開發者可以專注在業務邏輯和智能體設計上。
https://avoid.overfit.cn/post/a50b2cf5363046739250c9c284421d2f
作者:Sonika