作者:秦懷
1 簡介
計算機科學領域的任何問題都可以通過增加一個間接的中間層來解決,這句話就是整個計算機軟件以及系統設計中的核心思想,而緩存對這一思想的一種實踐。
緩存,總歸會受到存儲空間的限制,當緩存的空間不足的時候,如果在保持一定系統文檔的情況下,還能兼顧到緩存命中率呢?這就需要我們選擇合適的緩存淘汰算法。
緩存淘汰算法種類比較多,我們本次主要介紹 FIFO:
先進先出,類似隊列的特性,淘汰緩存中最早添加的記錄,該算法基於"最早被添加的數據,不再被使用的可能性最大"。要想實現這種算法,只需要使用一個隊列維護數據,並同時維護一個數據最大容量,每次新增數據都添加到隊尾,如果內存不夠,那麼就先淘汰掉隊頭的元素。
缺點:
FIFO 算法的缺點也很明顯,有些數據雖然被添加的比較早,但是使用頻率也會很高,在這種策略下會被頻繁添加進去,過一會又被淘汰掉,緩存命中率不高。
2 核心原理
下面是一些設計的思路:
- 存儲元素使用隊列,並且隊列容量有一定限制。但是為了兼顧查詢效率,需要同時使用哈希表來存儲 key 和 Element 的映射。
- 為了刪除的時候,能找到前後元素,隊列需要維護成 雙向隊列。
基本操作如下,為了處理併發時程序錯誤,需要在修改數據的時候加鎖:
-
Set :先查找是否存在,分別執行兩種操作。
- 新元素,追加在隊尾。
- 已存在的元素,直接修改。
-
Get:
- 按照 Key 在 Hash 表中查詢出來。
-
Delete:
- 先查找到元素,然後從鏈表以及哈希表中刪除,更新緩存狀態。
- Stat:獲取存儲的狀態
3 實現
3.1 使用自帶的雙向鏈表結構
本小節是最簡單粗暴的實現,直接使用原生的雙向隊列,下面是一些設計的思路,僅供參考。
3.1.1 實體設計
3.1.2 緩存狀態
緩存總的狀態維護,定義一個 stat.go 類:
type Stat struct {
// key 的個數
keyCount int64
// value 使用得最大的容量
maxBytes int64
// value 已使用得最大的容量
usedBytes int64
}3.1.3 核心接口
定義基礎能力接口 cache.go,除了增刪改查,還有獲取緩存狀態:
type Cache interface {
Set(key string, value []byte)
Get(key string) []byte
Del(key string)
Stat() Stat
}3.1.4 元素封裝
每個元素中,保存着 key 以及值,值統一使用 byte 數組進行存儲,之所以用 []byte ,不用具體的數據結構,是因為需要抽象,適配所有的類型。
但是使用 []byte 我們取值後還需要轉成 struct{},比較消耗 CPU,為什麼不使用 interface{} 呢?
網上看到的一個答案是:內存中存儲過多的 interface{} 會造成較大的 GC 影響:Getting to Go: The Journey of Go's Garbage Collector - The Go Programming Language
type entry struct {
key string
value []byte
}3.1.5 整體實現
fifo.go 文件中,存儲元素使用隊列,並且隊列容量有一定限制。但是為了兼顧查詢效率,需要同時使用哈希表來存儲 key 和 Element 的映射。
type fifo struct {
// 為了快速找到該value
cache map[string]*list.Element
// 按照添加順序保存的list
head *list.List
// 緩存數據
stat Stat
} 對外的初始化方法:
func New(maxBytes int64) Cache {
return &fifo{
cache: map[string]*list.Element{},
head: list.New(),
stat: Stat{
keyCount: 0,
maxBytes: maxBytes,
usedBytes: 0,
}, }}下面就是具體的實現:
import (
"container/list"
)
type fifo struct {
// 為了快速找到該value
cache map[string]*list.Element
// 按照添加順序保存的list
head *list.List
// 緩存數據
stat Stat
}
func (f *fifo) Set(key string, value []byte) {
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok && e != nil {
f.setDataExisted(e, value)
} else {
f.setDataNotExisted(key, value)
}}
func (f *fifo) setDataNotExisted(key string, value []byte) {
newEntry := &entry{
key: key,
value: value,
} if f.stat.maxBytes > 0 {
for f.stat.usedBytes+int64(len(key)+len(value)) > f.stat.maxBytes {
f.removeOldestElement()
} } e := f.head.PushBack(newEntry)
f.cache[key] = e
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes + int64(len(key)+len(value))
f.stat.keyCount++
}
func (f *fifo) setDataExisted(e *list.Element, value []byte) {
originEntry := e.Value.(*entry)
originSize := len(originEntry.value)
beRemoved := false
if f.stat.maxBytes > 0 {
for (int64)(len(value))-(int64)(originSize) > f.stat.maxBytes-f.stat.usedBytes {
if f.head.Front() == e {
beRemoved = true
}
f.removeOldestElement()
} } if beRemoved {
f.setDataNotExisted(originEntry.key, value)
return
}
originEntry.value = value
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes + (int64)(len(value)) - (int64)(originSize)
}
func (f *fifo) removeOldestElement() {
f.removeElement(f.head.Front())
}
func (f *fifo) removeElement(e *list.Element) {
if e == nil {
return
}
// 雙向鏈表的刪除
f.head.Remove(e)
originEntry := e.Value.(*entry)
f.stat.keyCount--
// 重新計算使用空間
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes - int64(len(originEntry.key)+len(originEntry.value))
// Hash表刪除
delete(f.cache, originEntry.key)
}
func (f *fifo) Get(key string) []byte {
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok {
return e.Value.(*entry).value
}
return nil
}
func (f *fifo) Del(key string) {
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok {
f.removeElement(e)
}}
func (f *fifo) Stat() Stat {
return f.stat
}
func New(maxBytes int64) Cache {
return &fifo{
cache: map[string]*list.Element{},
head: list.New(),
stat: Stat{
keyCount: 0,
maxBytes: maxBytes,
usedBytes: 0,
}, }}測試一下,編寫測試類 cache_test.go :
import (
"Go-Cache/00_fifo/character01"
"fmt" . "github.com/smartystreets/goconvey/convey"
"testing")
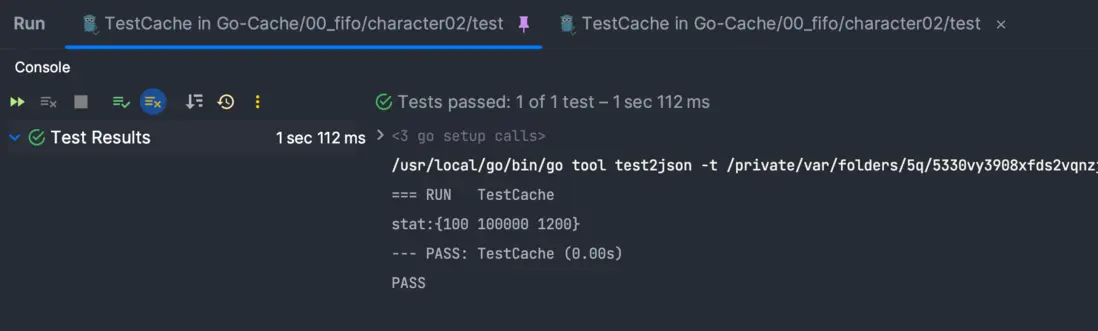
func TestCache(t *testing.T) {
Convey("TestApplyFunc", t, func() {
cache := character01.New(100)
stat := fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{0 100 0}")
cache.Set("hello", []byte("world"))
cache.Set("hello2", []byte("world2"))
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{2 100 22}")
cache.Set("hello2", []byte("changeWorld2"))
value := cache.Get("hello2")
So(string(value), ShouldEqual, "changeWorld2")
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{2 100 28}")
cache.Set("k1", []byte("longlonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglongV1"))
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{2 100 94}")
cache.Set("hello2", []byte("newHelloWorld2newHelloWorld2"))
value = cache.Get("hello2")
So(string(value), ShouldEqual, "newHelloWorld2newHelloWorld2")
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{1 100 34}")
cache.Set("num", character01.IntToBytes(1))
num := cache.Get("num")
So(character01.BytesToInt(num), ShouldEqual, 1)
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{2 100 45}")
cache.Set("num", nil)
So(cache.Get("num"), ShouldEqual, nil)
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{2 100 37}")
cache.Del("num")
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{1 100 34}")
})}3.2 增加鎖
但是明顯上面的代碼是有問題的,當併發到一定程度,就會出現併發寫的 panic:
func TestNoLock(t *testing.T) {
// 包名是上面小節的包名
cache := no_lock.New(100000)
num := 1000
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
index := i
wg.Add(1) //
go func() {
cache.Set("hello"+string(rune(index)), []byte("world"+string(rune(index))))
wg.Done() //5
}()
} wg.Wait()
fmt.Printf("stat:%v\n", cache.Stat())
}panic 的報錯:
fatal error: concurrent map read and map write
goroutine 40 [running]:
runtime.throw({0x1125cae?, 0x1?})
/usr/local/go/src/runtime/panic.go:992 +0x71 fp=0xc000133698 sp=0xc000133668 pc=0x1033791
runtime.mapaccess2_faststr(0x2?, 0x0?, {0xc0000960a8, 0x6})
/usr/local/go/src/runtime/map_faststr.go:117 +0x3d4 fp=0xc000133700 sp=0xc000133698 pc=0x1011c74
Go-Cache/00_fifo/character01.(*fifo).Set(0xc00006e4b0, {0xc0000960a8, 0x6}, {0xc0000960a0, 0x6, 0x8})那為了實現併發安全,我們需要增加一把鎖:
type fifo struct {
// 為了快速找到該value
cache map[string]*list.Element
// 按照添加順序保存的list
head *list.List
// 緩存數據
stat Stat
mutex sync.Mutex
}在所有可能修改數據的操作之前,加上鎖, 比如 set :
func (f *fifo) Set(key string, value []byte) {
f.mutex.Lock()
defer f.mutex.Unlock()
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok && e != nil {
f.setDataExisted(e, value)
} else {
f.setDataNotExisted(key, value)
}}fifo.go 文件改造如下:
import (
"container/list"
"sync" "time")
type fifo struct {
// 為了快速找到該value
cache map[string]*list.Element
// 按照添加順序保存的list
head *list.List
// 緩存數據
stat Stat
mutex sync.Mutex
}
func (f *fifo) Set(key string, value []byte) {
f.mutex.Lock()
defer f.mutex.Unlock()
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok && e != nil {
f.setDataExisted(e, value)
} else {
f.setDataNotExisted(key, value)
}}
func (f *fifo) setDataNotExisted(key string, value []byte) {
newEntry := &entry{
key: key,
value: value,
} if f.stat.maxBytes > 0 {
for f.stat.usedBytes+int64(len(key)+len(value)) > f.stat.maxBytes {
f.removeOldestElement()
} } e := f.head.PushBack(newEntry)
f.cache[key] = e
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes + int64(len(key)+len(value))
f.stat.keyCount++
}
func (f *fifo) setDataExisted(e *list.Element, value []byte) {
originEntry := e.Value.(*entry)
originSize := len(originEntry.value)
beRemoved := false
if f.stat.maxBytes > 0 {
for (int64)(len(value))-(int64)(originSize) > f.stat.maxBytes-f.stat.usedBytes {
if f.head.Front() == e {
beRemoved = true
}
f.removeOldestElement()
} } if beRemoved {
f.setDataNotExisted(originEntry.key, value)
return
}
originEntry.value = value
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes + (int64)(len(value)) - (int64)(originSize)
}
func (f *fifo) removeOldestElement() {
f.removeElement(f.head.Front())
}
func (f *fifo) removeElement(e *list.Element) {
if e == nil {
return
}
// 雙向鏈表的刪除
f.head.Remove(e)
originEntry := e.Value.(*entry)
f.stat.keyCount--
// 重新計算使用空間
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes - int64(len(originEntry.key)+len(originEntry.value))
// Hash表刪除
delete(f.cache, originEntry.key)
}
func (f *fifo) Get(key string) []byte {
f.mutex.Lock()
defer f.mutex.Unlock()
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok {
return e.Value.(*entry).value
}
return nil
}
func (f *fifo) Del(key string) {
f.mutex.Lock()
defer f.mutex.Unlock()
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok {
f.removeElement(e)
}}
func (f *fifo) Stat() Stat {
return f.stat
}
func New(maxBytes int64) Cache {
return &fifo{
cache: map[string]*list.Element{},
head: list.New(),
stat: Stat{
keyCount: 0,
maxBytes: maxBytes,
usedBytes: 0,
}, }}再測試一下, 一切正常:
func TestCache(t *testing.T) {
cache := character02.New(100000)
num := 100
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
index := i
wg.Add(1) //
go func() {
cache.Set("hello"+string(rune(index)), []byte("world"+string(rune(index))))
wg.Done() //5
}()
} wg.Wait()
fmt.Printf("stat:%v\n", cache.Stat())
}3.3 讀寫鎖
上面的鎖,是全局鎖,也就是不管是讀還是寫,都會上鎖,如果是讀多寫少的情況,我們希望讀是可以併發的,只有寫是獨佔的,這個時候就需要考慮讀寫鎖了。(緩存不一定適合使用讀寫鎖,這只是個思路,拋磚引玉。)
import (
"container/list"
"sync" "time")
type fifo struct {
// 為了快速找到該value
cache map[string]*list.Element
// 按照添加順序保存的list
head *list.List
// 緩存數據
stat Stat
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
func (f *fifo) Set(key string, value []byte) {
f.mutex.Lock()
defer f.mutex.Unlock()
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok && e != nil {
f.setDataExisted(e, value)
} else {
f.setDataNotExisted(key, value)
}}
func (f *fifo) setDataNotExisted(key string, value []byte) {
newEntry := &entry{
key: key,
value: value,
} if f.stat.maxBytes > 0 {
for f.stat.usedBytes+int64(len(key)+len(value)) > f.stat.maxBytes {
f.removeOldestElement()
} } e := f.head.PushBack(newEntry)
f.cache[key] = e
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes + int64(len(key)+len(value))
f.stat.keyCount++
}
func (f *fifo) setDataExisted(e *list.Element, value []byte) {
originEntry := e.Value.(*entry)
originSize := len(originEntry.value)
beRemoved := false
if f.stat.maxBytes > 0 {
for (int64)(len(value))-(int64)(originSize) > f.stat.maxBytes-f.stat.usedBytes {
if f.head.Front() == e {
beRemoved = true
}
f.removeOldestElement()
} } if beRemoved {
f.setDataNotExisted(originEntry.key, value)
return
}
originEntry.value = value
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes + (int64)(len(value)) - (int64)(originSize)
}
func (f *fifo) removeOldestElement() {
f.removeElement(f.head.Front())
}
func (f *fifo) removeElement(e *list.Element) {
if e == nil {
return
}
// 雙向鏈表的刪除
f.head.Remove(e)
originEntry := e.Value.(*entry)
f.stat.keyCount--
// 重新計算使用空間
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes - int64(len(originEntry.key)+len(originEntry.value))
// Hash表刪除
delete(f.cache, originEntry.key)
}
func (f *fifo) Get(key string) []byte {
f.mutex.RLock()
defer f.mutex.RUnlock()
// time.Sleep(1000000)
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok {
return e.Value.(*entry).value
}
return nil
}
func (f *fifo) Del(key string) {
f.mutex.Lock()
defer f.mutex.Unlock()
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok {
f.removeElement(e)
}}
func (f *fifo) Stat() Stat {
return f.stat
}
func New(maxBytes int64) Cache {
return &fifo{
cache: map[string]*list.Element{},
head: list.New(),
stat: Stat{
keyCount: 0,
maxBytes: maxBytes,
usedBytes: 0,
}, }}假設讀取 Cache 是比較耗時的,我們加點耗時在 Get 操作中:
func (f *fifo) Get(key string) []byte {
f.mutex.RLock()
defer f.mutex.RUnlock()
time.Sleep(1000000)
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok {
return e.Value.(*entry).value
}
return nil
}測試的數據如下,值得注意的是:如果讀競爭以及耗時不高,讀寫鎖會適得其反。
- 讀寫鎖:cost time: 4.560145ms
- 獨佔鎖:cost time:12.012624518s
// cost time:4.560145ms
func TestRWLock(t *testing.T) {
cache := character03.New(100000000000)
num := 10000
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
index := i
wg.Add(1) //
go func() {
cache.Set("hello"+string(rune(index)), []byte("world"+string(rune(index))))
wg.Done() //5
}()
} wg.Wait()
startTime := time.Now()
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
index := i
wg.Add(1) //
go func() {
cache.Get("hello" + string(rune(index)))
wg.Done()
}() } wg.Wait()
endTime := time.Now()
fmt.Printf("stat:%v\n", cache.Stat())
// cost time:31.587204813s
fmt.Printf("cost time:%v\n", endTime.Sub(startTime))
}
//cost time:12.012624518s
func TestLock(t *testing.T) {
cache := lock.New(100000000000)
num := 10000
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
index := i
wg.Add(1) //
go func() {
cache.Set("hello"+string(rune(index)), []byte("world"+string(rune(index))))
wg.Done()
}() } wg.Wait()
startTime := time.Now()
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
index := i
wg.Add(1) //
go func() {
cache.Get("hello" + string(rune(index)))
wg.Done() //5
}()
} wg.Wait()
endTime := time.Now()
fmt.Printf("stat:%v\n", cache.Stat())
//cost time:31.765169643s
fmt.Printf("cost time:%v\n", endTime.Sub(startTime))
}3.4 自實現雙向隊列
使用原生的雙向隊列,確實可以省事,但是作為一個程序員,還是有一種造輪子的想法,那就自己寫個雙向隊列,夠用就行,不用實現所有的方法:
type List struct {
head *Node // 表頭節點
tail *Node // 表尾節點
len int // 長度
}
type Node struct {
next, prev *Node
list *List
Value any
}
func NewList() *List {
return &List{}
}
func NewNode(v any) *Node {
return &Node{
Value: v,
}}
func (l *List) Front() *Node {
return l.head
}
func (l *List) Remove(node *Node) {
index := l.Find(node)
if index == -1 {
return
}
prev := node.prev
next := node.next
if prev == nil && next == nil {
l.len = 0
l.tail = nil
l.head = nil
return }
if prev == nil {
next := node.next
next.prev = nil
l.head = next
l.len--
return
}
if next == nil {
prev := node.prev
prev.next = nil
l.tail = prev
l.len--
return
}
prev.next = next
next.prev = prev
l.len--
return
}
func (l *List) Find(node *Node) int {
if l.len == 0 || node == nil {
return -1
}
index := 0
head := l.head
for head != nil {
if head != node {
head = head.next
index++
} else {
return index
}
} return -1
}
func (l *List) PushBack(v any) *Node {
node := NewNode(v)
if l.len == 0 {
node.prev = nil
node.next = nil
l.head = node
l.tail = node
} else {
tempTail := l.tail
tempTail.next = node
node.prev = tempTail
l.tail = node
}
l.len++
return node
}但凡使用到原生的 List 和 Node 的地方,都替換成自己實現的:
import (
"errors"
"log" "sync")
type fifo struct {
// 為了快速找到該value
cache map[string]*Node
// 按照添加順序保存的list
list *List
// 緩存數據
stat Stat
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
func (f *fifo) Set(key string, value []byte) {
f.mutex.Lock()
defer f.mutex.Unlock()
err := f.checkMaxBytes(key, value)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("checkMaxBytes err:%v\n", err)
return
}
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok && e != nil {
f.setDataExisted(e, value)
} else {
f.setDataNotExisted(key, value)
}}
func (f *fifo) checkMaxBytes(key string, value []byte) error {
if f.stat.maxBytes > 0 {
if f.stat.maxBytes < int64(len(key)+len(value)) {
return errors.New("over maxBytes")
} } return nil
}
func (f *fifo) setDataNotExisted(key string, value []byte) {
newEntry := &entry{
key: key,
value: value,
} if f.stat.maxBytes > 0 {
for f.stat.usedBytes+int64(len(key)+len(value)) > f.stat.maxBytes {
f.removeOldestElement()
} } e := f.list.PushBack(newEntry)
f.cache[key] = e
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes + int64(len(key)+len(value))
f.stat.keyCount++
}
func (f *fifo) setDataExisted(e *Node, value []byte) {
originEntry := e.Value.(*entry)
originSize := len(originEntry.value)
beRemoved := false
if f.stat.maxBytes > 0 {
for (int64)(len(value))-(int64)(originSize) > f.stat.maxBytes-f.stat.usedBytes {
if f.list.Front() == e {
beRemoved = true
}
f.removeOldestElement()
} } if beRemoved {
f.setDataNotExisted(originEntry.key, value)
return
}
originEntry.value = value
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes + (int64)(len(value)) - (int64)(originSize)
}
func (f *fifo) removeOldestElement() {
f.removeElement(f.list.Front())
}
func (f *fifo) removeElement(e *Node) {
if e == nil {
return
}
// 雙向鏈表的刪除
f.list.Remove(e)
originEntry := e.Value.(*entry)
f.stat.keyCount--
// 重新計算使用空間
f.stat.usedBytes = f.stat.usedBytes - int64(len(originEntry.key)+len(originEntry.value))
// Hash表刪除
delete(f.cache, originEntry.key)
}
func (f *fifo) Get(key string) []byte {
f.mutex.RLock()
defer f.mutex.RUnlock()
// time.Sleep(1000000)
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok {
return e.Value.(*entry).value
}
return nil
}
func (f *fifo) Del(key string) {
f.mutex.Lock()
defer f.mutex.Unlock()
if e, ok := f.cache[key]; ok {
f.removeElement(e)
}}
func (f *fifo) Stat() Stat {
return f.stat
}
func New(maxBytes int64) Cache {
return &fifo{
cache: map[string]*Node{},
list: NewList(),
stat: Stat{
keyCount: 0,
maxBytes: maxBytes,
usedBytes: 0,
}, }}簡單測試一下,符合預期:
func TestMyQueue(t *testing.T) {
Convey("TestApplyFunc", t, func() {
cache := character04.New(100)
stat := fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{0 100 0}")
cache.Set("hello", []byte("world"))
cache.Set("hello2", []byte("world2"))
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{2 100 22}")
cache.Set("hello2", []byte("changeWorld2"))
value := cache.Get("hello2")
So(string(value), ShouldEqual, "changeWorld2")
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{2 100 28}")
cache.Set("k1", []byte("longlonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglonglongV1"))
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{2 100 94}")
cache.Set("hello2", []byte("newHelloWorld2newHelloWorld2"))
value = cache.Get("hello2")
So(string(value), ShouldEqual, "newHelloWorld2newHelloWorld2")
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{1 100 34}")
cache.Set("num", character01.IntToBytes(1))
num := cache.Get("num")
So(character01.BytesToInt(num), ShouldEqual, 1)
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{2 100 45}")
cache.Set("num", nil)
So(cache.Get("num"), ShouldEqual, nil)
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{2 100 37}")
cache.Del("num")
stat = fmt.Sprintf("stat:%v", cache.Stat())
So(stat, ShouldEqual, "stat:{1 100 34}")
})}3.5 http 改造
一般緩存集成啓動後,除了能使用代碼直接操作,還會支持以 http 的方式操作,我們的也不能少了這個能力,那就來改造一下吧!
先封裝一個 server, 監聽 12345 端口,操作 Cache 和查詢狀態分別對應 cacheHandler 和 statHandler。
import (
"Go-Cache/00_fifo/character05"
"net/http")
type Server struct {
cache character05.Cache
}
func New(c character05.Cache) *Server {
return &Server{
c,
}}
func (s *Server) Listen() {
// 注意是 /cache/ 包括下面的子頁面
http.Handle("/cache/", s.cacheHandler())
http.Handle("/stat", s.statHandler())
http.ListenAndServe(":12345", nil)
}
func (s *Server) cacheHandler() *cacheHandler {
return &cacheHandler{
Server: s,
}}
func (s *Server) statHandler() *statHandler {
return &statHandler{
Server: s,
}}狀態查詢的 handler 實現:
import (
"encoding/json"
"log" "net/http")
type statHandler struct {
*Server
}
func (h *statHandler) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if r.Method != http.MethodGet {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusMethodNotAllowed)
return
}
b, e := json.Marshal(h.cache.Stat())
if e != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
res, err := w.Write(b)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
} log.Printf(string(rune(res)))
}操作緩存 handler 的實現:
import (
"io/ioutil"
"net/http" "strings")
type cacheHandler struct {
*Server
}
func (h *cacheHandler) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
key := strings.Split(r.URL.EscapedPath(), "/")[2]
if len(key) == 0 {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
m := r.Method
if m == http.MethodGet {
b := h.cache.Get(key)
if len(b) == 0 {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
return
}
w.Write(b)
return
}
if m == http.MethodPut {
b, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
if len(b) != 0 {
h.cache.Set(key, b)
} return
}
if m == http.MethodDelete {
h.cache.Del(key)
return
}
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusMethodNotAllowed)
}啓動類如下:
import (
"Go-Cache/00_fifo/character05"
"Go-Cache/00_fifo/character05/server")
func main() {
c := character05.New(0)
server.New(c).Listen()
}啓動之後,我們打開 http://localhost:12345/stat, 可以看到以下內容,就是啓動成功了:
下面是 curl 命令行操作:
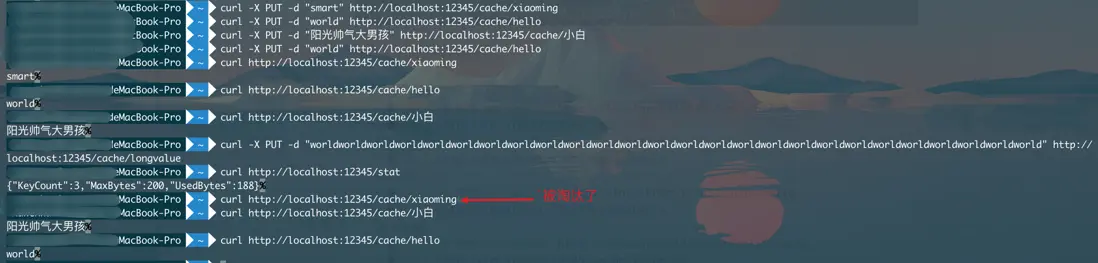
~ curl -X PUT -d "world" http://localhost:12345/cache/hello
~ curl http://localhost:12345/stat
{"KeyCount":1,"MaxBytes":0,"UsedBytes":10}%
~ curl http://localhost:12345/cache/hello
world%
~ curl -X PUT -d "world2" http://localhost:12345/cache/hello
~ curl http://localhost:12345/cache/hello
world2%
~ curl -X PUT -d "smart" http://localhost:12345/cache/xiaoming
~ curl http://localhost:12345/cache/xiaoming
smart%4 小結一下
總的來説,FIFO 是極其簡單的緩存淘汰算法,思路很清晰,初學者可以試試,它並不高效,但是它是最簡單粗暴的處理方法,先進先出,不會區別對待。