目錄
-
開撕MyBatis源碼
-
1. 手寫持久層框架-ipersistent
- 1.1 JDBC操作數據庫\_問題分析
- 1.2 JDBC問題分析&解決思路
-
1.3 自定義持久層框架\_思路分析
- 使用JDBC和使用持久層框架區別:
- 框架,除了思考本身的工程設計,還需要考慮到實際項目端的使用場景,干係方涉及兩端:
- 核心接口/類重點説明:
- 項目使用端:
- 自定義框架本身:
- 最終手寫的持久層框架結構參考:
- 1.4 自定義持久層框架\_編碼
- 1.5 自定義持久層框架\_優化
-
2. MyBatis架構原理&主要組件
- 2.1 MyBatis的架構設計
- 2.2 MyBatis主要組件及其相互關係
-
3. 源碼剖析-源碼環境搭建
- 3.1 源碼環境搭建
- 3.2 源碼導入&編譯
-
3.3 編寫測試代碼
- 3.3.1 配置sqlMapConfig.xml
- 3.3.2 配置UserMapper.xml
- 3.3.3 編寫User類
- 3.3.5 編寫測試類
-
4. 源碼剖析-初始化\_如何解析的全局配置文件?
- 前言
- 解析配置文件源碼流程:
- 入口:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build
-
XMLConfigBuilder#構造參數
- 1. XpathParser#構造函數
- 1.1 XPathParser#createDocument
- 2. XMLConfigBuilder#構造函數
- 2.1 Configuration#構造函數
-
XMLConfigBuilder#parse
- 1. XPathParser#evalNode(xpath語法)
- 2. XMLConfigBuilder#parseConfiguration(XNode)
-
5. 源碼剖析-初始化\_如何解析的映射配置文件?
- 前言
- 解析映射配置文件源碼流程:
- 入口:XMLConfigBuilder#mapperElement
-
\<package>子標籤
- 1. Configuration#addMappers
- 1.1 MapperRegistry#addMappers
- 1.1.1 MapperAnnotationBuilder#parse
- 1.1.1.1 MapperAnnotationBuilder#parseStatement
- 1.1.1.1.2 MapperBuilderAssistant#addMappedStatement
-
\<mapper>子標籤
- 1.XMLMapperBuilder#構造函數
- 1.1 XPathParser#構造函數
- 1.1.1 XPathParser#createDocument
- 1.2 XMLMapperBuilder#構造函數
- 1.2.1MapperBuilderAssistant#構造函數
- 2. XMLMapperBuilder#parse
- 2.1 XMLMapperBuilder#configurationElement
- 2.1.1 XMLMapperBuilder#buildStatementFromContext
- 2.1.1.1 XMLStatementBuilder#構造函數
- 2.1.1.2 XMLStatementBuilder#parseStatementNode
- 2.1.1.2.1 MapperBuilderAssistant#addMappedStatement
- 2.1.1.2.1.1 MappedStatement.Builder#構造函數
- 2.1.1.2.1.2 MappedStatement#build
-
6. 源碼剖析-SqlSource創建流程
- 相關類及對象
-
SqlSource創建流程
- 入口:XMLLanguageDriver#createSqlSource
- XMLScriptBuilder#構造函數
- 1.XMLScriptBuilder#initNodeHandlerMap
- XMLScriptBuilder#parseScriptNode
- 1 XMLScriptBuilder#parseDynamicTags
- 2. DynamicSqlSource#構造函數
- 3. RawSqlSource#構造函數
- 3.1 SqlSourceBuilder#parse
- 3.1.1 ParameterMappingTokenHandler#構造函數
- 3.1.2 GenericTokenParser#構造函數
- 3.1.3 GenericTokenParser#parse
- 3.1.4 StaticSqlSource#構造函數
-
7. 源碼剖析-揭秘SqlSession執行主流程
- 7.1 相關類與接口
- 7.2 流程分析
-
入口:DefaultSqlSession#selectList
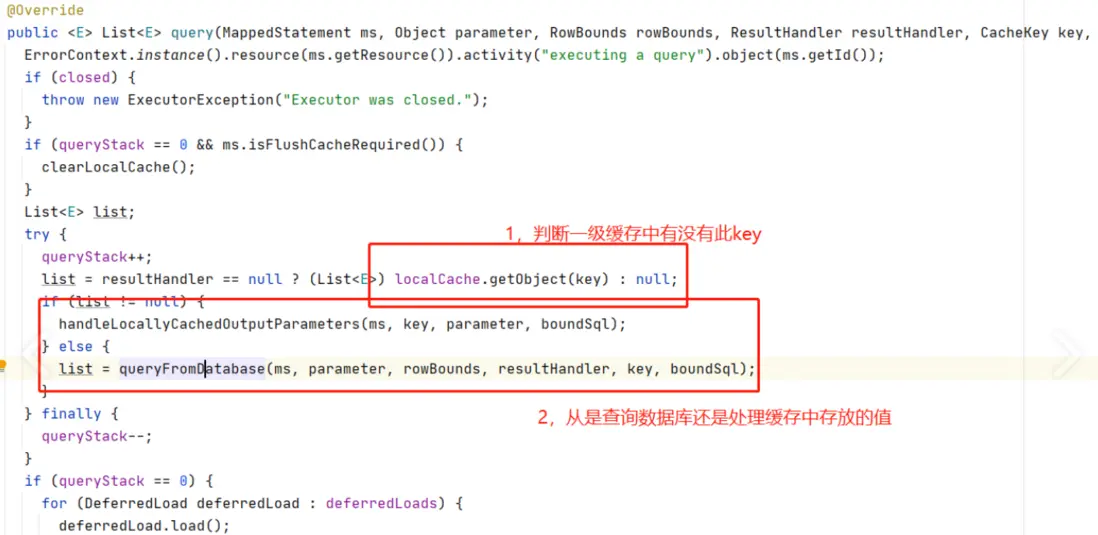
- 1. CachingExecutor#query
- 2. BaseExecutor#query
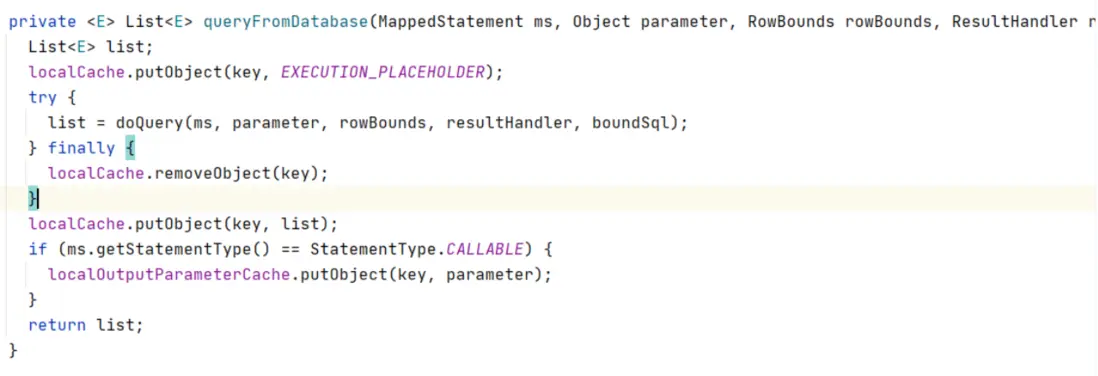
- 3. BaseExecutor#queryFromDatabase
- 4. SimpleExecutor#doQuery
- 4.1 Configuration#newStatementHandler
- 4.1.1 RoutingStatementHandler#構造函數
- 4.2 SimpleExecutor#prepareStatement
- 4.2.1 BaseExecutor#getConnection
- 4.2.2 BaseStatementHandler#prepare
- 4.2.2.1 PreparedStatementHandler#instantiateStatement
- 4.2.3 PreparedStatementHandler#parameterize
- 4.3 PreparedStatementHandler#query
- 4.3.1 PreparedStatement#execute
- 4.3.2 DefaultResultSetHandler#handleResultSets
- 執行sqlsession:參數有兩個(statementId和參數對象)
-
8. 源碼剖析-揭秘如何設置的參數?
-
入口:PreparedStatementHandler#parameterize方法
- DefaultParameterHandler#setParameters
- BaseTypeHandler#setParameter
- xxxTypeHandler#setNonNullParameter
-
-
9. 源碼剖析-結果集映射流程
-
入口:DefaultResultSetHandler#handleResultSets
- DefaultResultSetHandler#handleRowValues
- DefaultResultSetHandler#handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap
- 1. DefaultResultSetHandler#getRowValue
- 1.1 DefaultResultSetHandler#createResultObject
- 1.2 DefaultResultSetHandler#applyAutomaticMappings
- 1.3 DefaultResultSetHandler#applyPropertyMappings
-
-
10. 源碼剖析-獲取Mapper代理對象流程
-
入口:DefaultSqlSession#getMapper
- Configuration#getMapper
- 1. MapperRegistry#getMapper
- 1.1 MapperProxyFactory#newInstance
-
-
11. 源碼剖析-invoke方法
-
入口:MapperProxy#invoke
- MapperMethod
-
-
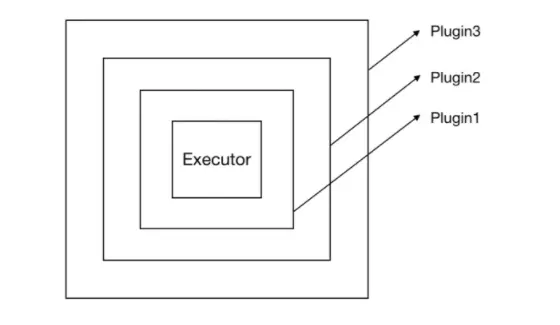
12. 源碼剖析-插件機制
- 12.1 插件概述
-
12.2 Mybatis插件介紹
- 能幹什麼?
- 如何自定義插件?
-
12.3 自定義插件
- 核心思想:
-
12.4 源碼分析-插件
- 插件配置信息的加載
- 代理對象的生成
- 攔截邏輯的執行
-
13. 源碼剖析-緩存策略
-
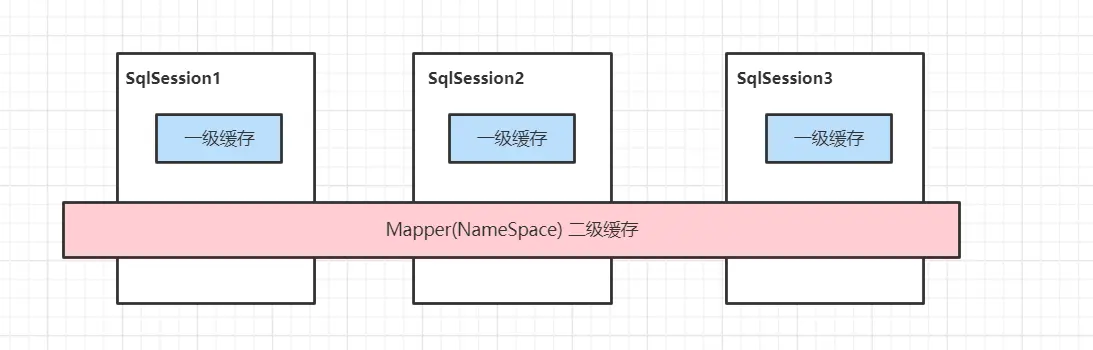
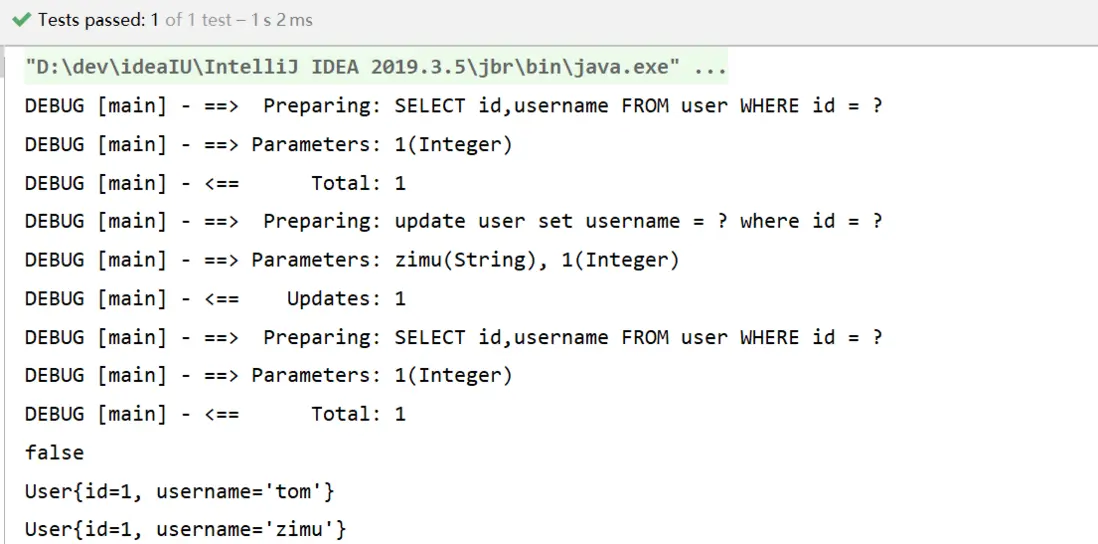
一級緩存
- 一級緩存原理探究與源碼分析
- 1. 一級緩存 底層數據結構到底是什麼?
- 2. 一級緩存的執行流程
- 一級緩存源碼分析結論:
-
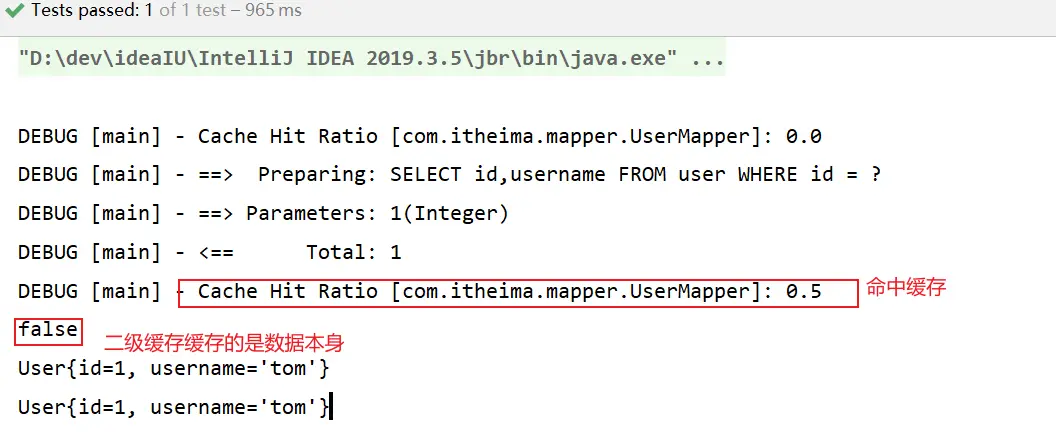
二級緩存
- 啓用二級緩存
- 二級緩存源碼分析
- 標籤 < cache/> 的解析
- buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));將Cache包裝到MappedStatement
- 查詢源碼分析
- CachingExecutor
- TransactionalCacheManager
- TransactionalCache
- 為何只有SqlSession提交或關閉之後?
- 二級緩存的刷新
- 總結:
-
-
開撕MyBatis源碼
* 手寫持久層框架-仿寫mybatis
* Mybatis架構設計&主要組件
* Mybatis如何完成的初始化?
* Mybatis如何完成的sql解析及執行?
* Mybatis如何設置的參數?
* Mybatis如何進行的類型轉換?
* Mybatis如何封裝的返回結果集?
* Mybatis插件原理是什?
* Mybatis緩存底層數據結構是什麼?1. 手寫持久層框架-ipersistent
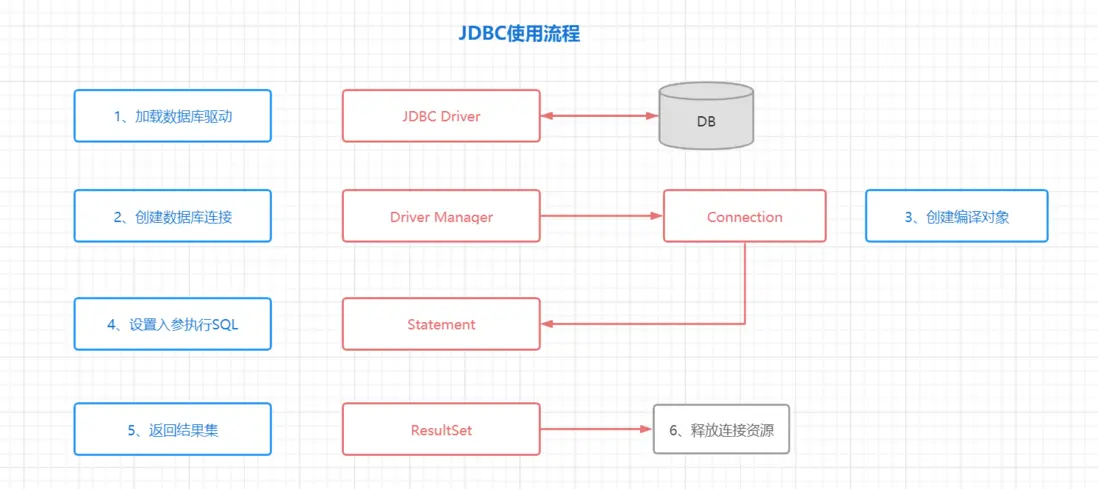
1.1 JDBC操作數據庫\_問題分析
JDBC API 允許應用程序訪問任何形式的表格數據,特別是存儲在關係數據庫中的數據
代碼示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 加載數據庫驅動
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 通過驅動管理類獲取數據庫鏈接
connection =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis? characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "root");
// 定義sql語句?表示佔位符
String sql = "select * from user where username = ?";
// 獲取預處理statement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 設置參數,第一個參數為sql語句中參數的序號(從1開始),第二個參數為設置的參數值 preparedStatement.setString(1, "tom");
// 向數據庫發出sql執行查詢,查詢出結果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 遍歷查詢結果集
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String username = resultSet.getString("username");
// 封裝User
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername(username);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 釋放資源
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}1.2 JDBC問題分析&解決思路
剖開代碼,逐個分析:
(1)加載驅動,獲取鏈接:
-
存在問題1:數據庫配置信息存在硬編碼問題。
優化思路:使用配置文件!
-
存在問題2:頻繁創建、釋放數據庫連接問題。
優化思路:使用數據連接池!
(2)定義sql、設置參數、執行查詢:
-
存在問題3:SQL語句、設置參數、獲取結果集參數均存在硬編碼問題 。
優化思路:使用配置文件!
(2)遍歷查詢結果集:
-
存在問題4:手動封裝返回結果集,較為繁瑣
優化思路:使用Java反射、內省!
針對JDBC各個環節中存在的不足,現在,我們整理出對應的優化思路,統一彙總:
| 存在問題 | 優化思路 |
|---|---|
| 數據庫配置信息存在硬編碼問題 | 使用配置文件 |
| 頻繁創建、釋放數據庫連接問題 | 使用數據連接池 |
| SQL語句、設置參數、獲取結果集參數均存在硬編碼問題 | 使用配置文件 |
| 手動封裝返回結果集,較為繁瑣 | 使用Java反射、內省 |
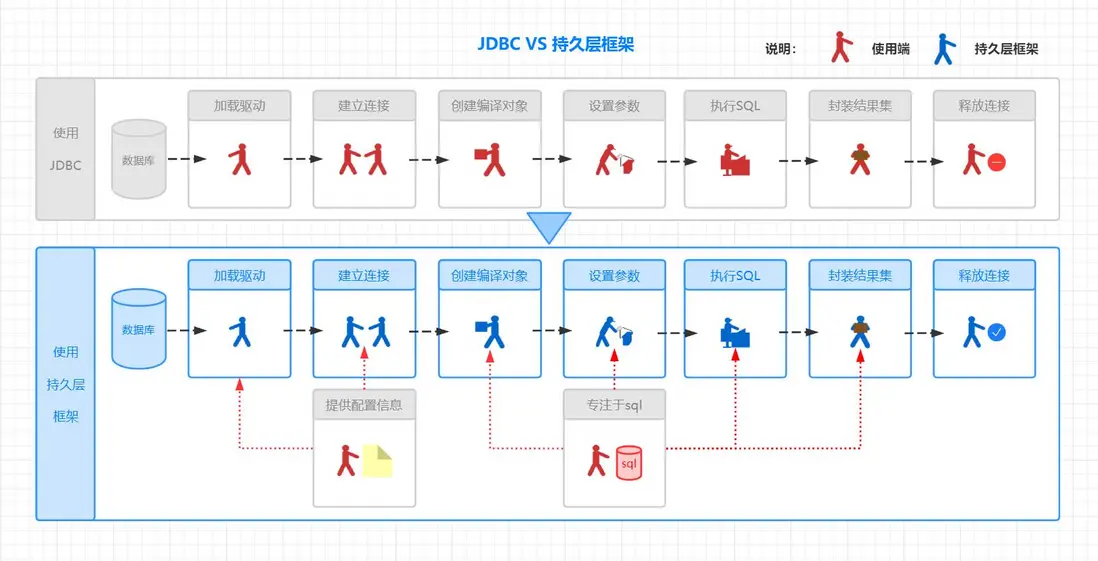
1.3 自定義持久層框架\_思路分析
JDBC是個人作戰,凡事親力親為,低效而高險,自己加載驅動,自己建連接,自己 …
而持久層框架好比是多工種協作,分工明確,執行高效,有專門負責解析註冊驅動建立連接的,有專門管理數據連接池的,有專門執行sql語句的,有專門做預處理參數的,有專門裝配結果集的 …
優化思路: 框架的作用,就是為了幫助我們減去繁重開發細節與冗餘代碼,使我們能更加專注於業務應用開發。
使用JDBC和使用持久層框架區別:
是不是發現,擁有這麼一套持久層框架是如此舒適,我們僅僅需要幹兩件事:
- 配置數據源(地址/數據名/用户名/密碼)
- 編寫SQL與參數準備(SQL語句/參數類型/返回值類型)
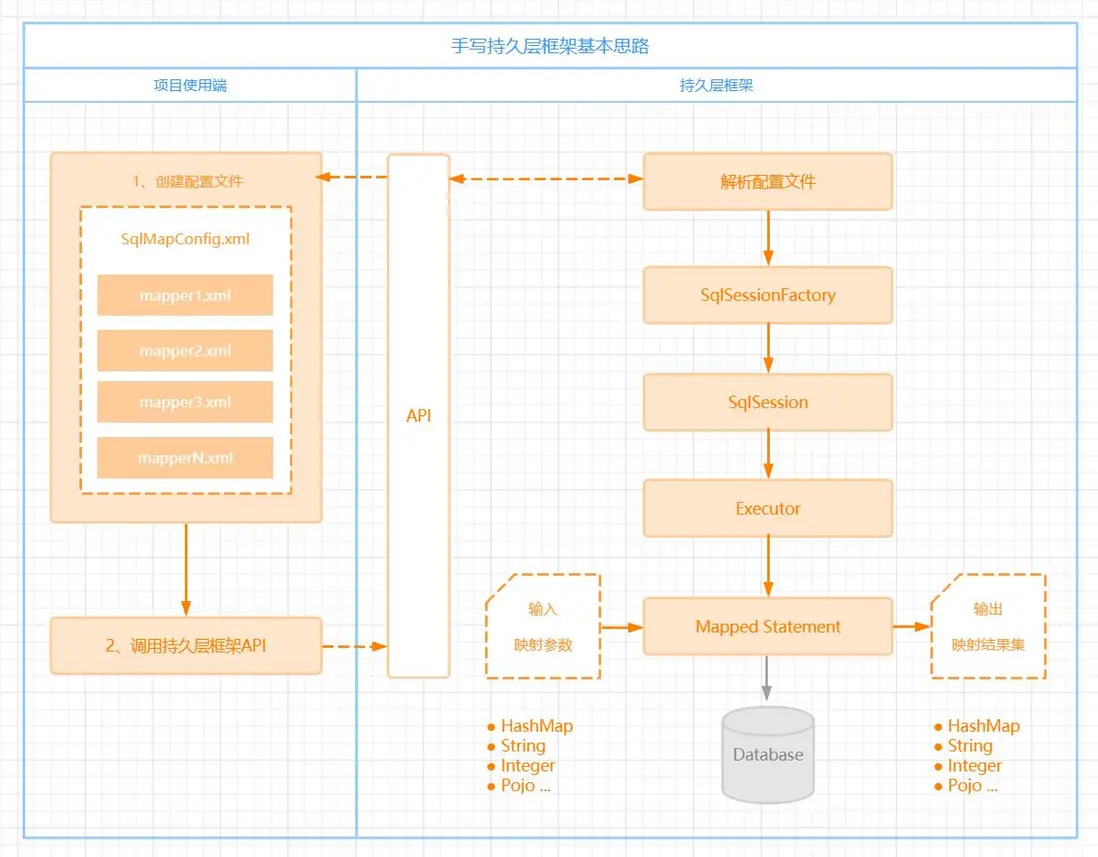
框架,除了思考本身的工程設計,還需要考慮到實際項目端的使用場景,干係方涉及兩端:
- 使用端(實際項目)
- 持久層框架本身
以上兩步,我們通過一張架構圖《 手寫持久層框架基本思路 》來梳理清楚:
核心接口/類重點説明:
| 分工協作 | 角色定位 | 類名定義 |
|---|---|---|
| 負責讀取配置文件 | 資源輔助類 | Resources |
| 負責存儲數據庫連接信息 | 數據庫資源類 | Configuration |
| 負責存儲SQL映射定義、存儲結果集映射定義 | SQL與結果集資源類 | MappedStatement |
| 負責解析配置文件,創建會話工廠SqlSessionFactory | 會話工廠構建者 | SqlSessionFactoryBuilder |
| 負責創建會話SqlSession | 會話工廠 | SqlSessionFactory |
| 指派執行器Executor | 會話 | SqlSession |
| 負責執行SQL (配合指定資源Mapped Statement) | 執行器 | Executor |
正常來説項目只對應一套數據庫環境,一般對應一個SqlSessionFactory實例對象,我們使用單例模式只創建一個SqlSessionFactory實例。
如果需要配置多套數據庫環境,那需要做一些拓展,例如Mybatis中通過environments等配置就可以支持多套測試/生產數據庫環境進行切換。
項目使用端:
(1)調用框架API,除了引入自定義持久層框架的jar包
(2)提供兩部分配置信息:1.sqlMapConfig.xml : 數據庫配置信息(地址/數據名/用户名/密碼),以及mapper.xml的全路徑
2.mapper.xml : SQL配置信息,存放SQL語句、參數類型、返回值類型相關信息
自定義框架本身:
1、加載配置文件:根據配置文件的路徑,加載配置文件成字節輸入流,存儲在內存中。
2、 創建兩個javaBean(容器對象):存放配置文件解析出來的內容
3、解析配置文件(使用dom4j) ,並創建SqlSession會話對象
4、創建SqlSessionFactory接口以及實現類DefaultSqlSessionFactory
5、創建SqlSession接口以及實現類DefaultSqlSession
6、創建Executor接口以及實現類SimpleExecutor
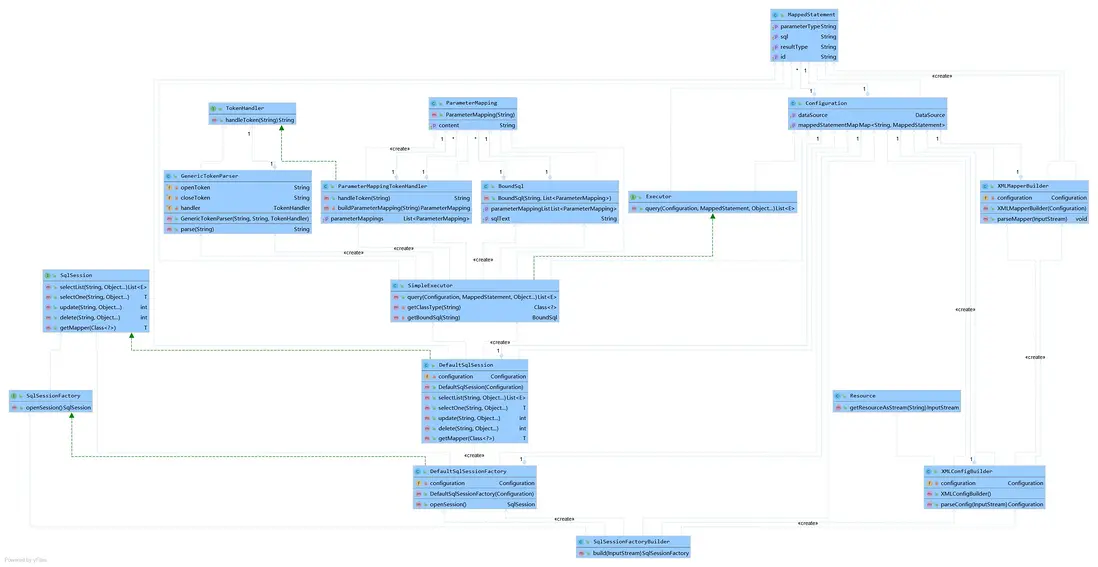
基本過程我們已經清晰,我們再細化一下類圖,更好的助於我們實際編碼:
最終手寫的持久層框架結構參考:
1.4 自定義持久層框架\_編碼
<properties>
<!-- Encoding -->
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
<java.version>11</java.version>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<!--引入ipersistent的依賴>在使用端項目中創建配置配置文件
創建 sqlMapConfig.xml
<configuration>
<!--1.配置數據庫配置信息-->
<dataSource>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///zdy_mybatis?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</dataSource>
<!--2.引入映射配置文件-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"></mapper>
</mappers>
</configuration> mapper.xml
<mapper namespace="User">
<!--根據條件查詢單個-->
<select id="selectOne" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User" parameterType="com.itheima.pojo.User">
select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{username}
</select>
<!--查詢所有-->
<select id="selectList" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User">
select * from user
</select>
</mapper>User實體
public class User {
//主鍵標識
private Integer id;
//用户名
private String username;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' + '}';
}
}再創建一個Maven子工程並且導入需要用到的依賴座標
<properties>
<!-- Encoding -->
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
<java.version>11</java.version>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- mysql 依賴-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit 依賴-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<!--作用域測試範圍-->
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--dom4j 依賴-->
<dependency>
<groupId>dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>1.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--xpath 依賴-->
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--druid連接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.21</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log日誌 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Resources
public class Resources {
/**
* 根據配置文件的路徑,加載成字節輸入流,存到內存中
* @param path
* @return
*/
public static InputStream getResourceAsSteam(String path){
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(path);
return resourceAsStream;
}Configuration
/**
* 存放核心配置文件解析的內容
*/
public class Configuration {
// 數據源對象
private DataSource dataSource;
// map : key :statementId value : 封裝好的MappedStatement
private Map<String,MappedStatement> mappedStatementMap = new HashMap<>();
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
public Map<String, MappedStatement> getMappedStatementMap() {
return mappedStatementMap;
}
public void setMappedStatementMap(Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatementMap) {
this.mappedStatementMap = mappedStatementMap;
}
}MappedStatement
/**
* 存放解析映射配置文件的內容
* <select id="selectOne" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User" parameterType="com.itheima.pojo.User">
* select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{username}
* </select>
*/
public class MappedStatement {
// 1.唯一標識 (statementId namespace.id)
private String statementId;
// 2.返回結果類型
private String resultType;
// 3.參數類型
private String parameterType;
// 4.要執行的sql語句
private String sql;
// 5.mapper代理:sqlcommandType
private String sqlcommandType;
public String getSqlcommandType() {
return sqlcommandType;
}
public void setSqlcommandType(String sqlcommandType) {
this.sqlcommandType = sqlcommandType;
}
public String getStatementId() {
return statementId;
}
public void setStatementId(String statementId) {
this.statementId = statementId;
}
public String getResultType() {
return resultType;
}
public void setResultType(String resultType) {
this.resultType = resultType;
}
public String getParameterType() {
return parameterType;
}
public void setParameterType(String parameterType) {
this.parameterType = parameterType;
}
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
public void setSql(String sql) {
this.sql = sql;
}
}SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
/**
* 1.解析配置文件,封裝Configuration 2.創建SqlSessionFactory工廠對象
* @return
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) throws DocumentException {
// 1.解析配置文件,封裝Configuration
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder();
Configuration configuration = xmlConfigBuilder.parse(inputStream);
SqlSessionFactory defatultSqlSessionFactory = new DefatultSqlSessionFactory(configuration);
return defatultSqlSessionFactory;
}
}XMLConfigerBuilder
public class XMLConfigBuilder {
private Configuration configuration;
public XMLConfigBuilder() {
configuration = new Configuration();
}
/**
* 使用dom4j解析xml文件,封裝configuration對象
* @param inputStream
* @return
*/
public Configuration parse(InputStream inputStream) throws DocumentException {
Document document = new SAXReader().read(inputStream);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
// 解析核心配置文件中數據源部分
List<Element> list = rootElement.selectNodes("//property");
// <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
Properties properties = new Properties();
for (Element element : list) {
String name = element.attributeValue("name");
String value = element.attributeValue("value");
properties.setProperty(name,value);
}
// 創建數據源對象(連接池)
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName(properties.getProperty("driverClassName"));
druidDataSource.setUrl(properties.getProperty("url"));
druidDataSource.setUsername(properties.getProperty("username"));
druidDataSource.setPassword(properties.getProperty("password"));
// 創建好的數據源對象封裝進configuration中、
configuration.setDataSource(druidDataSource);
// 解析映射配置文件
// 1.獲取映射配置文件的路徑 2.解析 3.封裝好mappedStatement
List<Element> mapperList = rootElement.selectNodes("//mapper");
for (Element element : mapperList) {
String mapperPath = element.attributeValue("resource");
InputStream resourceAsSteam = Resources.getResourceAsSteam(mapperPath);
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(configuration);
xmlMapperBuilder.parse(resourceAsSteam);
}
return configuration;
}
}XMLMapperBuilder
public class XMLMapperBuilder {
private Configuration configuration;
public XMLMapperBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
public void parse(InputStream inputStream) throws DocumentException, ClassNotFoundException {
Document document = new SAXReader().read(inputStream);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
String namespace = rootElement.attributeValue("namespace");
List<Element> select = rootElement.selectNodes("select");
for (Element element : select) { //id的值
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
String paramterType = element.attributeValue("paramterType");
String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType"); //輸入參數class
Class<?> paramterTypeClass = getClassType(paramterType);
//返回結果class
Class<?> resultTypeClass = getClassType(resultType);
//statementId
String key = namespace + "." + id;
//sql語句
String textTrim = element.getTextTrim();
//封裝 mappedStatement
MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement();
mappedStatement.setId(id);
mappedStatement.setParamterType(paramterTypeClass);
mappedStatement.setResultType(resultTypeClass);
mappedStatement.setSql(textTrim);
//填充 configuration
configuration.getMappedStatementMap().put(key, mappedStatement);
private Class<?> getClassType (String paramterType) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(paramterType);
return aClass;
}
}sqlSessionFactory 接口及D efaultSqlSessionFactory 實現類
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
/**
* 生產sqlSession :封裝着與數據庫交互的方法
* @return
*/
public SqlSession openSession();
}
public class DefatultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private Configuration configuration;
public DefatultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
// 執行器創建出來
Executor executor = new SimpleExecutor();
DefaultSqlSession defaultSqlSession = new DefaultSqlSession(configuration,executor);
return defaultSqlSession;
}
}
sqlSession 接口及 DefaultSqlSession 實現類
public interface SqlSession {
/**
* 查詢所有的方法 select * from user where username like '%aaa%' and sex = ''
* 參數1:唯一標識
* 參數2:入參
*/
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statementId,Object parameter) throws Exception;
/**
* 查詢單個的方法
*/
public <T> T selectOne(String statementId,Object parameter) throws Exception;
}
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Configuration configuration;
private Executor executor;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
}
@Override // user.selectList 1 tom user
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statementId, Object params) throws Exception {
MappedStatement mappedStatement = configuration.getMappedStatementMap().get(statementId);
// 將查詢操作委派給底層的執行器
List<E> list = executor.query(configuration,mappedStatement,params);
return list;
}
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statementId, Object params) throws Exception {
List<Object> list = this.selectList(statementId, params);
if(list.size() == 1){
return (T) list.get(0);
}else if(list.size() > 1){
throw new RuntimeException("返回結果過多");
}else {
return null;
}
}
} Executor
public interface Executor {
<E> List<E> query(Configuration configuration, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object params) throws Exception;
}
SimpleExecutor
public class SimpleExecutor implements Executor {
/**
* 執行JDBC操作
* @param configuration
* @param mappedStatement
* @param params
* @param <E>
* @return
*/
@Override // user product
public <E> List<E> query(Configuration configuration, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object params) throws Exception {
// 1. 加載驅動,獲取連接
Connection connection = configuration.getDataSource().getConnection();
// 2. 獲取prepareStatement預編譯對象
/*
select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{username}
select * from user where id = ? and username = ?
佔位符替換 :#{}替換成? 注意:#{id}裏面的id名稱要保存
*/
String sql = mappedStatement.getSql();
BoundSql boundSql = getBoundSQL(sql);
String finaLSql = boundSql.getFinaLSql();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(finaLSql);
// 3.設置參數
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if(parameterMappings.size() > 0){
// com.itheima.pojo.User
String parameterType = mappedStatement.getParameterType();
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = Class.forName(parameterType);
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
// id
String content = parameterMapping.getContent();
// 反射
Field declaredField = parameterTypeClass.getDeclaredField(content);
// 暴力訪問
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
Object value = declaredField.get(params);
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1 ,value);
}
}
// 4.執行sql,發起查詢
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
String resultType = mappedStatement.getResultType();
Class<?> resultTypeClass = Class.forName(resultType);
ArrayList<E> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 5.遍歷封裝
while (resultSet.next()){
// 元數據信息中包含了字段名 字段的值
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
Object obj = resultTypeClass.newInstance();
for (int i = 1; i <= metaData.getColumnCount() ; i++) {
// id username
String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnName);
// 屬性描述器
PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor = new PropertyDescriptor(columnName,resultTypeClass);
Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
writeMethod.invoke(obj,value);
}
list.add((E) obj);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 1.將sql中#{}替換成? 2.將#{}裏面的值保存
* @param sql
* @return
*/
private BoundSql getBoundSQL(String sql) {
// 標記處理器:配合標記解析器完成標記的解析工作
ParameterMappingTokenHandler parameterMappingTokenHandler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler();
// 標記解析器
GenericTokenParser genericTokenParser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", parameterMappingTokenHandler);
String finalSql = genericTokenParser.parse(sql);
// #{}裏面的值的集合
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = parameterMappingTokenHandler.getParameterMappings();
BoundSql boundSql = new BoundSql(finalSql, parameterMappings);
return boundSql;
}
}BoundSql
public class BoundSql {
//解析過後的sql語句
private String sqlText;
//解析出來的參數
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList = new ArrayList<ParameterMapping>();
public BoundSql(String sqlText, List<ParameterMapping>
parameterMappingList) {
this.sqlText = sqlText;
this.parameterMappingList = parameterMappingList;
}
public String getSqlText() {
return sqlText;
}
public void setSqlText(String sqlText) {
this.sqlText = sqlText;
}
public List<ParameterMapping> getParameterMappingList() {
return parameterMappingList;
}
public void setParameterMappingList(List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList) {
this.parameterMappingList = parameterMappingList;
}
}1.5 自定義持久層框架\_優化
通過上述我們的自定義框架,我們解決了JDBC操作數據庫帶來的一些問題:例如頻繁創建釋放數據庫連 接,硬編碼,手動封裝返回結果集等問題,但是現在我們繼續來分析剛剛完成的自定義框架代碼,有沒 有什麼問題?
問題如下:
- dao的實現類中存在重複的代碼,整個操作的過程模板重複(創建sqlsession,調用sqlsession方 法,關閉 sqlsession)
- dao的實現類中存在硬編碼,調用sqlsession的方法時,參數statement的id硬編碼
解決:使用代理模式來創建接口的代理對象
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
InputStream resourceAsSteam = Resources.getResourceAsSteam(path: "sqlMapConfig.xml")
SqlSessionFactory build = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsSteam);
SqlSession sqlSession = build.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setld(l);
user.setUsername("tom");
//代理對象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMappper(UserMapper.class);
User userl = userMapper.selectOne(user);
System・out.println(userl);
}在sqlSession中添加方法
public interface SqlSession {
public <T> T getMappper(Class<?> mapperClass);實現類
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Configuration configuration;
private Executor executor;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
}
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<?> c) {
// 基於JDK動態代理產生接口的代理對象
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(DefaultSqlSession.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{c}, new InvocationHandler() {
/*
o : 代理對象:很少用到
method :正在執行的方法
objects :方法的參數
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects) throws Throwable {
// findByCondition
String methodName = method.getName();
// com.itheima.dao.IUserDao
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
// 唯一標識:namespace.id com.itheima.dao.IUserDao.findByCondition
String statementId = className + "." +methodName;
MappedStatement mappedStatement = configuration.getMappedStatementMap().get(statementId);
String sql = mappedStatement.getSql();
// sqlcommandType select insert update delete
String sqlcommandType = mappedStatement.getSqlcommandType();
switch (sqlcommandType){
case "select":
// 查詢操作 問題來了:selectList 還是selectOne?
Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
// 判斷是否實現泛型類型參數化
if(genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
return selectList(statementId,objects);
}
return selectOne(statementId,objects);
case "update":
break;
// 更新操作
case "delete":
break;
// 刪除操作
case "insert":
break;
// 添加操作
}
return null;
}
});
return (T) proxy;
}2. MyBatis架構原理&主要組件
2.1 MyBatis的架構設計
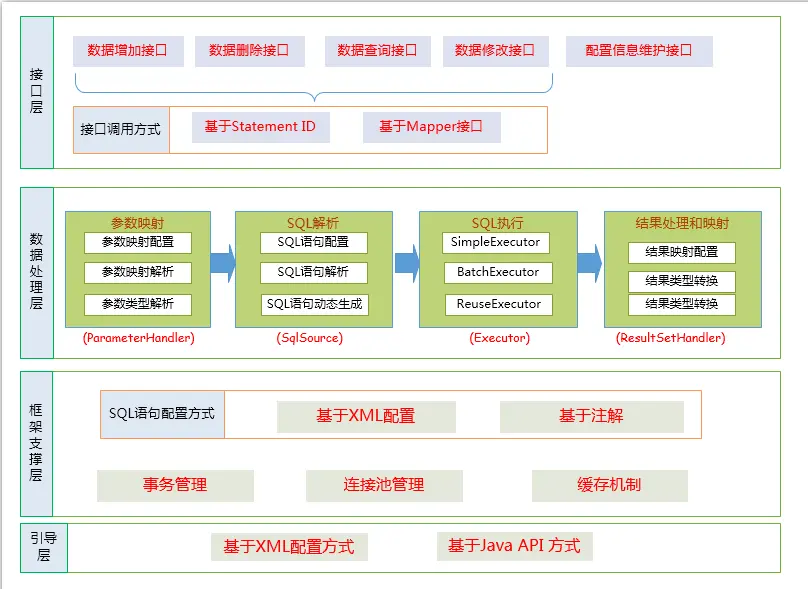
mybatis架構四層作用是什麼呢?
- Api接口層:提供API 增加、刪除、修改、查詢等接口,通過API接口對數據庫進行操作。
- 數據處理層:主要負責SQL的 查詢、解析、執行以及結果映射的處理,主要作用解析sql根據調用請求完成一次數據庫操作.
- 框架支撐層:負責通用基礎服務支撐,包含事務管理、連接池管理、緩存管理等共用組件的封裝,為上層提供基礎服務支撐.
- 引導層:引導層是配置和啓動MyBatis 配置信息的方式
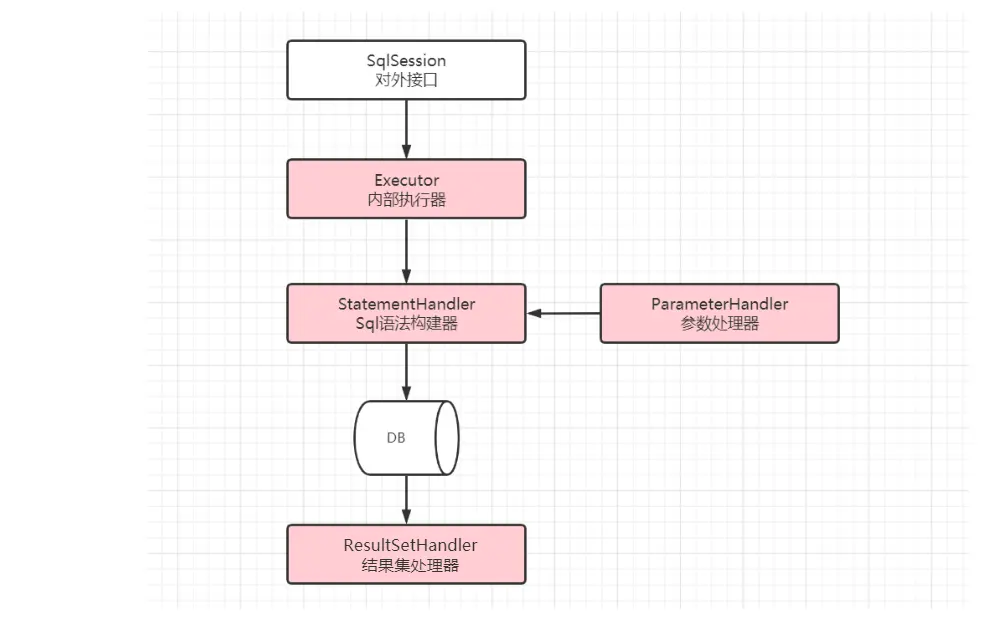
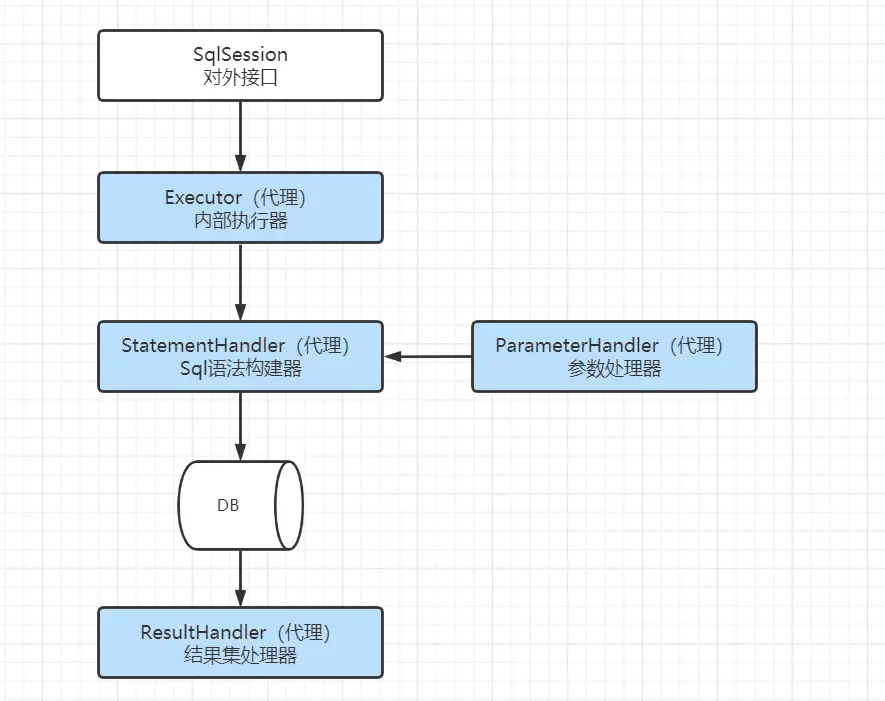
2.2 MyBatis主要組件及其相互關係
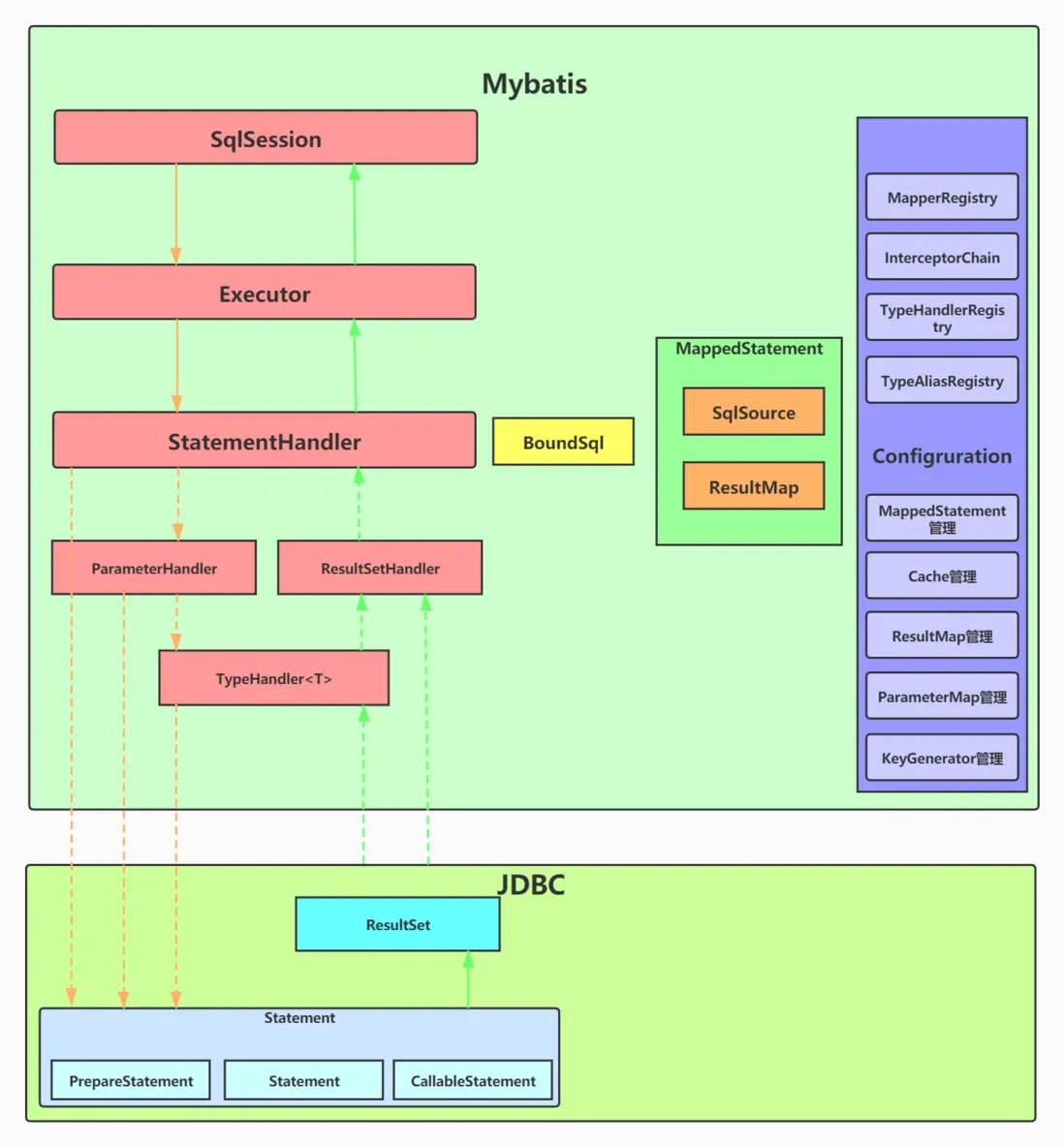
組件關係如下圖所示:
組件介紹:
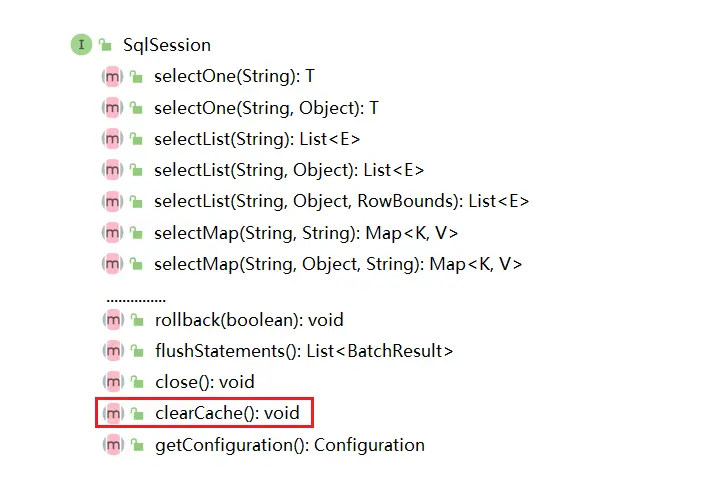
- SqlSession:是Mybatis對外暴露的核心API,提供了對數據庫的DRUD操作接口。
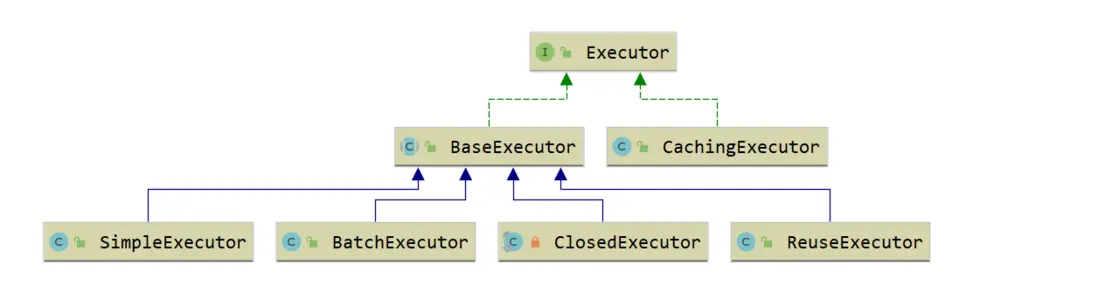
- Executor:執行器,由SqlSession調用,負責數據庫操作以及Mybatis兩級緩存的維護
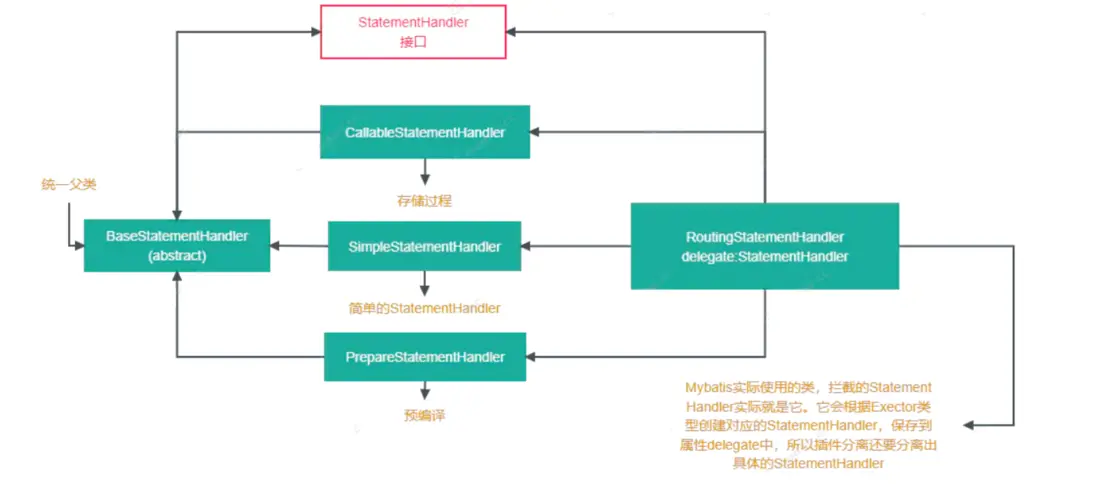
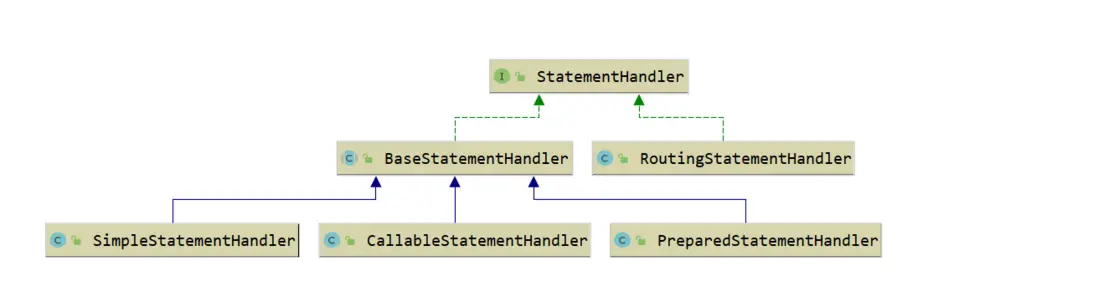
- StatementHandler:封裝了JDBC Statement操作,負責對Statement的操作,例如PrepareStatement參數的設置以及結果集的處理。
- ParameterHandler:是StatementHandler內部一個組件,主要負責對ParameterStatement參數的設置
- ResultSetHandler:是StatementHandler內部一個組件,主要負責對ResultSet結果集的處理,封裝成目標對象返回
- TypeHandler:用於Java類型與JDBC類型之間的數據轉換,ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler會分別使用到它的類型轉換功能
- MappedStatement:是對Mapper配置文件或Mapper接口方法上通過註解申明SQL的封裝
- Configuration:Mybatis所有配置都統一由Configuration進行管理,內部由具體對象分別管理各自的小功能模塊
3. 源碼剖析-源碼環境搭建
3.1 源碼環境搭建
- mybatis源碼地址:https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3
3.2 源碼導入&編譯
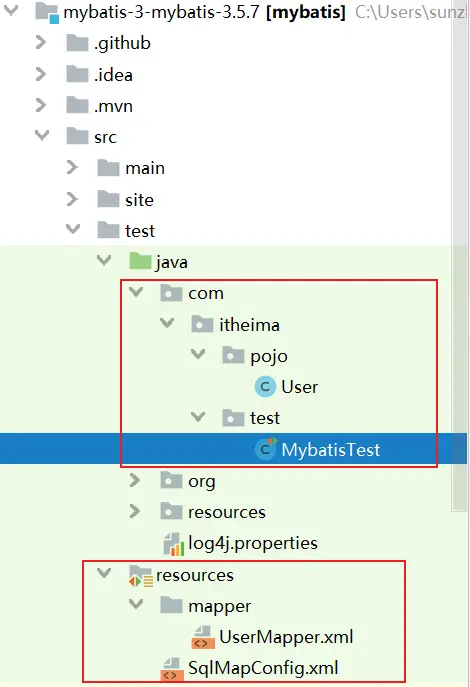
3.3 編寫測試代碼
3.3.1 配置sqlMapConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--第一部分:數據源配置-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!-- 使用jdbc事務管理 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 數據庫連接池 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:mysql:///zdy_mybatis?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--第二部分:引入映射配置文件-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"></mapper>
</mappers>
</configuration>3.3.2 配置UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="user">
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User">
SELECT id,username FROM user WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>3.3.3 編寫User類
package com.itheima.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class User {
// ID標識
private Integer id;
// 用户名
private String username;
}3.3.5 編寫測試類
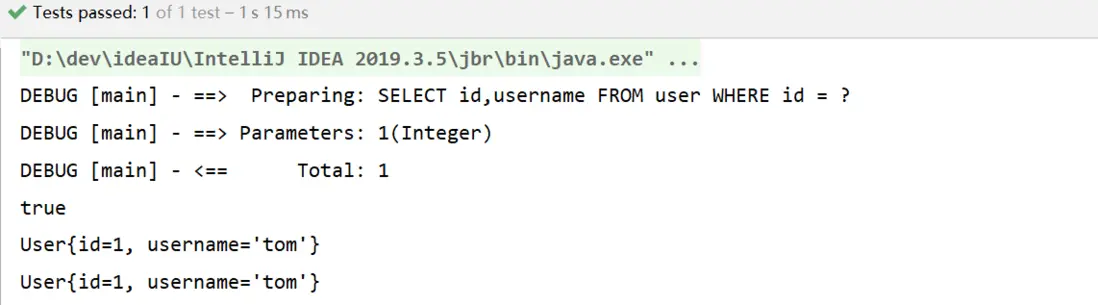
public class MybatisTest {
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("user.findUserById", user1);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println("MyBatis源碼環境搭建成功...");
sqlSession.close();
}
}輸出:
4. 源碼剖析-初始化\_如何解析的全局配置文件?
前言
全局配置文件可配置參數:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html
- Configuration對象
public class Configuration {
protected Environment environment;
// 允許在嵌套語句中使用分頁(RowBounds)。如果允許使用則設置為false。默認為false
protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled;
// 允許在嵌套語句中使用分頁(ResultHandler)。如果允許使用則設置為false
protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true;
// 是否開啓自動駝峯命名規則(camel case)映射,即從經典數據庫列名 A_COLUMN
// 到經典 Java 屬性名 aColumn 的類似映射。默認false
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase;
// 當開啓時,任何方法的調用都會加載該對象的所有屬性。否則,每個屬性會按需加載。默認值false (true in ≤3.4.1)
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading;
// 是否允許單一語句返回多結果集(需要兼容驅動)。
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
// 允許 JDBC 支持自動生成主鍵,需要驅動兼容。這就是insert時獲取mysql自增主鍵/oracle sequence的開關。
// 注:一般來説,這是希望的結果,應該默認值為true比較合適。
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys;
// 使用列標籤代替列名,一般來説,這是希望的結果
protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;
// 是否啓用緩存
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
// 指定當結果集中值為 null 的時候是否調用映射對象的 setter(map 對象時為 put)方法,
// 這對於有 Map.keySet() 依賴或 null 值初始化的時候是有用的。
protected boolean callSettersOnNulls;
// 允許使用方法簽名中的名稱作為語句參數名稱。 為了使用該特性,你的工程必須採用Java 8編譯,
// 並且加上-parameters選項。(從3.4.1開始)
protected boolean useActualParamName = true;
//當返回行的所有列都是空時,MyBatis默認返回null。 當開啓這個設置時,MyBatis會返回一個空實例。
// 請注意,它也適用於嵌套的結果集 (i.e. collectioin and association)。(從3.4.2開始)
// 注:這裏應該拆分為兩個參數比較合適, 一個用於結果集,一個用於單記錄。
// 通常來説,我們會希望結果集不是null,單記錄仍然是null
protected boolean returnInstanceForEmptyRow;
protected boolean shrinkWhitespacesInSql;
// 指定 MyBatis 增加到日誌名稱的前綴。
protected String logPrefix;
// 指定 MyBatis 所用日誌的具體實現,未指定時將自動查找。一般建議指定為slf4j或log4j
protected Class<? extends Log> logImpl;
// 指定VFS的實現, VFS是mybatis提供的用於訪問AS內資源的一個簡便接口
protected Class<? extends VFS> vfsImpl;
protected Class<?> defaultSqlProviderType;
// MyBatis 利用本地緩存機制(Local Cache)防止循環引用(circular references)和加速重複嵌套查詢。
// 默認值為 SESSION,這種情況下會緩存一個會話中執行的所有查詢。
// 若設置值為 STATEMENT,本地會話僅用在語句執行上,對相同 SqlSession 的不同調用將不會共享數據。
protected LocalCacheScope localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION;
// 當沒有為參數提供特定的 JDBC 類型時,為空值指定 JDBC 類型。 某些驅動需要指定列的 JDBC 類型,
// 多數情況直接用一般類型即可,比如 NULL、VARCHAR 或 OTHER。
protected JdbcType jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER;
// 指定對象的哪個方法觸發一次延遲加載。
protected Set<String> lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList("equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString"));
// 設置超時時間,它決定驅動等待數據庫響應的秒數。默認不超時
protected Integer defaultStatementTimeout;
// 為驅動的結果集設置默認獲取數量。
protected Integer defaultFetchSize;
// SIMPLE 就是普通的執行器;REUSE 執行器會重用預處理語句(prepared statements);
// BATCH 執行器將重用語句並執行批量更新。
protected ResultSetType defaultResultSetType;
// 默認執行器類型
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
// 指定 MyBatis 應如何自動映射列到字段或屬性。
// NONE 表示取消自動映射;
// PARTIAL 只會自動映射沒有定義嵌套結果集映射的結果集。
// FULL 會自動映射任意複雜的結果集(無論是否嵌套)。
protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL;
// 指定發現自動映射目標未知列(或者未知屬性類型)的行為。這個值應該設置為WARNING比較合適
protected AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior = AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.NONE;
// settings下的properties屬性
protected Properties variables = new Properties();
// 默認的反射器工廠,用於操作屬性、構造器方便
protected ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();
// 對象工廠, 所有的類resultMap類都需要依賴於對象工廠來實例化
protected ObjectFactory objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory();
// 對象包裝器工廠,主要用來在創建非原生對象,比如增加了某些監控或者特殊屬性的代理類
protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory();
// 延遲加載的全局開關。當開啓時,所有關聯對象都會延遲加載。特定關聯關係中可通過設置fetchType屬性來覆蓋該項的開關狀態
protected boolean lazyLoadingEnabled = false;
// 指定 Mybatis 創建具有延遲加載能力的對象所用到的代理工具。MyBatis 3.3+使用JAVASSIST
protected ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory(); // #224 Using internal Javassist instead of OGNL
// MyBatis 可以根據不同的數據庫廠商執行不同的語句,這種多廠商的支持是基於映射語句中的 databaseId 屬性。
protected String databaseId;
/**
* Configuration factory class.
* Used to create Configuration for loading deserialized unread properties.
*
* @see <a href='https://github.com/mybatis/old-google-code-issues/issues/300'>Issue 300 (google code)</a>
*/
protected Class<?> configurationFactory;
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
// mybatis插件列表
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry(this);
// 類型註冊器, 用於在執行sql語句的出入參映射以及mybatis-config文件裏的各種配置
// 比如<transactionManager type="JDBC"/><dataSource type="POOLED">時使用簡寫
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry();
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection")
.conflictMessageProducer((savedValue, targetValue) ->
". please check " + savedValue.getResource() + " and " + targetValue.getResource());
protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new StrictMap<>("Caches collection");
protected final Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<>("Result Maps collection");
protected final Map<String, ParameterMap> parameterMaps = new StrictMap<>("Parameter Maps collection");
protected final Map<String, KeyGenerator> keyGenerators = new StrictMap<>("Key Generators collection");
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<>();
protected final Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments = new StrictMap<>("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers");
protected final Collection<XMLStatementBuilder> incompleteStatements = new LinkedList<>();
protected final Collection<CacheRefResolver> incompleteCacheRefs = new LinkedList<>();
protected final Collection<ResultMapResolver> incompleteResultMaps = new LinkedList<>();
protected final Collection<MethodResolver> incompleteMethods = new LinkedList<>();
/*
* A map holds cache-ref relationship. The key is the namespace that
* references a cache bound to another namespace and the value is the
* namespace which the actual cache is bound to.
*/
protected final Map<String, String> cacheRefMap = new HashMap<>();
public Configuration(Environment environment) {
this();
this.environment = environment;
}
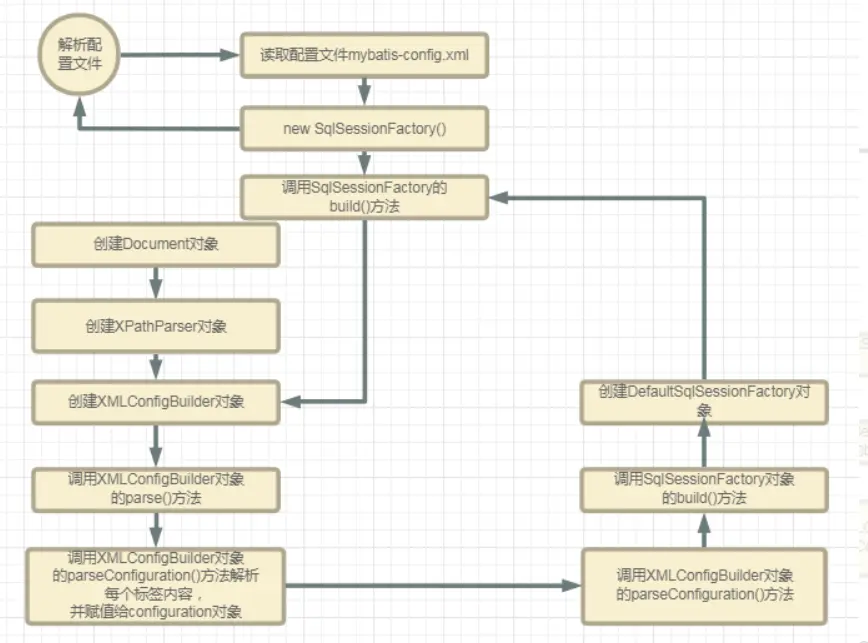
問題:核心配置文件&映射配置文件如何被解析的?
解析配置文件源碼流程:
入口:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
// XMLConfigBuilder:用來解析XML配置文件
// 使用構建者模式
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
// parser.parse():使用XPATH解析XML配置文件,將配置文件封裝為Configuration對象
// 返回DefaultSqlSessionFactory對象,該對象擁有Configuration對象(封裝配置文件信息)
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
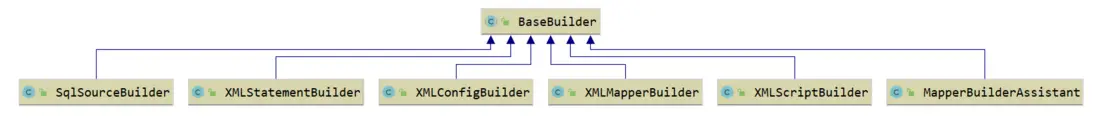
}創建XMLConfigBuilder對象,這個類是BaseBuilder的子類,BaseBuilder類圖:
看到這些子類基本上都是以Builder結尾,這裏使用的是Builder建造者設計模式。
XMLConfigBuilder#構造參數
XMLConfigBuilder:用來解析XML配置文件(使用構建者模式)
// XMLConfigBuilder:用來解析XML配置文件
// 使用構建者模式
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties); public XMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props) {
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);Mybatis對應解析包org.apache.ibatis.parsing:
XPathParser基於 Java XPath 解析器,用於解析 MyBatis中
- SqlMapConfig.xml
- mapper.xml
XPathParser主要內容:
1. XpathParser#構造函數
用來使用XPath語法解析XML的解析器
public XPathParser(InputStream inputStream, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
commonConstructor(validation, variables, entityResolver);
// 解析XML文檔為Document對象
this.document = createDocument(new InputSource(inputStream));
}1.1 XPathParser#createDocument
解析全局配置文件,封裝為Document對象(封裝一些子節點,使用XPath語法解析獲取)
private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) {
// important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor
try {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// 進行dtd或者Schema校驗
factory.setValidating(validation);
factory.setNamespaceAware(false);
// 設置忽略註釋為true
factory.setIgnoringComments(true);
// 設置是否忽略元素內容中的空白
factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false);
factory.setCoalescing(false);
factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true);
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver);
builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() {
@Override
public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
}
});
// 通過dom解析,獲取Document對象
return builder.parse(inputSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}2. XMLConfigBuilder#構造函數
創建Configuration對象,同時初始化內置類的別名
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
// 創建Configuration對象,並通過TypeAliasRegistry註冊一些Mybatis內部相關類的別名
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}2.1 Configuration#構造函數
創建Configuration對象,同時初始化內置類的別名
public Configuration() {
//TypeAliasRegistry(類型別名註冊器)
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JNDI", JndiDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("UNPOOLED", UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LRU", LruCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SOFT", SoftCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("WEAK", WeakCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("XML", XMLLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("RAW", RawLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SLF4J", Slf4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("COMMONS_LOGGING", JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J", Log4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J2", Log4j2Impl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDK_LOGGING", Jdk14LoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("STDOUT_LOGGING", StdOutImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("NO_LOGGING", NoLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("CGLIB", CglibProxyFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JAVASSIST", JavassistProxyFactory.class);
languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class);
languageRegistry.register(RawLanguageDriver.class);
}XMLConfigBuilder#parse
//使用XPATH解析XML配置文件,將配置文件封裝為Configuration對象
parser.parse();XMLConfigBuilder#parse
解析XML配置文件
/**
* 解析XML配置文件
* @return
*/
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// parser.evalNode("/configuration"):通過XPATH解析器,解析configuration根節點
// 從configuration根節點開始解析,最終將解析出的內容封裝到Configuration對象中
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}1. XPathParser#evalNode(xpath語法)
XPath解析器,專門用來通過Xpath語法解析XML返回XNode節點
public XNode evalNode(String expression) {
// 根據XPATH語法,獲取指定節點
return evalNode(document, expression);
}
public XNode evalNode(Object root, String expression) {
Node node = (Node) evaluate(expression, root, XPathConstants.NODE);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
return new XNode(this, node, variables);
}2. XMLConfigBuilder#parseConfiguration(XNode)
從configuration根節點開始解析,最終將解析出的內容封裝到Configuration對象中
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
// 解析</properties>標籤
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
// 解析</settings>標籤
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
// 解析</typeAliases>標籤
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
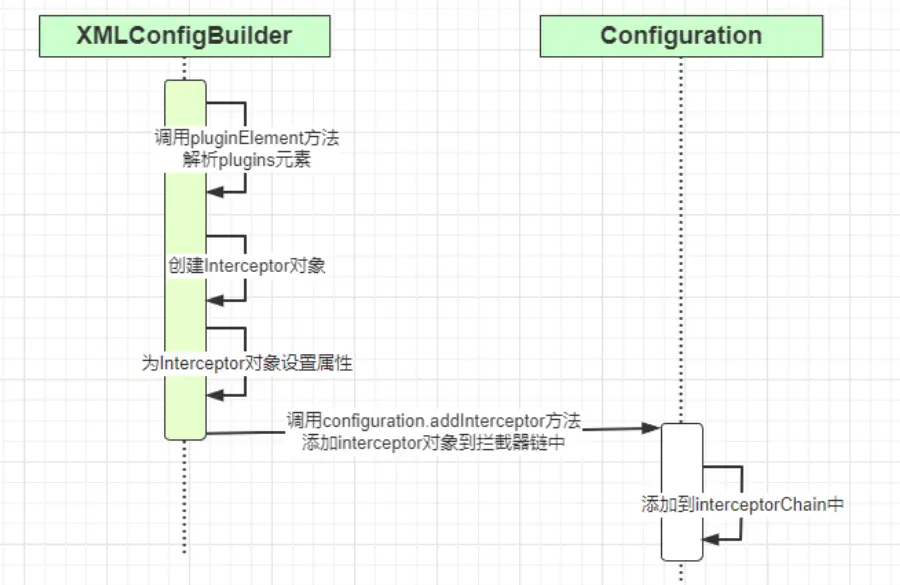
// 解析</plugins>標籤
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
// 解析</objectFactory>標籤
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
// 解析</objectWrapperFactory>標籤
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
// 解析</reflectorFactory>標籤
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
// 解析</environments>標籤
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
// 解析</databaseIdProvider>標籤
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
// 解析</typeHandlers>標籤
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 解析</mappers>標籤 加載映射文件流程主入口
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}### SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build
返回DefaultSqlSessionFactory對象,該對象擁有Configuration對象(封裝配置文件信息)
// 返回DefaultSqlSessionFactory對象,該對象擁有Configuration對象(封裝配置文件信息)
return build(parser.parse());public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
// 創建SqlSessionFactory接口的默認實現類
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}總結
5. 源碼剖析-初始化\_如何解析的映射配置文件?
前言
### select
select 元素允許你配置很多屬性來配置每條語句的行為細節
<select
id="select"
parameterType="int"
parameterMap="deprecated"
resultType="hashmap"
resultMap="personResultMap"
flushCache="false"
useCache="true"
timeout="10"
fetchSize="256"
statementType="PREPARED"
resultSetType="FORWARD_ONLY">### insert, update 和 delete
數據變更語句 insert,update 和 delete 的實現非常接近
<insert
id="insert"
parameterType="com.itheima.pojo.User"
flushCache="true"
statementType="PREPARED"
keyProperty=""
keyColumn=""
useGeneratedKeys=""
timeout="20">
<update
id="update"
parameterType="com.itheima.pojo.User"
flushCache="true"
statementType="PREPARED"
timeout="20">
<delete
id="delete"
parameterType="com.itheima.pojo.User"
flushCache="true"
statementType="PREPARED"
timeout="20">### 動態sql
藉助功能強大的基於 OGNL 的表達式,MyBatis 3 替換了之前的大部分元素,大大精簡了元素種類
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
MyBatis 提供了 choose 元素,它有點像 Java 中的 switch 語句
<select id="findActiveBlogLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND featured = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>問題:映射配置文件中標籤和屬性如何被解析封裝的?
問題:sql佔位符如何進行的替換?動態sql如何進行的解析?
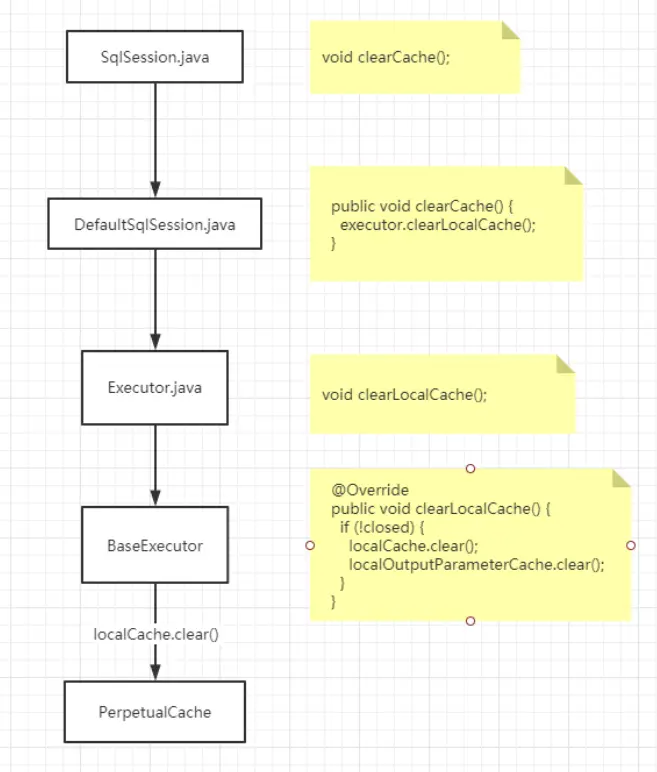
解析映射配置文件源碼流程:
入口:XMLConfigBuilder#mapperElement
解析全局配置文件中的
標籤
/**
* 解析<mappers>標籤
* @param parent mappers標籤對應的XNode對象
* @throws Exception
*/
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
// 獲取<mappers>標籤的子標籤
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// <package>子標籤
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
// 獲取mapper接口和mapper映射文件對應的package包名
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
// 將包下所有的mapper接口以及它的代理對象存儲到一個Map集合中,key為mapper接口類型,value為代理對象工廠
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {// <mapper>子標籤
// 獲取<mapper>子標籤的resource屬性
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
// 獲取<mapper>子標籤的url屬性
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
// 獲取<mapper>子標籤的class屬性
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// 它們是互斥的
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 專門用來解析mapper映射文件
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 通過XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 通過XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
// 將指定mapper接口以及它的代理對象存儲到一個Map集合中,key為mapper接口類型,value為代理對象工廠
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}\<package>子標籤
1. Configuration#addMappers
將包下所有的mapper接口以及它的代理對象存儲到一個Map集合中,key為mapper接口類型,value為代理對象工廠
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
mapperRegistry.addMappers(packageName);
}1.1 MapperRegistry#addMappers
將Mapper接口添加到MapperRegistry中
//1
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
addMappers(packageName, Object.class);
}
//2
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
// 根據package名稱,加載該包下Mapper接口文件(不是映射文件)
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
// 獲取加載的Mapper接口
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) {
// 將Mapper接口添加到MapperRegistry中
addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
//3
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
// 如果Map集合中已經有該mapper接口的映射,就不需要再存儲了
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 將mapper接口以及它的代理對象存儲到一個Map集合中,key為mapper接口類型,value為代理對象工廠
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
// 用來解析註解方式的mapper接口
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 解析註解方式的mapper接口
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}1.1.1 MapperAnnotationBuilder#parse
解析註解方式的mapper接口
public void parse() {
// 獲取mapper接口的全路徑
String resource = type.toString();
// 是否解析過該mapper接口
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 先解析mapper映射文件
loadXmlResource();
// 設置解析標識
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// Mapper構建者助手
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
// 解析CacheNamespace註解
parseCache();
// 解析CacheNamespaceRef註解
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) {
// 每個mapper接口中的方法,都解析成MappedStatement對象
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
//去檢查所有的incompleteMethods,如果可以解析了.那就移除
parsePendingMethods();
}1.1.1.1 MapperAnnotationBuilder#parseStatement
每個mapper接口中的方法,都解析成MappedStatement對象
void parseStatement(Method method) {
// 獲取Mapper接口的形參類型
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
// 解析Lang註解
LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
//
SqlSource sqlSource = getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(method, parameterTypeClass, languageDriver);
if (sqlSource != null) {
Options options = method.getAnnotation(Options.class);
// 組裝mappedStatementId
final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName();
Integer fetchSize = null;
Integer timeout = null;
StatementType statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
ResultSetType resultSetType = null;
// 獲取該mapper接口中的方法是CRUD操作的哪一種
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = getSqlCommandType(method);
// 是否是SELECT操作
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = !isSelect;
boolean useCache = isSelect;
// 主鍵生成器,用於主鍵返回
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyProperty = null;
String keyColumn = null;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) || SqlCommandType.UPDATE.equals(sqlCommandType)) {
// first check for SelectKey annotation - that overrides everything else
SelectKey selectKey = method.getAnnotation(SelectKey.class);
if (selectKey != null) {
keyGenerator = handleSelectKeyAnnotation(selectKey, mappedStatementId, getParameterType(method), languageDriver);
keyProperty = selectKey.keyProperty();
} else if (options == null) {
keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
} else {
keyGenerator = options.useGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
keyProperty = options.keyProperty();
keyColumn = options.keyColumn();
}
} else {
keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
if (options != null) {
if (FlushCachePolicy.TRUE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = true;
} else if (FlushCachePolicy.FALSE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = false;
}
useCache = options.useCache();
fetchSize = options.fetchSize() > -1 || options.fetchSize() == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? options.fetchSize() : null; //issue #348
timeout = options.timeout() > -1 ? options.timeout() : null;
statementType = options.statementType();
resultSetType = options.resultSetType();
}
// 處理ResultMap註解
String resultMapId = null;
ResultMap resultMapAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class);
if (resultMapAnnotation != null) {
String[] resultMaps = resultMapAnnotation.value();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String resultMap : resultMaps) {
if (sb.length() > 0) {
sb.append(",");
}
sb.append(resultMap);
}
resultMapId = sb.toString();
} else if (isSelect) {
resultMapId = parseResultMap(method);
}
// 通過Mapper構建助手,創建一個MappedStatement對象,封裝信息
assistant.addMappedStatement(
mappedStatementId,
sqlSource,
statementType,
sqlCommandType,
fetchSize,
timeout,
// ParameterMapID
null,
parameterTypeClass,
resultMapId,
getReturnType(method),
resultSetType,
flushCache,
useCache,
// TODO gcode issue #577
false,
keyGenerator,
keyProperty,
keyColumn,
// DatabaseID
null,
languageDriver,
// ResultSets
options != null ? nullOrEmpty(options.resultSets()) : null);
}
}1.1.1.1.2 MapperBuilderAssistant#addMappedStatement
通過Mapper構建助手,創建一個MappedStatement對象,封裝信息
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
//利用構建者模式,去創建MappedStatement.Builder,用於創建MappedStatement對象
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
// 通過MappedStatement.Builder,構建一個MappedStatement
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
// 將MappedStatement對象存儲到Configuration中的Map集合中,key為statement的id,value為MappedStatement對象
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}\<mapper>子標籤
1.XMLMapperBuilder#構造函數
專門用來解析mapper映射文件
public XMLMapperBuilder(InputStream inputStream, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver()),
configuration, resource, sqlFragments);
}1.1 XPathParser#構造函數
用來使用XPath語法解析XML的解析器
public XPathParser(InputStream inputStream, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
commonConstructor(validation, variables, entityResolver);
// 解析XML文檔為Document對象
this.document = createDocument(new InputSource(inputStream));
}1.1.1 XPathParser#createDocument
創建Mapper映射文件對應的Document對象
private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) {
// important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor
try {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// 進行dtd或者Schema校驗
factory.setValidating(validation);
factory.setNamespaceAware(false);
// 設置忽略註釋為true
factory.setIgnoringComments(true);
// 設置是否忽略元素內容中的空白
factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false);
factory.setCoalescing(false);
factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true);
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver);
builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() {
@Override
public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
}
});
// 通過dom解析,獲取Document對象
return builder.parse(inputSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}1.2 XMLMapperBuilder#構造函數
private XMLMapperBuilder(XPathParser parser, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.parser = parser;
this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments;
this.resource = resource;
}1.2.1MapperBuilderAssistant#構造函數
用於構建MappedStatement對象的
public MapperBuilderAssistant(Configuration configuration, String resource) {
super(configuration);
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
this.resource = resource;
}2. XMLMapperBuilder#parse
通過XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件
public void parse() {
// mapper映射文件是否已經加載過
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 從映射文件中的<mapper>根標籤開始解析,直到完整的解析完畢
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 標記已經解析
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}2.1 XMLMapperBuilder#configurationElement
從映射文件中的
根標籤開始解析,直到完整的解析完畢
/**
* 解析映射文件
* @param context 映射文件根節點<mapper>對應的XNode
*/
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// 獲取<mapper>標籤的namespace值,也就是命名空間
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
// 命名空間不能為空
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// 設置當前的命名空間為namespace的值
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// 解析<cache-ref>子標籤
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
// 解析<cache>子標籤
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
// 解析<parameterMap>子標籤
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
// 解析<resultMap>子標籤
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
// 解析<sql>子標籤,也就是SQL片段
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 解析<select>\<insert>\<update>\<delete>子標籤
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}2.1.1 XMLMapperBuilder#buildStatementFromContext
用來創建MappedStatement對象的
//1、構建MappedStatement
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
// 構建MappedStatement
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
//2、專門用來解析MappedStatement
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
// MappedStatement解析器
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
// 解析select等4個標籤,創建MappedStatement對象
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}2.1.1.1 XMLStatementBuilder#構造函數
專門用來解析MappedStatement
public XMLStatementBuilder(Configuration configuration, MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, XNode context, String databaseId) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = builderAssistant;
this.context = context;
this.requiredDatabaseId = databaseId;
}2.1.1.2 XMLStatementBuilder#parseStatementNode
解析
子標籤
/**
* 解析<select>\<insert>\<update>\<delete>子標籤
*/
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 獲取statement的id屬性(特別關鍵的值)
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
// 獲取入參類型
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
// 別名處理,獲取入參對應的Java類型
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
// 獲取ResultMap
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
// 獲取結果映射類型
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// 別名處理,獲取返回值對應的Java類型
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
// 設置默認StatementType為Prepared,該參數指定了後面的JDBC處理時,採用哪種Statement
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// 解析SQL命令類型是什麼?確定操作是CRUD中的哪一種
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
//是否查詢語句
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
// <include>標籤解析
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
// 解析<selectKey>標籤
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
// 創建SqlSource,解析SQL,封裝SQL語句(未參數綁定)和入參信息
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
// 通過構建者助手,創建MappedStatement對象
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}2.1.1.2.1 MapperBuilderAssistant#addMappedStatement
通過構建者助手,創建MappedStatement對象
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
//利用構建者模式,去創建MappedStatement.Builder,用於創建MappedStatement對象
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
// 通過MappedStatement.Builder,構建一個MappedStatement
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
// 將MappedStatement對象存儲到Configuration中的Map集合中,key為statement的id,value為MappedStatement對象
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}2.1.1.2.1.1 MappedStatement.Builder#構造函數
利用構建者模式,去創建MappedStatement.Builder,用於創建MappedStatement對象
public Builder(Configuration configuration, String id, SqlSource sqlSource, SqlCommandType sqlCommandType) {
mappedStatement.configuration = configuration;
mappedStatement.id = id;
mappedStatement.sqlSource = sqlSource;
mappedStatement.statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
mappedStatement.resultSetType = ResultSetType.DEFAULT;
mappedStatement.parameterMap = new ParameterMap.Builder(configuration, "defaultParameterMap", null, new ArrayList<>()).build();
mappedStatement.resultMaps = new ArrayList<>();
mappedStatement.sqlCommandType = sqlCommandType;
mappedStatement.keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
String logId = id;
if (configuration.getLogPrefix() != null) {
logId = configuration.getLogPrefix() + id;
}
mappedStatement.statementLog = LogFactory.getLog(logId);
mappedStatement.lang = configuration.getDefaultScriptingLanguageInstance();
}2.1.1.2.1.2 MappedStatement#build
通過MappedStatement.Builder,構建一個MappedStatement
public MappedStatement build() {
assert mappedStatement.configuration != null;
assert mappedStatement.id != null;
assert mappedStatement.sqlSource != null;
assert mappedStatement.lang != null;
mappedStatement.resultMaps = Collections.unmodifiableList(mappedStatement.resultMaps);
return mappedStatement;
}6. 源碼剖析-SqlSource創建流程
問題:sql佔位符如何進行的替換?動態sql如何進行的解析?
相關類及對象
- XMLLanguageDriver
- XMLScriptBuilder
- SqlSource接口
- SqlSourceBuilder
- DynamicSqlSource:主要是封裝動態SQL標籤解析之後的SQL語句和帶有${}的SQL語句
- RawSqlSource:主要封裝帶有#{}的SQL語句
- StaticSqlSource:是BoundSql中要存儲SQL語句的一個載體,上面兩個SqlSource的SQL語句,最終都會存儲到該SqlSource實現類
<select id="findActiveBlogLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE state = #{ACTIVE}
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND featured = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>SqlSource創建流程
入口:XMLLanguageDriver#createSqlSource
創建SqlSource,解析SQL,封裝SQL語句(未參數綁定)和入參信息
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 初始化了動態SQL標籤處理器
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
// 解析動態SQL
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}XMLScriptBuilder#構造函數
初始化了動態SQL標籤處理器
public XMLScriptBuilder(Configuration configuration, XNode context, Class<?> parameterType) {
super(configuration);
this.context = context;
this.parameterType = parameterType;
// 初始化動態SQL中的節點處理器集合
initNodeHandlerMap();
}1.XMLScriptBuilder#initNodeHandlerMap
初始化動態SQL中的節點處理器集合
private void initNodeHandlerMap() {
nodeHandlerMap.put("trim", new TrimHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("set", new SetHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForEachHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("choose", new ChooseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("when", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("otherwise", new OtherwiseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("bind", new BindHandler());
}XMLScriptBuilder#parseScriptNode
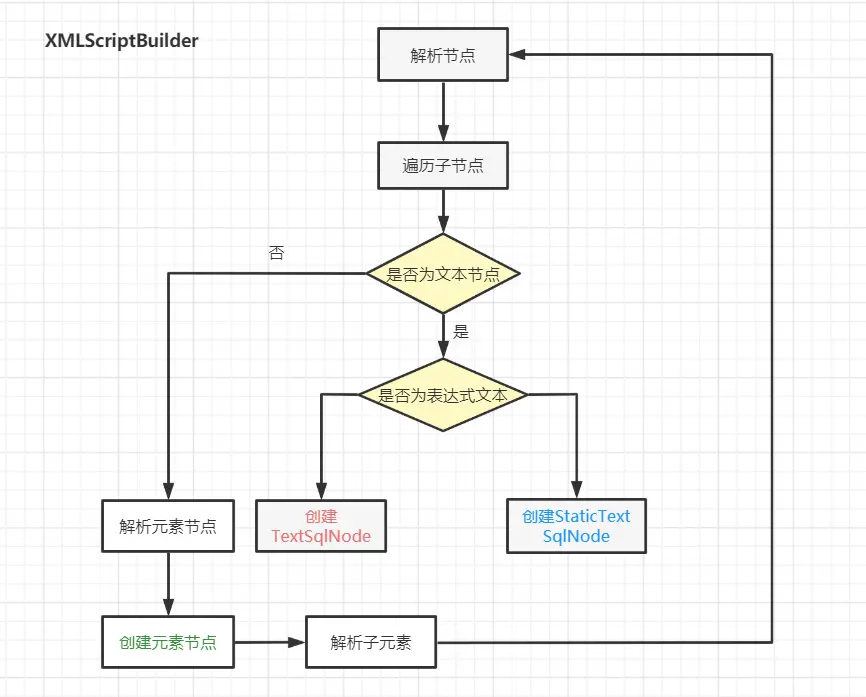
解析動態SQL
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
// 解析select\insert\ update\delete標籤中的SQL語句,最終將解析到的SqlNode封裝到MixedSqlNode中的List集合中
// ****將帶有${}號的SQL信息封裝到TextSqlNode
// ****將帶有#{}號的SQL信息封裝到StaticTextSqlNode
// ****將動態SQL標籤中的SQL信息分別封裝到不同的SqlNode中
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource = null;
// 如果SQL中包含${}和動態SQL語句,則將SqlNode封裝到DynamicSqlSource
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
// 如果SQL中包含#{},則將SqlNode封裝到RawSqlSource中,並指定parameterType
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}1 XMLScriptBuilder#parseDynamicTags
解析select\insert\ update\delete標籤中的SQL語句,最終將解析到的SqlNode封裝到MixedSqlNode中的List集合中。
- 將帶有${}號的SQL信息封裝到TextSqlNode;
- 將帶有#{}號的SQL信息封裝到StaticTextSqlNode
- 將動態SQL標籤中的SQL信息分別封裝到不同的SqlNode中
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
//獲取<select>\<insert>等4個標籤的子節點,子節點包括元素節點和文本節點
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
// 處理文本節點
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE
|| child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
String data = child.getStringBody("");
// 將文本內容封裝到SqlNode中
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
// SQL語句中帶有${}的話,就表示是dynamic的
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
// SQL語句中(除了${}和下面的動態SQL標籤),就表示是static的
// StaticTextSqlNode的apply只是進行字符串的追加操作
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
//處理元素節點
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // issue #628
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
// 動態SQL標籤處理器
// 思考,此處使用了哪種設計模式?---策略模式
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
// 動態SQL標籤是dynamic的
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}2. DynamicSqlSource#構造函數
如果SQL中包含${}和動態SQL語句,則將SqlNode封裝到DynamicSqlSource
public DynamicSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode;
}3. RawSqlSource#構造函數
如果SQL中包含#{},則將SqlNode封裝到RawSqlSource中,並指定parameterType
private final SqlSource sqlSource;
//先調用 getSql(configuration, rootSqlNode)獲取sql,再走下面的構造函數
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode, Class<?> parameterType) {
this(configuration, getSql(configuration, rootSqlNode), parameterType);
}
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 解析SQL語句
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
// 獲取入參類型
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
// 開始解析
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<String, Object>());
}
private static String getSql(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, null);
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
return context.getSql();
}3.1 SqlSourceBuilder#parse
解析SQL語句
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType,
additionalParameters);
// 創建分詞解析器
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
// 解析#{}
String sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
// 將解析之後的SQL信息,封裝到StaticSqlSource對象中
// SQL字符串是帶有?號的字符串,?相關的參數信息,封裝到ParameterMapping集合中
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}3.1.1 ParameterMappingTokenHandler#構造函數
public ParameterMappingTokenHandler(Configuration configuration, Class<?> parameterType,Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
super(configuration);
this.parameterType = parameterType;
this.metaParameters = configuration.newMetaObject(additionalParameters);
}3.1.2 GenericTokenParser#構造函數
創建分詞解析器,指定待分析的openToken和closeToken,並指定處理器
public GenericTokenParser(String openToken, String closeToken, TokenHandler handler) {
this.openToken = openToken;
this.closeToken = closeToken;
this.handler = handler;
}3.1.3 GenericTokenParser#parse
解析SQL語句,處理openToken和closeToken中的內容
/**
* 解析${}和#{}
* @param text
* @return
*/
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken, 0);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}#### 3.1.3.1 ParameterMappingTokenHandler#handleToken
處理token(#{}/${})
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
return "?";
}#### 3.1.3.1.1 ParameterMappingTokenHandler#buildParameterMapping
創建ParameterMapping對象
private ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(String content) {
Map<String, String> propertiesMap = parseParameterMapping(content);
String property = propertiesMap.get("property");
Class<?> propertyType;
if (metaParameters.hasGetter(property)) { // issue #448 get type from additional params
propertyType = metaParameters.getGetterType(property);
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterType)) {
propertyType = parameterType;
} else if (JdbcType.CURSOR.name().equals(propertiesMap.get("jdbcType"))) {
propertyType = java.sql.ResultSet.class;
} else if (property == null || Map.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterType)) {
propertyType = Object.class;
} else {
MetaClass metaClass = MetaClass.forClass(parameterType, configuration.getReflectorFactory());
if (metaClass.hasGetter(property)) {
propertyType = metaClass.getGetterType(property);
} else {
propertyType = Object.class;
}
}
ParameterMapping.Builder builder = new ParameterMapping.Builder(configuration, property, propertyType);
Class<?> javaType = propertyType;
String typeHandlerAlias = null;
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : propertiesMap.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
if ("javaType".equals(name)) {
javaType = resolveClass(value);
builder.javaType(javaType);
} else if ("jdbcType".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcType(resolveJdbcType(value));
} else if ("mode".equals(name)) {
builder.mode(resolveParameterMode(value));
} else if ("numericScale".equals(name)) {
builder.numericScale(Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if ("resultMap".equals(name)) {
builder.resultMapId(value);
} else if ("typeHandler".equals(name)) {
typeHandlerAlias = value;
} else if ("jdbcTypeName".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcTypeName(value);
} else if ("property".equals(name)) {
// Do Nothing
} else if ("expression".equals(name)) {
throw new BuilderException("Expression based parameters are not supported yet");
} else {
throw new BuilderException("An invalid property '" + name + "' was found in mapping #{" + content
+ "}. Valid properties are " + parameterProperties);
}
}
if (typeHandlerAlias != null) {
builder.typeHandler(resolveTypeHandler(javaType, typeHandlerAlias));
}
return builder.build();
}3.1.4 StaticSqlSource#構造函數
將解析之後的SQL信息,封裝到StaticSqlSource
private final String sql;
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
private final Configuration configuration;
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql) {
this(configuration, sql, null);
}
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.configuration = configuration;
}7. 源碼剖析-揭秘SqlSession執行主流程
7.1 相關類與接口
- DefaultSqlSession:SqlSession接口的默認實現類
- Executor接口
- BaseExecutor:基礎執行器,封裝了子類的公共方法,包括一級緩存、延遲加載、回滾、關閉等功能;
- SimpleExecutor:簡單執行器,每執行一條 sql,都會打開一個 Statement,執行完成後關閉;
- ReuseExecutor:重用執行器,相較於 SimpleExecutor 多了 Statement 的緩存功能,其內部維護一個
Map<String, Statement>,每次編譯完成的 Statement 都會進行緩存,不會關閉; - BatchExecutor:批量執行器,基於 JDBC 的
addBatch、executeBatch功能,並且在當前 sql 和上一條 sql 完全一樣的時候,重用 Statement,在調用doFlushStatements的時候,將數據刷新到數據庫; - CachingExecutor:緩存執行器,裝飾器模式,在開啓緩存的時候。會在上面三種執行器的外面包上 CachingExecutor;
- StatementHandler接口:
- RoutingStatementHandler:路由。Mybatis實際使用的類,攔截的StatementHandler實際就是它。它會根據Exector類型創建對應的StatementHandler,保存到屬性delegate中
- PreparedStatementHandler:預編譯Statement
- ResultSetHandler接口:處理Statement執行後產生的結果集,生成結果列表;處理存儲過程執行後的輸出參數
- DefaultResultSetHandler:ResultSetHandler的 默認實現類
7.2 流程分析
入口:DefaultSqlSession#selectList
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
// 根據傳入的statementId,獲取MappedStatement對象
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 調用執行器的查詢方法
// RowBounds是用來邏輯分頁(按照條件將數據從數據庫查詢到內存中,在內存中進行分頁)
// wrapCollection(parameter)是用來裝飾集合或者數組參數
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}1. CachingExecutor#query
Configuration中cacheEnabled屬性值默認為true
//第一步
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 獲取綁定的SQL語句,比如“SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = ? ”
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 生成緩存Key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
//第二步
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 獲取二級緩存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
// 當為select語句時,flushCache默認為false,表示任何時候語句被調用,都不會去清空本地緩存和二級緩存
// 當為insert、update、delete語句時,useCache默認為true,表示會將本條語句的結果進行二級緩存
// 刷新二級緩存 (存在緩存且flushCache為true時)
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
// 從二級緩存中查詢數據
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
// 如果二級緩存中沒有查詢到數據,則查詢數據庫
if (list == null) {
// 委託給BaseExecutor執行
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// 委託給BaseExecutor執行
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}2. BaseExecutor#query
二級緩存設置開啓且緩存中沒有或者未開啓二級緩存,則從一級緩存中查找結果集
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
// 從一級緩存中獲取數據
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 如果一級緩存沒有數據,則從數據庫查詢數據
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}3. BaseExecutor#queryFromDatabase
如果一級緩存沒有數據,則從數據庫查詢數據
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 執行查詢
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
//移除一級緩存中原有值
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//往一級緩存中存值
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}4. SimpleExecutor#doQuery
- BaseStatementHandler:基礎語句處理器(抽象類),它基本把語句處理器接口的核心部分都實現了,包括配置綁定、執行器綁定、映射器綁定、參數處理器構建、結果集處理器構建、語句超時設置、語句關閉等,並另外定義了新的方法 instantiateStatement 供不同子類實現以便獲取不同類型的語句連接,子類可以普通執行 SQL 語句,也可以做預編譯執行,還可以執行存儲過程等。
- SimpleStatementHandler:普通語句處理器,繼承 BaseStatementHandler 抽象類,對應 java.sql.Statement 對象的處理,處理普通的不帶動態參數運行的 SQL,即執行簡單拼接的字符串語句,同時由於 Statement 的特性,SimpleStatementHandler 每次執行都需要編譯 SQL (注意:我們知道 SQL 的執行是需要編譯和解析的)。
- PreparedStatementHandler:預編譯語句處理器,繼承 BaseStatementHandler 抽象類,對應 java.sql.PrepareStatement 對象的處理,相比上面的普通語句處理器,它支持可變參數 SQL 執行,由於 PrepareStatement 的特性,它會進行預編譯,在緩存中一旦發現有預編譯的命令,會直接解析執行,所以減少了再次編譯環節,能夠有效提高系統性能,並預防 SQL 注入攻擊(所以是系統默認也是我們推薦的語句處理器)。
- CallableStatementHandler:存儲過程處理器,繼承 BaseStatementHandler 抽象類,對應 java.sql.CallableStatement 對象的處理,很明瞭,它是用來調用存儲過程的,增加了存儲過程的函數調用以及輸出/輸入參數的處理支持。
- RoutingStatementHandler:路由語句處理器,直接實現了 StatementHandler 接口,作用如其名稱,確確實實只是起到了路由功能,並把上面介紹到的三個語句處理器實例作為自身的委託對象而已,所以執行器在構建語句處理器時,都是直接 new 了 RoutingStatementHandler 實例。
執行查詢
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 獲取Configuration對象
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 創建RoutingStatementHandler,用來處理Statement
// RoutingStatementHandler類中初始化delegate類(SimpleStatementHandler、PreparedStatementHandler)
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds,
resultHandler, boundSql);
// 子流程1:設置參數
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 子流程2:執行SQL語句(已經設置過參數),並且映射結果集
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}4.1 Configuration#newStatementHandler
創建StatementHandler,用來執行MappedStatement對象
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement,
Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 創建路由功能的StatementHandler,根據MappedStatement中的StatementType
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject,
rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}4.1.1 RoutingStatementHandler#構造函數
創建路由功能的StatementHandler,根據MappedStatement中的StatementType
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}4.2 SimpleExecutor#prepareStatement
設置參數
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 獲取連接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 創建Statement(PreparedStatement、Statement、CallableStatement)
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// SQL參數設置
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}4.2.1 BaseExecutor#getConnection
獲取數據庫連接
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = transaction.getConnection();
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return connection;
}
}4.2.2 BaseStatementHandler#prepare
創建Statement(PreparedStatement、Statement、CallableStatement)
@Override
public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql());
Statement statement = null;
try {
// 實例化Statement,比如PreparedStatement
statement = instantiateStatement(connection);
// 設置查詢超時時間
setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout);
setFetchSize(statement);
return statement;
} catch (SQLException e) {
closeStatement(statement);
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
closeStatement(statement);
throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}4.2.2.1 PreparedStatementHandler#instantiateStatement
實例化PreparedStatement
@Override
protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
// 獲取帶有佔位符的SQL語句
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// 處理帶有主鍵返回的SQL
if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) {
String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns();
if (keyColumnNames == null) {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
} else {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames);
}
} else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() == ResultSetType.DEFAULT) {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql);
} else {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
}
}4.2.3 PreparedStatementHandler#parameterize
SQL參數設置,參數映射流程會詳細分解
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
// 通過ParameterHandler處理參數
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}4.3 PreparedStatementHandler#query
執行SQL語句(已經設置過參數),並且映射結果集
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
// 執行PreparedStatement,也就是執行SQL語句
ps.execute();
// 處理結果集
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}4.3.1 PreparedStatement#execute
調用JDBC的api執行Statement
4.3.2 DefaultResultSetHandler#handleResultSets
處理結果集 ,結果映射流程會詳細分解
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
// <select>標籤的resultMap屬性,可以指定多個值,多個值之間用逗號(,)分割
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
// 這裏是獲取第一個結果集,將傳統JDBC的ResultSet包裝成一個包含結果列元信息的ResultSetWrapper對象
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
// 這裏是獲取所有要映射的ResultMap(按照逗號分割出來的)
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
// 要映射的ResultMap的數量
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
// 循環處理每個ResultMap,從第一個開始處理
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
// 得到結果映射信息
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
// 處理結果集
// 從rsw結果集參數中獲取查詢結果,再根據resultMap映射信息,將查詢結果映射到multipleResults中
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
// 對應<select>標籤的resultSets屬性,一般不使用該屬性
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
// 如果只有一個結果集合,則直接從多結果集中取出第一個
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}四、總結
執行sqlsession:參數有兩個(statementId和參數對象)
- 根據statementId,去Configuration中的MappedStatement集合中查找
對應的MappedStatement對象; - 取出MappedStatement中的SQL信息;
-
取出MappedStatement中的statementType,用來創建Statement對象;
- 取出MappedStatement中的Configuration對象,通過Configuration對象,獲取DataSource對象,通過DataSource對象,創建Connection,通過Connection創建Statement對象。
- 設置參數
- 執行Statement
- 處理結果集
8. 源碼剖析-揭秘如何設置的參數?
入口:PreparedStatementHandler#parameterize方法
設置PreparedStatement的參數
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
// 通過ParameterHandler處理參數
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}DefaultParameterHandler#setParameters
設置參數
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
// 獲取要設置的參數映射信息
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
// 只處理入參
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
// 獲取屬性名稱
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
// 獲取每個參數的類型處理器,去設置入參和獲取返回值
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
// 獲取每個參數的JdbcType
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
// 給PreparedStatement設置參數
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException e) {
throw new TypeException(
"Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException(
"Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}BaseTypeHandler#setParameter
給PreparedStatement設置參數
@Override
public void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
if (parameter == null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
throw new TypeException(
"JDBC requires that the JdbcType must be specified for all nullable parameters.");
}
try {
ps.setNull(i, jdbcType.TYPE_CODE);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . "
+ "Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different jdbcTypeForNull configuration property. "
+ "Cause: " + e, e);
}
} else {
try {
// 通過PreparedStatement的API去設置非空參數
setNonNullParameter(ps, i, parameter, jdbcType);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting non null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType
+ " . "
+ "Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different configuration property. "
+ "Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}xxxTypeHandler#setNonNullParameter
通過PreparedStatement的API去設置非空參數
例如:ArrayTypeHandler
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Object parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
ps.setArray(i, (Array) parameter);
}9. 源碼剖析-結果集映射流程
入口:DefaultResultSetHandler#handleResultSets
從rsw結果集參數中獲取查詢結果,再根據resultMap映射信息,將查詢結果映射到multipleResults中
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
// <select>標籤的resultMap屬性,可以指定多個值,多個值之間用逗號(,)分割
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
// 這裏是獲取第一個結果集,將傳統JDBC的ResultSet包裝成一個包含結果列元信息的ResultSetWrapper對象
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
// 這裏是獲取所有要映射的ResultMap(按照逗號分割出來的)
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
// 要映射的ResultMap的數量
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
// 循環處理每個ResultMap,從第一個開始處理
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
// 得到結果映射信息
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
// 處理結果集
// 從rsw結果集參數中獲取查詢結果,再根據resultMap映射信息,將查詢結果映射到multipleResults中
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
// 對應<select>標籤的resultSets屬性,一般不使用該屬性
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
// 如果只有一個結果集合,則直接從多結果集中取出第一個
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}DefaultResultSetHandler#handleRowValues
處理行數據,其實就是完成結果映射
public void handleRowValues(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler<?> resultHandler,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
// 是否有內置嵌套的結果映射
if (resultMap.hasNestedResultMaps()) {
ensureNoRowBounds();
checkResultHandler();
// 嵌套結果映射
handleRowValuesForNestedResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
} else {
// 簡單結果映射
handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
}
}DefaultResultSetHandler#handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap
簡單結果映射
private void handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap,
ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
DefaultResultContext<Object> resultContext = new DefaultResultContext<>();
// 獲取結果集信息
ResultSet resultSet = rsw.getResultSet();
// 使用rowBounds的分頁信息,進行邏輯分頁(也就是在內存中分頁)
skipRows(resultSet, rowBounds);
while (shouldProcessMoreRows(resultContext, rowBounds) && !resultSet.isClosed() && resultSet.next()) {
// 通過<resultMap>標籤的子標籤<discriminator>對結果映射進行鑑別
ResultMap discriminatedResultMap = resolveDiscriminatedResultMap(resultSet, resultMap, null);
// 將查詢結果封裝到POJO中
Object rowValue = getRowValue(rsw, discriminatedResultMap, null);
// 處理對象嵌套的映射關係
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, resultSet);
}
}1. DefaultResultSetHandler#getRowValue
將查詢結果封裝到POJO中
private Object getRowValue(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
// 延遲加載的映射信息
final ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader = new ResultLoaderMap();
// 創建要映射的PO類對象
Object rowValue = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, lazyLoader, columnPrefix);
if (rowValue != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) {
final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(rowValue);
boolean foundValues = this.useConstructorMappings;
// 是否應用自動映射,也就是通過resultType進行映射
if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) {
// 根據columnName和type屬性名映射賦值
foundValues = applyAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix) || foundValues;
}
// 根據我們配置ResultMap的column和property映射賦值
// 如果映射存在nestedQueryId,會調用getNestedQueryMappingValue方法獲取返回值
foundValues = applyPropertyMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, lazyLoader, columnPrefix) || foundValues;
foundValues = lazyLoader.size() > 0 || foundValues;
rowValue = foundValues || configuration.isReturnInstanceForEmptyRow() ? rowValue : null;
}
return rowValue;
}1.1 DefaultResultSetHandler#createResultObject
創建映射結果對象
private Object createResultObject(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader,
String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
this.useConstructorMappings = false; // reset previous mapping result
final List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes = new ArrayList<>();
final List<Object> constructorArgs = new ArrayList<>();
// 創建結果映射的PO類對象
Object resultObject = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
if (resultObject != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) {
// 獲取要映射的PO類的屬性信息
final List<ResultMapping> propertyMappings = resultMap.getPropertyResultMappings();
for (ResultMapping propertyMapping : propertyMappings) {
// issue gcode #109 && issue #149
// 延遲加載處理
if (propertyMapping.getNestedQueryId() != null && propertyMapping.isLazy()) {
// 通過動態代理工廠,創建延遲加載的代理對象
resultObject = configuration.getProxyFactory().createProxy(resultObject, lazyLoader, configuration,
objectFactory, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs);
break;
}
}
}
this.useConstructorMappings = resultObject != null && !constructorArgTypes.isEmpty(); // set current mapping
// result
return resultObject;
}
private Object createResultObject(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes,
List<Object> constructorArgs, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
final Class<?> resultType = resultMap.getType();
final MetaClass metaType = MetaClass.forClass(resultType, reflectorFactory);
final List<ResultMapping> constructorMappings = resultMap.getConstructorResultMappings();
if (hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultType)) {
return createPrimitiveResultObject(rsw, resultMap, columnPrefix);
} else if (!constructorMappings.isEmpty()) {
return createParameterizedResultObject(rsw, resultType, constructorMappings, constructorArgTypes,
constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
} else if (resultType.isInterface() || metaType.hasDefaultConstructor()) {
// 對象工廠創建對象
return objectFactory.create(resultType);
} else if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) {
return createByConstructorSignature(rsw, resultType, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
}
throw new ExecutorException("Do not know how to create an instance of " + resultType);
}1.2 DefaultResultSetHandler#applyAutomaticMappings
根據columnName和type屬性名映射賦值
private boolean applyAutomaticMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject,
String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
List<UnMappedColumnAutoMapping> autoMapping = createAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
if (!autoMapping.isEmpty()) {
for (UnMappedColumnAutoMapping mapping : autoMapping) {
final Object value = mapping.typeHandler.getResult(rsw.getResultSet(), mapping.column);
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
if (value != null || (configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls() && !mapping.primitive)) {
// gcode issue #377, call setter on nulls (value is not 'found')
metaObject.setValue(mapping.property, value);
}
}
}
return foundValues;
}1.3 DefaultResultSetHandler#applyPropertyMappings
根據我們配置ResultMap的column和property映射賦值,如果映射存在nestedQueryId,會調用getNestedQueryMappingValue方法獲取返回值
private boolean applyPropertyMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject,
ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
final List<String> mappedColumnNames = rsw.getMappedColumnNames(resultMap, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
final List<ResultMapping> propertyMappings = resultMap.getPropertyResultMappings();
for (ResultMapping propertyMapping : propertyMappings) {
String column = prependPrefix(propertyMapping.getColumn(), columnPrefix);
if (propertyMapping.getNestedResultMapId() != null) {
// the user added a column attribute to a nested result map, ignore it
column = null;
}
if (propertyMapping.isCompositeResult()
|| (column != null && mappedColumnNames.contains(column.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH)))
|| propertyMapping.getResultSet() != null) {
Object value = getPropertyMappingValue(rsw.getResultSet(), metaObject, propertyMapping, lazyLoader,
columnPrefix);
// issue #541 make property optional
final String property = propertyMapping.getProperty();
if (property == null) {
continue;
} else if (value == DEFERRED) {
foundValues = true;
continue;
}
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
if (value != null || (configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls()
&& !metaObject.getSetterType(property).isPrimitive())) {
// gcode issue #377, call setter on nulls (value is not 'found')
metaObject.setValue(property, value);
}
}
}
return foundValues;
}10. 源碼剖析-獲取Mapper代理對象流程
入口:DefaultSqlSession#getMapper
從Configuration對象中,根據Mapper接口,獲取Mapper代理對象
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 從Configuration對象中,根據Mapper接口,獲取Mapper代理對象
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}Configuration#getMapper
獲取Mapper代理對象
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}1. MapperRegistry#getMapper
通過代理對象工廠,獲取代理對象:
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 根據Mapper接口的類型,從Map集合中獲取Mapper代理對象工廠
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 通過MapperProxyFactory生產MapperProxy,通過MapperProxy產生Mapper代理對象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}1.1 MapperProxyFactory#newInstance
調用JDK的動態代理方式,創建Mapper代理
//1
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// 使用JDK動態代理方式,生成代理對象
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
//2
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 根據Mapper接口的類型,從Map集合中獲取Mapper代理對象工廠
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 通過MapperProxyFactory生產MapperProxy,通過MapperProxy產生Mapper代理對象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}11. 源碼剖析-invoke方法
// 通過JDK動態代理生成並獲取代理對象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 代理對象對象調用方法,底層執行invoke方法
List<User> allUser = userMapper.findAllUser();在動態代理返回了示例後,我們就可以直接調用mapper類中的方法了,但代理對象調用方法,執行是在MapperProxy中的invoke方法,該類實現InvocationHandler接口,並重寫invoke()方法。
問題:invoke方法執行邏輯是什麼?
入口:MapperProxy#invoke
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 如果是 Object 定義的方法,直接調用
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
// 獲得 MapperMethod 對象
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
// 重點在這:MapperMethod最終調用了執行的方法
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}MapperMethod
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
//判斷mapper中的方法類型,最終調用的還是SqlSession中的方法
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
// 轉換參數
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 執行 INSERT 操作
// 轉換 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
// 轉換參數
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 轉換 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
// 轉換參數
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 轉換 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
// 無返回,並且有 ResultHandler 方法參數,則將查詢的結果,提交給 ResultHandler 進行處理
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
// 執行查詢,返回列表
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
// 執行查詢,返回 Map
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
// 執行查詢,返回 Cursor
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
// 執行查詢,返回單個對象
} else {
// 轉換參數
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 查詢單條
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional() &&
(result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
// 返回結果為 null ,並且返回類型為基本類型,則拋出 BindingException 異常
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
// 返回結果
return result;
}12. 源碼剖析-插件機制
12.1 插件概述
- 問題:什麼是Mybatis插件?有什麼作用?
一般開源框架都會提供擴展點,讓開發者自行擴展,從而完成邏輯的增強。
基於插件機制可以實現了很多有用的功能,比如説分頁,字段加密,監控等功能,這種通用的功能,就如同AOP一樣,橫切在數據操作上
而通過Mybatis插件可以實現對框架的擴展,來實現自定義功能,並且對於用户是無感知的。
12.2 Mybatis插件介紹
Mybatis插件本質上來説就是一個攔截器,它體現了JDK動態代理和責任鏈設計模式的綜合運用
Mybatis中針對四大組件提供了擴展機制,這四個組件分別是:
Mybatis中所允許攔截的方法如下:
- Executor 【SQL執行器】【update,query,commit,rollback】
- StatementHandler 【Sql語法構建器對象】【prepare,parameterize,batch,update,query等】
- ParameterHandler 【參數處理器】【getParameterObject,setParameters等】
- ResultSetHandler 【結果集處理器】【handleResultSets,handleOuputParameters等】
能幹什麼?
- 分頁功能:mybatis的分頁默認是基於內存分頁的(查出所有,再截取),數據量大的情況下效率較低,不過使用mybatis插件可以改變該行為,只需要攔截StatementHandler類的prepare方法,改變要執行的SQL語句為分頁語句即可
- 性能監控:對於SQL語句執行的性能監控,可以通過攔截Executor類的update, query等方法,用日誌記錄每個方法執行的時間
如何自定義插件?
在使用之前,我們先來看看Mybatis提供的插件相關的類,過一遍它們分別提供了哪些功能,最後我們自己定義一個插件
用於定義插件的類
前面已經知道Mybatis插件是可以對Mybatis中四大組件對象的方法進行攔截,那攔截器攔截哪個類的哪個方法如何知道,就由下面這個註解提供攔截信息
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Intercepts {
Signature[] value();
}由於一個攔截器可以同時攔截多個對象的多個方法,所以就使用了Signture數組,該註解定義了攔截的完整信息
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({})
public @interface Signature {
// 攔截的類
Class<?> type();
// 攔截的方法
String method();
// 攔截方法的參數
Class<?>[] args();
} 已經知道了該攔截哪些對象的哪些方法,攔截後要幹什麼就需要實現Intercetor#intercept方法,在這個方法裏面實現攔截後的處理邏輯
public interface Interceptor {
/**
* 真正方法被攔截執行的邏輯
*
* @param invocation 主要目的是將多個參數進行封裝
*/
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
// 生成目標對象的代理對象
default Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
// 可以攔截器設置一些屬性
default void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// NOP
}
}12.3 自定義插件
需求:把Mybatis所有執行的sql都記錄下來
步驟:① 創建Interceptor的實現類,重寫方法
② 使用@Intercepts註解完成插件簽名 説明插件的攔截四大對象之一的哪一個對象的哪一個方法
③ 將寫好的插件註冊到全局配置文件中
①.創建Interceptor的實現類
public class MyPlugin implements Interceptor {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
// //這裏是每次執行操作的時候,都會進行這個攔截器的方法內
Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
//增強邏輯
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
logger.info("mybatis intercept sql:{}", sql);
return invocation.proceed(); //執行原方法
}
/**
*
* ^Description包裝目標對象 為目標對象創建代理對象
* @Param target為要攔截的對象
* @Return代理對象
*/
Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
System.out.println("將要包裝的目標對象:"+target);
return Plugin.wrap(target,this);
}
/**獲取配置文件的屬性**/
//插件初始化的時候調用,也只調用一次,插件配置的屬性從這裏設置進來
Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
System.out.println("插件配置的初始化參數:"+properties );
}
}② 使用@Intercepts註解完成插件簽名 説明插件的攔截四大對象之一的哪一個對象的哪一個方法
@Intercepts({ @Signature(type = StatementHandler.class,
method = "prepare",
args = { Connection.class, Integer.class}) })
public class SQLStatsInterceptor implements Interceptor {③ 將寫好的插件註冊到全局配置文件中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.itheima.interceptor.MyPlugin">
<property name="dialect" value="mysql" />
</plugin>
</plugins>
</configuration>核心思想:
就是使用JDK動態代理的方式,對這四個對象進行包裝增強。具體的做法是,創建一個類實現Mybatis的攔截器接口,並且加入到攔截器鏈中,在創建核心對象的時候,不直接返回,而是遍歷攔截器鏈,把每一個攔截器都作用於核心對象中。這麼一來,Mybatis創建的核心對象其實都是代理對象,都是被包裝過的。
12.4 源碼分析-插件
- 插件的初始化:插件對象是如何實例化的? 插件的實例對象如何添加到攔截器鏈中的? 組件對象的代理對象是如何產生的?
- 攔截邏輯的執行
插件配置信息的加載
我們定義好了一個攔截器,那我們怎麼告訴Mybatis呢?Mybatis所有的配置都定義在XXx.xml配置文件中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.itheima.interceptor.MyPlugin">
<property name="dialect" value="mysql" />
</plugin>
</plugins>
</configuration>對應的解析代碼如下(XMLConfigBuilder#pluginElement):
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 獲取攔截器
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
// 獲取配置的Properties屬性
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 根據配置文件中配置的插件類的全限定名 進行反射初始化
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// 將屬性添加到Intercepetor對象
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
// 添加到配置類的InterceptorChain屬性,InterceptorChain類維護了一個List<Interceptor>
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}主要做了以下工作:
- 遍歷解析plugins標籤下每個plugin標籤
- 根據解析的類信息創建Interceptor對象
- 調用setProperties方法設置屬性
- 將攔截器添加到Configuration類的IntercrptorChain攔截器鏈中
對應時序圖如下:
代理對象的生成
Executor代理對象(Configuration#newExecutor)
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 生成Executor代理對象邏輯
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}ParameterHandler代理對象(Configuration#newParameterHandler)
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
// 生成ParameterHandler代理對象邏輯
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}ResultSetHandler代理對象(Configuration#newResultSetHandler)
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
// 生成ResultSetHandler代理對象邏輯
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}StatementHandler代理對象(Configuration#newStatementHandler)
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 生成StatementHandler代理對象邏輯
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}通過查看源碼會發現,所有代理對象的生成都是通過InterceptorChain#pluginAll方法來創建的,進一步查看pluginAll方法
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}InterceptorChain#pluginAll內部通過遍歷Interceptor#plugin方法來創建代理對象,並將生成的代理對象又賦值給target,如果存在多個攔截器的話,生成的代理對象會被另一個代理對象所代理,從而形成一個代理鏈,執行的時候,依次執行所有攔截器的攔截邏輯代碼,我們再跟進去
default Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}Interceptor#plugin方法最終將目標對象和當前的攔截器交給Plugin.wrap方法來創建代理對象。該方法是默認方法,是Mybatis框架提供的一個典型plugin方法的實現。讓我們看看在Plugin#wrap方法中是如何實現代理對象的
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 1.解析該攔截器所攔截的所有接口及對應攔截接口的方法
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 2.獲取目標對象實現的所有被攔截的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
// 3.目標對象有實現被攔截的接口,生成代理對象並返回
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
// 通過JDK動態代理的方式實現
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
// 目標對象沒有實現被攔截的接口,直接返回原對象
return target;
}最終我們看到其實是通過JDK提供的Proxy.newProxyInstance方法來生成代理對象
以上代理對象生成過程的時序圖如下:
攔截邏輯的執行
通過上面的分析,我們知道Mybatis框架中執行Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler和StatementHandler中的方法時真正執行的是代理對象對應的方法。而且該代理對象是通過JDK動態代理生成的,所以執行方法時實際上是調用InvocationHandler#invoke方法(Plugin類實現InvocationHandler接口),下面是Plugin#invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}注:一個對象被代理很多次
問題:同一個組件對象的同一個方法是否可以被多個攔截器進行攔截?
答案是肯定的,所以我們配置在最前面的攔截器最先被代理,但是執行的時候卻是最外層的先執行。
具體點:
假如依次定義了三個插件:插件1,插件2 和 插件3。
那麼List中就會按順序存儲:插件1,插件2 和 插件3。
而解析的時候是遍歷list,所以解析的時候也是按照:插件1 ,插件2,插件3的順序。
但是執行的時候就要反過來了,執行的時候是按照:插件3,插件2和插件1的順序進行執行。
當 Executor 的某個方法被調用的時候,插件邏輯會先行執行。執行順序由外而內,比如上圖的執行順序為 plugin3 → plugin2 → Plugin1 → Executor。
13. 源碼剖析-緩存策略
緩存就是內存中的數據,常常來自對數據庫查詢結果的保存。使用緩存,我們可以避免頻繁的與數據庫進行交互,進而提高響應速度MyBatis也提供了對緩存的支持,分為一級緩存和二級緩存,可以通過下圖來理解:
①、一級緩存是SqlSession級別的緩存。在操作數據庫時需要構造sqlSession對象,在對象中有一個數據結構(HashMap)用於存儲緩存數據。不同的sqlSession之間的緩存數據區域(HashMap)是互相不影響的。
②、二級緩存是mapper級別的緩存,多個SqlSession去操作同一個Mapper的sql語句,多個SqlSession可以共用二級緩存,二級緩存是跨SqlSession的
一級緩存
默認是開啓的
①、我們使用同一個sqlSession,對User表根據相同id進行兩次查詢,查看他們發出sql語句的情況
@Test
public void firstLevelCacheTest() throws IOException {
// 1. 通過類加載器對配置文件進行加載,加載成了字節輸入流,存到內存中 注意:配置文件並沒有被解析
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
// 2. (1)解析了配置文件,封裝configuration對象 (2)創建了DefaultSqlSessionFactory工廠對象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
// 3.問題:openSession()執行邏輯是什麼?
// 3. (1)創建事務對象 (2)創建了執行器對象cachingExecutor (3)創建了DefaultSqlSession對象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 4. 委派給Executor來執行,Executor執行時又會調用很多其他組件(參數設置、解析sql的獲取,sql的執行、結果集的封裝)
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper.findByCondition", 1);
User user2 = sqlSession.selectOne("com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper.findByCondition", 1);
System.out.println(user == user2);
sqlSession.close();
}查看控制枱打印情況:
② 同樣是對user表進行兩次查詢,只不過兩次查詢之間進行了一次update操作。
@Test
public void test3() throws IOException {
// 1. 通過類加載器對配置文件進行加載,加載成了字節輸入流,存到內存中 注意:配置文件並沒有被解析
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
// 2. (1)解析了配置文件,封裝configuration對象 (2)創建了DefaultSqlSessionFactory工廠對象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
// 3.問題:openSession()執行邏輯是什麼?
// 3. (1)創建事務對象 (2)創建了執行器對象cachingExecutor (3)創建了DefaultSqlSession對象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 4. 委派給Executor來執行,Executor執行時又會調用很多其他組件(參數設置、解析sql的獲取,sql的執行、結果集的封裝)
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper.findByCondition", 1);
User user1 = new User();
user1.setId(1);
user1.setUsername("zimu");
sqlSession.update("com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper.updateUser",user1);
sqlSession.commit();
User user2 = sqlSession.selectOne("com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper.findByCondition", 1);
System.out.println(user == user2);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(user2);
System.out.println("MyBatis源碼環境搭建成功....");
sqlSession.close();
}查看控制枱打印情況:
③、總結
1、第一次發起查詢用户id為1的用户信息,先去找緩存中是否有id為1的用户信息,如果沒有,從 數據庫查詢用户信息。得到用户信息,將用户信息存儲到一級緩存中。
2、 如果中間sqlSession去執行commit操作(執行插入、更新、刪除),則會清空SqlSession中的 一級緩存,這樣做的目的為了讓緩存中存儲的是最新的信息,避免髒讀。
3、 第二次發起查詢用户id為1的用户信息,先去找緩存中是否有id為1的用户信息,緩存中有,直 接從緩存中獲取用户信息
一級緩存原理探究與源碼分析
問題1:一級緩存 底層數據結構到底是什麼?
問題2:一級緩存的工作流程是怎樣的?
1. 一級緩存 底層數據結構到底是什麼?
之前説不同SqlSession的一級緩存互不影響,所以我從SqlSession這個類入手
可以看到,org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession中有一個和緩存有關的方法——clearCache()刷新緩存的方法,點進去,找到它的實現類DefaultSqlSession
@Override
public void clearCache() {
executor.clearLocalCache();
}再次點進去executor.clearLocalCache(),再次點進去並找到其實現類BaseExecutor,
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
localCache.clear();
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
進入localCache.clear()方法。進入到了org.apache.ibatis.cache.impl.PerpetualCache類中
package org.apache.ibatis.cache.impl;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.CacheException;
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class PerpetualCache implements Cache {
private final String id;
private Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<Object, Object>();
public PerpetualCache(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
//省略部分...
@Override
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
}
//省略部分...
}
我們看到了PerpetualCache類中有一個屬性private Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<Object, Object>(),很明顯它是一個HashMap,我們所調用的.clear()方法,實際上就是調用的Map的clear方法
得出結論:
一級緩存的數據結構確實是HashMap
2. 一級緩存的執行流程
我們進入到org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor中
看到一個方法CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) ,見名思意是一個創建CacheKey的方法
找到它的實現類和方法org.apache.ibatis.executor.BaseExecuto.createCacheKey
我們分析一下創建CacheKey的這塊代碼:
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//初始化CacheKey
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
//存入statementId
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
//分別存入分頁需要的Offset和Limit
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
//把從BoundSql中封裝的sql取出並存入到cacheKey對象中
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
//下面這一塊就是封裝參數
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
//從configuration對象中(也就是載入配置文件後存放的對象)把EnvironmentId存入
/**
* <environments default="development">
* <environment id="development"> //就是這個id
* <!--當前事務交由JDBC進行管理-->
* <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
* <!--當前使用mybatis提供的連接池-->
* <dataSource type="POOLED">
* <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
* <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
* <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
* <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
* </dataSource>
* </environment>
* </environments>
*/
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
// issue #176
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
//返回
return cacheKey;
}我們再點進去cacheKey.update()方法看一看
public class CacheKey implements Cloneable, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1146682552656046210L;
public static final CacheKey NULL_CACHE_KEY = new NullCacheKey();
private static final int DEFAULT_MULTIPLYER = 37;
private static final int DEFAULT_HASHCODE = 17;
private final int multiplier;
private int hashcode;
private long checksum;
private int count;
//值存入的地方
private transient List<Object> updateList;
//省略部分方法......
//省略部分方法......
public void update(Object object) {
int baseHashCode = object == null ? 1 : ArrayUtil.hashCode(object);
count++;
checksum += baseHashCode;
baseHashCode *= count;
hashcode = multiplier * hashcode + baseHashCode;
//看到把值傳入到了一個list中
updateList.add(object);
}
//省略部分方法......
}我們知道了那些數據是在CacheKey對象中如何存儲的了。下面我們返回createCacheKey()方法。
我們進入BaseExecutor,可以看到一個query()方法:
這裏我們很清楚的看到,在執行query()方法前,CacheKey方法被創建了
我們可以看到,創建CacheKey後調用了query()方法,我們再次點進去:
在執行SQL前如何在一級緩存中找不到Key,那麼將會執行sql,我們來看一下執行sql前後會做些什麼,進入list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
分析一下:
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
//1. 把key存入緩存,value放一個佔位符
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
//2. 與數據庫交互
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
//3. 如果第2步出了什麼異常,把第1步存入的key刪除
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//4. 把結果存入緩存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}一級緩存源碼分析結論:
- 一級緩存的數據結構是一個
HashMap<Object,Object>,它的value就是查詢結果,它的key是CacheKey,CacheKey中有一個list屬性,statementId,params,rowbounds,sql等參數都存入到了這個list中 - 先創建
CacheKey,會首先根據CacheKey查詢緩存中有沒有,如果有,就處理緩存中的參數,如果沒有,就執行sql,執行sql後執行sql後把結果存入緩存
二級緩存
注意:Mybatis的二級緩存不是默認開啓的,是需要經過配置才能使用的
啓用二級緩存
分為三步走:
1)開啓映射器配置文件中的緩存配置:
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>- 在需要使用二級緩存的Mapper配置文件中配置標籤
<!--type:cache使用的類型,默認是PerpetualCache,這在一級緩存中提到過。
eviction: 定義回收的策略,常見的有FIFO,LRU。
flushInterval: 配置一定時間自動刷新緩存,單位是毫秒。
size: 最多緩存對象的個數。
readOnly: 是否只讀,若配置可讀寫,則需要對應的實體類能夠序列化。
blocking: 若緩存中找不到對應的key,是否會一直blocking,直到有對應的數據進入緩存。
-->
<cache></cache>3)在具體CURD標籤上配置 useCache=true
<select id="findById" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User" useCache="true">
select * from user where id = #{id}
</select>** 注意:實體類要實現Serializable接口,因為二級緩存會將對象寫進硬盤,就必須序列化,以及兼容對象在網絡中的傳輸
具體實現
/**
* 測試一級緩存
*/
@Test
public void secondLevelCacheTest() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
// 2. (1)解析了配置文件,封裝configuration對象 (2)創建了DefaultSqlSessionFactory工廠對象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
// 3.問題:openSession()執行邏輯是什麼?
// 3. (1)創建事務對象 (2)創建了執行器對象cachingExecutor (3)創建了DefaultSqlSession對象
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 發起第一次查詢,查詢ID為1的用户
User user1 = sqlSession1.selectOne("com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper.findByCondition", 1);
// ***必須調用sqlSession1.commit()或者close(),一級緩存中的內容才會刷新到二級緩存中
sqlSession1.commit();// close();
// 發起第二次查詢,查詢ID為1的用户
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User user2 = sqlSession2.selectOne("com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper.findByCondition", 1);
System.out.println(user1 == user2);
System.out.println(user1);
System.out.println(user2);
sqlSession1.close();
sqlSession2.close();
}二級緩存源碼分析
問題:
① cache標籤如何被解析的(二級緩存的底層數據結構是什麼?)?
② 同時開啓一級緩存二級緩存,優先級?
③ 為什麼只有執行sqlSession.commit或者sqlSession.close二級緩存才會生效
④ 更新方法為什麼不會清空二級緩存?
標籤 < cache/> 的解析
二級緩存和具體的命名空間綁定,一個Mapper中有一個Cache, 相同Mapper中的MappedStatement共用同一個Cache
根據之前的mybatis源碼剖析,xml的解析工作主要交給XMLConfigBuilder.parse()方法來實現
// XMLConfigBuilder.parse()
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));// 在這裏
return configuration;
}
// parseConfiguration()
// 既然是在xml中添加的,那麼我們就直接看關於mappers標籤的解析
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
Properties settings = settingsAsPropertiess(root.evalNode("settings"));
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectionFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectionFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 就是這裏
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// mapperElement()
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// 按照我們本例的配置,則直接走該if判斷
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 生成XMLMapperBuilder,並執行其parse方法
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
} 我們來看看解析Mapper.xml
// XMLMapperBuilder.parse()
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 解析mapper屬性
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingChacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
// configurationElement()
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
// 最終在這裏看到了關於cache屬性的處理
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 這裏會將生成的Cache包裝到對應的MappedStatement
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// cacheElement()
private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//解析<cache/>標籤的type屬性,這裏我們可以自定義cache的實現類,比如redisCache,如果沒有自定義,這裏使用和一級緩存相同的PERPETUAL
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 構建Cache對象
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}先來看看是如何構建Cache對象的
MapperBuilderAssistant.useNewCache()
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass,
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
// 1.生成Cache對象
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
//這裏如果我們定義了<cache/>中的type,就使用自定義的Cache,否則使用和一級緩存相同的PerpetualCache
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
// 2.添加到Configuration中
configuration.addCache(cache);
// 3.並將cache賦值給MapperBuilderAssistant.currentCache
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}我們看到一個Mapper.xml只會解析一次
標籤,也就是隻創建一次Cache對象,放進configuration中,並將cache賦值給MapperBuilderAssistant.currentCache
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));將Cache包裝到MappedStatement
// buildStatementFromContext()
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
//buildStatementFromContext()
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
// 每一條執行語句轉換成一個MappedStatement
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
// XMLStatementBuilder.parseStatementNode();
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
...
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
...
// 創建MappedStatement對象
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
// builderAssistant.addMappedStatement()
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
...) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
//創建MappedStatement對象
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
...
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);// 在這裏將之前生成的Cache封裝到MappedStatement
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}我們看到將Mapper中創建的Cache對象,加入到了每個MappedStatement對象中,也就是同一個Mapper中所有的MappedStatement中的cache屬性引用的是同一個
有關於
標籤的解析就到這了。
查詢源碼分析
CachingExecutor
// CachingExecutor
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 創建 CacheKey
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 從 MappedStatement 中獲取 Cache,注意這裏的 Cache 是從MappedStatement中獲取的
// 也就是我們上面解析Mapper中<cache/>標籤中創建的,它保存在Configration中
// 我們在上面解析blog.xml時分析過每一個MappedStatement都有一個Cache對象,就是這裏
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 如果配置文件中沒有配置 <cache>,則 cache 為空
if (cache != null) {
//如果需要刷新緩存的話就刷新:flushCache="true"
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
// 訪問二級緩存
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
// 緩存未命中
if (list == null) {
// 如果沒有值,則執行查詢,這個查詢實際也是先走一級緩存查詢,一級緩存也沒有的話,則進行DB查詢
list = delegate.<E>query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// 緩存查詢結果
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E>query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}如果設置了flushCache="true",則每次查詢都會刷新緩存
<!-- 執行此語句清空緩存 -->
<select id="findbyId" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.user" useCache="true" flushCache="true" >
select * from t_demo
</select>如上,注意二級緩存是從 MappedStatement 中獲取的。由於 MappedStatement 存在於全局配置中,可以多個 CachingExecutor 獲取到,這樣就會出現線程安全問題。除此之外,若不加以控制,多個事務共用一個緩存實例,會導致髒讀問題。至於髒讀問題,需要藉助其他類來處理,也就是上面代碼中 tcm 變量對應的類型。下面分析一下。
TransactionalCacheManager
/** 事務緩存管理器 */
public class TransactionalCacheManager {
// Cache 與 TransactionalCache 的映射關係表
private final Map<Cache, TransactionalCache> transactionalCaches = new HashMap<Cache, TransactionalCache>();
public void clear(Cache cache) {
// 獲取 TransactionalCache 對象,並調用該對象的 clear 方法,下同
getTransactionalCache(cache).clear();
}
public Object getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) {
// 直接從TransactionalCache中獲取緩存
return getTransactionalCache(cache).getObject(key);
}
public void putObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key, Object value) {
// 直接存入TransactionalCache的緩存中
getTransactionalCache(cache).putObject(key, value);
}
public void commit() {
for (TransactionalCache txCache : transactionalCaches.values()) {
txCache.commit();
}
}
public void rollback() {
for (TransactionalCache txCache : transactionalCaches.values()) {
txCache.rollback();
}
}
private TransactionalCache getTransactionalCache(Cache cache) {
// 從映射表中獲取 TransactionalCache
TransactionalCache txCache = transactionalCaches.get(cache);
if (txCache == null) {
// TransactionalCache 也是一種裝飾類,為 Cache 增加事務功能
// 創建一個新的TransactionalCache,並將真正的Cache對象存進去
txCache = new TransactionalCache(cache);
transactionalCaches.put(cache, txCache);
}
return txCache;
}
}TransactionalCacheManager 內部維護了 Cache 實例與 TransactionalCache 實例間的映射關係,該類也僅負責維護兩者的映射關係,真正做事的還是 TransactionalCache。TransactionalCache 是一種緩存裝飾器,可以為 Cache 實例增加事務功能。下面分析一下該類的邏輯。
TransactionalCache
public class TransactionalCache implements Cache {
//真正的緩存對象,和上面的Map<Cache, TransactionalCache>中的Cache是同一個
private final Cache delegate;
private boolean clearOnCommit;
// 在事務被提交前,所有從數據庫中查詢的結果將緩存在此集合中
private final Map<Object, Object> entriesToAddOnCommit;
// 在事務被提交前,當緩存未命中時,CacheKey 將會被存儲在此集合中
private final Set<Object> entriesMissedInCache;
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
// 查詢的時候是直接從delegate中去查詢的,也就是從真正的緩存對象中查詢
Object object = delegate.getObject(key);
if (object == null) {
// 緩存未命中,則將 key 存入到 entriesMissedInCache 中
entriesMissedInCache.add(key);
}
if (clearOnCommit) {
return null;
} else {
return object;
}
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object object) {
// 將鍵值對存入到 entriesToAddOnCommit 這個Map中中,而非真實的緩存對象 delegate 中
entriesToAddOnCommit.put(key, object);
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
clearOnCommit = true;
// 清空 entriesToAddOnCommit,但不清空 delegate 緩存
entriesToAddOnCommit.clear();
}
public void commit() {
// 根據 clearOnCommit 的值決定是否清空 delegate
if (clearOnCommit) {
delegate.clear();
}
// 刷新未緩存的結果到 delegate 緩存中
flushPendingEntries();
// 重置 entriesToAddOnCommit 和 entriesMissedInCache
reset();
}
public void rollback() {
unlockMissedEntries();
reset();
}
private void reset() {
clearOnCommit = false;
// 清空集合
entriesToAddOnCommit.clear();
entriesMissedInCache.clear();
}
private void flushPendingEntries() {
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entriesToAddOnCommit.entrySet()) {
// 將 entriesToAddOnCommit 中的內容轉存到 delegate 中
delegate.putObject(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) {
if (!entriesToAddOnCommit.containsKey(entry)) {
// 存入空值
delegate.putObject(entry, null);
}
}
}
private void unlockMissedEntries() {
for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) {
try {
// 調用 removeObject 進行解鎖
delegate.removeObject(entry);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("...");
}
}
}
}存儲二級緩存對象的時候是放到了TransactionalCache.entriesToAddOnCommit這個map中,但是每次查詢的時候是直接從TransactionalCache.delegate中去查詢的,所以這個二級緩存查詢數據庫後,設置緩存值是沒有立刻生效的,主要是因為直接存到 delegate 會導致髒數據問題
為何只有SqlSession提交或關閉之後?
那我們來看下SqlSession.commit()方法做了什麼
SqlSession
@Override
public void commit(boolean force) {
try {
// 主要是這句
executor.commit(isCommitOrRollbackRequired(force));
dirty = false;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error committing transaction. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
// CachingExecutor.commit()
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
delegate.commit(required);
tcm.commit();// 在這裏
}
// TransactionalCacheManager.commit()
public void commit() {
for (TransactionalCache txCache : transactionalCaches.values()) {
txCache.commit();// 在這裏
}
}
// TransactionalCache.commit()
public void commit() {
if (clearOnCommit) {
delegate.clear();
}
flushPendingEntries();//這一句
reset();
}
// TransactionalCache.flushPendingEntries()
private void flushPendingEntries() {
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entriesToAddOnCommit.entrySet()) {
// 在這裏真正的將entriesToAddOnCommit的對象逐個添加到delegate中,只有這時,二級緩存才真正的生效
delegate.putObject(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) {
if (!entriesToAddOnCommit.containsKey(entry)) {
delegate.putObject(entry, null);
}
}
}二級緩存的刷新
我們來看看SqlSession的更新操作
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
int var4;
try {
this.dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = this.configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
var4 = this.executor.update(ms, this.wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception var8) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + var8, var8);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
return var4;
}
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
this.flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
return this.delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
//獲取MappedStatement對應的Cache,進行清空
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
//SQL需設置flushCache="true" 才會執行清空
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
this.tcm.clear(cache);
}
}MyBatis二級緩存只適用於不常進行增、刪、改的數據,比如國家行政區省市區街道數據。一但數據變更,MyBatis會清空緩存。因此二級緩存不適用於經常進行更新的數據。
總結:
在二級緩存的設計上,MyBatis大量地運用了裝飾者模式,如CachingExecutor, 以及各種Cache接口的裝飾器。
- 二級緩存實現了Sqlsession之間的緩存數據共享,屬於namespace級別
- 二級緩存具有豐富的緩存策略。
- 二級緩存可由多個裝飾器,與基礎緩存組合而成
- 二級緩存工作由 一個緩存裝飾執行器CachingExecutor和 一個事務型預緩存TransactionalCache 完成