在前面的課程中,我們利用所學的 RAG 知識,搭建了一個基於論文的問答系統。但是當論文數量比較多時,針對一些統計信息,比如某個方向的論文數量、某個會議的論文數量等,如果只通過傳統的 RAG 是沒辦法對這些信息進行檢索的。
對此,本章將先簡單回顧之前內容,並在此基礎上再做升級,完成一個集統計分析和知識問答功能於一體的智能問答系統。
一、上節回顧
為了更好地理解本章內容,我們先簡要回顧前兩章的關鍵內容。
第14講介紹了論文問答系統的構建過程,依次講解了核心組件,如解析器、retriever、reranker 等,並展示瞭如何逐步搭建一個完整的 RAG 系統。同時,我們也探討了一些進階技巧,以提升系統的性能與靈活性。
不過,這一系統仍屬於傳統 RAG 架構。在第15講中,我們進一步指出了傳統 RAG 在處理統計類問題時的侷限性,並提出了應對思路,如結合 SQL 數據庫、Text2SQL 技術及 sql_tool 工具。然而,前章僅提出了理論方案,尚未給出完整的實踐示例。
因此,本章將在此基礎上,結合實際案例,構建一個更完整、 更具實用性的統計問答系統,進一步拓展 RAG 在結構化數據處理方面的能力。
二、本節概覽
在本講中,我們將在已有的論文問答系統基礎上進一步拓展其功能,使系統不僅能夠進行知識問答,還具備處理統計分析任務的能力。為此,我們需要對傳統的 RAG 架構進行調整,增強其在統計場景下的適應性。
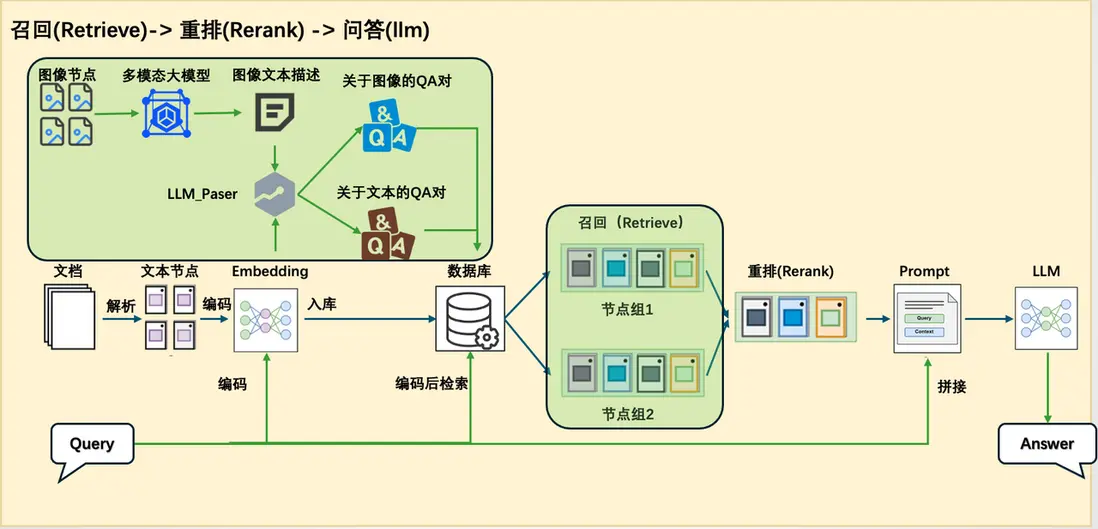
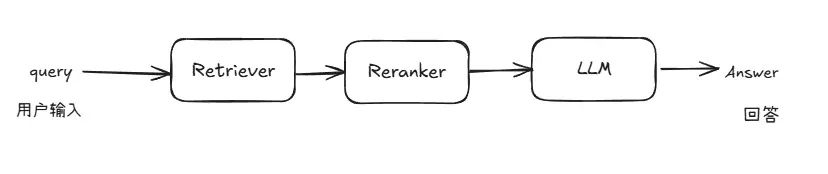
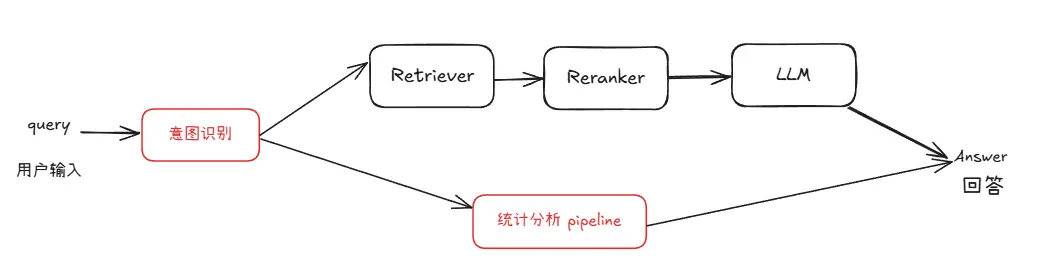
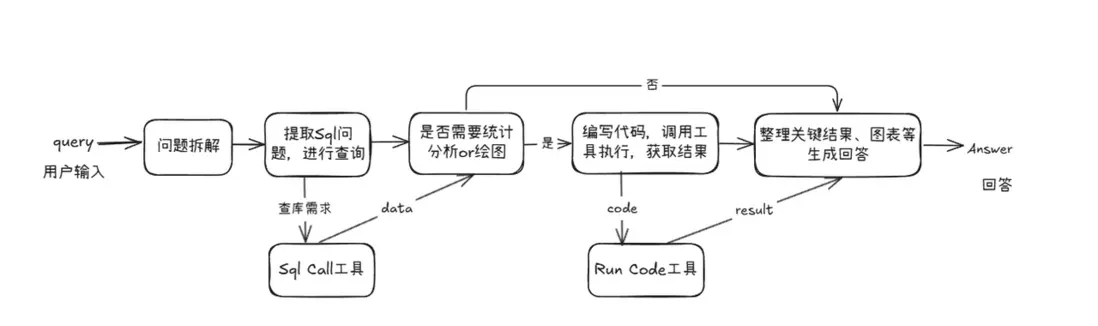
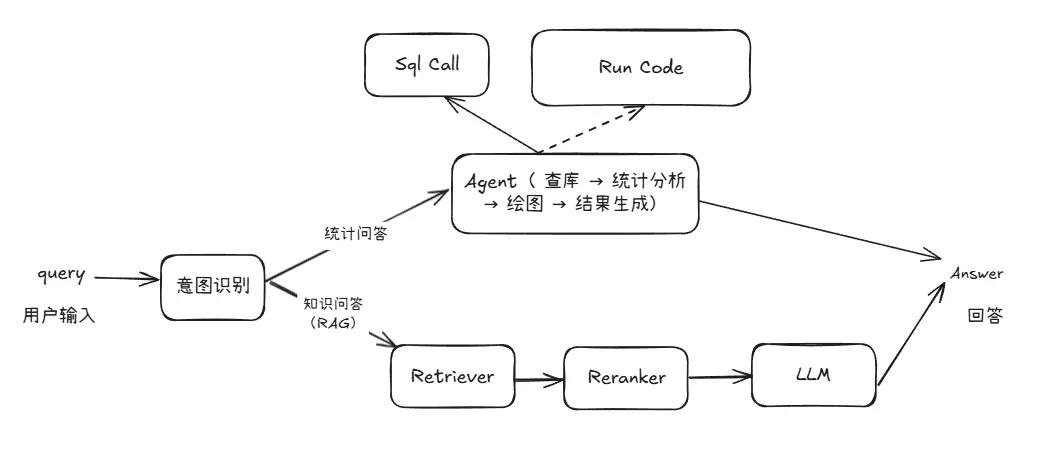
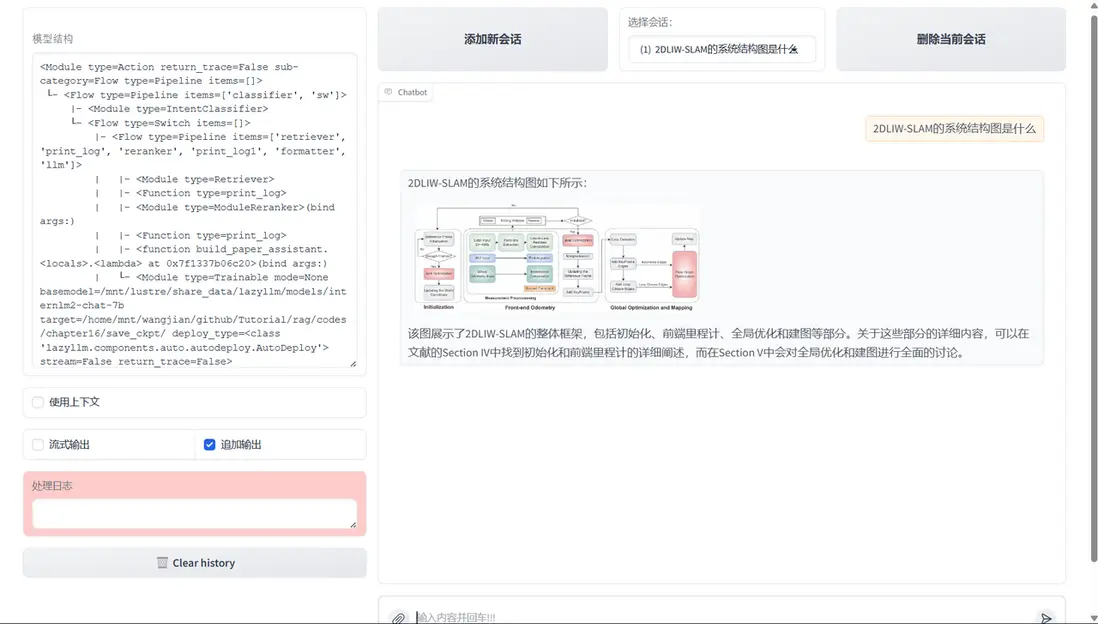
由於知識問答與統計問答在處理邏輯和所依賴的信息類型上存在顯著差異,採用統一的 pipeline 來應對兩種需求在實踐中存在較大困難。因此,我們在原有 RAG pipeline 的基礎上新增了一條專門處理統計任務的 pipeline,實現從【圖1】到【圖2】的系統結構變化。
圖1 原論文系統架構圖
圖2 具備統計能力的問答系統架構圖
在複用現有模塊的基礎上,我們新增了用於數據庫查詢、統計分析和圖表生成的統計分析 pipeline。該 pipeline 與 RAG pipeline 並行運行,並通過一個意圖識別模塊進行統一調度。該模塊負責判斷用户查詢屬於知識問答還是統計分析,從而引導請求進入合適的處理流程。
為實現這一增強系統,我們還需要引入若干關鍵的技術模塊。接下來將在完成數據準備後逐一介紹這些新增模塊及其在系統中的作用。
三、數據準備
這裏我們以 ArXivQA(https://github.com/taesiri/ArXivQA)數據集為例,從 Papers-2024.md 中抽取了前面100篇來演示,在執行代碼之前您需要先下載Papers-2024.md,可以離線下載或者以下命令進行下載。該文件包含了論文信息和下載鏈接。
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/taesiri/ArXivQA/main/Papers-2024.md -O 2024.md
我們需要從兩方面去準備數據:
- 知識庫(下載論文文件到指定目錄下) ,用於知識問答;
- 數據庫(構建論文信息的表格存入本地數據庫),用於統計問答,論文信息如title、author等。
以下腳本可以同時實現將論文下載到指定文件夾同時構建論文信息的數據庫。
(代碼塊GitHub鏈接🔗:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/7abc91dbb82a007a78731845dd8c360ac0cc1e75/rag/codes/chapter16/CreateDataBase.py#L1)
import re
import requests
import time
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 下載文件的函數
def spider(url, save_dir='./rag_data/papers'):
response = requests.get(url)
# 檢查請求是否成功
res = {}
if response.status_code == 200:
# 解析網頁內容
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
elements = soup.find_all(class_='title mathjax')
for ele in elements:
res['title'] = ele.get_text().replace("Title:", '')
elements = soup.find_all(class_='authors')
authors = []
for ele in elements:
links = ele.find_all('a')
for link in links:
authors.append(link.get_text())
res['author'] = ';'.join(authors)
elements = soup.find_all(class_='tablecell subjects')
for ele in elements:
res['subject'] = ele.get_text()
# 保存論文
file_path = os.path.join(save_dir, res['title'] + '.pdf')
with open(file_path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.content)
print(f"已保存 PDF 到 {file_path}")
return res
else:
print(f"網頁加載失敗,狀態碼:{response.status_code}")
def get_information():
with open('2024.md')as f:
texts = f.readlines()[2:102]
reses = []
for text in tqdm(texts):
abs_url = re.findall(r'\[.*?\]\((https?://arxiv.*?)\)', text)
if len(abs_url) > 0:
res = spider(abs_url[0])
reses.append(res)
time.sleep(5)
with open('test.txt', 'w')as f:
json.dump({"data": reses}, f)
上面這是一個獲取文檔信息腳本,負責解析 2024.md 中的數據,並取100篇為例,然後解析對應的 url ,然後通過獲取每個 url 對應的論文標題、作者和主題的信息,並記錄下來。
(代碼塊GitHub鏈接🔗:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/7abc91dbb82a007a78731845dd8c360ac0cc1e75/rag/codes/chapter16/CreateDataBase.py#L52)
import sqlite3
import json
def write_into_table():
with open('test.txt', 'r')as f:
data = json.load(f)
data = data['data']
# 連接到 SQLite 數據庫(如果數據庫不存在,它會被創建)
conn = sqlite3.connect('papers.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 創建表格
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS papers (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
title TEXT,
author TEXT,
subject TEXT
)
''')
# 插入數據
for paper in data:
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO papers (title, author, subject)
VALUES (?, ?, ?)
''', (paper['title'], paper['author'], paper['subject']))
# 提交併關閉連接
conn.commit()
conn.close()
上面的代碼是根據獲取的信息,創建對應的數據庫信息,並把記錄信息寫入,用於 SQL Call 的查詢。
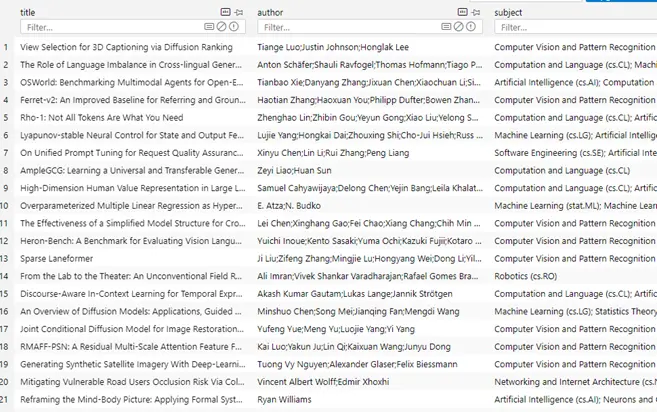
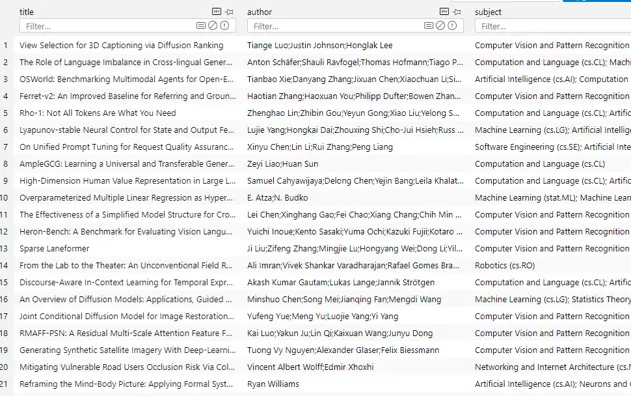
現在完成數據準備,我們得到了固定目錄下已經下載好的論文:
以及數據庫文件papers.db 。
四、依賴模塊詳解
為了構建支持統計分析的問答系統,我們需要掌握幾個核心模塊的原理和實現方式,分別包括意圖識別、SQL 調用、統計分析及圖表生成。
(一)意圖識別
首先是意圖識別模塊。該模塊的主要職責是分析用户的輸入內容,判斷其意圖屬於傳統的知識問答,還是涉及到結構化數據處理的統計問答。
LazyLLM內置了用於對意圖進行分析的 IntentClassifier 類,具體介紹如下:
IntentClassifier是一個基於語言模型的意圖識別器,用於根據用户提供的輸入文本及對話上下文識別預定義的意圖,並通過預處理和後處理步驟確保準確識別意圖。
對於 IntentClassifier ,我們提供了以下參數:
- llm: 用於意圖識別的語言模型對象,OnlineChatModule或TrainableModule類型
- intent_list (list): 包含所有可能意圖的字符串列表。可以包含中文或英文的意圖。
- prompt (str): 用户附加的提示詞。
- constrain (str): 用户附加的限制。
- examples (list[list]): 額外的示例,格式為 [[query, intent], [query, intent], ...]。
- return_trace (bool, 可選): 如果設置為 True,則將結果記錄在trace中。默認為 False。
ch_prompt_classifier_template = """
## role:意圖分類器
你是一個意圖分類引擎,負責根據對話信息分析用户輸入文本並確定唯一的意圖類別。{user_prompt}
## 限制:
你只需要回覆意圖的名字即可,不要額外輸出其他字段,也不要進行翻譯。{user_constrains}
## 注意:
{attention}
## 文本格式
輸入文本為JSON格式,"human_input"中內容為用户的原始輸入,"intent_list"為所有意圖名列表
## 示例
User: {{"human_input": "北京明天天氣怎麼樣?", "intent_list": ["查看天氣", "搜索引擎檢索", "查看監控", "週報總結", "聊天"]}}
Assistant: 查看天氣
{user_examples}
## 歷史對話
人類和助手之間的聊天記錄存儲在下面的 <histories></histories> XML 標記中。
<histories>
{history_info}
</histories>
輸入文本如下:
""" # noqa E501
在 IntentClassifier 內,內置瞭如上所示的模板,用於將上述參數傳入給大模型。IntentClassifier 的調用非常簡單,下面就是兩個完整調用的例子:
(代碼塊GitHub鏈接🔗:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/7abc91dbb82a007a78731845dd8c360ac0cc1e75/rag/codes/chapter16/intent_classifier.py#L1)
import lazyllm
from lazyllm.tools import IntentClassifier
classifier_llm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule()
chatflow_intent_list = ["翻譯服務", "天氣查詢", "內容推薦", "金融行情查詢"]
classifier = IntentClassifier(classifier_llm, intent_list=chatflow_intent_list)
while True:
query = input("輸入您的問題:\n")
print(f"\n識別到的意圖是:\n {classifier(query)}\n" + "-"*40)
# 今天天氣怎麼樣 ➔ 天氣查詢
# A股行情怎麼樣 ➔ 金融行情查詢
# 給我推薦一部科幻電影 ➔ 內容推薦
# 幫我把這邊論文譯為中文 ➔ 翻譯服務
1.意圖識別-高級用法
通過with語法,使得意圖識別模塊能夠直接跟隨具體的指令。
base = TrainableModule('internlm2-chat-7b')
with IntentClassifier(base) as ic:
ic.case['聊天', base]
ic.case['語⾳識別', TrainableModule('SenseVoiceSmall')]
ic.case['圖⽚問答', TrainableModule('Mini-InternVL-Chat-2B-V1-5').deploy_method(deploy.LMDeploy)]
ic.case['畫圖', pipeline(base.share().prompt(painter_prompt),
TrainableModule('stable-diffusion-3-medium'))]
ic.case['⽣成⾳樂', pipeline(base.share().prompt(musician_prompt), TrainableModule('musicgen-small'))]
ic.case['⽂字轉語⾳', TrainableModule('ChatTTS')]
WebModule(ic, history=[base], audio=True, port=8847).start().wait()
使用方式有case[a, b],case[a: b]和case[a::b]三種,可以根據個人習慣選擇使用三者無區別:
with IntentClassifier(base) as ic:
ic.case['聊天', base]
ic.case['語⾳識別': TrainableModule('SenseVoiceSmall')]
ic.case['圖⽚問答'::TrainableModule('Mini-InternVL-Chat-2B-V1-5').deploy_method(deploy.LMDeploy)]
(二)Sql Manager
接下來,我們解決統計問答流程中的第一環節:數據庫查詢與數據獲取。
在之前的學習內容中,雖然我們以 SQLite 為例講解了數據庫的基本使用流程,但在真實的生產環境裏,使用的數據庫種類遠不止 SQLite。
常見的關係型數據庫還包括 MySQL、PostgreSQL、SQL Server、Oracle 等,而在雲端,諸如阿里雲 RDS、騰訊雲 CynosDB、AWS RDS 這樣的數據庫服務也被廣泛使用。
為了方便地連接和操作不同類型的數據庫,我們可以使用 Python 中非常流行的 ORM 框架——SQLAlchemy。
SQLAlchemy 提供了統一的數據庫操作接口,不僅支持本地數據庫,也支持各種主流雲數據庫,極大地提升了數據庫交互的靈活性和可擴展性。
以下為通過SQLAlchemy連接本地和遠程數據庫的代碼。
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# 創建 SQLite 本地數據庫連接
engine = create_engine('sqlite:///local_database.db')
# 創建遠程 MySQL 數據庫連接
# 格式:mysql+pymysql://用户名:密碼@服務器地址:端口/數據庫名
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://user:password@host:3306/database_name')
# 測試連接
with engine.connect() as connection:
result = connection.execute("SELECT 1")
print(result.fetchone())
在 lazyllm 框架中,也對這一功能進行了封裝,提供了內置的 SQLManager 模塊。通過 SQLManager,用户可以非常簡單地連接本地或雲上的數據庫,統一調用 SQL 查詢、執行 SQL-call 相關操作,無需關心底層連接的複雜細節。只需在配置中指定數據庫地址、賬號密碼等信息,就可以一鍵啓動數據庫交互能力,為後續的結構化問答打下堅實基礎。
(代碼塊GitHub鏈接🔗:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/7abc91dbb82a007a78731845dd8c360ac0cc1e75/rag/codes/chapter16/sql_manager.py#L1)
from lazyllm.tools import SqlManager
# 連接本地數據庫
sql_manager = SqlManager("sqlite", None, None, None, None, db_name="papers.db", tables_info_dict=table_info)
# 連接遠程數據庫
# sql_manager = SqlManager(type="PostgreSQL", user="", password="", host="",port="", name="",)
# 查詢所有論文數量
res = sql_manager.execute_query("select count(*) as total_papser from papers;")
>>> [{"total_papser": 100}]
# 查詢帶有 LLM 的論文標題
res = sql_manager.execute_query("select title from papers where title like '%LLM%'")
>>> [{"title": "AmpleGCG: Learning a Universal and Transferable Generative Model of Adversarial Suffixes for Jailbreaking Both Open and Closed LLMs"}, {"title": "Learning to Localize Objects Improves Spatial Reasoning in Visual-LLMs"}, {"title": "LLMs in Biomedicine: A study on clinical Named Entity Recognition"}, {"title": "VLLMs Provide Better Context for Emotion Understanding Through Common Sense Reasoning"}]
注意,db\_name 參數需要傳入構建好的數據庫文件路徑,tables\_info_dict 參數需傳入數據庫基本信息字典(表名、列名等),我們以論文數據庫為例,基本信息的定義如下。
table_info = {
"tables": [{
"name": "papers",
"comment": "論文數據",
"columns": [
{
"name": "id",
"data_type": "Integer",
"comment": "序號",
"is_primary_key": True,
},
{"name": "title", "data_type": "String", "comment": "標題"},
{"name": "author", "data_type": "String", "comment": "作者"},
{"name": "subject", "data_type": "String", "comment": "領域"},
],
}]
}
(三)Sql Call
SQL Call 模塊依賴於Sql Manager,它能夠根據用户問題生成符合語義意圖的 SQL 查詢語句,並對接後端數據庫獲取原始數據。這一模塊不僅是統計分析的入口,也是確保結果準確性的關鍵。
我們先來看一下數據準備階段我們已經構建的數據庫文件 papers.db 的內容,該庫中只有一張表,包含文章的title、author 和 subject 信息:
接下來開始定義 sql call:
- 通過指定數據庫名稱和數據表信息創建 sql_manager,同時實例化一個大模型用於實現text2sql。
- 將二者傳入以構建一個 SQL Call 工作流
該工作流支持將自然語言查詢轉化為 SQL 語句並執行查詢,最終返回結果。
(代碼塊GitHub鏈接🔗:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/7abc91dbb82a007a78731845dd8c360ac0cc1e75/rag/codes/chapter16/sql_call.py#L1)
from lazyllm.tools import SqlManager, SqlCall
sql_manager = SqlManager("sqlite", None, None, None, None, db_name="papers.db", tables_info_dict=table_info)
sql_llm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule()
sql_call = SqlCall(sql_llm, sql_manager,
use_llm_for_sql_result=False)
query = "庫中一共多少篇文章"
print(sql_call(query))
>>> [{"total_papers": 200}]
while True:
query = input("請輸入您的問題:")
print("answer:")
print(sql_call(query))
# 庫中一共多少篇論文
# 庫中最多的三個subject是什麼
# 查詢數據庫並返回 subject 包含Computer Vision的論文題目的結果
(四)統計分析agent
獲取數據的問題解決後,我們將進入統計分析的核心流程。本模塊基於sql call實現整條統計分析pipeline,可以看作一個面向統計任務的智能agent,能夠根據用户問題自動完成 數據庫查詢 → 數據分析 → 圖表生成 → 結果彙總 的完整閉環流程。為用户提供圖文並茂的答案。
1. 代碼編寫
我們首先定義兩個工具(Tool),分別用於 SQL 查詢 和 代碼執行,並將它們作為可選工具提供給 Agent,支持其在執行任務過程中完成數據庫查詢和統計分析。
- run\_sql\_query 方法基於上一節構建的 SQL Call 工作流封裝而成,Agent 可在從用户查詢中解析出 SQL 相關需求後調用該方法,獲取結構化查詢結果。
- run_code 方法用於接收並執行大模型生成的統計分析代碼。該方法會返回關鍵結果或報錯信息,為大模型下一步的決策和行動提供反饋依據。
這兩個工具配合使用,使 Agent 能夠動態完成從數據獲取到分析執行的全流程任務。
@fc_register("tool")
def run_sql_query(query):
"""
Automatically generates and executes an SQL query based on a natural language request.
Given a natural language query describing a data retrieval task, this function generates the corresponding SQL
statement, executes it against the database, and returns the result.
Args:
query (str): A natural language description of the desired database query.
Returns:
list[dict]: A list of records returned from the SQL query, where each record is represented as a dictionary.
"""
sql_manager = SqlManager("sqlite", None, None, None, None, db_name="papers.db", tables_info_dict=table_info)
sql_llm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="sensenova")
sql_call = SqlCall(sql_llm, sql_manager, use_llm_for_sql_result=False)
return sql_call(query)
@fc_register("tool")
def run_code(code: str):
"""
Run the given code in a separate thread and return the result.
Args:
code (str): code to run.
Returns:
dict: {
"text": str,
"error": str or None,
}
"""
result = {
"text": "",
"error": None,
}
def code_thread():
nonlocal result
stdout = io.StringIO()
try:
with contextlib.redirect_stdout(stdout):
exec_globals = {}
exec(code, exec_globals)
except Exception:
result["error"] = traceback.format_exc()
result["text"] = stdout.getvalue()
thread = threading.Thread(target=code_thread)
thread.start()
thread.join(timeout=10)
if thread.is_alive():
result["error"] = "Execution timed out."
thread.join()
return result
注意!在撰寫函數時,一定要在函數下方加上註釋,格式如下:
def myfunction(arg1: str, arg2: Dict[str, Any], arg3: Literal["aaa", "bbb", "ccc"]="aaa"):
'''
Function description ...
Args:
arg1 (str): arg1 description.
arg2 (Dict[str, Any]): arg2 description
arg3 (Literal["aaa", "bbb", "ccc"]): arg3 description
'''
在大模型調用該函數時,將通過函數的描述,以及參數的表述,決定何時調用以及傳入參數。
接下來我們實現agent定義,這裏我們使用lazyllm內置的ReactAgent工具,將前文中定義的兩個工具傳入tools參數,即可實現模型自動調用。
ReactAgent是按照 Thought->Action->Observation->Thought...->Finish 的流程,一步一步的通過LLM和工具調用來顯示解決用户問題的步驟,最後輸出最終答案。
from lazyllm.tools.agent import ReactAgent
agent = ReactAgent(
llm=lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(stream=False),
tools=['run_code', 'run_sql_query'],
return_trace=True,
max_retries=3,
)
然後基於上述agent,我們定義prompt,並搭建支持統計問題的sql問答流程:
sql_prompt = """
你是一位資深數據科學家,需要基於給定的問題進行必要的統計分析和繪圖,來回答用户提出的統計問題。
你的工作流程如下:
1. 理解問題並進行數據查詢
- 拆解問題中需要查詢數據庫的部分,調用相應工具進行數據獲取。
2. 判斷根據數據是否可直接得出統計問題的答案
- 如果數據可以直接回答統計問題,則直接輸出結果,必要時補充繪製圖表。
- 如果不足以回答,則先進行必要的數據分析,再根據需要繪製圖表。
3. 通過編寫代碼並執行並獲取結果的方式實現數據分析和繪圖
- 編寫完整可執行的 Python 代碼,包含所有必要的 import、數據加載、分析邏輯、繪圖代碼、結果輸出。
- 使用常見數據科學工具包(如 pandas、numpy、scikit-learn 等)進行數據分析。
- 使用可視化工具(如 matplotlib、seaborn)進行圖表繪製。
4. 圖像保存
- 所有生成的圖像必須保存到以下路徑:
{image_path}
- 保存成功後,使用以下格式將圖片展示在最終回答中(Answer部分)(image_name為保存的文件名,image_path為完整路徑):

5. 錯誤處理
- 如果代碼執行失敗,請根據報錯信息自動修改代碼並重新執行,直到成功。
問題:
{query}
"""
with pipeline() as sql_ppl:
sql_ppl.formarter = lambda query: sql_prompt.format(query=query, image_path=IMAGE_PATH)
sql_ppl.agent = ReactAgent(
llm=lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(stream=False),
tools=['run_code', 'run_sql_query'],
return_trace=True,
max_retries=3,
)
sql_ppl.clean_output = lazyllm.ifs(lambda x: "Answer:" in x, lambda x: x.split("Answer:")[-1], lambda x:x)
if __name__ == '__main__':
lazyllm.WebModule(sql_ppl, port=23456, static_paths=image_save_path).start().wait()
五、構建支持統計分析的論文問答系統
在掌握了系統所依賴的各項關鍵技術之後,我們便可以開始動手構建一個實際可用的系統,以支持統計分析與知識問答的融合能力。
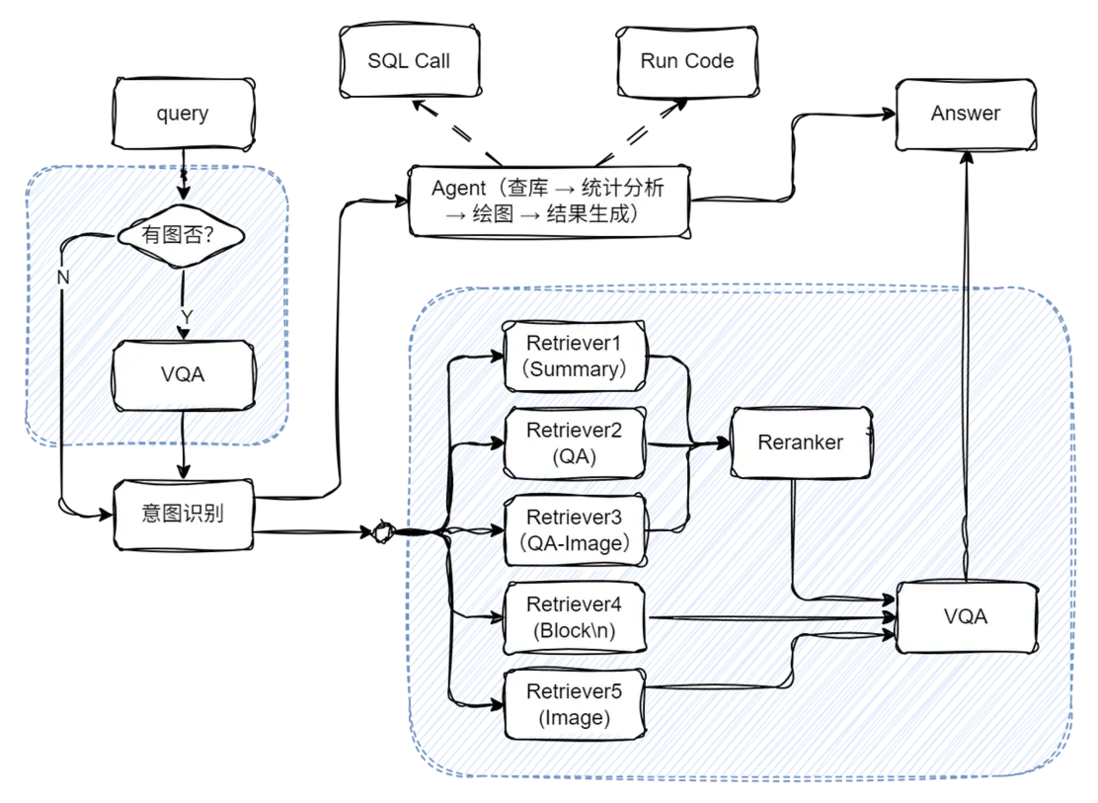
整個系統的架構如下:
代碼實現
我們來看怎麼利用上文已經給出的結構搭建完整的多功能問答工作流。整體思路如下:
我們首先分別定義兩個子工作流:
- chat_ppl:用於處理基於 RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation)的通用問答任務;
- sql_ppl:用於處理與統計分析相關的 SQL 問答任務。
隨後,在主工作流中引入一個意圖識別模塊,用於解析用户的查詢意圖,並據此在 chat\_ppl 與 sql\_ppl 兩條子工作流中選擇適合的路徑進行處理。通過這樣的結構設計,系統能夠根據用户問題的類型自動匹配合適的工作流,實現對自然語言問答和統計分析任務的統一調度與處理。
注意,在第9、10行,我們通過模塊導入的方式導入在第14講介紹的rag pipeline(build\_paper\_rag())和上文定義的 sql pipeline(build\_statistical\_agent()),在此不在重複編碼。
(代碼GitHub鏈接🔗:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/7abc91dbb82a007a78731845dd8c360ac0cc1e75/rag/codes/chapter16/statistical_agent.py#L1)
import lazyllm
from lazyllm import OnlineChatModule, pipeline, _0
from lazyllm.tools import IntentClassifier
from statistical_agent import build_statistical_agent
from paper_rag import build_paper_rag
# 構建 rag 工作流和統計分析工作流
rag_ppl = build_paper_rag()
sql_ppl = build_statistical_agent()
# 搭建具備知識問答和統計問答能力的主工作流
def build_paper_assistant():
llm = OnlineChatModule(source='qwen', stream=False)
intent_list = [
"論文問答",
"統計問答",
]
with pipeline() as ppl:
ppl.classifier = IntentClassifier(llm, intent_list=intent_list)
with lazyllm.switch(judge_on_full_input=False).bind(_0, ppl.input) as ppl.sw:
ppl.sw.case[intent_list[0], rag_ppl]
ppl.sw.case[intent_list[1], sql_ppl]
return ppl
if __name__ == "__main__":
main_ppl = build_paper_assistant()
lazyllm.WebModule(main_ppl, port=23459, static_paths="./images").start().wait()
然後我們就可以啓動這個工作流了。我們使用WebModule來啓動服務,通過 WebModule 把上面定義的工作流創建成一個 web 服務,這裏需要注意,啓動 WebModule 時,需要傳入圖片的保存路徑,這樣就可以把該目錄設置為靜態目錄,gradio 就可以直接訪問該目錄下的圖片文件了。
當 web 服務啓動成功後,則根據啓動後的 ip 和 port,我們就可以在瀏覽器中體驗使用了。
(一)簡單統計問題(不需要畫圖)
處理流程分析:
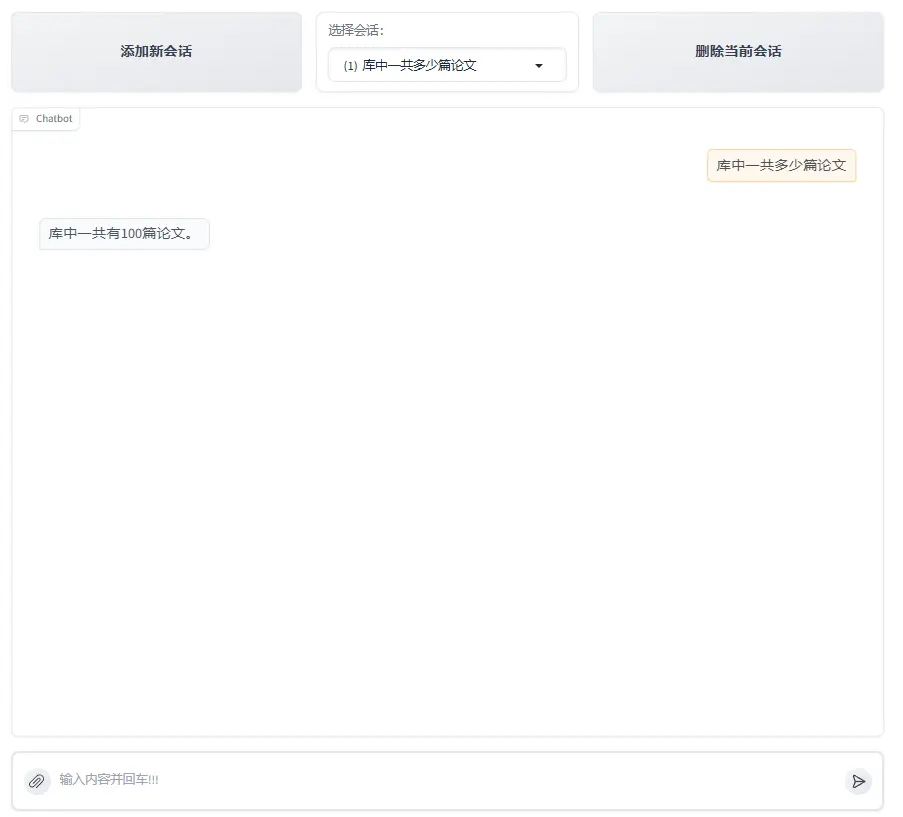
- 用户輸入query "庫中一共有多少篇論文"
- 大模型提取數據查詢問題"庫中一共多少篇論文" 調用SqlCall:
input:
"庫中一共多少篇論文"
text2sql:
select count(*) as total_papser from papers;
output:
[{"total_papers": 100}]
3. 模型判斷該結果已經可以回答query的問題,直接輸出回答”庫中一共有100篇論文“。
【附:執行日誌】
(二)簡單統計問題(需要畫圖)
處理流程分析:
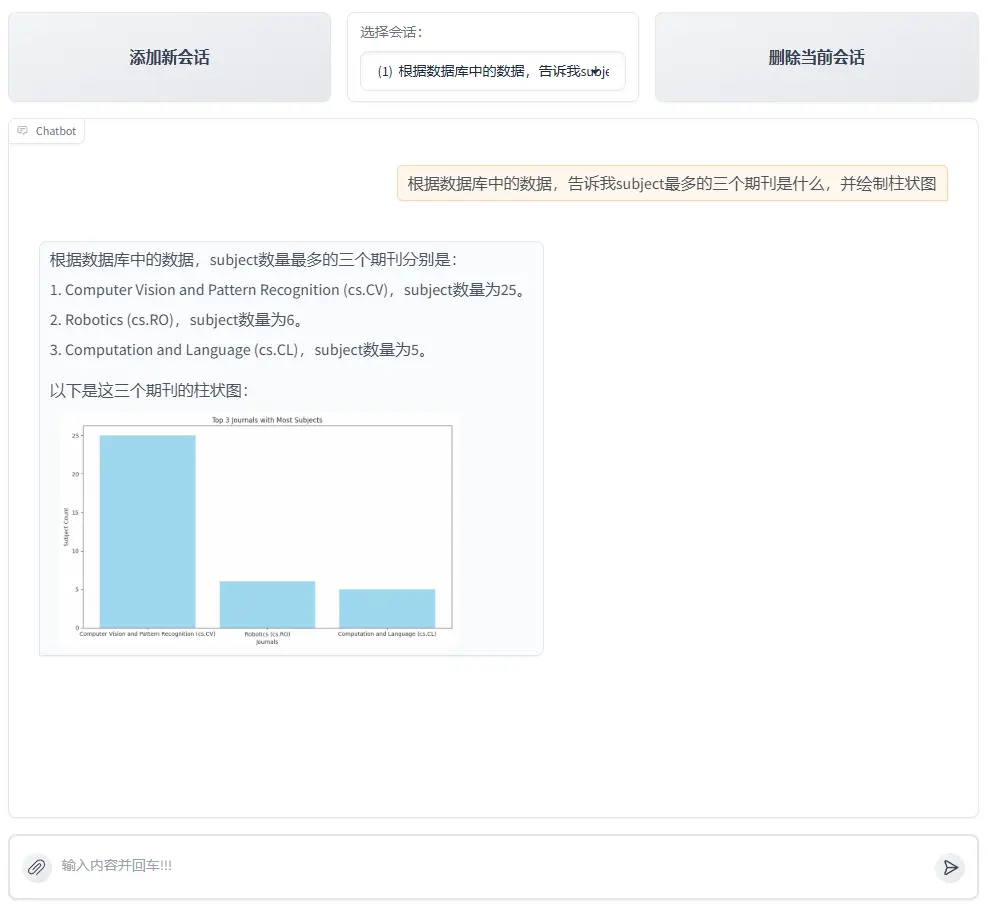
1. 用户輸入query "根據數據庫裏的數據,告訴我最多的三個subject是什麼,並繪製柱狀圖"
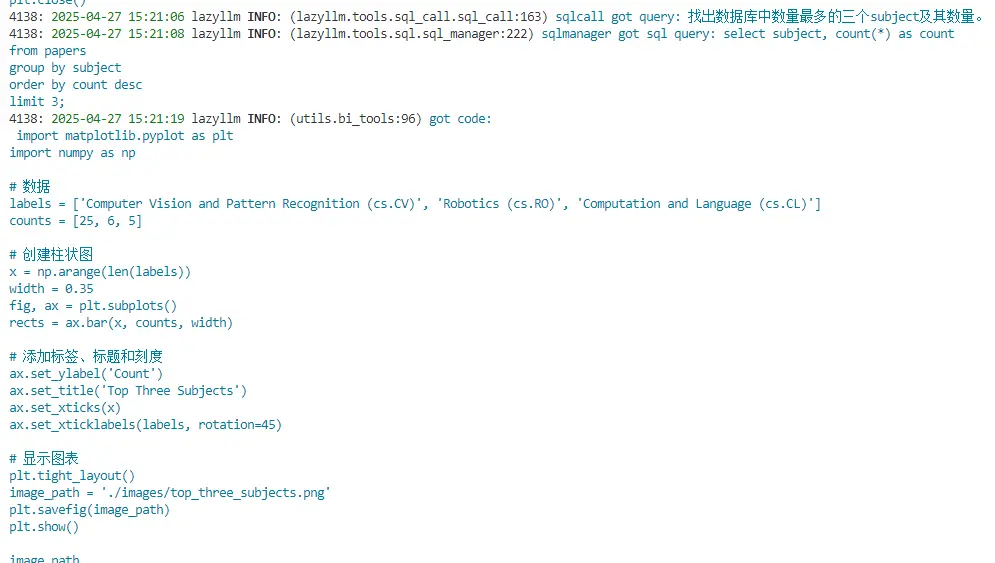
2. 大模型將對傳入的query進行分析,判定需要調用run\_sql\_query工具獲取數據,其會調用lazyllm內置的Sql調度工具SqlCall,它可以自動執行相應的sql查詢語句,從數據庫中獲得相應的結果,結果如下。
input:
"找出數據庫中數量最多的三個subject及其數量"
text2sql:
select subject, count(*) as count
from papsers
group by count desc
limit 3;
output:
[{"subject": "\nComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)", "count": 25}, {"subject": "\nRobotics (cs.RO)", "count": 6}, {"subject": "\nComputation and Language (cs.CL)", "count": 5}]
3. 模型判斷該結果已經可以回答query的問題,不需要進一步進行統計分析,但是query中包含作圖需求,因此其編寫僅用於作圖的python代碼並調用run_code工具執行,以下為大模型編寫的代碼。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 數據
labels = ['Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)', 'Robotics (cs.RO)', 'Computation and Language (cs.CL)']
counts = [25, 6, 5]
# 創建柱狀圖
x = np.arange(len(labels))
width = 0.35
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rects = ax.bar(x, counts, width)
# 添加標籤、標題和刻度
ax.set_ylabel('Count')
ax.set_title('Top Three Subjects')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(labels, rotation=45)
# 顯示圖表
plt.tight_layout()
image_path = './images/top_three_subjects.png'
plt.savefig(image_path)
4. 作圖完成後大模型根據圖片路徑並整合之前的結果為用户生成最終的圖文並茂的回答。
【附:執行日誌】
(三)複雜統計問題(需要畫圖)
處理流程分析:
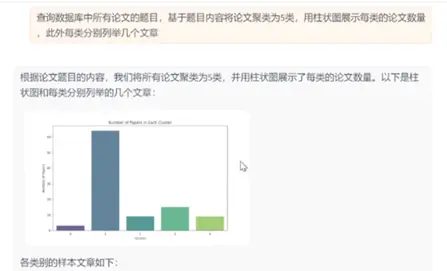
1. 用户輸入query "查詢數據庫中所有論文的題目,基於題目內容將論文聚類為5類,每類分別列舉幾個文章,並用柱狀圖展示每類的論文數量"
2. 大模型提取數據查詢問題"庫中一共多少篇論文" 調用SqlCall:
input:
"查詢庫中所有論文題目"
text2sql:
select title from papers;
output:
["View Selection for 3D Captioning via Diffusion Ranking", "The Role of Language Imbalance in Cross-lingual Generalisation: Insights from Cloned Language Experiments", "OSWorld: Benchmarking Multimodal Agents for Open-Ended Tasks in Real Computer Environments", "Ferret-v2: An Improved Baseline for Referring and Grounding with Large Language Models", "Rho-1: Not All Tokens Are What You Need", "Lyapunov-stable Neural Control for State and Output Feedback: A Novel Formulation", "On Unified Prompt Tuning for Request Quality Assurance in Public Code Review", "AmpleGCG: Learning a Universal and Transferable Generative Model of Adversarial Suffixes for Jailbreaking Both Open and Closed LLMs", "High-Dimension Human Value Representation in Large Language Models", "Overparameterized Multiple Linear Regression as Hyper-Curve Fitting", ...]
3. 模型編寫程序進一步進行統計分析任務,並調用 run code 工具執行。
(完整代碼GitHub鏈接🔗:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/7abc91dbb82a007a78731845dd8c360ac0cc1e75/rag/codes/chapter16/chat_sql_qa.py#L1)
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
# Load data
data = ["View Selection for 3D Captioning via Diffusion Ranking", "The Role of Language Imbalance in Cross-lingual Generalisation: Insights from Cloned Language Experiments", "OSWorld: Benchmarking Multimodal Agents for Open-Ended Tasks in Real Computer Environments", "Ferret-v2: An Improved Baseline for Referring and Grounding with Large Language Models", "Rho-1: Not All Tokens Are What You Need", "Lyapunov-stable Neural Control for State and Out..."]
# Create DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['title'])
# Vectorize titles
tfidf = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words='english')
X = tfidf.fit_transform(df['title'])
# Perform K-means clustering
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=5, random_state=42)
df['cluster'] = kmeans.fit_predict(X)
# Count papers per cluster
cluster_counts = df['cluster'].value_counts().sort_index()
# Plot cluster counts
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
cluster_counts.plot(kind='bar', color='skyblue')
plt.title('Number of Papers per Cluster')
plt.xlabel('Cluster')
plt.ylabel('Count')
plt.xticks(rotation=0)
# Save plot
os.makedirs('./images', exist_ok=True)
image_path = './images/cluster_counts.png'
plt.savefig(image_path)
plt.close()
# Print cluster counts and example titles
print("Cluster Counts:")
print(cluster_counts)
print("\nExample Titles per Cluster:")
for cluster in range(5):
print(f"\nCluster {cluster}:")
print(df[df['cluster'] == cluster]['title'].head(3).to_string(index=False))
print(f"\nImage saved at: {image_path}")
4. 執行完畢後大模型接收到圖片路徑和每類的結果,為用户生成圖文並茂的回答。
【附:運行日誌】
(四)知識問答
至此,我們構建了一個同時具備知識庫問答與統計分析能力的智能問答系統。該系統不僅支持用户圍繞文獻內容進行語義提問,還能夠針對數據庫中的結構化信息執行統計分析與圖表繪製,從而支持全局的數據觀察需求。
六、RAG論文系統綜合多模態方案
主要代碼實現:
# 構建 rag 工作流和統計分析工作流
rag_ppl = build_paper_rag()
sql_ppl = build_statistical_agent()
# 搭建具備知識問答和統計問答能力的主工作流
def build_paper_assistant():
llm = OnlineChatModule(source='qwen', stream=False)
vqa = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="sensenova",\
model="SenseNova-V6-Turbo").prompt(lazyllm.ChatPrompter(gen_prompt))
with pipeline() as ppl:
ppl.ifvqa = lazyllm.ifs(
lambda x: x.startswith('<lazyllm-query>'),
lambda x: vqa(x), lambda x:x)
with IntentClassifier(llm) as ppl.ic:
ppl.ic.case["論文問答", rag_ppl]
ppl.ic.case["統計問答", sql_ppl]
return ppl
if __name__ == "__main__":
main_ppl = build_paper_assistant()
lazyllm.WebModule(main_ppl, port=23459, static_paths="./images", encode_files=True).start().wait()
擴展閲讀:從知識庫構建數據庫
代碼實現:
import lazyllm
from lazyllm.tools import SqlManager
# 創建SQL管理器
sql_manager = SqlManager(db_type="SQLite", user=None,
password=None, host=None, port=None, db_name="doc.db")
# 創建知識庫
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path='/path/to/kb', create_ui=False)
# 配置提取字段
refined_schema = [
{"key": "document_title", "desc": "The title of the paper.", "type": "text"},
{"key": "author_name", "desc": "The names of the author of the paper.", "type": "text"},
{"key": "keywords", "desc": "Key terms or themes discussed in the paer.", "type": "text"},
{"key": "content_summary", "desc": "A brief summary of the paper's main content", "type": "text"},
]
# 知識庫連接到SQL並設置待提取字段
documents.connect_sql_manager(
sql_manager=sql_manager,
schma=refined_schema,
force_refresh=True,
)
# 開始提取知識庫到數據集
documents.update_database(llm=lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="qwen"))
# 展示提取到的內容:
str_result = sql_manager.execute_query(f"select * from {documents._doc_to_db_processor.doc_table_name}")
print(f"str_result: {str_result}")
效果展示:
[
{
"lazyllm_uuid": "2c42c181-bc26-43ca-a822-505b22f5d19e",
"lazyllm_created_at": "2025-05-16 19:10:12.014368",
"lazyllm_doc_path": "/path/to/pdfs/DeepSeek_R1.pdf",
"document_title": "DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning",
"author_name": "DeepSeek-AI",
"keywords": "DeepSeek-R1-Zero, DeepSeek-R1, reinforcement learning, reasoning models, multi-stage training, open-source, dense models, distilled models, Qwen, Llama",
"content_summary": "The paper introduces the first-generation reasoning models, DeepSeek-R1-Zero and DeepSeek-R1. DeepSeek-R1-Zero is trained using large-scale reinforcement learning without supervised fine-tuning and demonstrates strong reasoning capabilities but faces challenges such as poor readability and language mixing. To improve upon this, DeepSeek-R1 incorporates multi-stage training and cold-start data before reinforcement learning, achieving performance comparable to OpenAI-o1-1217 on reasoning tasks. The research community is supported by the open-sourcing of DeepSeek-R1-Zero, DeepSeek-R1, and six dense models distilled from DeepSeek-R1 based on Qwen and Llama."
}
]
更多技術內容,歡迎移步 “LazyLLM” 討論!