我們知道,剛開始接觸C語言編程,一般都是在一個.c或者.cpp(以下只説.c)的文件中編寫代碼,其中一定會有一個入口函數,
也就是main()函數,你可以將程序代碼全部寫在main函數裏,當然如果你想要程序更加模塊化,也可以將一些操作寫在一個函數
裏,這些函數的聲明和定義也都是在main函數中。
想想,隨着你的代碼量越來越大,實現的功能越來越多,在一個.c文件中,你定義了許許多多的函數,這些函數實現着不同功能,
並且都是混雜在一起,你會不會感覺看着自己寫的代碼感覺自己的腦子也亂了?在這裏我找到了一個方法來將程序變得更加模塊化,
更加有條理。總的做法分以下幾步:
1.將功能相近的自定義函數的聲明寫在一個.h文件中(比如:Math.h)
2.將這些函數的具體實現寫在.c文件中(比如:Math.c 注意要包含頭文件 #include "Math.h" )
3.在你的主程序(支持.c文件格式)中包含頭文件(#include "Math.h"),在主程序就可以調用這些自定義函數了
我們現在想要C函數模塊,該模塊提供數學計算的功能(例如加、減、乘、除等計算功能),自定義函數寫在Math.h中,函數的
實現寫在Math.c中,在主函數main.c中調用這些函數進行測試。
一、編寫Math.h文件
1 #ifndef _MATH_H
2 #define _MATH_H
3
4 #include <stdio.h>
5
6 /*
7 自定義函數的聲明
8 */
9 //加
10 int Add(int a,in b);
11 //減
12 int Sub(int a,int b);
13 //乘
14 int Multi(int a,int b);
15 //除
16 double Dev(int a,int b);
17 // ...
18 #endif
二、編寫Math.c文件
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include "Math.h" //必須添加!!!
3
4 int Add(int a,int b)
5 {
6 return a+b;
7 }
8
9 int Sub(int a,int b)
10 {
11 return a-b;
12 }
13
14 int Multi(int a,int b)
15 {
16 return a*b;
17 }
18
19 double Dev(int a,int b)
20 {
21 if(b==0)
22 {
23 printf("\n除數不能為0.");
24 return 0.0;
25 }
26 return (double)a/b;
27 }
三、測試:main.c(支持.c文件格式)調用模塊中的函數
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <conio.h>
3 #include "Math.h" //添加自定義函數的頭文件
4
5 void main()
6 {
7 int a=15,b=10;
8
9 //調用自定義函數
10 printf("a+b=%d\n", Add(a,b) );
11 printf("a-b=%d\n", Sub(a,b) );
12 printf("a*b=%d\n", Multi(a,b) );
13 printf("a/b=%f\n", Dev(a,b) );
14
15 getch();
16 return;
17 }
注意:在VC6.0中添加主程序代碼時需要添加.c格式的(main.c),添加.cpp格式的(main.cpp)會報錯,
具體原因還不知道,希望知道的可以告知!
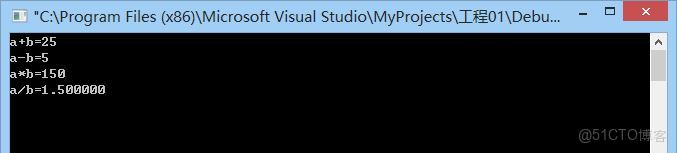
程序運行的結果: