前置內容
索引模塊
一、整體框架
1.整體架構目標
- 功能定位:提供一個輕量級、可嵌入的本地搜索引擎後端模塊。
- 輸入:原始文檔集合路徑(用於建索引);用户查詢字符串(用於搜索)。
- 輸出:結構化 JSON 格式的搜索結果(含標題、摘要、URL、相關性權重等)
2.包含功能
①初始化模塊
功能:創建索引
void InitSearcher(std::string &input)
{
//1.獲取或創建index對象
//2.根據index對象創建索引
}②搜索模塊
功能:主要模塊,根據搜索詞查找索引並返回包含搜索詞的文檔
void Search(std::string& query, std::string *json_string)
{}參數解釋:query:用户搜索的詞
json_string:返回給用户的搜索結果
二、初始化模塊
1.單例模式
初始化創建index對象並根據index對象創建索引,因為創建索引只需要一次就夠了,為防止多次創建對象浪費資源,所以index模塊我們使用單例模式
Class index
{
private:
Index(){}
Index(const Index&) = delete;
Index& operator=(const Index&) = delete;
static Index* instance;
static std::mutex mutex;
public:
//獲取單例
static Index* GetInstance()
{
if(nullptr == instance)//雙層鎖減少加鎖,提高效率
{
mutex.lock();
if(nullptr == instance)
{
instance = new Index();
}
mutex.unlock();
}
return instance;
}
};
Index* Index::instance = nullptr;創建單例思路:通過使用雙檢鎖機制確保在多線程環境下僅創建一個Index類的實例,並且該實例只能通過靜態方法GetInstance訪問。為避免頻繁加鎖帶來的性能損耗,在首次檢查確認實例未創建後才進行加鎖操作,並在加鎖後再做一次檢查以防止多個線程同時創建實例的情況。此外,為了保證單例的有效性,刪除了拷貝構造函數和賦值操作符,阻止了通過拷貝方式生成新的實例。實例化過程採用懶加載策略,即實例在第一次調用GetInstance方法時才會被創建,這樣可以節省資源,特別適合初始化成本較高的場景。
2.初始化的構建
思路:首先根據單例創建索引對象,然後調用對象的構建索引的模塊就完啦,太簡單了
void InitSearcher(const std::string &input)
{
//1.獲取或創建index對象
index = ns_index::Index::GetInstance();
std::cout << "獲取單例成功" << std::endl;
//2.根據index對象創建索引
index->BuildIndex(input);
std::cout << "創建索引成功" << std::endl;
}不解釋
三、搜索模塊
1.思路
①分詞:對我們的query進行按照searcher的要求進行分詞
②觸發:就是根據分詞的各個"詞",按照index進行查找
③合併排序:彙總查找,按照相關性(weight)降序排序
④構建:根據查找出來的結果,構建json串
2.分詞
使用工具類Util中的CutString函數
std::vector<:string> words;
Util::JiebaUtil::CutString(query, &words);3.觸發
①功能:根據用户輸入的一組分詞(words),從倒排索引中查找每個詞對應的文檔列表(倒排拉鍊),並將所有結果合併到一個統一的列表 inverted_list_all 中
②思路
struct InvertElem
{
std::string word;
uint64_t doc_id;
int weight;//權重
};
//倒排拉鍊:存儲所有文檔中的同一個單詞的InvertElem,裏邊記錄這這個單詞所處id和權重,方便根據權重展示
typedef std::vector InvertList;- 創建一個空的倒排列表
inverted_list_all,用於收集所有匹配詞項對應的文檔ID及其相關信息(如詞頻、位置等,取決於InvertList的定義)。 - 使用
boost::to_lower將其轉換為小寫,保證查詢與索引時的大小寫一致(通常索引構建時也會轉小寫,以實現大小寫不敏感搜索)。 - 調用索引對象
index的GetInvertList(word)方法,嘗試獲取該詞對應的倒排拉鍊(即包含該詞的所有文檔ID列表)。 - 如果返回
nullptr,説明該詞不在索引中(例如是停用詞或未被索引的詞),則跳過該詞。 - 將當前詞的倒排拉鍊中的所有元素(文檔記錄)追加到
inverted_list_all的末尾。
ns_index::InvertList inverted_list_all;//根據單詞找到id存入其中
for(auto word : words)
{
boost::to_lower(word);
//根據單詞獲取倒排拉鍊
ns_index::InvertList* inverted_list = index->GetInvertList(word);
if(nullptr == inverted_list)
{
continue;
}
inverted_list_all.insert(inverted_list_all.end(), inverted_list->begin(), inverted_list->end());
}執行完這一步後inverted_list_all裏邊存的是包含搜索詞的InvertElem的集合
4.合併排序
功能:按照相關性進行降序排序
std::sort(inverted_list_all.begin(), inverted_list_all.end(),
[](const ns_index::InvertElem& e1, const ns_index::InvertElem& e2){
return e1.weight > e2.weight;//降序>, 升序<
});執行完這一步後inverted_list_all中就會按weight的順序將InvertedElem進行降序
小技巧:編寫仿函數時降序用>,升序用<
5.構建
①功能:根據查找出來的結果,構建json串
②Json的使用
請移步下邊的文章
③思路
遍歷inverted_list_all,根據其中元素的id值查找正排索引,就可以得到文檔的全部內容,然後就能構建Json串了
Json::Value root;
for(auto &item : inverted_list_all)
{
ns_index::DocInfo* doc = index->GetForwordIndex(item.doc_id);
if(nullptr == doc)
{
continue;
}
Json::Value elem;
elem["title"] = doc->title;
elem["desc"] = GetDesc(doc->content, item.word);
// elem["desc"] = doc->content;//content是文檔去標籤後的結果,但不是我們想要的,我們要的是一部分
elem["url"] = doc->url;
elem["id"] = item.doc_id;
elem["weight"] = item.weight;
root.append(elem);
}
Json::StyledWriter writer;
*json_string = writer.write(root);④GetDesc的實現
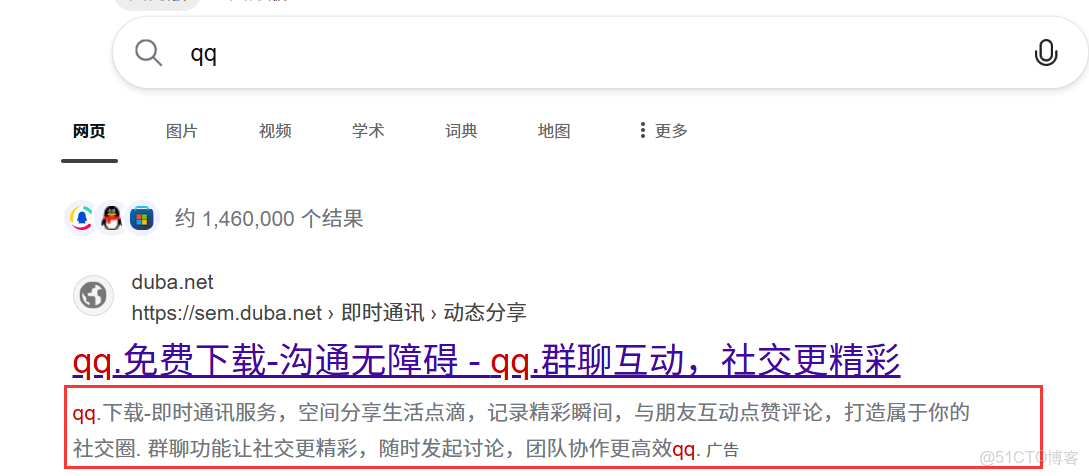
功能:提取文檔內容中的一部分,而不是全部展示出來
類似下圖中框起來的部分,不設置的話就會將文檔內容全部展示出來,不夠清晰
思路:我們採用的是將搜索詞的前50個字符和後100個字符顯示出來作為概要
①找到首次出現的位置
②獲取開始位置和結束位置
③返回字符串
std::string GetDesc(std::string& content, std::string& word)
{
//找到word在content中首次出現的位置,然後往前找50個字節(不夠從頭開始),往後找100個字節(不夠到結尾)
const int prev_step = 50;
const int next_step = 100;
//1.找到首次出現
auto iter = std::search(content.begin(), content.end(),word.begin(),word.end(),
[](int x, int y){
return (std::tolower(x) == std::tolower(y));
});
if(iter == content.end()){
return "None";
}
std::size_t pos = std::distance(content.begin(),iter);
//下邊這種寫法有坑:讀取的是文檔中的內容,例如:文檔中Split,而word是split,無法區分大小寫
// std::size_t pos = content.find(word);
// if(pos == std::string::npos)
// return "None";
//2.獲取開始和結束位置
std::size_t start = 0;
std::size_t end = content.size();
if(pos > start + prev_step) start = pos-prev_step;
if(pos + next_step < end) end = pos+next_step;
//3.返回字串
if(start >= end) return "None1";
return content.substr(start, end-start);
}四、代碼展示
#pragma once
#include "index.hpp"
#include
namespace ns_searcher
{
class Searcher
{
private:
ns_index::Index* index;//供系統進行查找索引
public:
void InitSearcher(const std::string &input)
{
//1.獲取或創建index對象
index = ns_index::Index::GetInstance();
std::cout << "獲取單例成功" << std::endl;
//2.根據index對象創建索引
index->BuildIndex(input);
std::cout << "創建索引成功" << std::endl;
}
//query:搜索的詞
//json_string:返回給用户的搜索結果
void Search(std::string &query, std::string *json_string)
{
//1.分詞:對我們的query進行按照searcher的要求進行分詞
std::vector<:string> words;
Util::JiebaUtil::CutString(query, &words);
//2.觸發:就是根據分詞的各個“詞”,按照index查找
ns_index::InvertList inverted_list_all;//根據單詞找到id存入其中
for(auto word : words)
{
boost::to_lower(word);
//根據單詞獲取倒排拉鍊
ns_index::InvertList* inverted_list = index->GetInvertList(word);
if(nullptr == inverted_list)
{
continue;
}
inverted_list_all.insert(inverted_list_all.end(), inverted_list->begin(), inverted_list->end());
}
//3.合併排序:彙總查找結果,按照相關性(weight)降序排序
std::sort(inverted_list_all.begin(), inverted_list_all.end(),
[](const ns_index::InvertElem& e1, const ns_index::InvertElem& e2){
return e1.weight > e2.weight;//降序>, 升序<
});
//4.構建:根據查找出來的結果,構建json串
Json::Value root;
for(auto &item : inverted_list_all)
{
ns_index::DocInfo* doc = index->GetForwordIndex(item.doc_id);
if(nullptr == doc)
{
continue;
}
Json::Value elem;
elem["title"] = doc->title;
elem["desc"] = GetDesc(doc->content, item.word);
// elem["desc"] = doc->content;//content是文檔去標籤後的結果,但不是我們想要的,我們要的是一部分,稍後處理
elem["url"] = doc->url;
elem["id"] = item.doc_id;
elem["weight"] = item.weight;
root.append(elem);
}
Json::StyledWriter writer;
*json_string = writer.write(root);
}
std::string GetDesc(std::string& content, std::string& word)
{
//找到word在content中首次出現的位置,然後往前找50個字節(不夠從頭開始),往後找100個字節(不夠到結尾)
const int prev_step = 50;
const int next_step = 100;
//1.找到首次出現
auto iter = std::search(content.begin(), content.end(),word.begin(),word.end(),
[](int x, int y){
return (std::tolower(x) == std::tolower(y));
});
if(iter == content.end()){
return "None";
}
std::size_t pos = std::distance(content.begin(),iter);
//下邊這種寫法有坑:讀取的是文檔中的內容,例如:文檔中Split,而word是split,無法區分大小寫
// std::size_t pos = content.find(word);
// if(pos == std::string::npos)
// return "None";
//2.獲取開始和結束位置
std::size_t start = 0;
std::size_t end = content.size();
if(pos > start + prev_step) start = pos-prev_step;
if(pos + next_step < end) end = pos+next_step;
//3.返回字串
if(start >= end) return "None1";
return content.substr(start, end-start);
}
};
}