前言
Runtime.exec()創建用的過於頻繁,而進程有一套複雜的管理模式註定新啓的進程並不可以直接忽略不管。在執行常駐進程的時候必須對新建進程加以管理。生產環境過量資源的浪費、阻塞會導致程序卡死系統崩潰。
以下是本文創建進程的實踐:
- 複雜系統命令使用字符串數組傳遞參數
- 生產環境進程關閉標準輸入輸出、新建進程必須及時處理流的緩衝區。
- java創建進程必須調用process.waitFor();防止殭屍進程佔用資源創建進程的方式
Runtime.exec()是有隱患的,不全文閲讀的話希望大家着重注意以上三點
java有兩種創建新進程的方式
- new ProcessBuilder(String[] cmd).start()方法
- Runtime.getRuntime().exec()
Runtime的底層是使用ProcessBuilder來實現的,如果你想更細緻的操作進程,重定向標準錯誤、標準輸入輸出等、應該使用ProcessBuilder來創建進程。
public class Runtime{
...
public Process exec(String[] cmdarray, String[] envp, File dir)
throws IOException {
return new ProcessBuilder(cmdarray)
.environment(envp)
.directory(dir)
.start();
}
...
}常見錯誤演示
首先定義一個打印進程輸出的方法(標準輸出和錯誤輸出)
private static void printResult(Process exec) throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(()->{
try (
BufferedReader inputReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(exec.getInputStream()));
) {
String line;
while ((line = inputReader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
try (
BufferedReader inputReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(exec.getErrorStream()));
) {
String line;
while ((line = inputReader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}基礎錯誤 複雜命令不使用數組傳參
Process exec = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("ps -aux | grep amhome");
printResult(exec);看一下輸出,
error: user name does not exist
Usage:
ps [options]
Try 'ps --help <simple|list|output|threads|misc|all>'
or 'ps --help <s|l|o|t|m|a>'
for additional help text.
For more details see ps(1).很明顯,這個命令已經識別不了了,需要寫出完整命令行。當碰到一些特殊字符比如管道符|,重定向符號<>的時候,請使用數組來傳遞參數
Process exec = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[]{"/bin/bash", "-c","ps -aux | grep amhome"});嚴重錯誤1 未及時讀出緩衝區導致進程阻塞
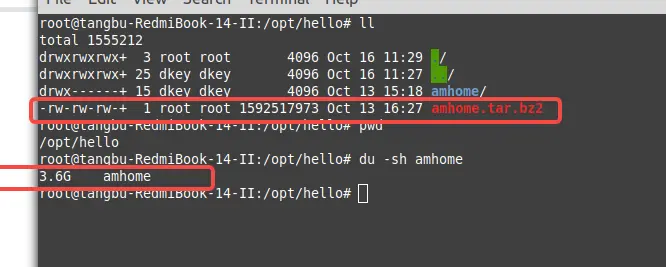
筆者工作電腦下有一個文件夾amhome.tar.bz2壓縮包和amhome文件夾,大小如下圖所示
原文件夾有3.6G,壓縮後的文件在1.6G左右。現在刪除amhome原文件夾並使用以下代碼來進行系統命令解壓縮
String[] cmd = new String[]{"tar", "-jxvf","/opt/hello/amhome.tar.bz2", "-C", "/opt/hello"};
Process exec = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
Thread.sleep(1000000L);經過很久的等待amhome文件夾最終解壓停留在1024M的大小,而且查看解壓的進程,已經處在S休眠狀態,進程被阻塞了。
原因:每一個進程都會有標準輸入、標準輸出、標準錯誤三個流。並且配備三個緩衝區。緩衝區滿了之後進程會被阻塞,直到緩衝區被讀取完成,進程會繼續往下執行,本案例中系統命令tar的標準輸出太多,緩衝區滿,阻塞了進程。
所以,需要單獨的線程不停的讀取進程的標準輸出執行命令的方法如下
public final static List<String> process(String[] cmd) throws IOException {
List<String> output = new ArrayList<>();
ProcessBuilder processBuilder = new ProcessBuilder(cmd);
processBuilder.redirectErrorStream(true);
Process process = processBuilder.start();
new Thread(() -> {
try (
BufferedReader inputReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
){
String line;
while ((line = inputReader.readLine()) != null) {
output.add(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
return output;
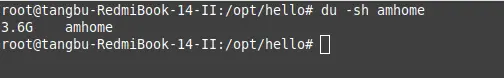
}最終,文件停留了3.6G的大小,解壓成功。
嚴重錯誤2 異步執行進程未回收導致殭屍進程問題
- linux中程序是以進程的形式存在,開機時最先啓動1號init進程或者是systemd進程,然後通過fork系統調用創建子進程。
- 子進程退出時父進程需要對子進程回收,父進程創建子進程的時候需要向操作系統註冊子進程回收函數,如果父進程先於子進程退出,子進程則由1號進程接管,該進程的父進程變成1號進程。
- 如果子進程先退出,父進程又沒有清理子進程的資源,子進程就變成了殭屍進程。系統資源有限,大量的殭屍進程會導致系統無法繼續創建進程。
而jvm並不會為我們自動清理子進程的資源,是通過process.waitFor()來回收。因此,創建異步新進程的時候我們需要在新線程裏繼續waitFor等待清理系統資源。
因此建議使用以下代碼
public final static List<String> process(String[] cmd, boolean block) throws IOException {
ProcessBuilder pb = new ProcessBuilder(cmd);
List<String> output = new ArrayList<>();
pb.redirectErrorStream(true);
Process p = pb.start();
logger.warn("Invoke cmd: " + StringUtils.join(cmd, " "));
Thread readThread = new Thread(() -> {
try (
BufferedReader inputReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(p.getInputStream()));
){
String line;
while ((line = inputReader.readLine()) != null) {
logger.debug(line);
output.add(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.warn("input stream buffer handle exception", e);
}
});
readThread.start();
if (block){
while (readThread.isAlive()){
try {
readThread.join();
p.waitFor();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
continue;
}
}
}else {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
while (p.isAlive()) {
try {
p.waitFor();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.warn("p.waitFor() exception", e);
}
}
});
thread.start();
}
return output;
}