目標
遍歷請求時,讓請求依次執行(等待前一次請求響應後再發起下一次請求)並且等待所有請求完成。
示例
前置物料
// 模擬一個用於將名字轉換為大寫的請求
const asyncUppercase = (value) =>
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('sent');
const timer = Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000);
setTimeout(() => resolve(value.toUpperCase()), timer);
});for(數組和對象)
(async () => {
const items = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
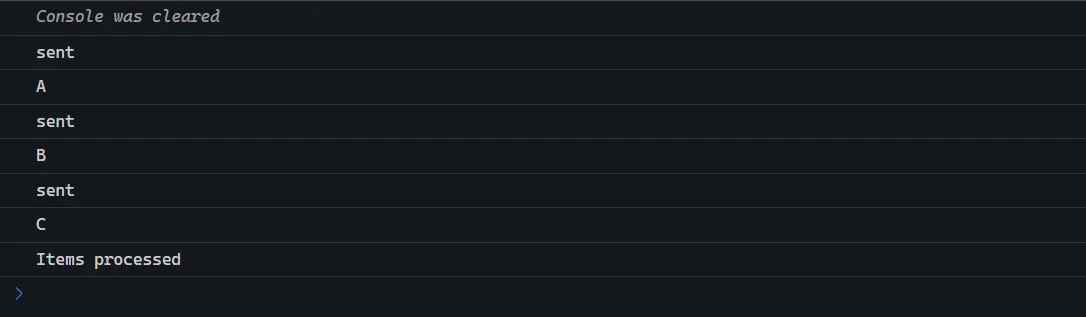
for (let index = 0; index < items.length; index++) {
const item = items[index];
const uppercaseItem = await asyncUppercase(item);
console.log(uppercaseItem);
}
console.log('Items processed');
})();輸出結果:請求依次執行並且等待所有請求完成。
for of(適用於數組)
(async () => {
const items = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
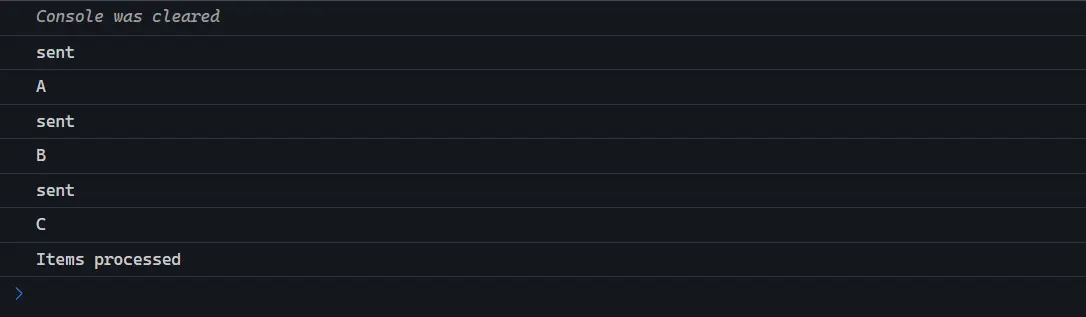
for (const item of items) {
const uppercaseItem = await asyncUppercase(item);
console.log(uppercaseItem);
}
console.log('Items processed');
})();輸出結果:請求依次執行並且等待所有請求完成。
for in(適用於對象)
(async () => {
const items = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
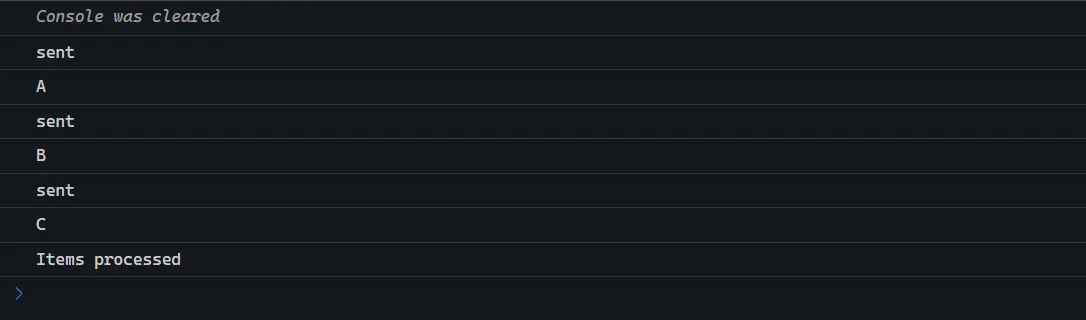
for (const item in items) {
const uppercaseItem = await asyncUppercase(items[item]);
console.log(uppercaseItem);
}
console.log('Items processed');
})();輸出結果:請求依次執行並且等待所有請求完成。
注意事項
Array.prototype.map + Promise.all
如果不要求依次執行,Array.prototype.map + Promise.all將是一個更好的選擇。
因為Array.prototype.map是迭代器模式的實現,讓我們無需關心迭代的細節。
(async () => {
const items = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
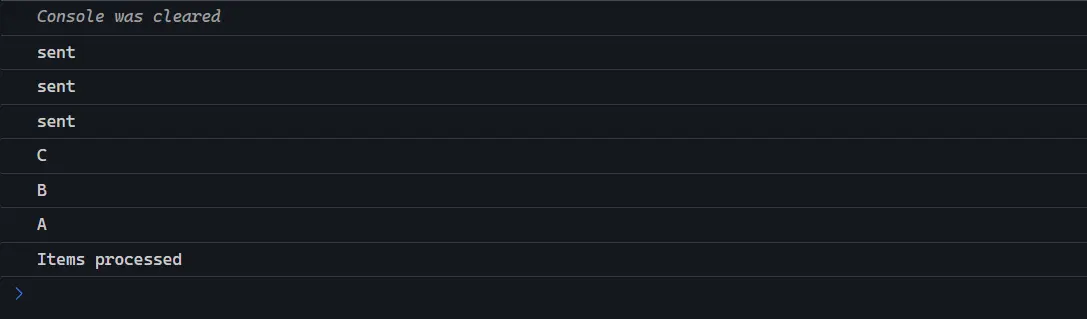
await Promise.all(items.map(async (item) => {
const uppercaseItem = await asyncUppercase(item);
console.log(uppercaseItem);
}));
console.log('Items processed');
})();輸出結果:請求沒有依次執行,但是可以藉助Promise.all等待所有請求完成。
Array.prototype.forEach是無法等待前一次請求響應的
通過觀察forEach的實現,會發現它只是簡單的同步執行了我們傳入的函數callback.call(T, kValue, k, O);。
// Production steps of ECMA-262, Edition 5, 15.4.4.18
// Reference: http://es5.github.io/#x15.4.4.18
if (!Array.prototype.forEach) {
Array.prototype.forEach = function(callback, thisArg) {
var T, k;
if (this === null) {
throw new TypeError(' this is null or not defined');
}
// 1. Let O be the result of calling toObject() passing the
// |this| value as the argument.
var O = Object(this);
// 2. Let lenValue be the result of calling the Get() internal
// method of O with the argument "length".
// 3. Let len be toUint32(lenValue).
var len = O.length >>> 0;
// 4. If isCallable(callback) is false, throw a TypeError exception.
// See: http://es5.github.com/#x9.11
if (typeof callback !== "function") {
throw new TypeError(callback + ' is not a function');
}
// 5. If thisArg was supplied, let T be thisArg; else let
// T be undefined.
if (arguments.length > 1) {
T = thisArg;
}
// 6. Let k be 0
k = 0;
// 7. Repeat, while k < len
while (k < len) {
var kValue;
// a. Let Pk be ToString(k).
// This is implicit for LHS operands of the in operator
// b. Let kPresent be the result of calling the HasProperty
// internal method of O with argument Pk.
// This step can be combined with c
// c. If kPresent is true, then
if (k in O) {
// i. Let kValue be the result of calling the Get internal
// method of O with argument Pk.
kValue = O[k];
// ii. Call the Call internal method of callback with T as
// the this value and argument list containing kValue, k, and O.
callback.call(T, kValue, k, O);
}
// d. Increase k by 1.
k++;
}
// 8. return undefined
};
}當然你也可以通過一個額外的變量來達到和Array.prototype.map一樣的效果,只是沒有必要。
(async () => {
const items = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
const pros = [];
items.forEach((item) => {
const func = async () => {
const uppercaseItem = await asyncUppercase(item);
console.log(uppercaseItem);
};
pros.push(func());
});
await Promise.all(pros);
console.log('Items processed');
})();