react-router簡介
- react-router包含3個庫,react-router、react-router-dom和react-router-native。
- react-router提供最基本的路路由功能,實際使⽤的時候我們不會直接安裝react-router,⽽是根據應⽤運行的環境選擇安裝 react-router-dom(在瀏覽器器中使⽤)或react-router-native(在rn中使⽤)。
- react-router-dom和 react-router-native都依賴react-router,所以在安裝時,react-router也會自動安裝,
react-Routerg(中文官網):http://react-router.docschina...
創建web應用的使用:
yarn add react-router-domreact-Router的基本使用
import React,{Component} from 'react'
import { BrowserRouter as Router,Route, Link, Switch} from "react-router-dom";
import HomePage from './pages/HomePage'
import LoginPage from './pages/LoginPage'
import UserPage from './pages/UserPage'
import _404Page from './pages/_404Page'
export default function App(){
return(
<div className="app">
<Router>
<Link to='/'>
首頁
</Link>
<Link to='/user'>
用户中心
</Link>
<Link to='/login'>
登陸
</Link>
<Link to="/product/123">
商品
</Link>
<Switch>
{/* 沒有swtich 就會把匹配到的進行現實*/}
// exact精確的
<Route exact path="/"
children={()=><div>HomePage-children</div>}
component={HomePage}
render={()=><div>HomePage-render</div>}
></Route>
{/* 優先級順序 */}
// 三個都存在,只渲染一個;都可以獲取到`router props`
// children 不管location 是否匹配了,都會現實
{/* children>componentrender */}
<Route path="/user" component={UserPage}></Route>
<Route path="/login" component={LoginPage}></Route>
<Route component={_404Page}></Route>
</Switch>
</Router>
</div>
)
}
當 Switch 標籤沒有包裹需要渲染的Route組建時,如果又一個路由 寫了children 渲染方式,那麼每一個路徑都會渲染這個children;
當然這個404 也會這樣一直存在。
Switch 用於渲染與路徑匹配的第一個<Route> 或 <Redirect>
children 被使用的場景,比如導航、菜單,每次都需要被渲染出來。當然一般導航 我們用組建複合比較多。children 也是一種可以實現的方式。
component: component
合理使用 children、component、render
import React, {Component, useEffect} from "react";
import {BrowserRouter as Router, Route} from "react-router-dom";
export default class RouteComponentPage extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { count: 0 };
}
render() {
const {count} = this.state;
return (
<div>
<h3>RouteComponentPage</h3>
<button
onClick={() => {
this.setState({count: count + 1});
}}>
click change count {count}
</button>
<Router>
{/* 渲染component的時候會調⽤用React.createElement,如果使⽤用下⾯面這種匿匿名函數的 形式,每次都會⽣生成⼀一個新的匿匿名的函數,
導致⽣生成的組件的type總是不不相同,這個時候會產⽣生重複的卸載和掛載 */}
{/* 錯誤舉例例 觀察下child的didMount和willUnmount函數 */}
{/* <Route component={() => <Child count={count} />} />
<Route component={() => <FunctionChild count={count} />} /> */}
{/* 下⾯面才是正確的示範 */}
{/* <Route render={() => <Child count={count} />} /> */}
<Route render={() => <FunctionChild count={count} />} />
{/* children 呢 */}
{/* <Route children={() => <Child count={count} />} /> */}
<Route children={() => <FunctionChild count={count} />} />
</Router>
</div>
);
}
}
class Child extends Component {
componentDidMount(){
console.log("componentDidMount") //sy-log
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("componentWillUnmount")//sy-log
}
render() {
return <div>child-{this.props.count}</div>;
}
}
function FunctionChild(props) {
useEffect(() => {
return () => {
console.log("FunctionChild-WillUnmount"); //sy-log
};
}, [])
return (<div>child-{props.count}</div>)
}
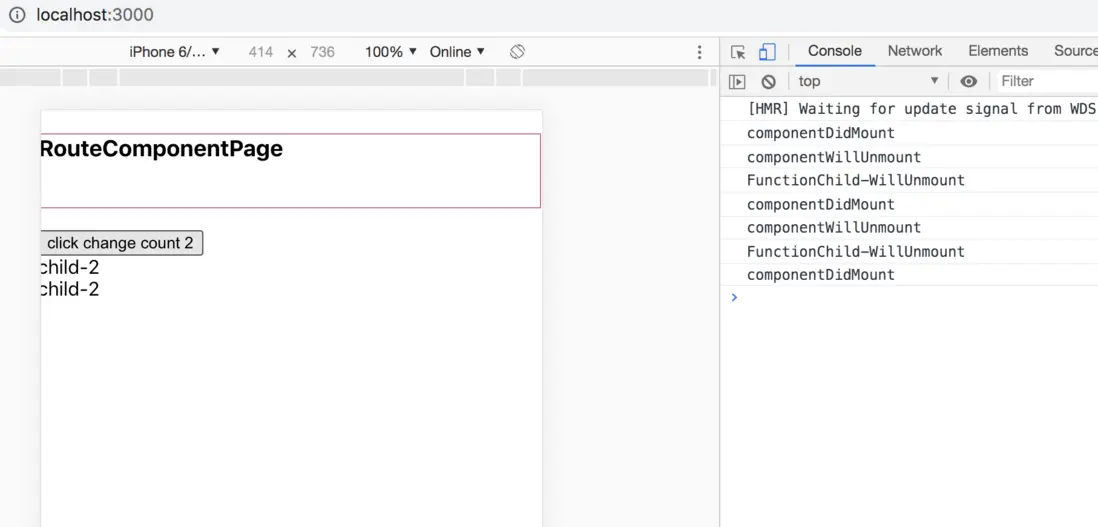
當我們去執行
<Route component={() => <Child count={count} >/>} /> <Route component={() => <FunctionChild count={count} />} />首次加載的時候會執行,Child裏面的componentDidMount
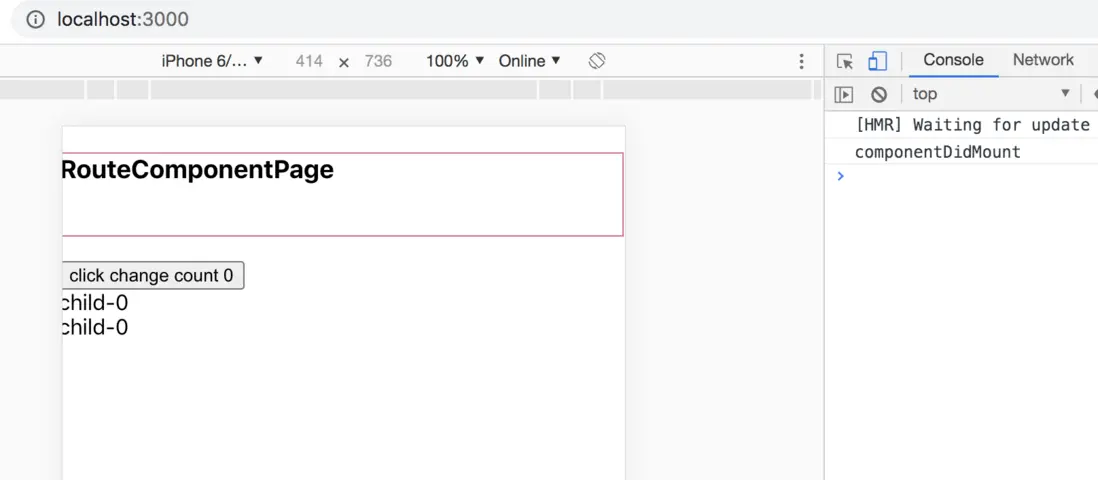
- 當我們點擊按鈕疊加時
無論時函數組建,還是class 組建 都會出現,頻繁加載
componentDidMount、componentWillUnmount
這是十分消耗性能的
所以我們最好時使用 render 和 child來加載組建
我們需要合理選用:route在沒有swtich的情況下,匹配到才進行渲染,我們選擇render和component,組建選擇 component,匿名函數選擇render
接下來我們看下三種渲染方式時如何執行的
三種渲染方式的執行
Rputer 核心渲染源碼:
return(
<RouterConetxt.Provider value={props}>
{props.match // match的情況下
? children // 先判斷 children 是否匹配
// children 的數據類型: fn, 對象, 數組
? typeof children === 'function' // 如果是fn
? __DEV__
? evalChilderDev(children,props,this.props.path)
:children(props) // 執行fn 函數
:children // children 存在,但是不是fn;組建複合的形式存在,就直接渲染children
: component // 如果沒有children;判斷component, 優先級第二
? React.createElement(component, props) // component 存在,使用React.createElement(),渲染當前的組建
: render // component 也不存在,最後判斷render
? render(props) // render 存在,直接執行
: null // 都不存在 返回null
: typeof children === 'function' // 不match,不匹配的情況直接看children是不是一個fn
? __DEV__
? evalChilderDev(children,props, this.props.path)
:children(props) // 是fn 直接執行
:null // 不是返回null
}
</RouterConetxt.Provider>
)
// 不管是否匹配都會渲染children,但是呢,如果不匹配只去渲染,children是fn的情況
- 匹配porps.match; 三元表達式,首先匹配是否是children;
- children 可以是function類型,在組建符合的情況下,children可以是單一的對象,還可以是一個數組;數組也被稱之為對象。
嚴格來説,children有三種結構:
- 函數
- 組建複合中的對象
- 數組的形式
動態路由
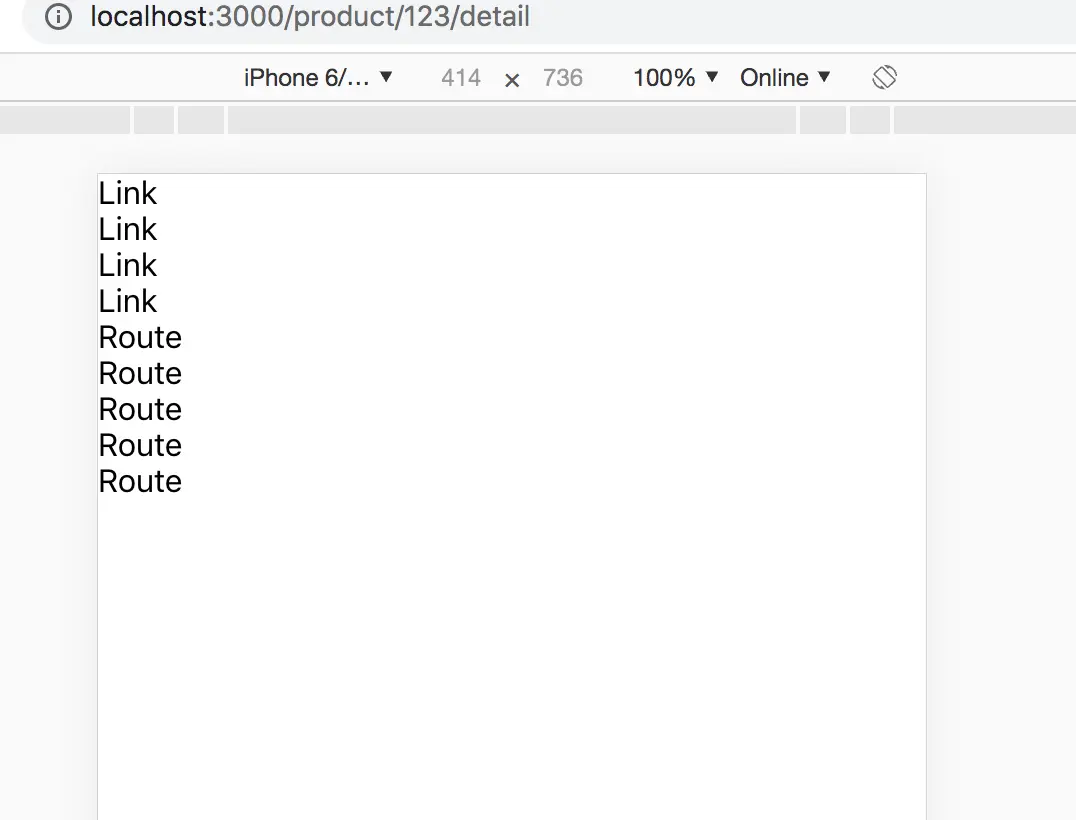
<Link to="/product/123">
商品
</Link><Route path="/product/:id" component={Product}></Route>function Product(props){
console.log('Product-props:', props)
const {match} = props
const {id} =match.params
return <div>Product- id:{id}</div>
}嵌套路由
<Link to="/product/123">
商品
</Link>// 用 render 或者 children 或者component 都是可以的,都能拿到props,我就是多些幾種方式而已
<Route path="/product/:id" children={(props)=><Product {...props}></Product>}></Route>function Product(props){
console.log('Product-props:', props)
// useEffect(() => {
// // effect
// return () => {
// console.log('cleanup')
// // cleanup
// }
// }, [])
const {match} = props
const {params,url} =match
const {id} =params
return <div>
<h3>Product- id:{id}</h3>
<div>
<Link to={url+'/detail'}>詳情</Link>
<Route path={url+'/detail'} component={Detail}/>
</div>
</div>
}
//Detail 商品詳情
function Detail(){
return<div>
<h4>
詳情來了———————— Detail
</h4>
</div>
}實現react-Router來了~~~
my-react-router-dom實現
我們只需要實現 BrowserRouter、Link、Route
1. 初步搭建
BrowserRouter.js
Router主要是分為:
- BrowserRouter
- HashRouter
- MemoryRouter
- NativeRouter
- StaticRouter
Router的不同主要是history不同
// BrowserRouter ,組建複合,我們在使用的時候,也是在其中進行children。
import react,{Component} from 'react'
import {createBrowserHistory} from 'history' // 安裝了 react-router-dom ;就不需要在安裝history了;已經涵蓋
import Router from './Router'
// BrowserRouter 是基於Router來進行實現的
export default class BrowserRouter extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.history = createBrowserHistory()
}
render() {
return(
<div>
<Router children={this.props.children} history={this.history}/>
</div>
)
}
}
children 是在使用BrowserRouter的時候,我們起了個別名Router;<Router>這裏面就是children內容</Router>
Router.js
import React,{Component} from 'react'
export default class Router extends Component{
constructor(){
super()
}
render(){
const{ history, children} =this.props
// 主要目的是返回children
return children
}
}Route.js
import React,{Component} from 'react'
export default class Route extends Component{
constructor(){
super()
}
render(){
return(
<div>
Route
</div>
)
}
}Link.js
import React,{Component} from 'react'
export default class Link extends Component{
constructor(){
super()
}
render(){
return(
<div>
Link
</div>
)
}
}目前頁面的展示
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Link, // Switch } from "./my-react-router-dom";最後實現Switch
2. 完善
Router.js
import React,{Component} from 'react'
import {RouterContext} from './Context'
export default class Router extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
// 用於路由變化匹配path用的參數
this.state={
location: props.history.location
}
// 監聽history
props.history.listen(location=>{
// 改變了就修改location
this.setState(location)
})
}
render(){
const{ history, children} =this.props
console.log(history,'history')
// 主要目的是返回children
return <RouterContext.Provider value={{history, location:this.state.location}}>
{children}
</RouterContext.Provider>
;
}
}創建 Context.js,來解決跨層級通訊
這麼沒有什麼要説明的,就是跨組建通訊
import React from 'react'
const RouterConetxt =React.createContext()
export {RouterConetxt}Link.js
平時我們是如何使用Link
<Link to='/'> 首頁 </Link>Link組建
- to
- 首頁相當於children
import React,{Component} from 'react'
export default class Link extends Component{
constructor(){
super()
}
render(){
const {to, children, ...restProps} = this.props
return(
<a href={to} {...restProps}>{children}</a>
)
}
}處理link a標籤的默認事件
- 去除默認事件,可以用點擊事件中添加“e.preventDefalut”
- 去掉之後,那麼href事件就會被禁止,我們就需要手動去跳轉,命令式修改路由
- 命令式:
history.push(this.props.to)考慮到兼容問題,不採用window.history; 其實在最開始,
BrowserRouter中,我們往下穿了一個history;組建通訊,跨層級使用;這個時候我們可以考慮用context來進行傳遞下來,這樣其他的組建,比如Route也可以使用到history
import React,{Component} from 'react'
import { RouterConetxt } from './Conetxt';
export default class Link extends Component{
// 引用
static contextType = RouterConetxt
constructor(){
super()
}
handleClick=(e)=>{
e.preventDefault();
// 跳轉
this.context.history.push(this.props.to)
}
render(){
const {to, children, ...restProps} = this.props
return(
<a href={to} {...restProps} onClick={this.handleClick}>{children}</a>
)
}
}Route.js
根據路由,匹配到對應的path,展示對應的組建內容
首先先渲染component
我們平時的使用
<Route path="/user" component={UserPage}></Route>
參數為:
- path
- component
import React,{Component} from 'react'
import { RouterContext } from './Context';
export default class Route extends Component{
constructor(){
super()
}
render(){
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{
context=>{
const {location} = context
const {path,component} =this.props
// 目前component 還不是一個組建,所以我們需要用到React.createElement() 來進行創建
// 用來判斷,篩選到的路由進行展示
// 如果用 window.location;只會首次渲染,只有state發生改變的時候才會重新render
const match= location.pathname === path
//為true 就展示,為false就返回null
return match?React.createElement(component):null
}
}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
)
}
}Route.js 繼續完善,實現children、render的渲染
是我們最開始分析的 router的核心,一串三目表達式
// 將props 進行一個組合為的是更好的傳遞參數 const props={ ...context, location, match } // match 匹配到:優先級-children>component>render|| null // match 不匹配到: children是function形式 || null return match? (children?():()) : (typeof children==='function'? children(props) : >null)
// match 匹配到:優先級-children>component>render|| null
// match 不匹配到: children是function形式 || null
return match?
children?
(typeof children==='function'?
// 是函數就直接執行
children(props)
// 組建複合
:children
)
:
(component?
(React.createElement(component,props))
:(render?render(props):null)
)
:
(typeof children==='function'? children(props) : null)404頁面展示現實
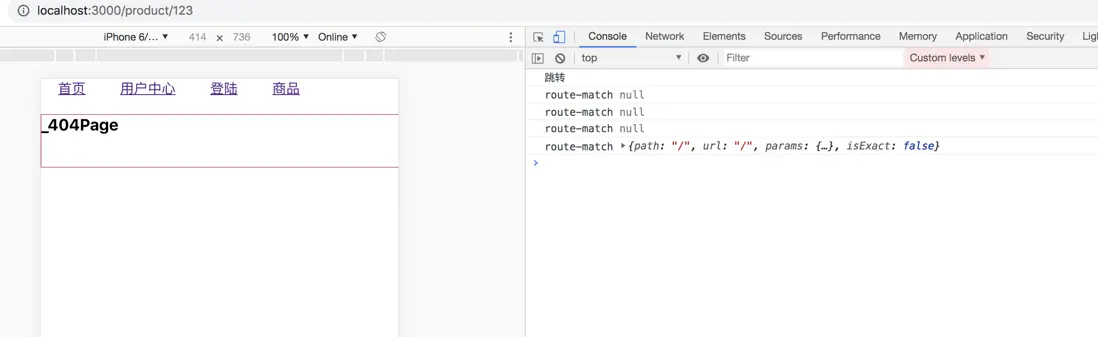
- 在route頁面,我們做的match判斷是必須匹配,才會進行渲染;
- 但是404頁面,在沒有switch 的情況下,應該是每個路由都會被渲染出來;沒有寫path值默認應該是匹配404頁面狀態;需要加一個默認的match值。
- 在router中添加默認的match值,不寫path值,返回默認的match;
- 接下來了我們會將mtch儲存為一個對象
源碼中,有一個
matchpath.js的文件,主要是將match處理成一個對象
首先 Router.js 的修改
修改的部分
// 默認match // 不寫match的情況下,默認返回 path:'/' 的對象 // 這一段是直接從源碼中抄的 static computeRootMatch(pathname){ return {path:'/',url:'/',params:{}, isExact: >pathname==='/'} }render(){ return <RouterContext.Provider value={{ >match:Router.computeRootMatch(this.state.location.pathname) }}> {children} </RouterContext.Provider> ; }
完整版Router.js
import React,{Component} from 'react'
import {RouterContext} from './Context'
export default class Router extends Component{
// 默認match
// 不寫match的情況下,默認返回 path:'/' 的對象
// 這一段是直接從源碼中抄的
static computeRootMatch(pathname){
return {path:'/',url:'/',params:{}, isExact: pathname==='/'}
}
constructor(props){
super(props)
// 用於路由變化匹配path用的參數
this.state={
location: props.history.location
}
// 監聽history
props.history.listen(location=>{
// 改變了就修改location
this.setState({location})
})
}
render(){
const{ history, children} =this.props
// 主要目的是返回children
return <RouterContext.Provider value={{
history,
location:this.state.location,
match:Router.computeRootMatch(this.state.location.pathname)
}}>
{children}
</RouterContext.Provider>
;
}
}static的解釋
這裏涉及到了ES6的class,我們定義一個組件的時候通常是定義了一個類,而static則是創建了一個屬於這個類的屬性或者方法。
組件則是這個類的一個實例,component的props和state是屬於這個實例的,所以實例還未創建,我們又怎麼可能讀得到props和state呢?
總結來説static並不是react定義的,而加上static關鍵字,就表示該方法不會被實例繼承,而是直接通過類來調用
-------百度搜索而來 ---------
matchPath.js
去源碼中找也是一樣的,如果我寫的這個版本不是最新的可以去源碼中找,但這個文件被修改和調整,目測可能性不太大。
import pathToRegexp from "path-to-regexp";
const cache = {};
const cacheLimit = 10000;
let cacheCount = 0;
function compilePath(path, options) {
const cacheKey = `${options.end}${options.strict}${options.sensitive}`;
const pathCache = cache[cacheKey] || (cache[cacheKey] = {});
if (pathCache[path]) return pathCache[path];
const keys = [];
const regexp = pathToRegexp(path, keys, options);
const result = { regexp, keys };
if (cacheCount < cacheLimit) {
pathCache[path] = result;
cacheCount++;
}
return result;
}
/**
* Public API for matching a URL pathname to a path.
*/
function matchPath(pathname, options = {}) {
if (typeof options === "string" || Array.isArray(options)) {
options = { path: options };
}
const { path, exact = false, strict = false, sensitive = false } = options;
const paths = [].concat(path);
return paths.reduce((matched, path) => {
if (!path && path !== "") return null;
if (matched) return matched;
const { regexp, keys } = compilePath(path, {
end: exact,
strict,
sensitive
});
const match = regexp.exec(pathname);
if (!match) return null;
const [url, ...values] = match;
const isExact = pathname === url;
if (exact && !isExact) return null;
return {
path, // the path used to match
url: path === "/" && url === "" ? "/" : url, // the matched portion of the URL
isExact, // whether or not we matched exactly
params: keys.reduce((memo, key, index) => {
memo[key.name] = values[index];
return memo;
}, {})
};
}, null);
}
export default matchPath;Route.js 的修改
修改的部分
// 用來判斷,篩選到的路由進行展示 // match:首先判斷 path是否存在? // 存在使用matchPath來進行正則匹配,兩個參數一個是:location.path、 this.props // 不存在 使用頂層傳進來的默認的match,context中的。 const match= path? matchPath(location.pathname,this.props):context.match
完整版Route.js
import React,{Component} from 'react'
import { RouterContext } from './Context';
import matchPath from './matchPath';
export default class Route extends Component{
constructor(){
super()
}
render(){
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{
context=>{
// 這個是Router 使用contex傳進來的參數
const {location} = context
// 這個是組建調用傳進來的參數
const {path,component,children,render} =this.props
// 用來判斷,篩選到的路由進行展示
// match:首先判斷 path是否存在?
// 存在使用matchPath來進行正則匹配,兩個參數一個是:location.path、 this.props
// 不存在 使用頂層傳進來的默認的match,context中的。
const match= path? matchPath(location.pathname,this.props):context.match
console.log('route-match', match)
// 將props 進行一個組合為的是更好的傳遞參數
const props={
...context,
location,
match
}
// match 匹配到:優先級-children>component>render|| null
// match 不匹配到: children是function形式 || null
return match?
children?
(typeof children==='function'?
// 是函數就直接執行
children(props)
// 組建複合
:children
)
:
(component?
(React.createElement(component,props))
:(render?render(props):null)
)
:
(typeof children==='function'? children(props) : null)
}
}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
)
}
}目前404頁面展示效果
頁面代碼
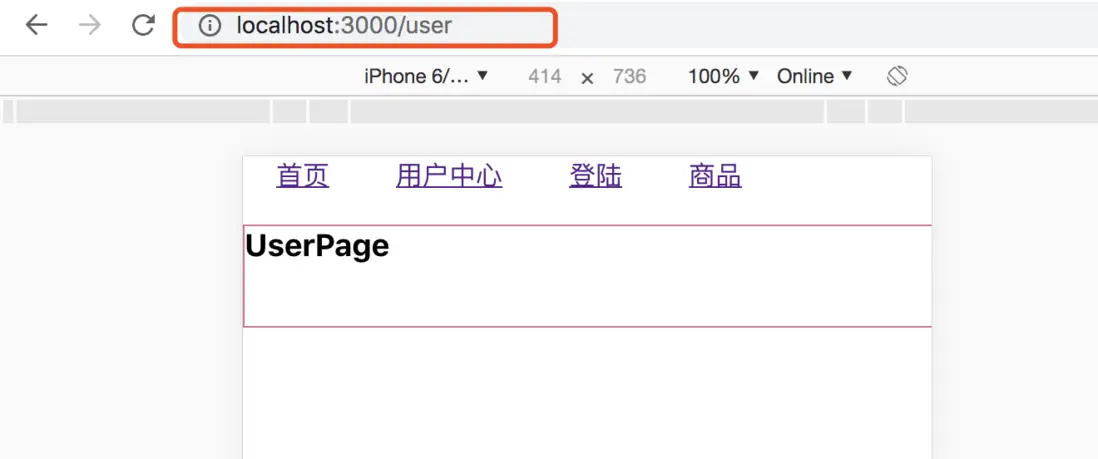
export default function App(){
return(
<div className="app">
<Router>
<Link to='/'>
首頁
</Link>
<Link to='/user'>
用户中心
</Link>
<Link to='/login'>
登陸
</Link>
<Link to="/product/123">
商品
</Link>
<Route exact path="/"
// children={()=><div>HomePage-children</div>}
// component={HomePage}
render={()=><div>HomePage-render</div>}
></Route>
<Route path="/user" component={UserPage}></Route>
<Route path="/login" component={LoginPage}></Route>
<Route component={_404Page}></Route>
</Router>
</div>
)
}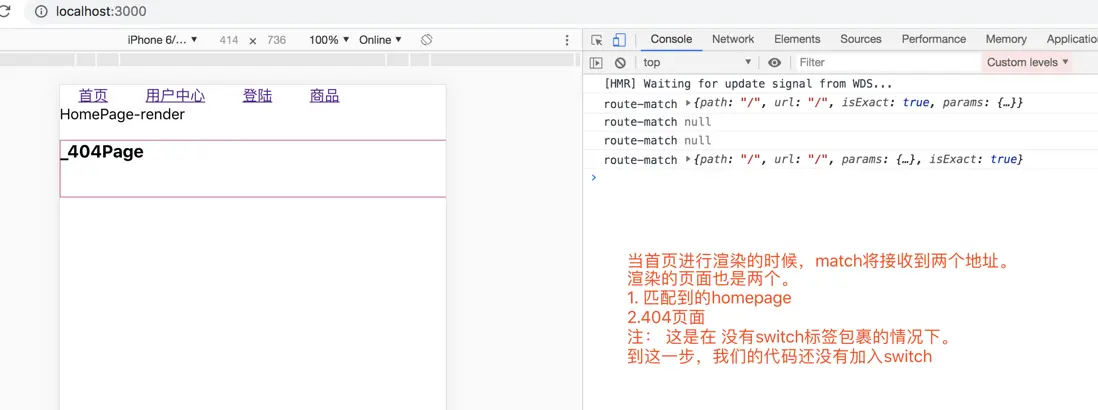
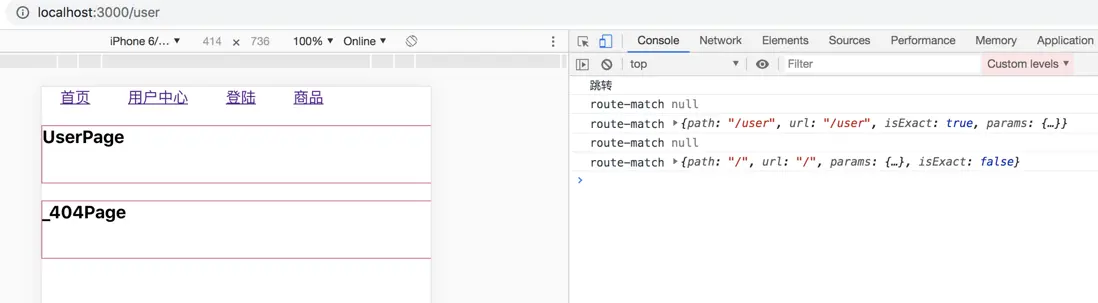
現實 Switch 獨佔路由
組建複合
Switch 要做的是將children遍歷一遍,找到第一個匹配項之後展示
children的數據類型,可以有一個{}或者多個[]
初步搭建import React, { Component } from 'react' export default class Switch extends Component { render() { let match; // 找到匹配的元素,match設置為true let element; // 匹配的元素,沒有匹配到就沒有初始值 // 還需要做的是查找到匹配到的元素 // ......... // 在Switch這塊,element 這塊已經是一個元素了。 // 如果找到匹配的元素 ?就顯示elment,克隆一下是待會兒會加屬性 : null return match? React.cloneElement(element,{}):null } }
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import matchPath from './matchPath';
import { RouterContext } from './Context';
export default class Switch extends Component {
render() {
return (<RouterContext.Consumer>
{context=> {
const {location} =context
console.log('Switch=====location',location)
let match; // 找到匹配的元素,match設置為true
let element; // 匹配的元素,沒有匹配到就沒有初始值
const {children}= this.props
// 還需要做的是查找到匹配到的元素
React.Children.forEach(children, child=>{
// if條件 :match 我們最上面定義是undefined,所以用==;&& 有有效的element元素
if(match==null &&React.isValidElement(child)){
element= child
const {path}= child.props
// path路徑匹配到 ? matchPath(location, ...),這塊就需要用到Conetxt: 不匹配就用傳下來的默認match
match = path? matchPath(location.pathname, child.props):context.match
}
})
// 在Switch這塊,element 這塊已經是一個元素了。
// 如果找到匹配的元素 ?就顯示elment,克隆一下是待會兒會加屬性 : null
return match? React.cloneElement(element,{}):null
}
}
</RouterContext.Consumer>)
}
}React.children.forEarch 介紹: https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/d...
調整 Route
src/my-react-router-dom/Route.js
// computedMatch 是從Switch裏面傳進來的,用來match判斷,優先使用
const {path,component,children,render,computedMatch} =this.props// 用來判斷,篩選到的路由進行展示
// match:首先判斷computedMatch 在判斷path是否存在?
// 存在使用matchPath來進行正則匹配,兩個參數一個是:location.path、 this.props
// 不存在 使用頂層傳進來的默認的match,context中的。
const match= computedMatch
?computedMatch
:path
? matchPath(location.pathname,this.props)
:context.matchmy-react-router-dom中 hooks方法的實現
例子
router中<Route path="/product/:id" children={(props)=><Product {...props}></Product>}></Route>如果我們需要在函數組建中,用到props,我們只能這樣去使用,進行參數的傳遞
Productfunction Product(props){ console.log('Product-props:', props) const {match} = props const {params,url} =match const {id} =params return <div> <h3>Product- id:{id}</h3> <div> <Link to={url+'/detail'}>詳情</Link> <Route path={url+'/detail'} component={Detail}/> </div> </div> }如果我們不進行props參數的傳遞,可以使用hooks的方法來獲取到
<Route path="/product/:id" children={()=><Product></Product>}></Route>import { useRouteMatch, useHistory, useParams, useLocation } from "react-router-dom";function Product(props){ const match =useRouteMatch() const history =useHistory() const location =useLocation() const Params = useParams() // 參數 console.log('match:',match); console.log('history:',history); console.log('location:',location); console.log('Params:',Params); }
hook.js
index.js 調整
src/my-react-router-dom/index.js
import BrowserRouter from './BrowserRouter'
import Route from './Route'
import Link from './Link'
import Switch from './Switch'
import {
useLocation,
useRouteMatch,
useParmas,
useHistory
} from './hook'
export {BrowserRouter, Route, Link,Switch,useLocation,useRouteMatch,useParmas,useHistory }src/my-react-router-dom/hook.js
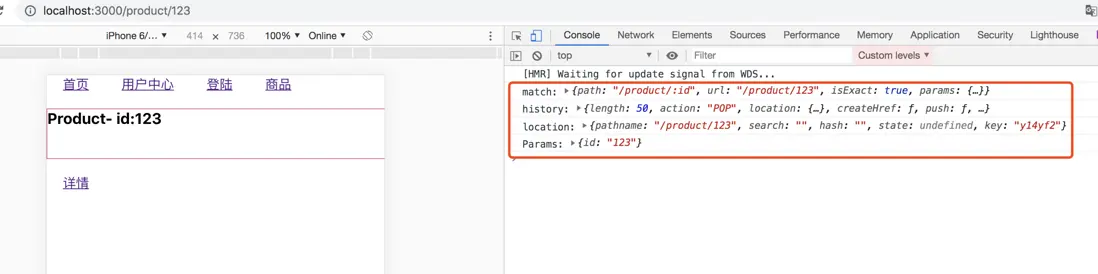
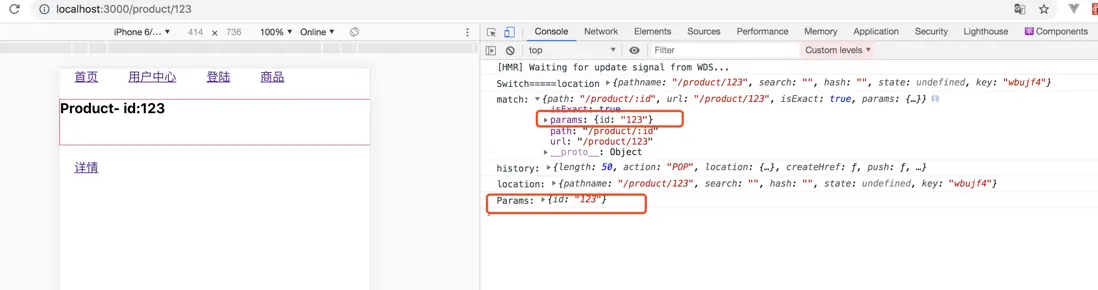
// 就是History對象 export function useHistory(){ } // useLocation: // {pathname: "/product/123", search: "", hash: "", state: undefined, key: "y14yf2"} // hash: "" // key: "y14yf2" // pathname: "/product/123" // search: "" // state: undefined // } export function useLocation(){ } // match: // {path: "/product/:id", url: "/product/123", isExact: true, params: {…}} // isExact: true // params: {id: "123"} // path: "/product/:id" // url: "/product/123" // } export function useRouteMatch(){ } // useParams: // {id: "123"} export function useParams(){ }
useHistory
// 就是History對象
export function useHistory(){
// 返回的就是history對象
// 在BrowserRouter中,我們使用import {createBrowserHistory} from 'history';const history= createBrowserHistory()
// 在hook對象中,我們要使用 usecontext;
return context = useContext(RouterContext).history;
}useLocation
export function useLocation(){
return useContext(RouterContext).location;
}我們現在打印看下:
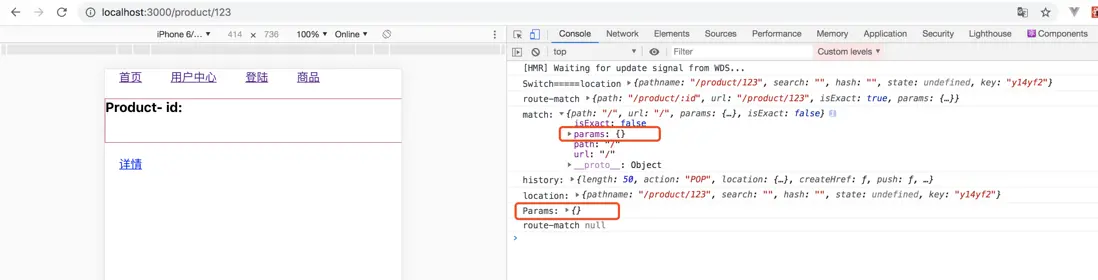
這裏,useParams沒有進行展示,而在match是展示的,我們默認的參數,我們寫的默認值,也就是説,當match進行修改了之後,context中的match沒有進行修改。所以我們需要在修改match的地方進行context中重新賦值。
Route.js 調整
src/my-react-router-dom/Route.js
return(
<RouterContext.Provider value={props}>
{
match?
children?
(typeof children==='function'?
// 是函數就直接執行
children(props)
// 組建複合
:children
)
:
(component?
(React.createElement(component,props))
:(render?render(props):null)
)
:
(typeof children==='function'? children(props) : null)
}
</RouterContext.Provider>
)又包了一層RouterContext,在使用useParams時,往上找參數,當找到RouterContext 就會停止在往上查找。
打印內容:
到這裏react——router的hook方法就已經就已經實現了。
現在我們思考一個問題,如果是class組建在不傳遞props的情況下如何實現,在class組建內獲取props
class Product extends Component{
render() {
// const {id} = this.props
console.log(this.props,'props')
return<div>
{/* <h3>Product- id:{id}</h3> */}
<h3>Product- id</h3>
</div>
}
}react-router中有一個高階組建,withRouter;
接下來我們來實現下withRouter
實現withRouter
src/my-react-router-dom/withRouter.js
// 高階組建
import React from 'react'
import {RouterContext} from './Context'
const withRouter= WrappendComponent=>props=>{
// 需要用到context 可以傳遞location match 等參數;因為在context中有記錄
return <RouterContext.Consumer>
{context=><WrappendComponent {...props} {...context}></WrappendComponent>}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
}
export default withRouter實現prompt
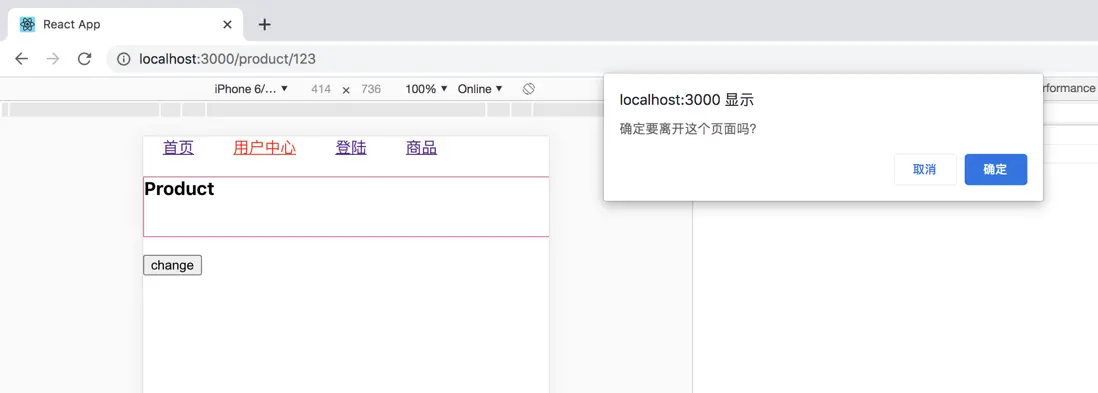
首先我們來使用一下
class Product extends Component{
constructor(){
super()
this.state={
cofirm:true,
}
}
change=()=>{
this.setState({
cofirm: !this.state.cofirm
})
}
render(){
console.log('this.state.cofirm',this.state.cofirm)
return(
<div>
<h3>Product</h3>
<button onClick={this.change}>change</button>
<Prompt when={this.state.cofirm} message="確定要離開這個頁面嗎?"></Prompt>
</div>
)
}
}Prompt 是react-router 的方法;
屬性 when:為true,跳轉其他頁面時,會出現彈窗提示
屬性 message:彈窗中的消息
src/my-react-router-dom/Prompt.js
import React from 'react'
import { RouterContext } from './Context';
import LifeCycle from './LifeCycle'
// 接收兩個參數
// when 是一個Boolean
// message 是一個String|| function
export default function Prompt({when=true,message}){
// 我們需要用到histroy,path來判斷跳轉,所以用到context
return(
<RouterContext.Consumer>{
context=>{
// 當首次進來時,when是true;history.block方法已經掛載在組建上。
// 當設置為false的時候,history.block還會執行們因為沒有卸載。所以還需要在LifeCycle中進行卸載
if(!when){
return null
}
const method = context.history.block
console.log('method:',method)
// render返回組件必須是<Component/>,所以不能直接寫 return context.history.block;需要用到LifeCycle
//在這裏假設可以接收到LifeCycle的this,參數self,
return <LifeCycle onMount={
(self)=>{
//設置一個方法release,
self.release=method(message)
}}
onUnmount={(self)=>{
self.release()
}}
></LifeCycle>
}
}</RouterContext.Consumer>
)
}src/my-react-router-dom/LifeCycle.js
import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class LifeCycle extends Component {
// 掛載
componentDidMount(){
// 當前的方法都定義在this裏面,
console.log('componentDidMount',this)
if(this.props.onMount){
this.props.onMount.call(this,this)
}
}
// 取消掛載
componentWillUnmount(){
console.log('componentWillUnmount', this)
if(this.props.onUnmount){
this.props.onUnmount.call(this,this)
}
}
render() {
return null
}
}