摘要
Netty源碼系列-Netty如何使用零拷貝
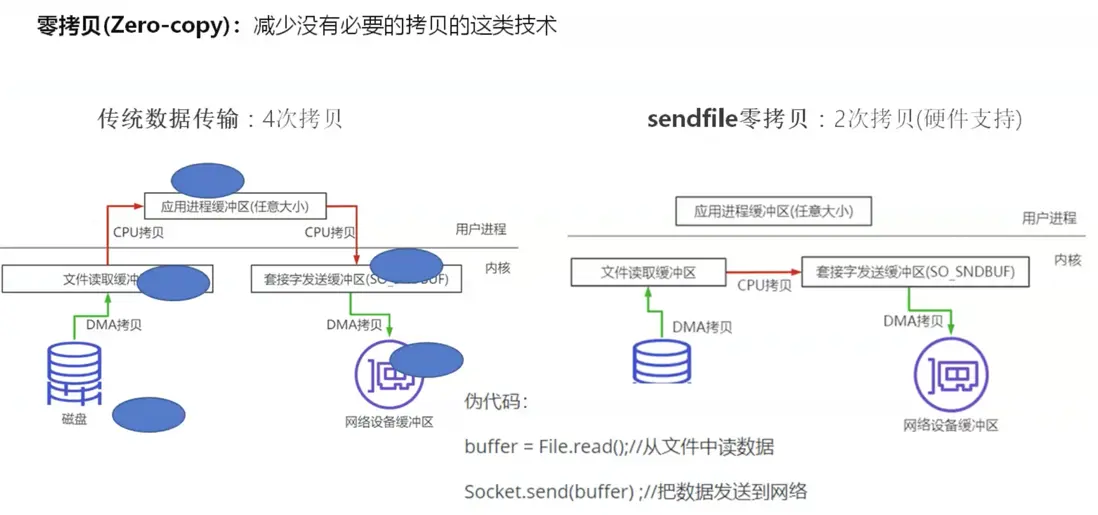
1、零拷貝
Netty為了加快文件傳輸速度,採用了零拷貝技術。
sendFile(Kafka也是用該技術優化性能):發送文件描述符,如果硬件支持,圖二的文件緩衝區和Socket緩衝區可以共享,只需要兩次DMA拷貝就可以
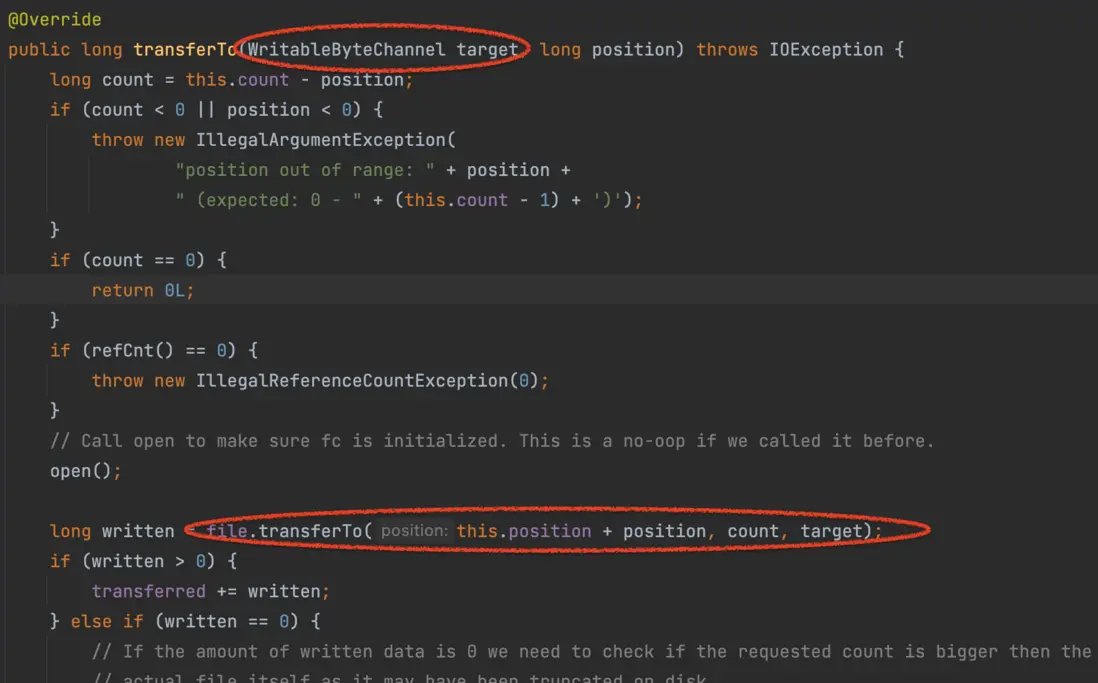
1.1 、源碼DefaultFileRegion.transferto()方法
我們看一下源碼,Netty的文件傳輸零拷貝方法就是該方法(如下圖),方法下面圈出來的一行是(FileChannel)file.tranferto (java API)就是 sendFile,採用零拷貝技術,省去了從用户空間中轉的過程(見上圖)
1.2 我們通過一個案例看一下零拷貝和普通拷貝的區別
我們嘗試傳輸一個大小230M的文件,來看下普通傳輸和零拷貝性能的差異。
下面我們創建一個普通ServerSocket服務端,一個傳統的文件傳輸方式的TranditionClient,一個零拷貝傳輸方式的NewIOClient,兩者都想服務端傳輸同一個文件,比較傳輸時間。代碼如下:
1.2.1 首先寫一個Server
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//創建serversocket 對象--8088服務
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8088);
//循環監聽連接
while (true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();//客户端發起網絡請求---連接
//創建輸⼊流對象
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new
DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
int byteCount=0;
try{
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; //創建緩衝區字節數組
while(true){
int readCount = dataInputStream.read(bytes, 0,
bytes.length);
byteCount=byteCount+readCount;
if(readCount==-1){
System.out.println("服務端接受:"+byteCount+"字節");
break;
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}1.2.2 普通文件傳輸方式
public class TranditionClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost",8088);
// 文件大小230M
String fileName = "/Users/bing/Downloads/Joplin-3.0.14-arm64.DMG";
//創建輸⼊流對象
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(fileName);
//創建輸出流
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new
DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
long readCount = 0;
long total=0;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//TODO 這裏要發生2次copy
while ((readCount=inputStream.read(buffer))>=0){
total+=readCount;
//TODO 網絡發送:這裏要發生2次copy
dataOutputStream.write(buffer);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("發送總字節數:"+total+",耗時:"+(endTime-startTime)+" ms");
//釋放資源
dataOutputStream.close();
socket.close();
inputStream.close();
}
}1.2.3 零拷貝傳輸方式
public class NewIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//socket套接字
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",8088));
socketChannel.configureBlocking(true);
//文件 大小230M
String fileName = "/Users/bing/Downloads/Joplin-3.0.14-arm64.DMG";
//FileChannel 文件讀寫、映射和操作的通道
FileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream(fileName).getChannel();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//transferTo⽅法⽤到了零拷⻉,底層是sendfile,這裏只需要發生2次copy和2次上下文切換
long transferCount = fileChannel.transferTo(0, fileChannel.size(), socketChannel);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("發送總字節數:"+transferCount+"耗時:"+(endTime-startTime)+" ms");
//釋放資源
fileChannel.close();
socketChannel.close();
}
}1.2.4 結果
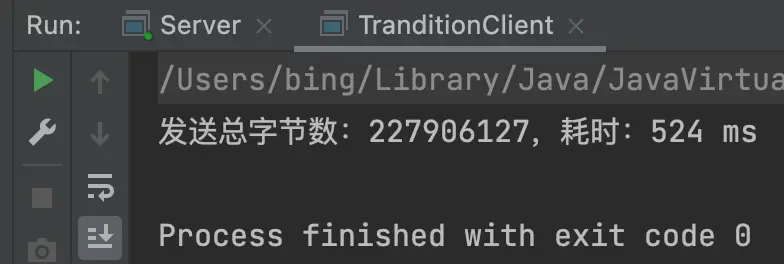
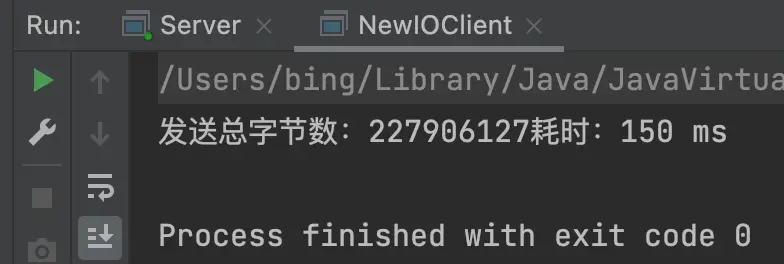
通過多次測試得到結果,零拷貝方式比傳統方式快很多,如下:
- 1)傳統傳輸方式,耗時530ms左右:
- 2)零拷貝方式,耗時150ms左右: