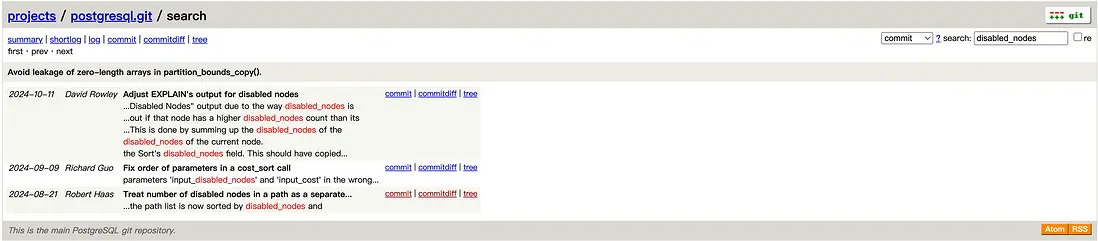
在HOW2025大會優化專場,老楊分享了修改disable_cost為GUC結合pg_hint_plan實現精準執行計劃控制的實踐。
主要是舉例了一個極端case,在17版本依然需要disable_cost的動態調整來實現hint精準指定索引。
對於disable_cost的討論早在2019年就開始了,一直持續到現在,可參考社區郵件。郵件前期主要是討論disable_cost默認常量值不足,往往導致set guc to off不能達到預期,執行計劃跑偏。期間也有人提交patch意圖調整這裏的邏輯。最近老楊再去看最新進展時發現disable_cost基本要退出歷史舞台了,18版本有了更優的邏輯來控制代價。
再實測這個極端case,獲得了意外之喜,直呼PG牛X!!! 18版本優化器代價預估邏輯優化後,hint已經能夠精準指定索引了。當然18版本帶來的驚喜可不止這個,大家敬請期待吧!
本文較長,希望大家能感興趣耐心看完。
1 問題回顧
顛覆認知的limit
本質上是優化器limit算子代價預估模型缺陷,沒有考慮數據分佈,導致ordering index的代價預估存在偏差。
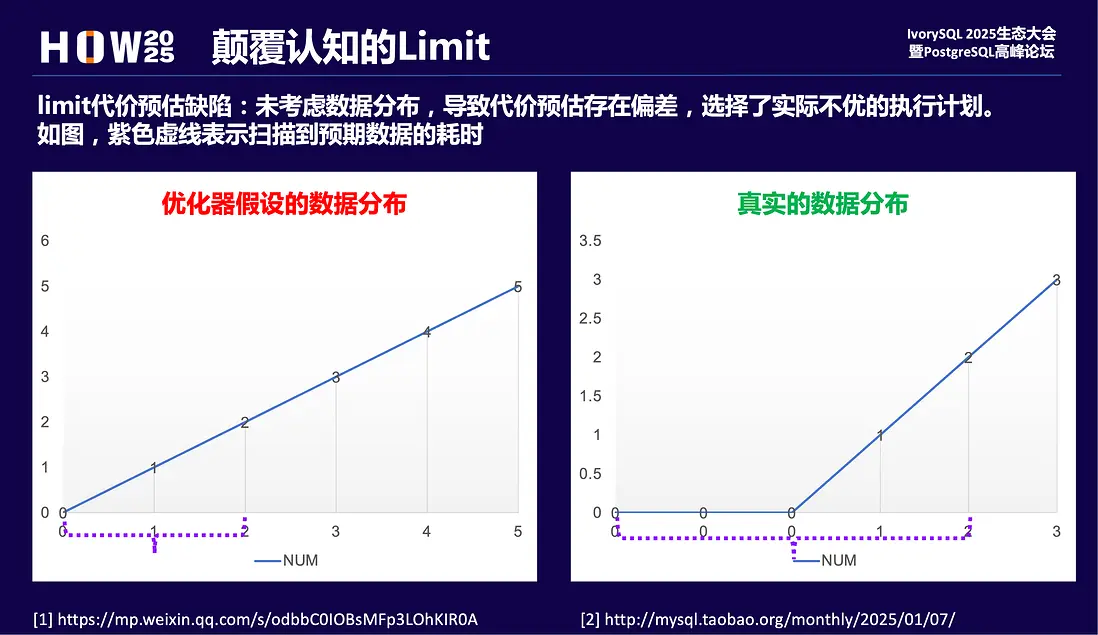
limit 1居然慢了數萬倍,是代價預估偏差,走了不優的計劃。可以看到走了“錯誤的”索引,導致回表檢索全表數據,耗時久。
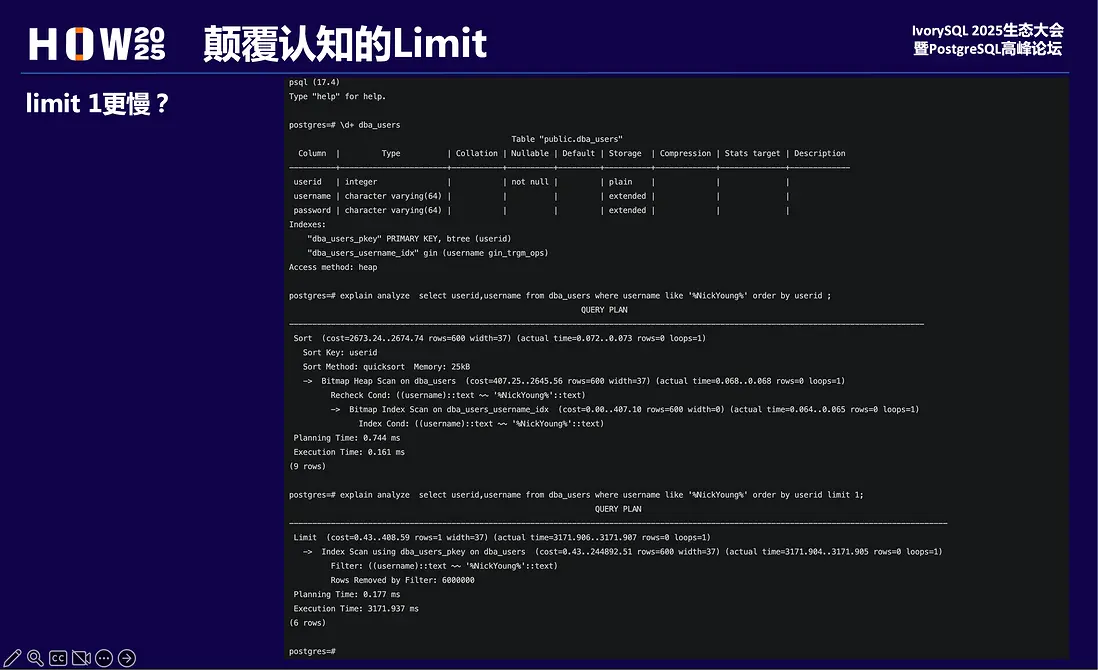
對於這個問題,老楊也曾嘗試修改過limit代價預估的邏輯,雖然是草台班子玩法,但效果還是槓槓的。感興趣的老鐵可以看下這篇。
當然更推薦大家去看下專業開發者的方案。
不過到目前為止,社區還沒有做相關優化,這個問題可能短期內會一直存在。
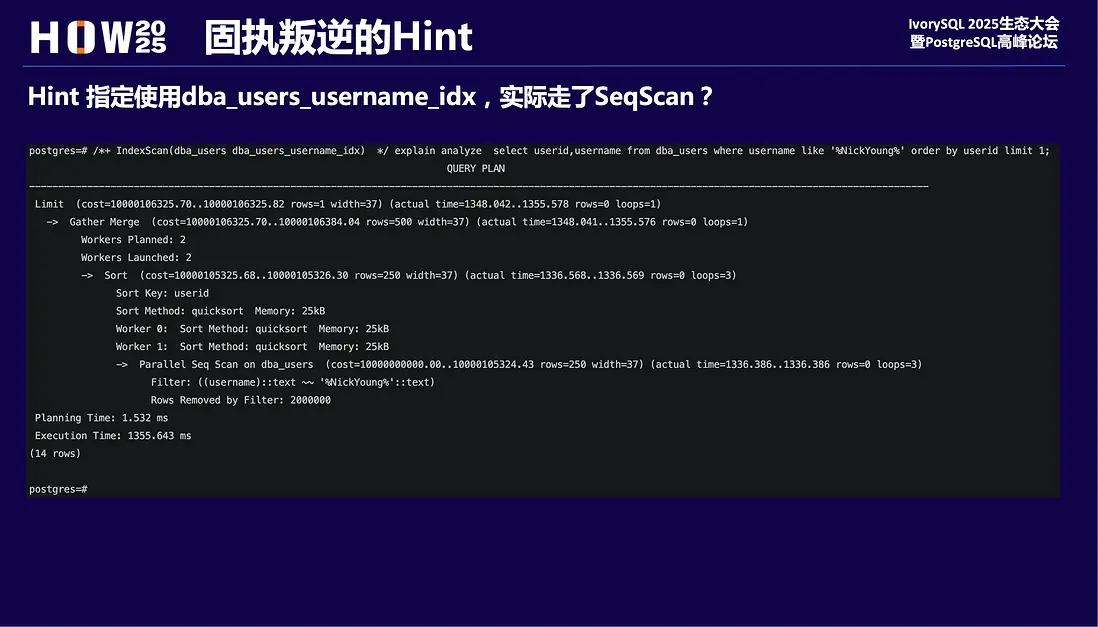
所以,當遇到這個場景,我們會使用pg_hint_plan來指定索引。但在17版本及以下實際效果不盡人意。
指定走某個索引,卻走了順序掃描,有種“這把槍彈道偏左”的感覺。
固執叛逆的hint
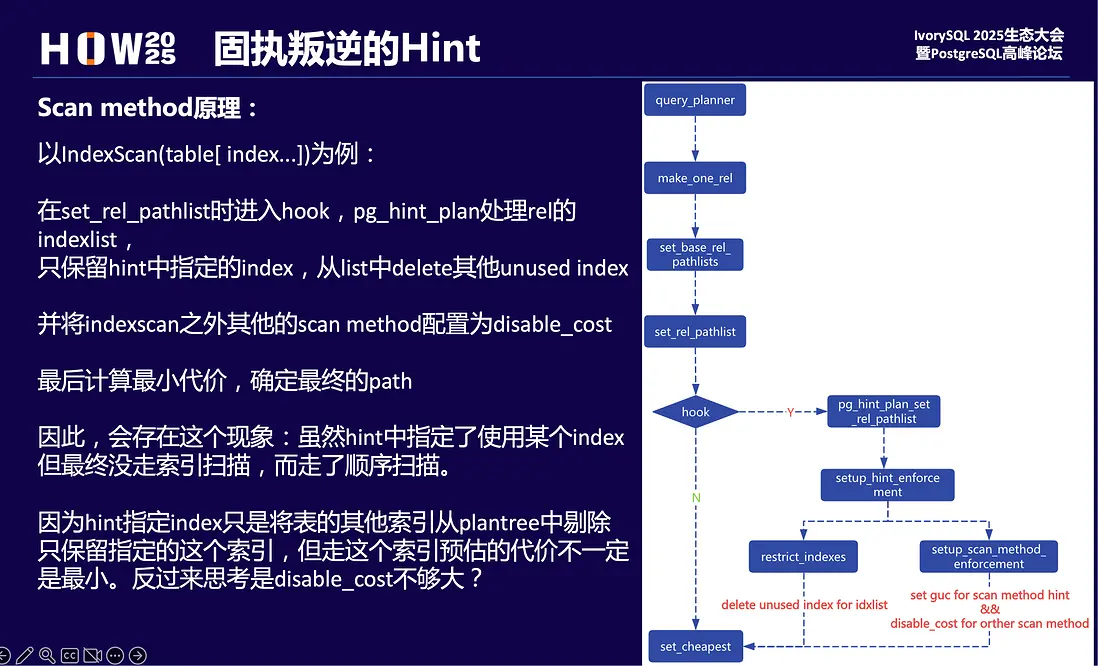
這個和hint原理相關: IndexScan指定走某個索引,主要在創建rel pathlist環節做兩件事:
- 將hint之外的索引從IndexList中剔除,對於Indexscan的path只保留了預期的index;
- 設置enable_indexscan=on,設置enable_seqscan、enable_bitmapscan、enable_tidscan為off,其實就是給這幾種ScanMethod的startup_cost加上disable_cost (1e+10)
看起來似乎可以按預期走指定的索引掃描。事實上即使增加其他了掃描方式的cost,但有可能cost的值不夠大,這樣在優化器計算最小代價時,還是其他執行路徑代價更小,所以就不會走索引掃描。
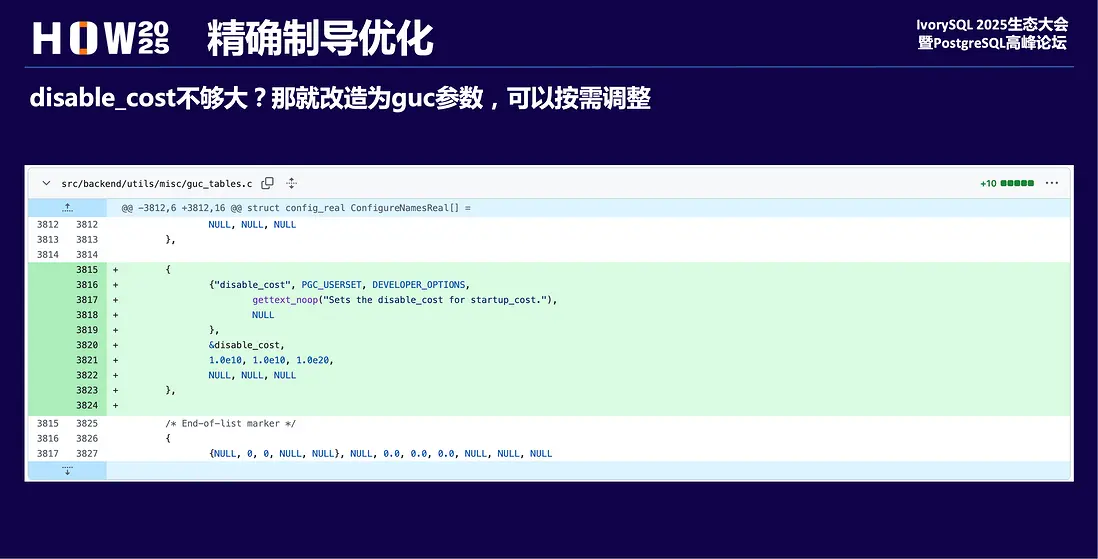
精確制導優化
disable_cost不夠大,那將其改造為guc參數可動態調整,就可以和hint一起精準打擊。
2 意外之喜
看到社區對disable_cost討論的最新進展後,再測這個case,發現18版本hint已經可以精確指定索引。
至於為什麼是Bitmap Index Scan,那是因為gin索引本來就是這樣設計的。
[postgres@Nick ~]$ psql
psql (18beta2)
Type "help"forhelp.
postgres=# /*+ IndexScan(dba_users dba_users_username_idx) */ explain analyze select username from dba_users where username like '%NickYoung%' order by userid limit 1;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=2618.81..2618.81 rows=1 width=37) (actual time=0.100..0.101 rows=0.00 loops=1)
Buffers: shared hit=18
-> Sort (cost=2618.81..2620.31 rows=600 width=37) (actual time=0.098..0.099 rows=0.00 loops=1)
Sort Key: userid
Sort Method: quicksort Memory: 25kB
Buffers: shared hit=18
-> Bitmap Heap Scan on dba_users (cost=377.50..2615.81 rows=600 width=37) (actual time=0.055..0.055 rows=0.00 loops=1)
Disabled: true
Recheck Cond: ((username)::text ~~ '%NickYoung%'::text)
Buffers: shared hit=15
-> Bitmap Index Scan on dba_users_username_idx (cost=0.00..377.35 rows=600 width=0) (actual time=0.048..0.048 rows=0.00 loops=1)
Index Cond: ((username)::text ~~ '%NickYoung%'::text)
Index Searches: 1
Buffers: shared hit=15
Planning:
Buffers: shared hit=133
Planning Time: 1.711 ms
Execution Time: 0.287 ms
(18 rows)
postgres=# 不過從執行計劃limit節點的cost來看,代價很小,已經看不到disable_cost的影子了。
3 原理分析
具體的變化來自這個commit。
簡單來説,就是disable_cost的玩法,在很多場景下表現都很糟糕。這個巨大的cost本身就不夠優雅,會導致兩條路徑的模糊成本一致,導致代價預估偏差大。
因此Robert Haas大師,提出並實現了“禁用路徑,而不是增加cost”的方案。
在cost預估中,去除了幾乎所有disable_cost邏輯,Path結構體新增int類型變量disabled_nodes,在各node裏初始值為0。
比如當set enable_seqscan to off時會執行disabled_nodes++ ,這個時候值為1,這個變量值會繼續傳遞到後續的計劃節點。後續join的時候,如果set enable_nestloop to off,先將當前節點的disabled_nodes++為1,再將inner和outer的disabled_nodes值傳遞過來, 這樣整體路徑的disabled_nodes為4, disabled_nodes一直會傳遞到最終節點。
void
initial_cost_nestloop(PlannerInfo *root, JoinCostWorkspace *workspace,
JoinType jointype,
Path *outer_path, Path *inner_path,
JoinPathExtraData *extra)
{
int disabled_nodes;
Cost startup_cost = 0;
Cost run_cost = 0;
double outer_path_rows = outer_path->rows;
Cost inner_rescan_start_cost;
Cost inner_rescan_total_cost;
Cost inner_run_cost;
Cost inner_rescan_run_cost;
/* Count up disabled nodes. */
disabled_nodes = enable_nestloop ? 0 : 1;
disabled_nodes += inner_path->disabled_nodes;
disabled_nodes += outer_path->disabled_nodes;
/* estimate costs to rescan the inner relation */
cost_rescan(root, inner_path,
&inner_rescan_start_cost,
&inner_rescan_total_cost);
/* 省略 */
}在代價比較時,邏輯也與之前不同,優先比較兩條路徑的disabled_nodes的值,小的為更優路徑。
在disabled_nodes一致的情況下,再比較total_cost,然後再比較startup_cost。
所以最小代價計算的邏輯也不同了,優先考慮比較禁用路徑數量,這樣要比僅比較cost穩妥的多。
compare_path_costs_fuzzily(模糊比較)、compare_path_costs(精確比較)、compare_fractional_path_costs(折衷比較)都是先比較disabled_nodes。
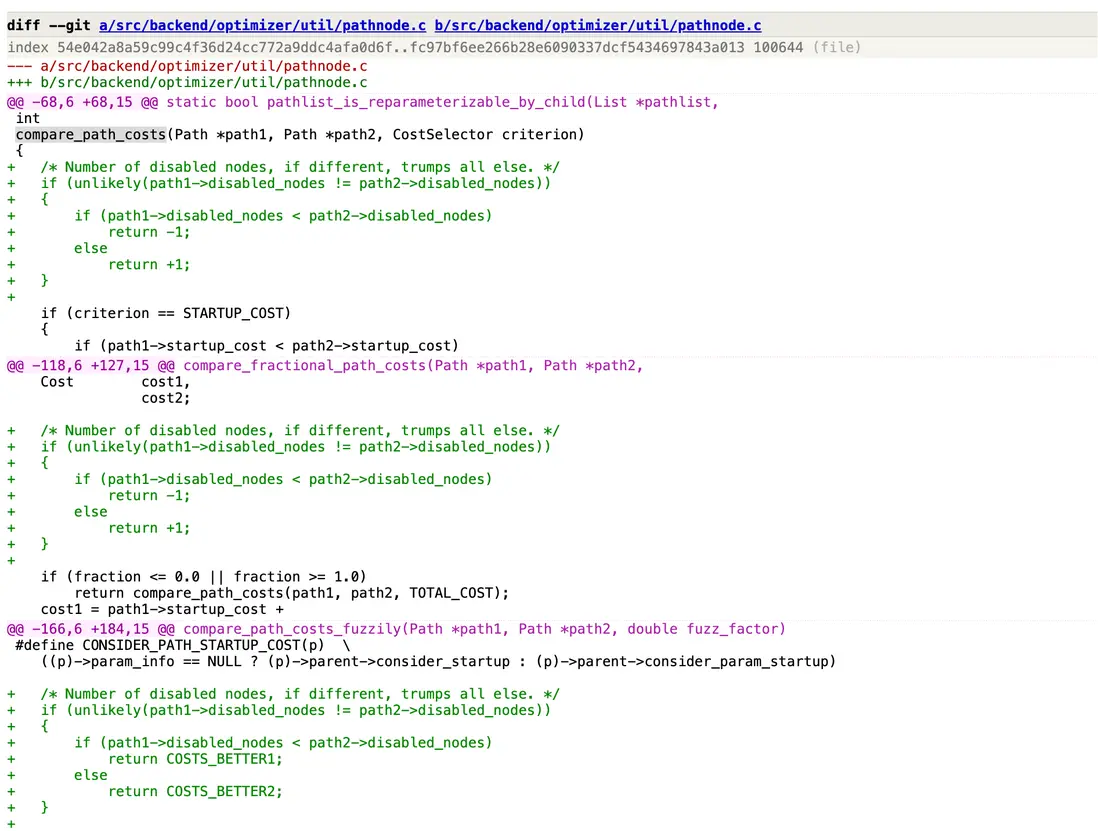
用框圖簡單描述下最優代價預估的過程。
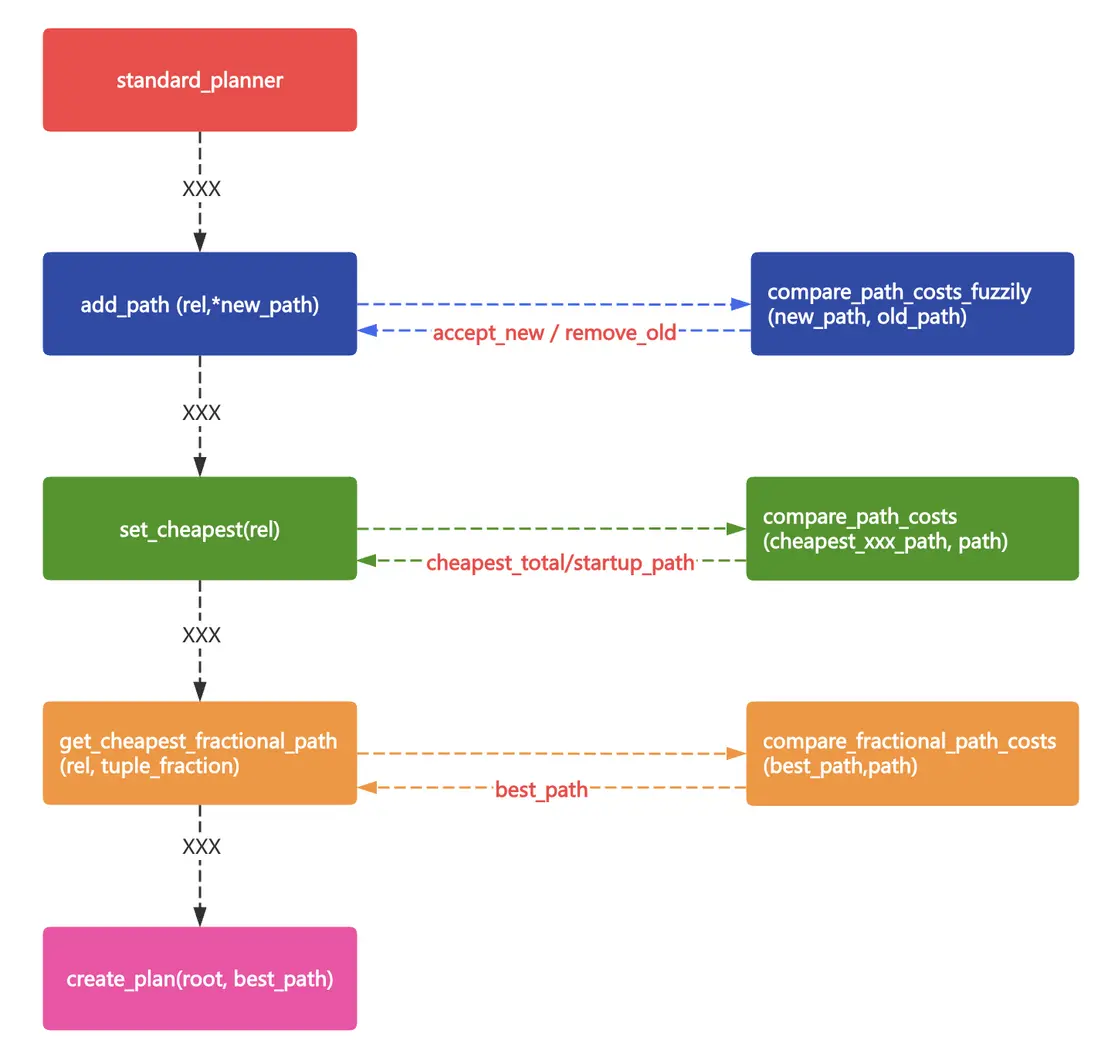
另外,disable_cost的邏輯是全部剔除了嗎? 縱覽代碼,只剩一處了。在final_cost_hashjoin中,用來評估work_mem是否足夠inner_path_row * mcv 生成hash。 如果預估需要的hash_mem大於work_mem,則給startup_cost加disable_cost。
void
final_cost_hashjoin(PlannerInfo *root, HashPath *path,
JoinCostWorkspace *workspace,
JoinPathExtraData *extra)
{
/* 省略 */
/*
* If the bucket holding the inner MCV would exceed hash_mem, we don't
* want to hash unless there is really no other alternative, so apply
* disable_cost. (The executor normally copes with excessive memory usage
* by splitting batches, but obviously it cannot separate equal values
* that way, so it will be unable to drive the batch size below hash_mem
* when this is true.)
*/
if (relation_byte_size(clamp_row_est(inner_path_rows * innermcvfreq),
inner_path->pathtarget->width) > get_hash_memory_limit())
startup_cost += disable_cost;
/* 省略 */
}
size_t
get_hash_memory_limit(void)
{
double mem_limit;
/* Do initial calculation in double arithmetic */
mem_limit = (double) work_mem * hash_mem_multiplier * 1024.0;
/* Clamp in case it doesn't fit in size_t */
mem_limit = Min(mem_limit, (double) SIZE_MAX);
return (size_t) mem_limit;
}
4 測試驗證
默認走dba_users_pkey索引,實際性能差,耗時3s+。
psql (18beta2)
Type "help"forhelp.
postgres=# explain analyze select username from dba_users where username like '%NickYoung%' order by userid limit 1;
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=0.43..408.59 rows=1 width=37) (actual time=3490.601..3490.603 rows=0.00 loops=1)
Buffers: shared hit=90471
-> Index Scan using dba_users_pkey on dba_users (cost=0.43..244894.43 rows=600 width=37) (actual time=3490.599..3490.599 rows=0.00 loops=1)
Filter: ((username)::text ~~ '%NickYoung%'::text)
Rows Removed by Filter: 6000000
Index Searches: 1
Buffers: shared hit=90471
Planning:
Buffers: shared hit=126
Planning Time: 1.674 ms
Execution Time: 3490.653 ms
(11 rows)
postgres=# 使用hint指定走dba_users_username_idx,耗時1ms。
postgres=# /*+ IndexScan(dba_users dba_users_username_idx) */ explain analyze select username from dba_users where username like '%NickYoung%' order by userid limit 1;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=2618.81..2618.81 rows=1 width=37) (actual time=0.069..0.070 rows=0.00 loops=1)
Buffers: shared hit=15
-> Sort (cost=2618.81..2620.31 rows=600 width=37) (actual time=0.067..0.068 rows=0.00 loops=1)
Sort Key: userid
Sort Method: quicksort Memory: 25kB
Buffers: shared hit=15
-> Bitmap Heap Scan on dba_users (cost=377.50..2615.81 rows=600 width=37) (actual time=0.060..0.061 rows=0.00 loops=1)
Disabled: true
Recheck Cond: ((username)::text ~~ '%NickYoung%'::text)
Buffers: shared hit=15
-> Bitmap Index Scan on dba_users_username_idx (cost=0.00..377.35 rows=600 width=0) (actual time=0.048..0.048 rows=0.00 loops=1)
Index Cond: ((username)::text ~~ '%NickYoung%'::text)
Index Searches: 1
Buffers: shared hit=15
Planning:
Buffers: shared hit=2
Planning Time: 1.234 ms
Execution Time: 0.123 ms
(18 rows)
postgres=# debug這個SQL最優路徑選取以及hint生效的過程。
dba_users表有兩個index:
"dba_users_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (userid)
"dba_users_username_idx" gin (username gin_trgm_ops)
1、set_rel_pathlist創建表的掃描路徑,我們先關注下所有index路徑的創建。
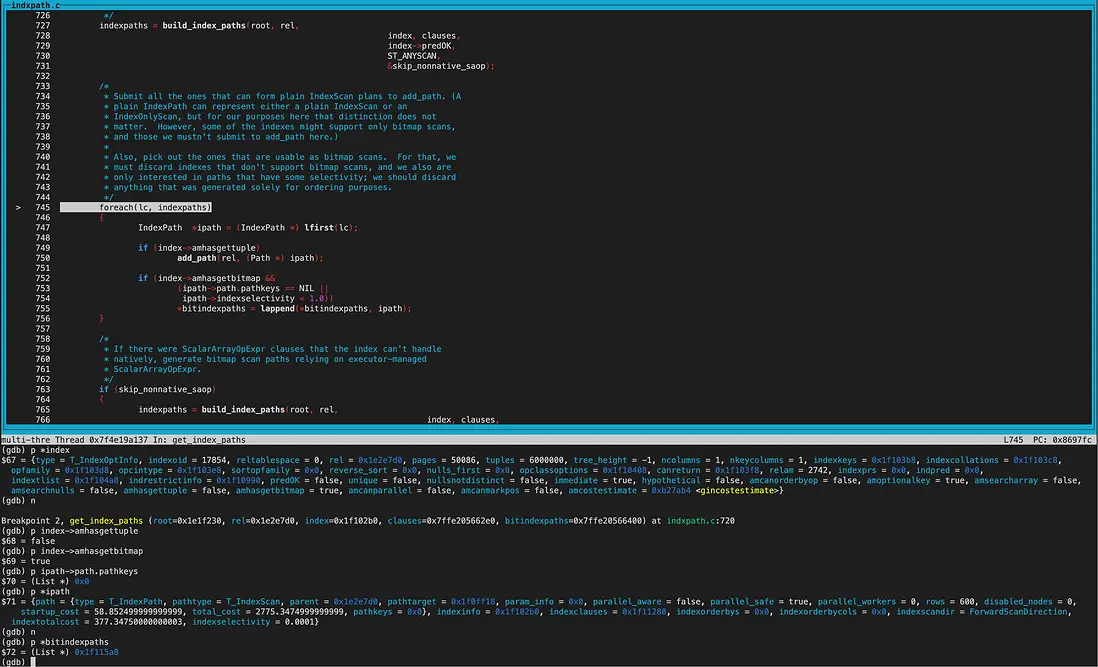
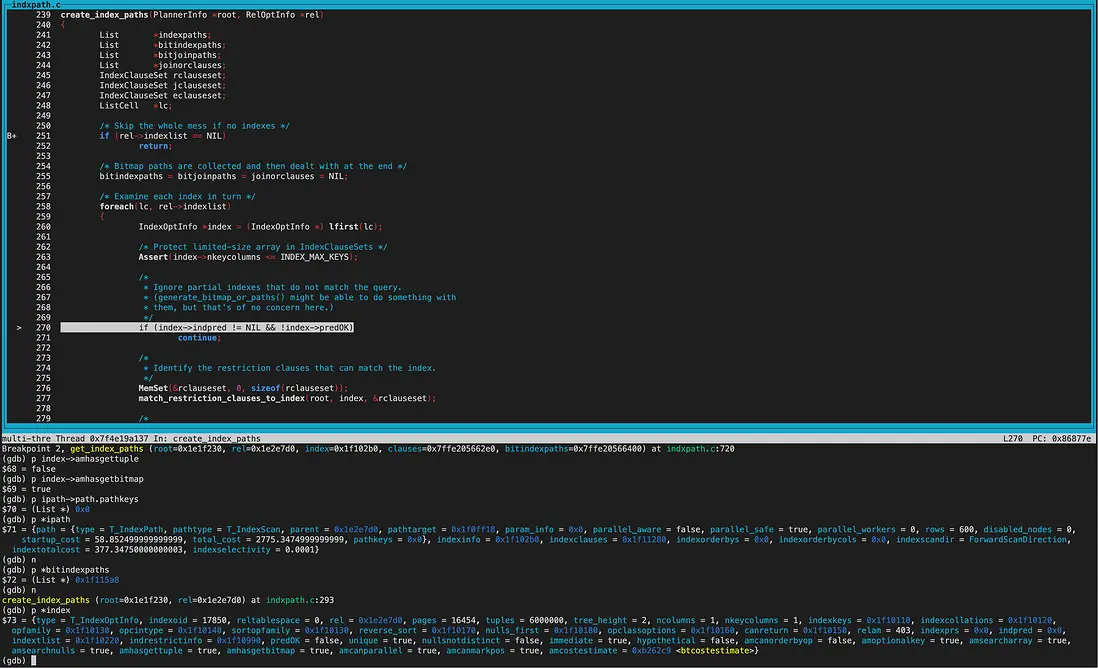
create_index_paths函數裏,可以看到rel->indexlist長度為2,遍歷list獲取到的第一個index為gin索引。
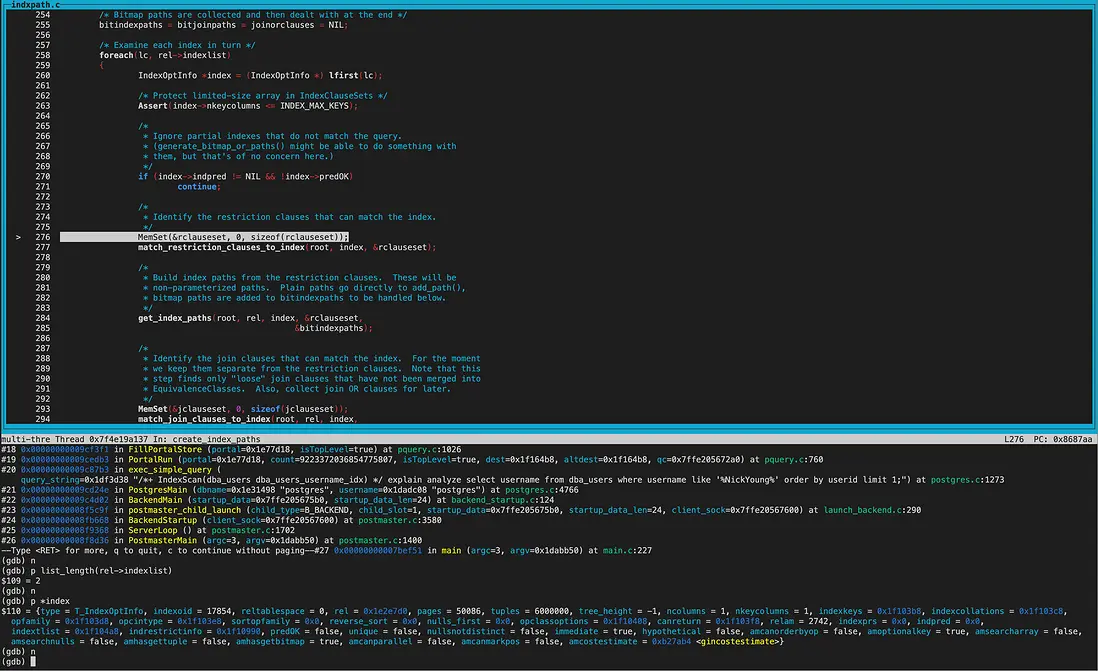
調用get_index_paths函數給gin索引生成路徑。 gin索引amhasgettuple為NULL(ginhandler中初始化),所以gin索引不創建IndexScan Path。
而amhasgetbitmap為true(ginhandler中初始化),也就是可以生成Bitmap Index scan路徑,不過同時還要滿足pathkey為NULL。從打印的結果看確實都滿足,所以給gin索引創建了bitindexpaths即Bitmap Index scan path。
生成BitmapHeapScan path
這裏解釋下pathkey:和索引的order屬性相關,gin索引sortopfamily為NULL,amcanorderbyop為false,所以useful_pathkeys為null,即pathkey為NULL。
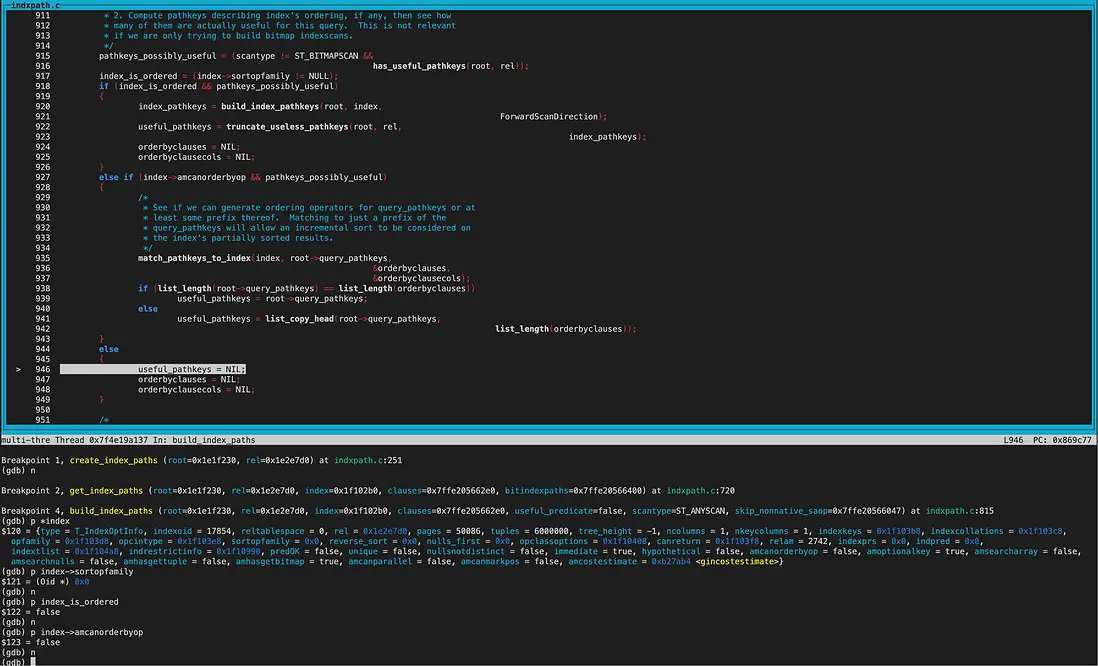
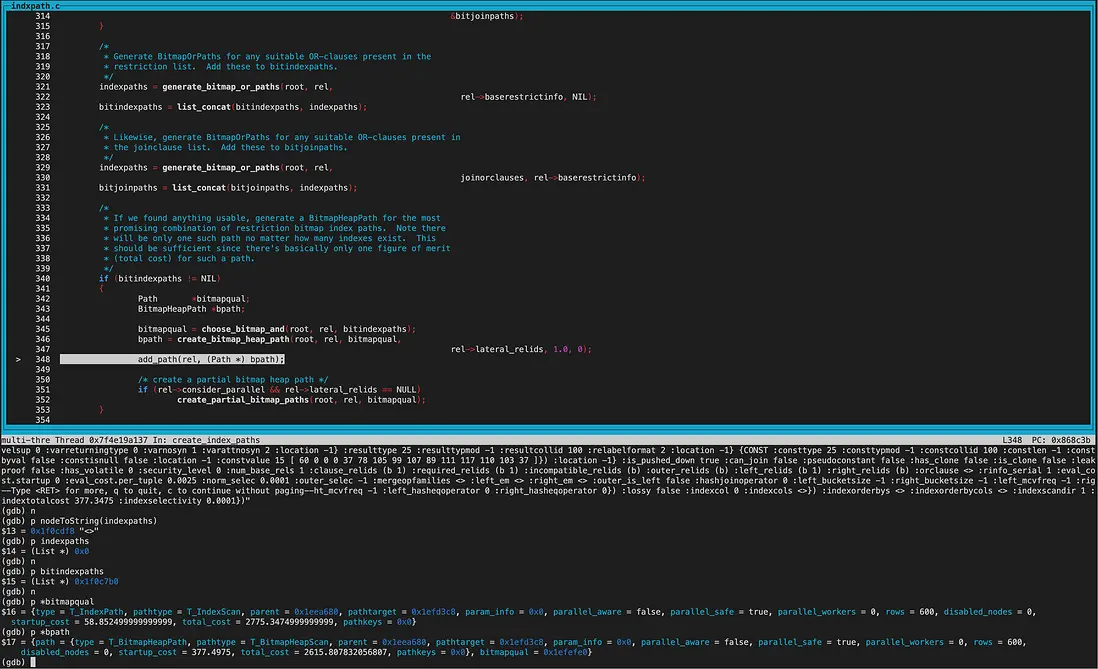
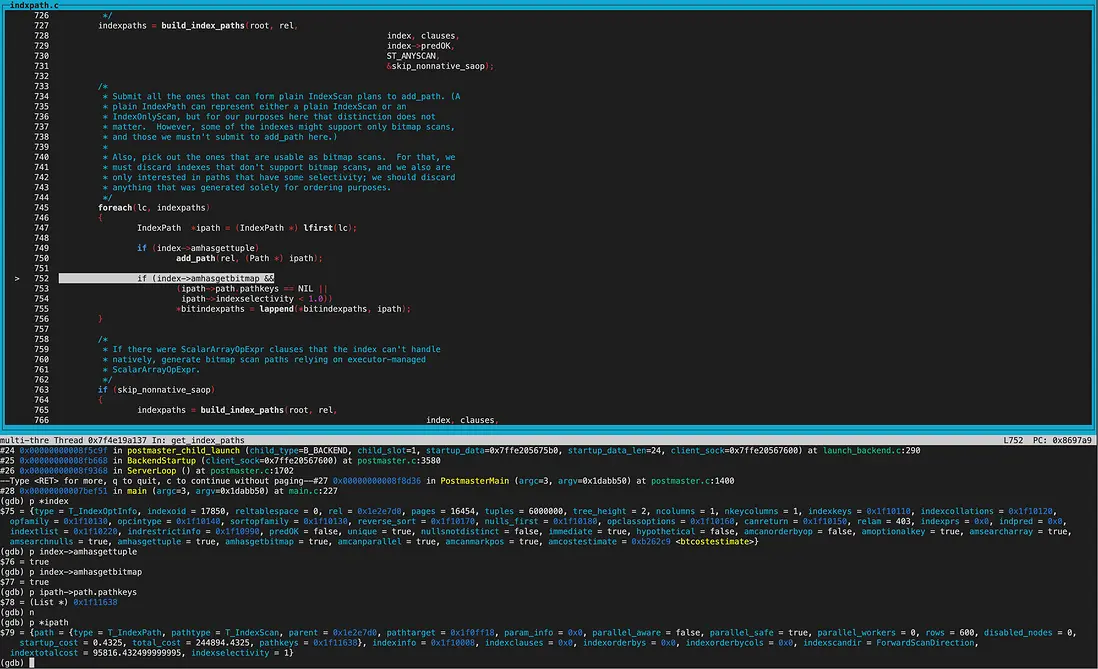
create_index_paths函數裏,第二次遍歷到的index為btree索引。
調用get_index_paths函數給btree索引生成路徑。 btree索引amhasgettuple為true(bthandler中初始化),所以生成IndexScan path。 而amhasgetbitmap為true(bthandler中初始化),不過pathkey不為null,因此沒有生成bitindexpaths,不生成BitmapIndexscan path。
因為sortopfamily非NULL,所以生成useful_pathkeys,即pathkey非NULL。
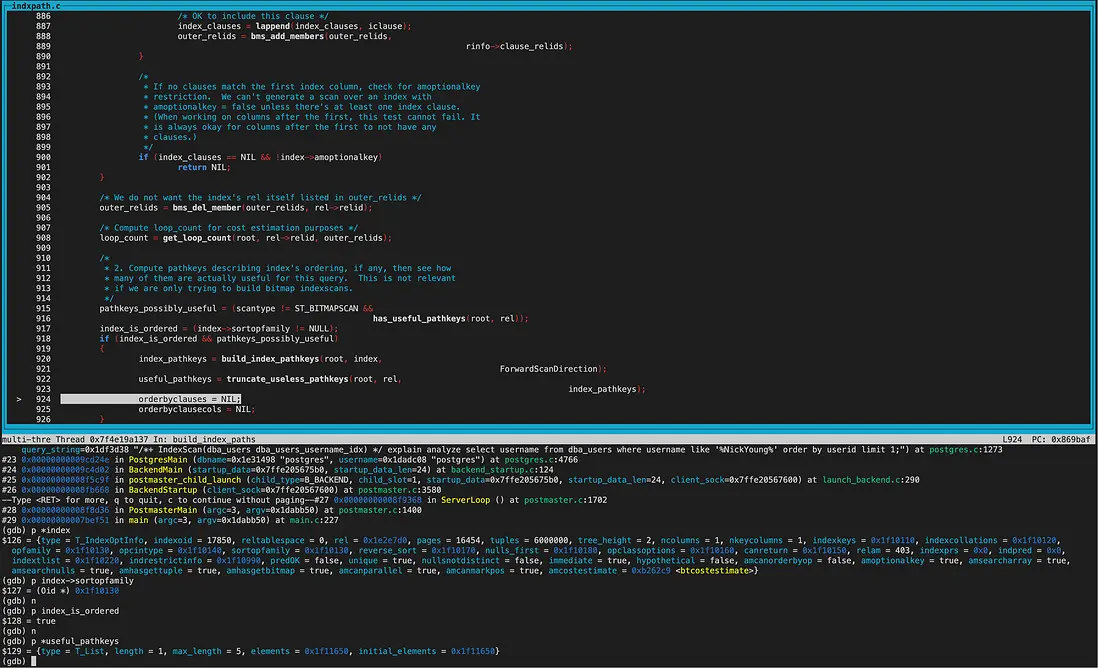
當然創建路徑時都會比較cost,我們放到下一環節討論。
至此,對於dba_users_pkey路徑為Indexscan, 對於dba_users_username_idx路徑為BitmapIndexscan。
2、來看rel_pathlist中的cost比較。
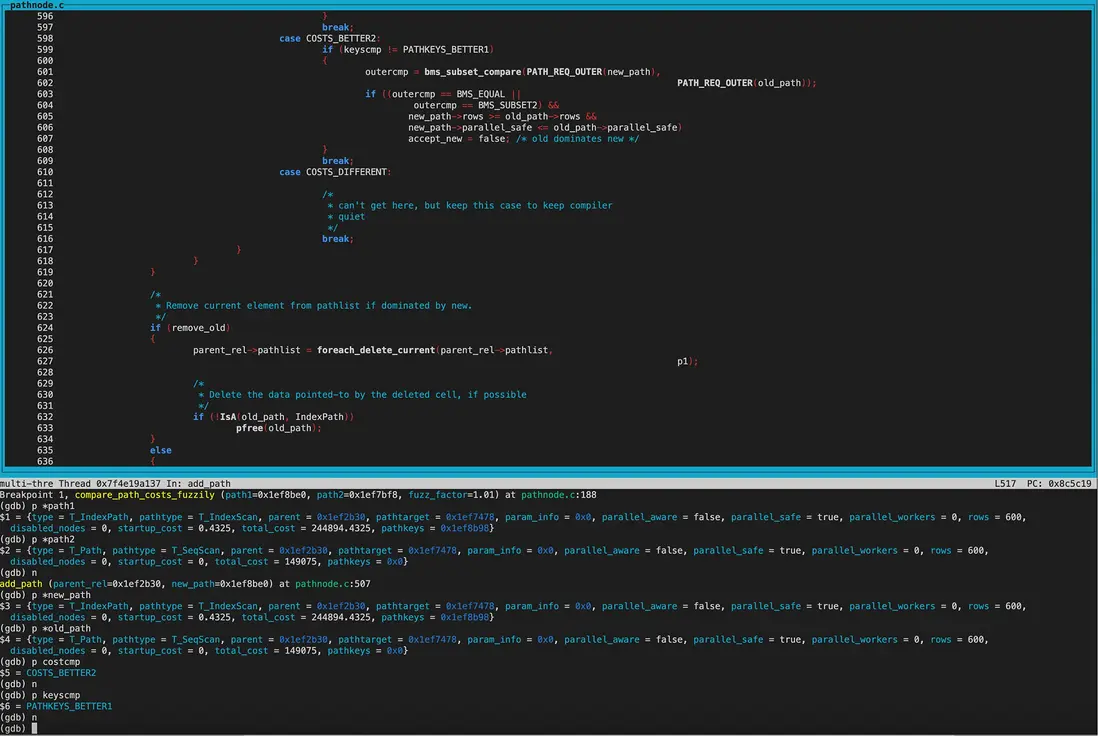
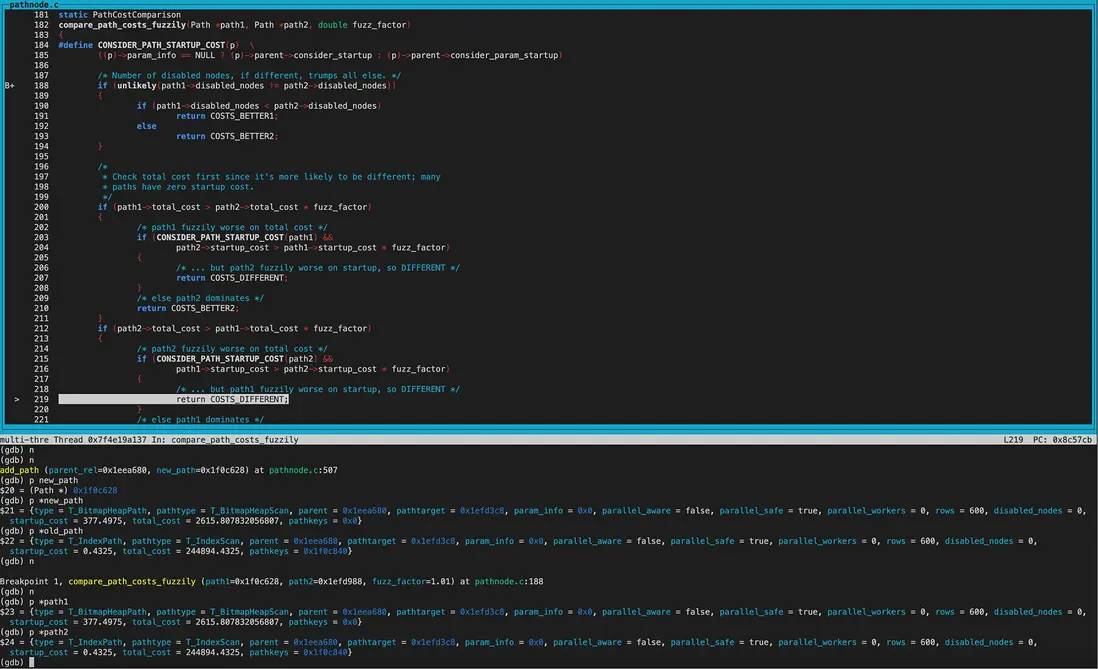
compare_path_costs_fuzzily(模糊比較)
首先比較的new_path為IndexScan,old_path為SeqScan。 因為目前還沒走到hint階段,當前guc參數都為on,因此兩個path的disabled_nodes相同(都為0)。接着比較total_cost,old_path的total_cost和startup_cost都優於new_path,因此返回COST_BETTER2
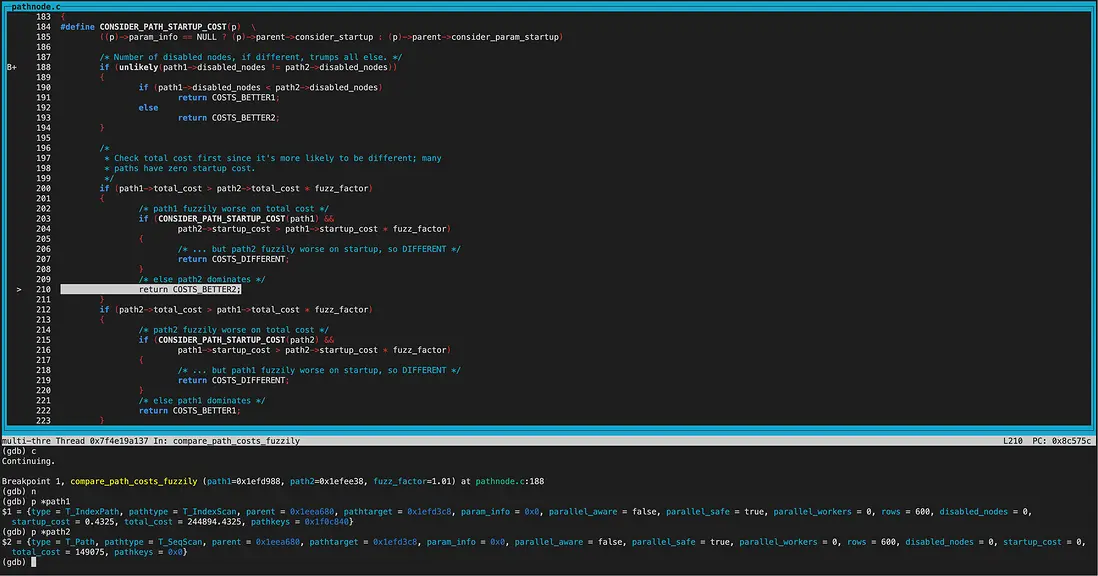
在add_path中costcmp為COST_BETTER2,keyscmp為PATHKRYS_BETTER1,所以沒有標記accept_new為false。
accept_new為true,因此將Indexscan加入pathlist。
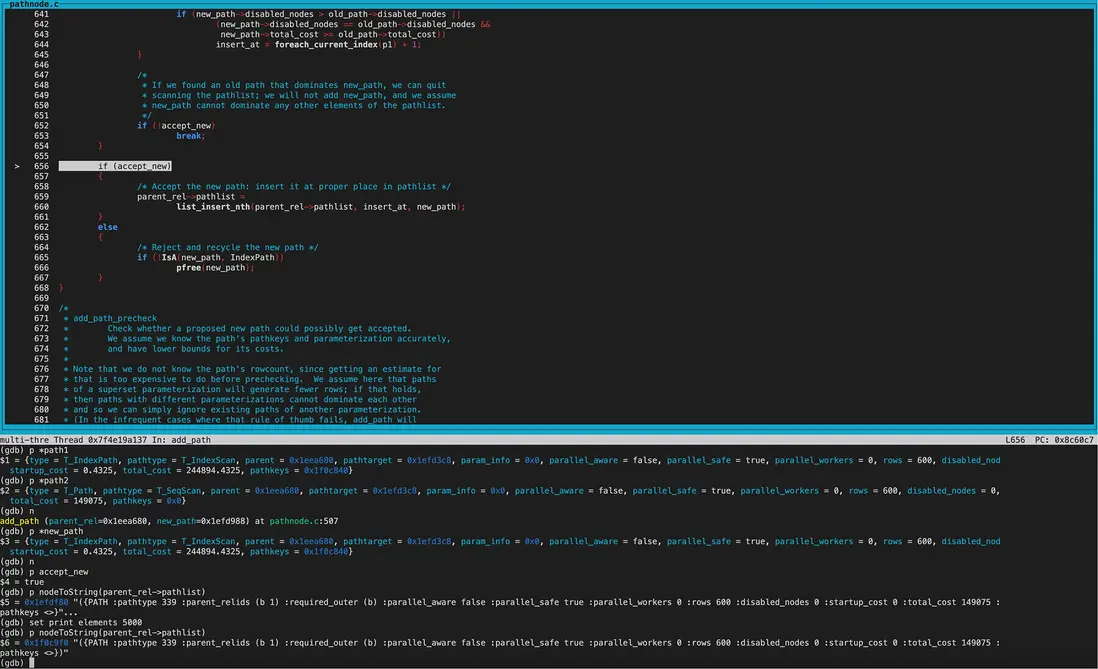
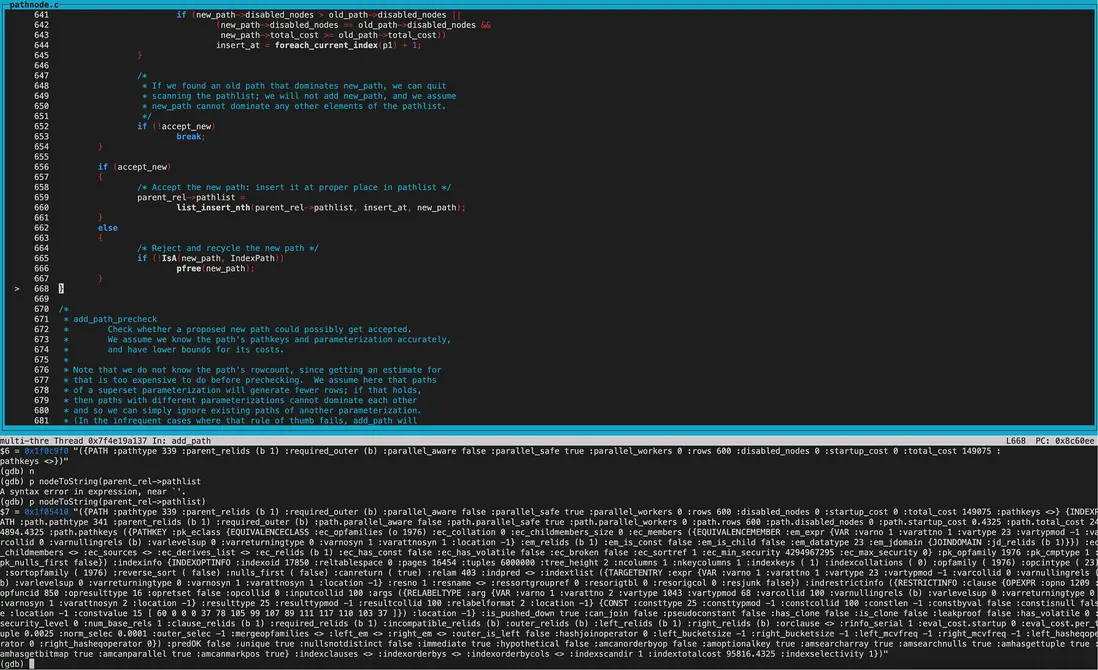
再來看new_path為BitmapHeapScan,old_path為IndexScan的cost模糊比較。
disabled_nodes相同,均為0。接着比較total_cost,new_path的total_cost優於old_path,但startup_cost更大。因此返回COST_DIFFERENT,兩個path都保留。
3、hint的處理
修改Indexlist:
hint為:/+ IndexScan(dba_users dba_users_username_idx) /
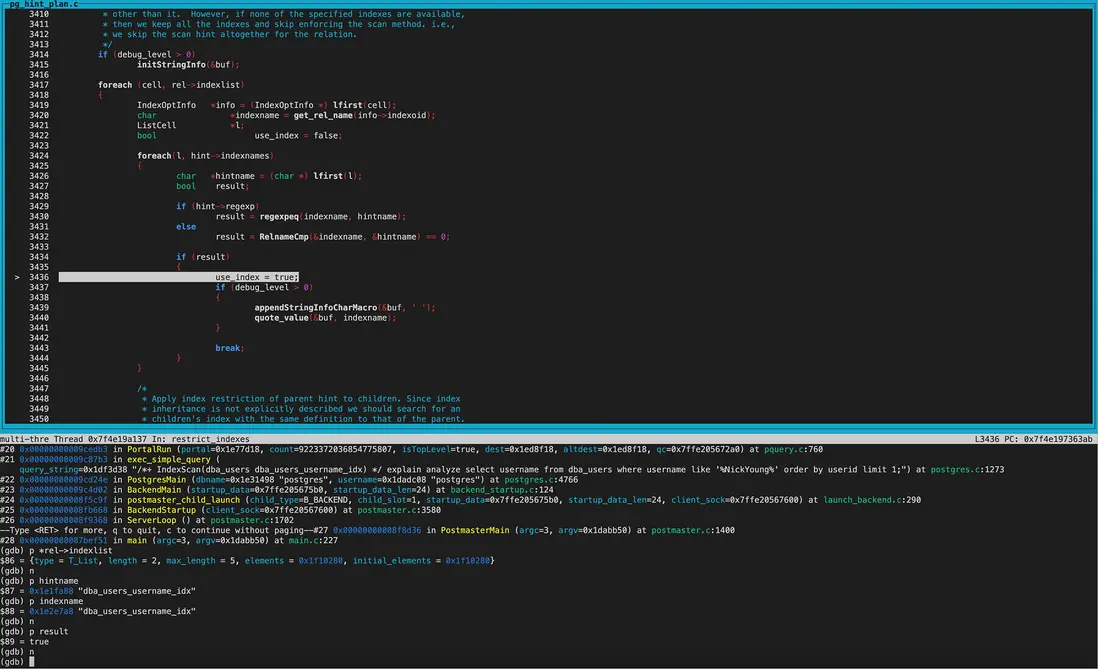
在restrict_indexes函數中第一次遍歷indexlist得到的indexname為dba_users_username_idx,和hintname一致,因此標記used_index=true;
第二次遍歷的indexname為dba_users_pkey和hintname不一致,則添加到unused_indexes列表。
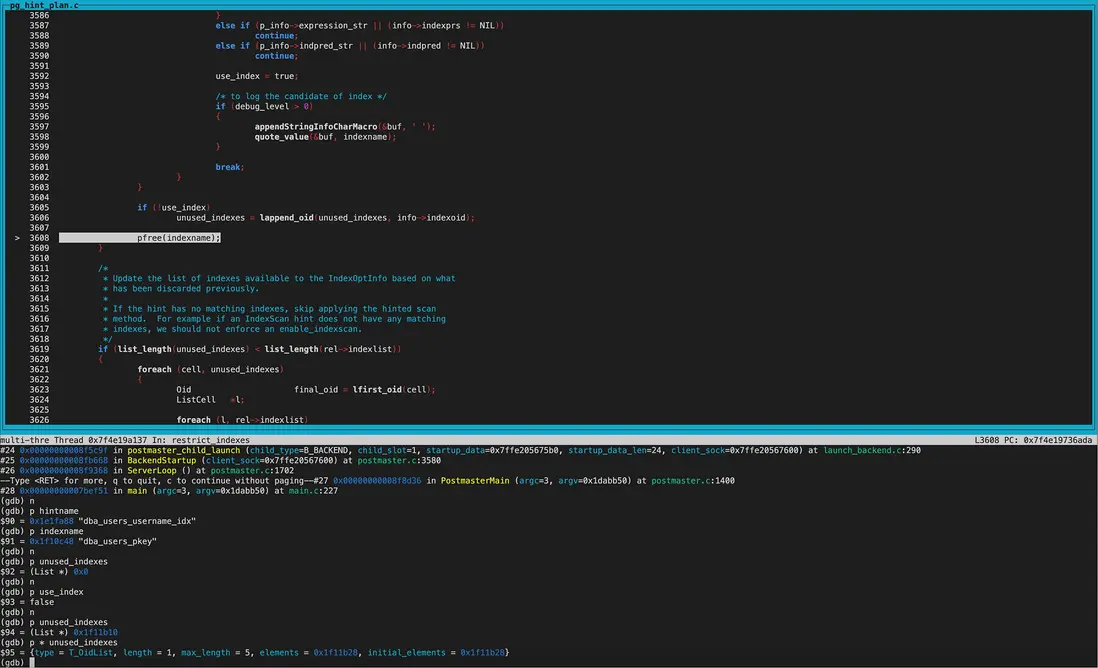
然後使用foreach_delete_current函數將unused_indexes從rel->indexlist中剔除。 剔除後indexlist僅剩一個member,即dba_users_username_idx這個gin索引。
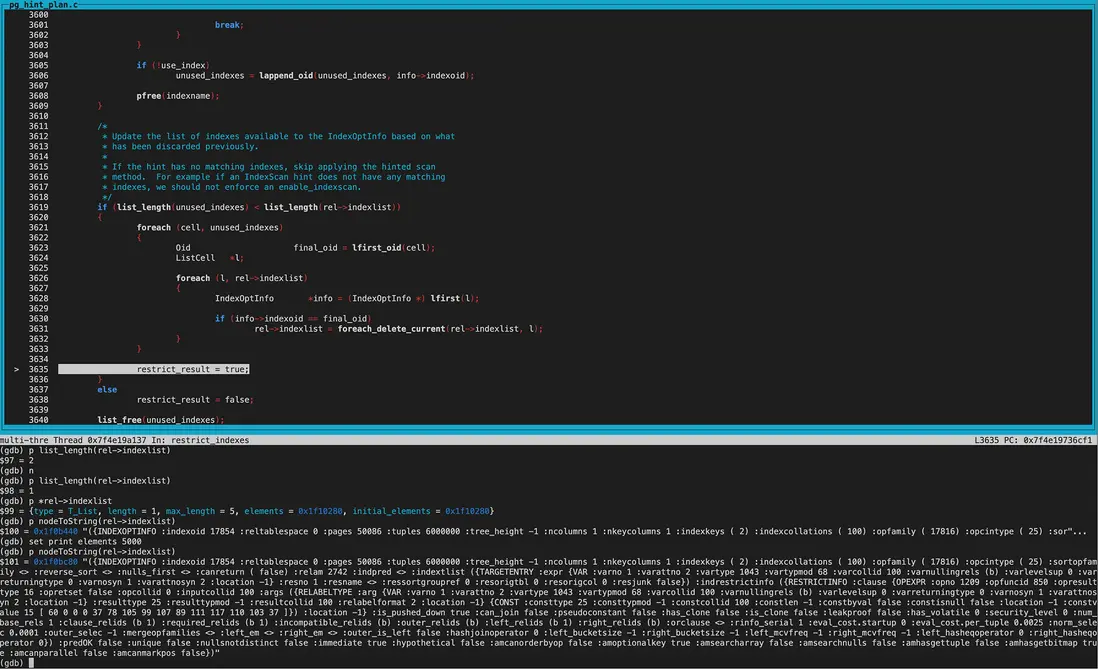
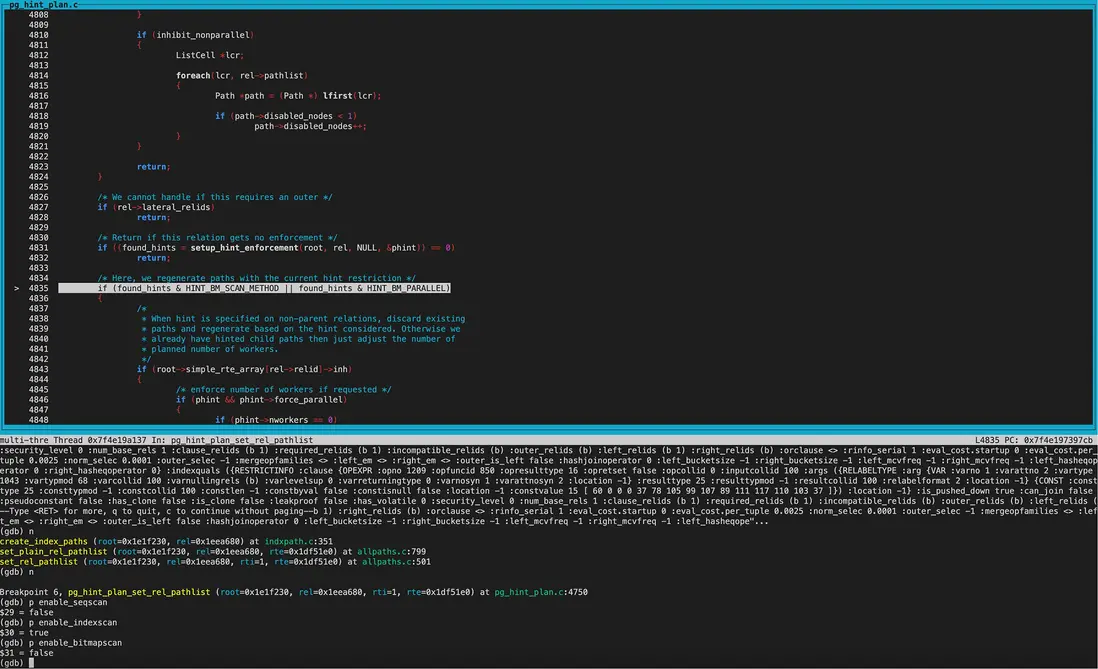
設置disabled_nodes:
除enable_indexscan外,其他方式設置為off,即為其他方式設置disabled_nodes。
再次進行cost模糊比較,兩個path的disabled_nodes相同,都為1。接着比較tocal_cost,兩個path的total_cost及startup_cost的大小關係相反,因此返回COST_DIFFERENT,這兩條path都保留。
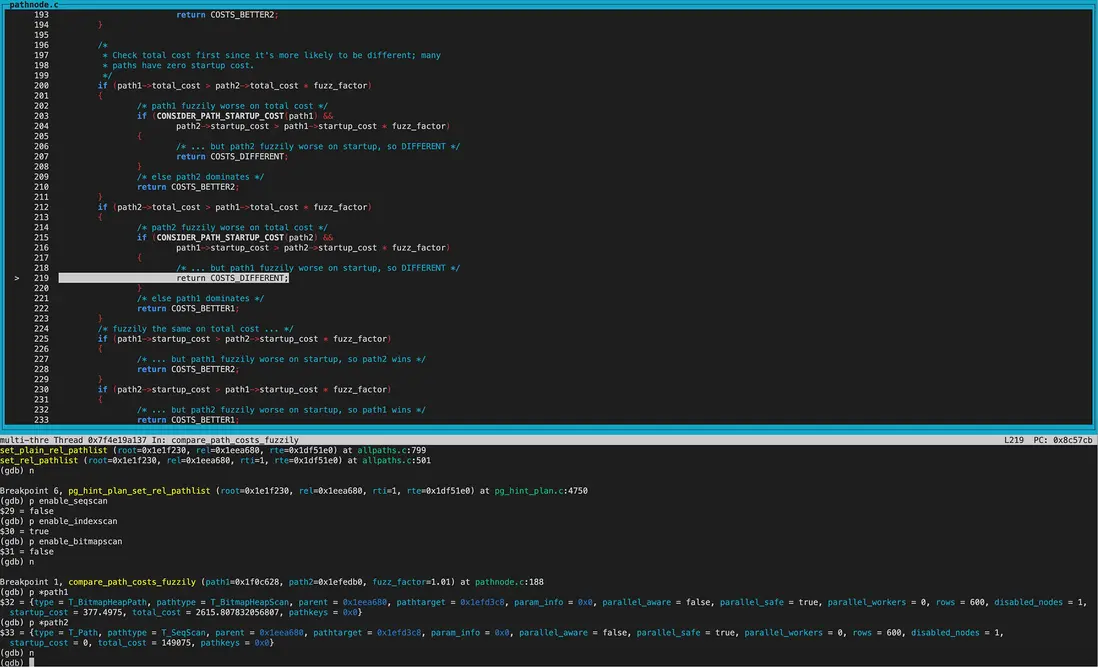
經過hint處理後,對於rel_pathlist就剩下SeqScan和BitmapHeapScan兩個path。
4、最小代價選擇
set_cheapest:
經過幾輪調用compare_path_costs(精確比較)
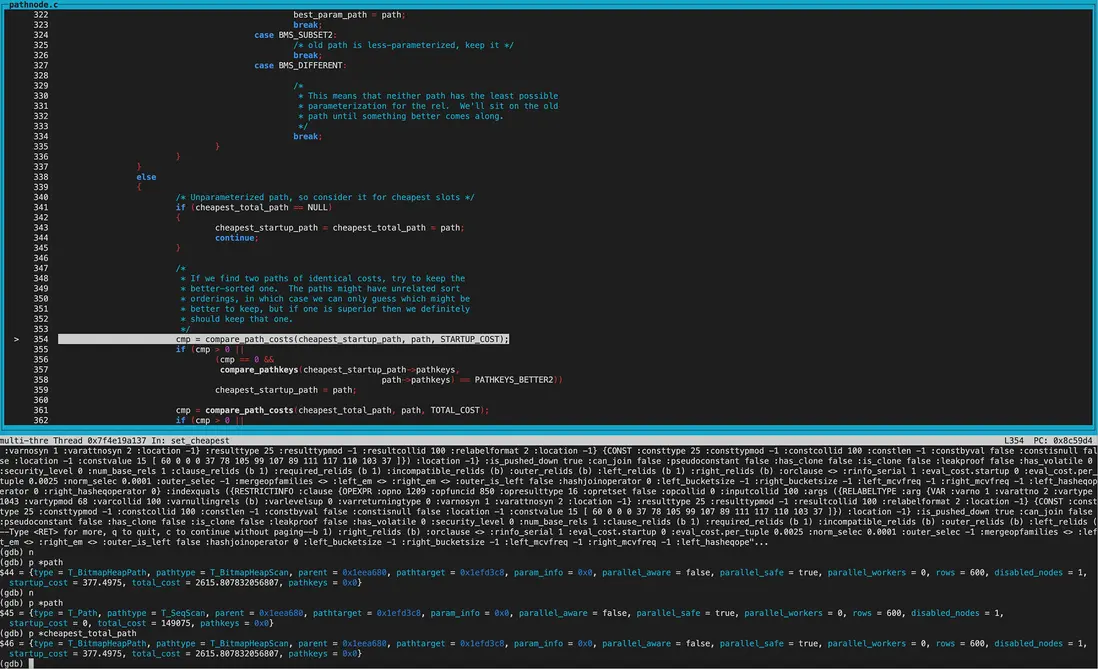
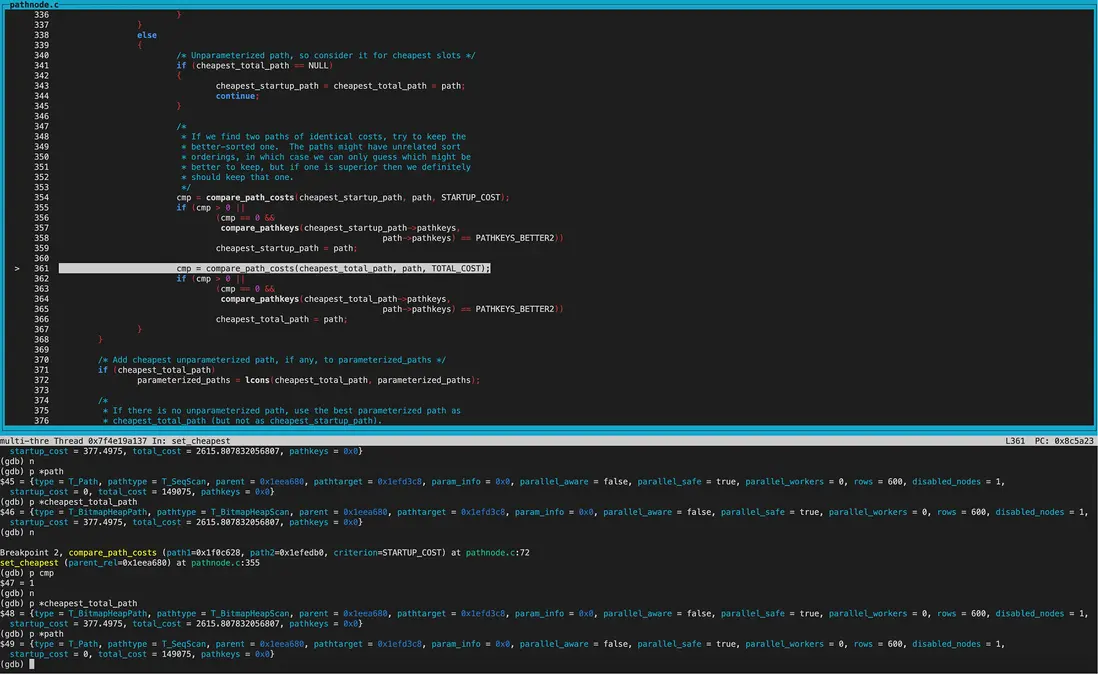
得到cheapest_startup_path為SeqScan,startup_cost為0; cheapest_total_path為BitmapHeapscan,total_cost為2615.81
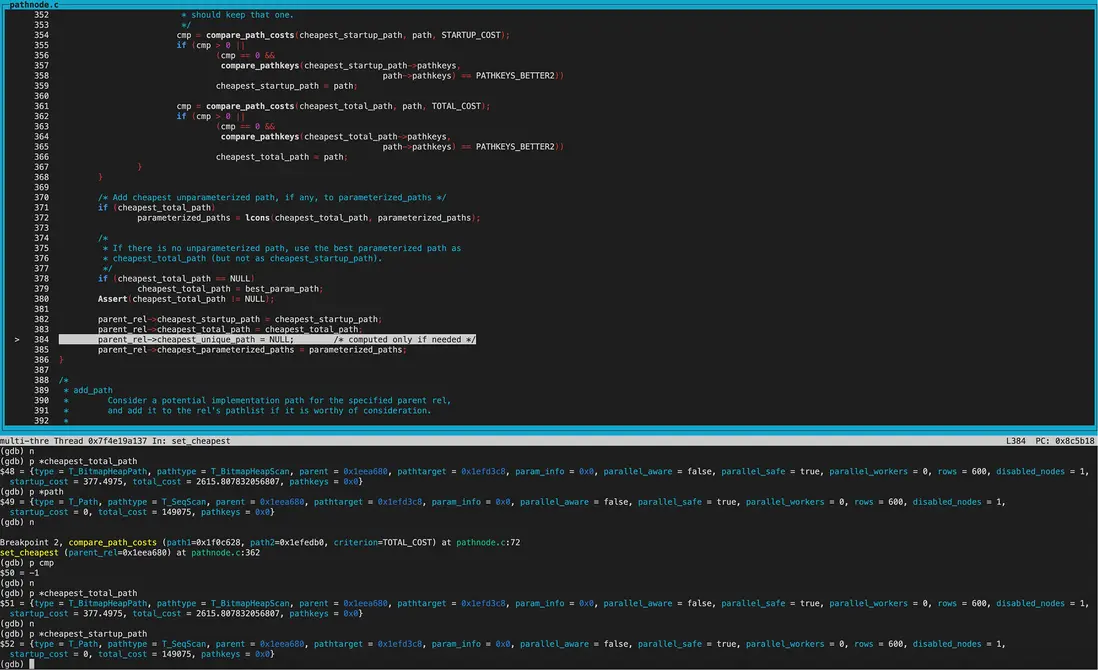
後續還進行了Sort、GatherMerge等node的代價比較, 最終保留Sort並加入pathlist。
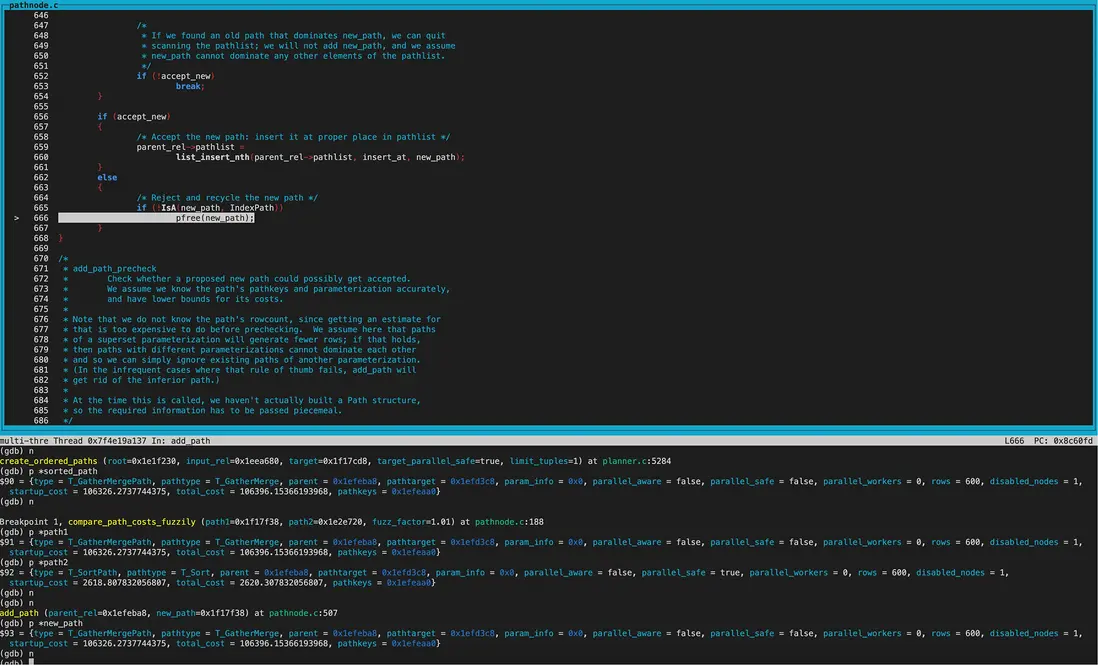
接下來就是創建limit節點了。
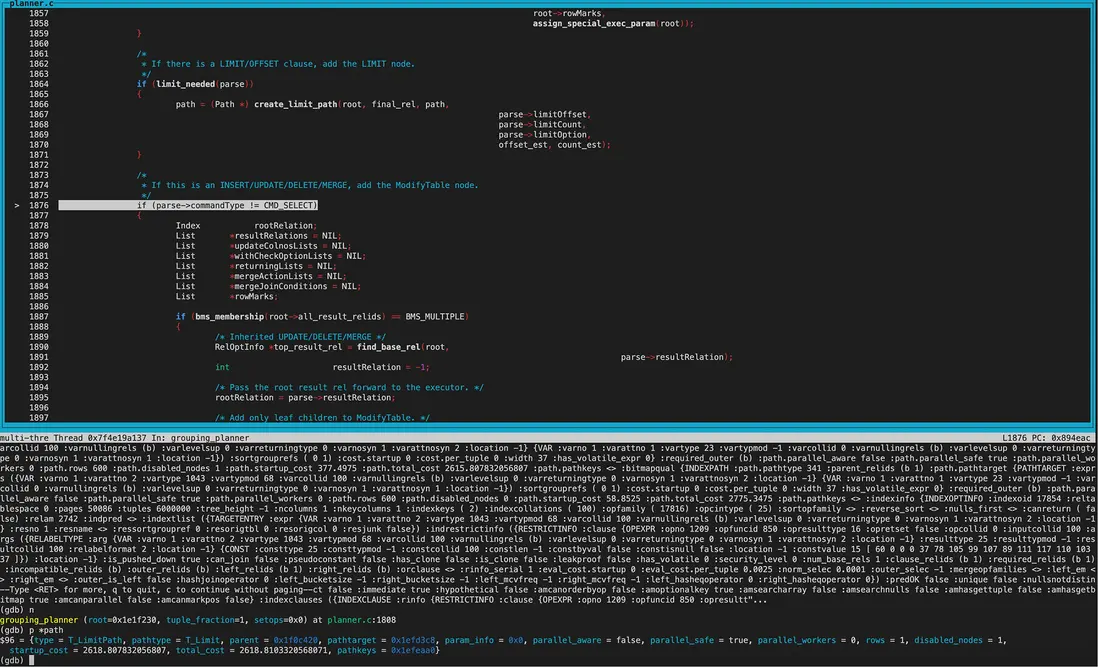
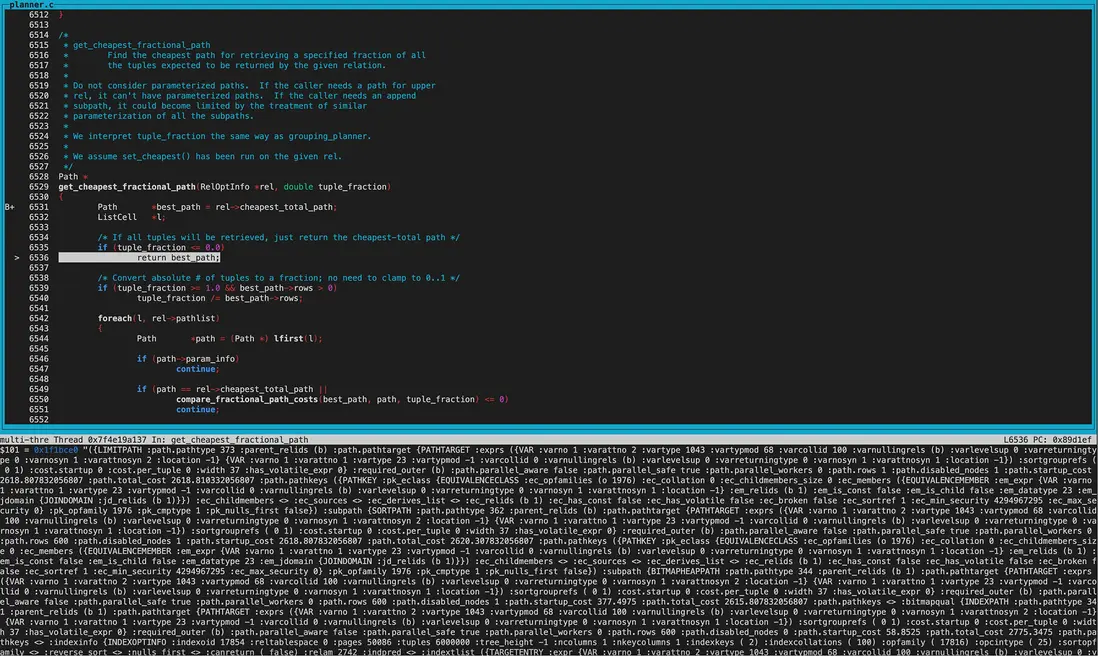
創建好Limit節點後,進行了幾輪cost精確比較,cheapest_startup_path和cheapest_total_path均為Limit,startup_cost和total_cost均為2618.81
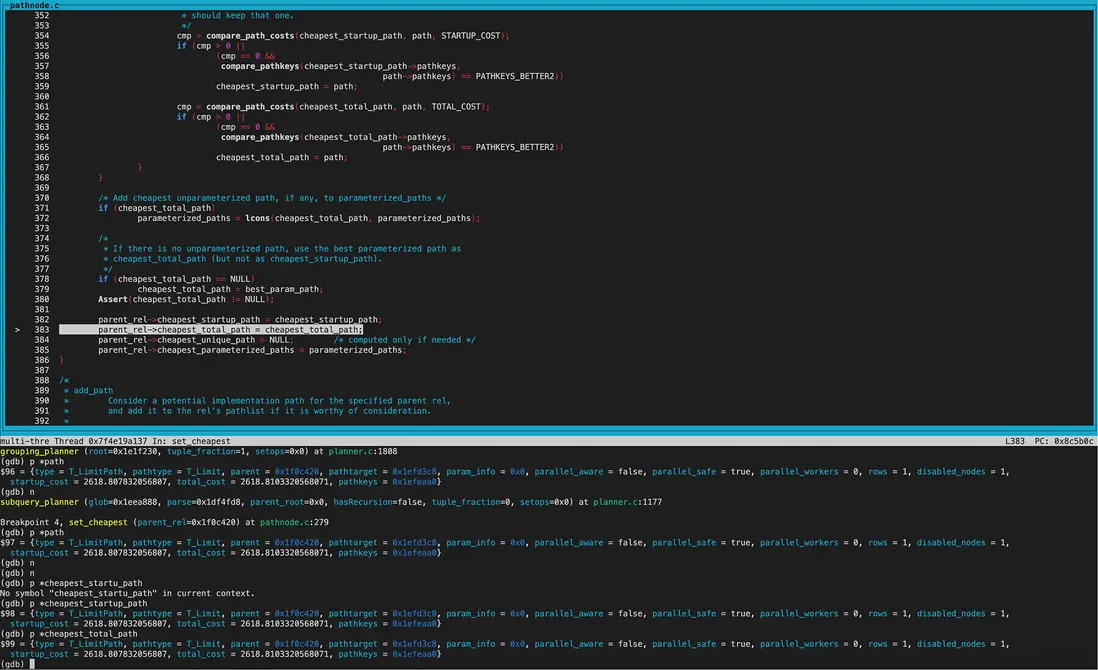
get_cheapest_fractional_path函數中獲得best_path。
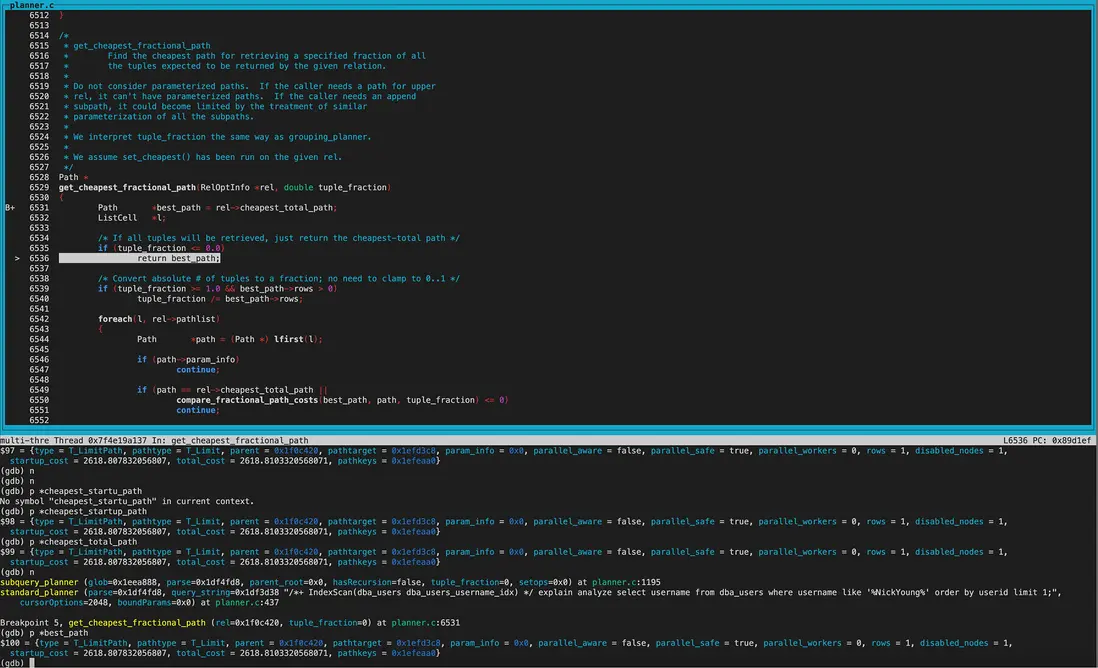
可以看到best_path結構為Limit -> Sort -> BitmapheapScan -> BitmapIndexScan。 並且從各自node的cost來看就是最終的執行計劃。
5 總結
從disable_cost到disabled_nodes,給優化器最小代價預估帶來了質的飛躍。感謝Robert Haas、Richard Guo、David Rowley幾位巨佬,我相信PG會越來越好。