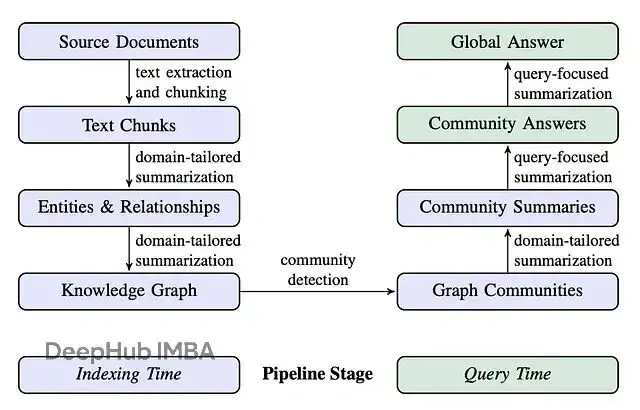
微軟的GraphRAG算得上是最早一批成熟的GraphRAG系統,它把索引階段(抽取實體、關係、構建層級社區並生成摘要)和查詢階段的高級能力整合到了一起。這套方案的優勢在於,可以藉助預先計算好的實體、關係、社區摘要來回答那些宏觀的、主題性的問題,這恰恰是傳統RAG系統基於文檔檢索難以做到的。
本文的重點是DRIFT搜索:Dynamic Reasoning and Inference with Flexible Traversal,翻譯過來就是"動態推理與靈活遍歷"。這是一種相對較新的檢索策略,兼具全局搜索和局部搜索的特點。
DRIFT的工作流程是這樣的:先通過向量搜索建立一個寬泛的查詢起點,再利用羣信息把原始問題拆解成更細粒度的後續查詢。然後動態地在知識圖譜上游走,抓取實體、關係等局部細節。這種設計在計算效率和答案質量之間找到了一個不錯的平衡點。

上圖為使用 LlamaIndex 工作流和 Neo4j 實現的 DRIFT 搜索,核心流程分一下幾步:
首先是HyDE生成,基於一份樣例社區報告構造假設性答案,用來改善查詢的向量表示。
接着社區搜索登場,通過向量相似度找出最相關的社區報告,給查詢提供宏觀上下文。系統會分析這些結果,輸出一個初步的中間答案,同時生成一批後續查詢用於深挖。
這些後續查詢會在局部搜索階段並行執行,從知識圖譜裏撈出文本塊、實體、關係、以及更多社區報告。這個過程可以迭代多輪,每輪都可能產生新的後續查詢。
最後是答案生成,把過程中積累的所有中間答案彙總起來,融合社區級別的宏觀洞察和局部細節,生成最終響應。整體思路就是先鋪開、再聚焦,層層遞進。
本文用的是《愛麗絲夢遊仙境》,劉易斯·卡羅爾的經典作品,這部小説角色眾多、場景豐富、事件環環相扣,拿來演示GraphRAG的能力再合適不過。
數據導入

整個pipeline遵循標準的GraphRAG流程,分三個階段:
class MSGraphRAGIngestion(Workflow):
@step
async def entity_extraction(self, ev: StartEvent) -> EntitySummarization:
chunks = splitter.split_text(ev.text)
await ms_graph.extract_nodes_and_rels(chunks, ev.allowed_entities)
return EntitySummarization()
@step
async def entity_summarization(
self, ev: EntitySummarization
) -> CommunitySummarization:
await ms_graph.summarize_nodes_and_rels()
return CommunitySummarization()
@step
async def community_summarization(
self, ev: CommunitySummarization
) -> CommunityEmbeddings:
await ms_graph.summarize_communities()
return CommunityEmbeddings()先從文本塊裏抽取實體和關係,再給節點和關係生成摘要,最後構建層級社區並生成社區摘要。
摘要做完之後,要給社區和實體都生成向量嵌入,這樣才能支持相似性檢索。社區嵌入的代碼長這樣:
@step
async def community_embeddings(self, ev: CommunityEmbeddings) -> EntityEmbeddings:
# Fetch all communities from the graph database
communities = ms_graph.query(
"""
MATCH (c:__Community__)
WHERE c.summary IS NOT NULL AND c.rating > $min_community_rating
RETURN coalesce(c.title, "") + " " + c.summary AS community_description, c.id AS community_id
""",
params={"min_community_rating": MIN_COMMUNITY_RATING},
)
if communities:
# Generate vector embeddings from community descriptions
response = await client.embeddings.create(
input=[c["community_description"] for c in communities],
model=TEXT_EMBEDDING_MODEL,
)
# Store embeddings in the graph and create vector index
embeds = [
{
"community_id": community["community_id"],
"embedding": embedding.embedding,
}
for community, embedding in zip(communities, response.data)
]
ms_graph.query(
"""UNWIND $data as row
MATCH (c:__Community__ {id: row.community_id})
CALL db.create.setNodeVectorProperty(c, 'embedding', row.embedding)""",
params={"data": embeds},
)
ms_graph.query(
"CREATE VECTOR INDEX community IF NOT EXISTS FOR (c:__Community__) ON c.embedding"
)
return EntityEmbeddings()實體嵌入同理,這樣DRIFT搜索需要的向量索引就都建好了。
DRIFT搜索
DRIFT的檢索思路其實很符合簡單:先看大圖,再挖細節。它不會一上來就在文檔或實體層面做精確匹配,而是先去查羣的摘要,因為這些摘要是對知識圖譜主要主題的高層次概括。
拿到相關的高層信息後,DRIFT會智能地派生出後續查詢,去精確檢索特定實體、關係、源文檔。這種兩階段的做法其實很像人類查資料的習慣:先大致瞭解情況再針對性地追問細節。既有全局搜索的覆蓋面,又有局部搜索的精準度,而且不用把所有社區報告或文檔都過一遍,計算開銷控制得不錯。
下面拆解一下各個階段的實現。
羣搜索
DRIFT用了HyDE技術來提升向量檢索的準確率。不是直接拿用户query做embedding,而是先讓模型生成一個假設性的答案,再用這個答案去做相似性搜索。道理很簡單:假設答案在語義上跟真實的摘要更接近。
@step
async def hyde_generation(self, ev: StartEvent) -> CommunitySearch:
# Fetch a random community report to use as a template for HyDE generation
random_community_report = driver.execute_query(
"""
MATCH (c:__Community__)
WHERE c.summary IS NOT NULL
RETURN coalesce(c.title, "") + " " + c.summary AS community_description""",
result_transformer_=lambda r: r.data(),
)
# Generate a hypothetical answer to improve query representation
hyde = HYDE_PROMPT.format(
query=ev.query, template=random_community_report[0]["community_description"]
)
hyde_response = await client.responses.create(
model="gpt-5-mini",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": hyde}],
reasoning={"effort": "low"},
)
return CommunitySearch(query=ev.query, hyde_query=hyde_response.output_text)拿到HyDE query之後,做embedding,然後通過向量相似度撈出top 5的報告。接着讓LLM基於這些報告生成一個初步答案,同時識別出需要深挖的後續查詢。將初步答案存起來然後進行後續查詢全部並行分發到局部搜索階段。
@step
async def community_search(self, ctx: Context, ev: CommunitySearch) -> LocalSearch:
# Create embedding from the HyDE-enhanced query
embedding_response = await client.embeddings.create(
input=ev.hyde_query, model=TEXT_EMBEDDING_MODEL
)
embedding = embedding_response.data[0].embedding
# Find top 5 most relevant community reports via vector similarity
community_reports = driver.execute_query(
"""
CALL db.index.vector.queryNodes('community', 5, $embedding) YIELD node, score
RETURN 'community-' + node.id AS source_id, node.summary AS community_summary
""",
result_transformer_=lambda r: r.data(),
embedding=embedding,
)
# Generate initial answer and identify what additional info is needed
initial_prompt = DRIFT_PRIMER_PROMPT.format(
query=ev.query, community_reports=community_reports
)
initial_response = await client.responses.create(
model="gpt-5-mini",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": initial_prompt}],
reasoning={"effort": "low"},
)
response_json = json_repair.loads(initial_response.output_text)
print(f"Initial intermediate response: {response_json['intermediate_answer']}")
# Store the initial answer and prepare for parallel local searches
async with ctx.store.edit_state() as ctx_state:
ctx_state["intermediate_answers"] = [
{
"intermediate_answer": response_json["intermediate_answer"],
"score": response_json["score"],
}
]
ctx_state["local_search_num"] = len(response_json["follow_up_queries"])
# Dispatch follow-up queries to run in parallel
for local_query in response_json["follow_up_queries"]:
ctx.send_event(LocalSearch(query=ev.query, local_query=local_query))
return None這就是DRIFT的核心思路,先用HyDE增強的社區搜索鋪開,再用後續查詢往下鑽。
局部搜索
局部搜索階段把後續查詢並行跑起來,深入到具體細節。每個查詢通過實體向量檢索拿到目標上下文,生成中間答案,可能還會產出更多後續查詢。
@step(num_workers=5)
async def local_search(self, ev: LocalSearch) -> LocalSearchResults:
print(f"Running local query: {ev.local_query}")
# Create embedding for the local query
response = await client.embeddings.create(
input=ev.local_query, model=TEXT_EMBEDDING_MODEL
)
embedding = response.data[0].embedding
# Retrieve relevant entities and gather their associated context:
# - Text chunks where entities are mentioned
# - Community reports the entities belong to
# - Relationships between the retrieved entities
# - Entity descriptions
local_reports = driver.execute_query(
"""
CALL db.index.vector.queryNodes('entity', 5, $embedding) YIELD node, score
WITH collect(node) AS nodes
WITH
collect {
UNWIND nodes as n
MATCH (n)<-[:MENTIONS]->(c:__Chunk__)
WITH c, count(distinct n) as freq
RETURN {chunkText: c.text, source_id: 'chunk-' + c.id}
ORDER BY freq DESC
LIMIT 3
} AS text_mapping,
collect {
UNWIND nodes as n
MATCH (n)-[:IN_COMMUNITY*]->(c:__Community__)
WHERE c.summary IS NOT NULL
WITH c, c.rating as rank
RETURN {summary: c.summary, source_id: 'community-' + c.id}
ORDER BY rank DESC
LIMIT 3
} AS report_mapping,
collect {
UNWIND nodes as n
MATCH (n)-[r:SUMMARIZED_RELATIONSHIP]-(m)
WHERE m IN nodes
RETURN {descriptionText: r.summary, source_id: 'relationship-' + n.name + '-' + m.name}
LIMIT 3
} as insideRels,
collect {
UNWIND nodes as n
RETURN {descriptionText: n.summary, source_id: 'node-' + n.name}
} as entities
RETURN {Chunks: text_mapping, Reports: report_mapping,
Relationships: insideRels,
Entities: entities} AS output
""",
result_transformer_=lambda r: r.data(),
embedding=embedding,
)
# Generate answer based on the retrieved context
local_prompt = DRIFT_LOCAL_SYSTEM_PROMPT.format(
response_type=DEFAULT_RESPONSE_TYPE,
context_data=local_reports,
global_query=ev.query,
)
local_response = await client.responses.create(
model="gpt-5-mini",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": local_prompt}],
reasoning={"effort": "low"},
)
response_json = json_repair.loads(local_response.output_text)
# Limit follow-up queries to prevent exponential growth
response_json["follow_up_queries"] = response_json["follow_up_queries"][:LOCAL_TOP_K]
return LocalSearchResults(results=response_json, query=ev.query)下一步負責編排迭代深化的過程。用
collect_events等所有並行搜索跑完,然後判斷要不要繼續往下挖。如果當前深度還沒到上限(這裏設的max depth=2),就把所有結果裏的後續查詢提取出來,存好中間答案分發下一輪並行搜索。
@step
async def local_search_results(
self, ctx: Context, ev: LocalSearchResults
) -> LocalSearch | FinalAnswer:
local_search_num = await ctx.store.get("local_search_num")
# Wait for all parallel searches to complete
results = ctx.collect_events(ev, [LocalSearchResults] * local_search_num)
if results is None:
return None
intermediate_results = [
{
"intermediate_answer": event.results["response"],
"score": event.results["score"],
}
for event in results
]
current_depth = await ctx.store.get("local_search_depth", default=1)
query = [ev.query for ev in results][0]
# Continue drilling down if we haven't reached max depth
if current_depth < MAX_LOCAL_SEARCH_DEPTH:
await ctx.store.set("local_search_depth", current_depth + 1)
follow_up_queries = [
query
for event in results
for query in event.results["follow_up_queries"]
]
# Store intermediate answers and dispatch next round of searches
async with ctx.store.edit_state() as ctx_state:
ctx_state["intermediate_answers"].extend(intermediate_results)
ctx_state["local_search_num"] = len(follow_up_queries)
for local_query in follow_up_queries:
ctx.send_event(LocalSearch(query=query, local_query=local_query))
return None
else:
return FinalAnswer(query=query)這樣就形成了一個迭代細化的循環,每一層都在前一層的基礎上繼續深挖。達到最大深度後,觸發最終答案生成。
最終答案
最後一步把整個DRIFT搜索過程中積攢的所有中間答案彙總成一個完整的響應:這裏包括社區搜索的初步答案,以及局部搜索各輪迭代產出的答案。
@step
async def final_answer_generation(self, ctx: Context, ev: FinalAnswer) -> StopEvent:
# Retrieve all intermediate answers collected throughout the search process
intermediate_answers = await ctx.store.get("intermediate_answers")
# Synthesize all findings into a comprehensive final response
answer_prompt = DRIFT_REDUCE_PROMPT.format(
response_type=DEFAULT_RESPONSE_TYPE,
context_data=intermediate_answers,
global_query=ev.query,
)
answer_response = await client.responses.create(
model="gpt-5-mini",
input=[
{"role": "developer", "content": answer_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": ev.query},
],
reasoning={"effort": "low"},
)
return StopEvent(result=answer_response.output_text)總結
DRIFT搜索提供了一個挺有意思的思路,在全局搜索的廣度和局部搜索的精度之間找到了平衡。從社區級上下文切入,通過迭代的後續查詢逐層下探,既避免了遍歷所有社區報告的計算負擔,又保證了覆蓋面。
這裏還有改進空間,比如目前的實現對所有中間答案一視同仁,如果能根據置信度分數做個篩選,最終答案的質量應該會更好,噪聲也能降下來。後續查詢也可以先按相關性或信息增益排個序,優先追蹤最有價值的線索。
另一個值得嘗試的方向是加一個查詢精煉步驟,用LLM分析所有生成的後續查詢,把相似的歸併起來避免重複搜索,過濾掉那些大概率沒什麼收穫的查詢。這樣能大幅減少局部搜索的次數,同時不影響答案質量。
完整代碼
https://avoid.overfit.cn/post/5eaca452dcc7422d8c2308586e7cfe56
有興趣的可以自己跑跑看,或者在這個基礎上做些改進。
作者:Tomaz Bratanic