本文首發國內開源代碼託管平台Gitee
文章地址:
https://gitee.com/gooder4j/compose-hub/issues/I4U78Q覺得不錯的話,你的star是對我最大的支持!
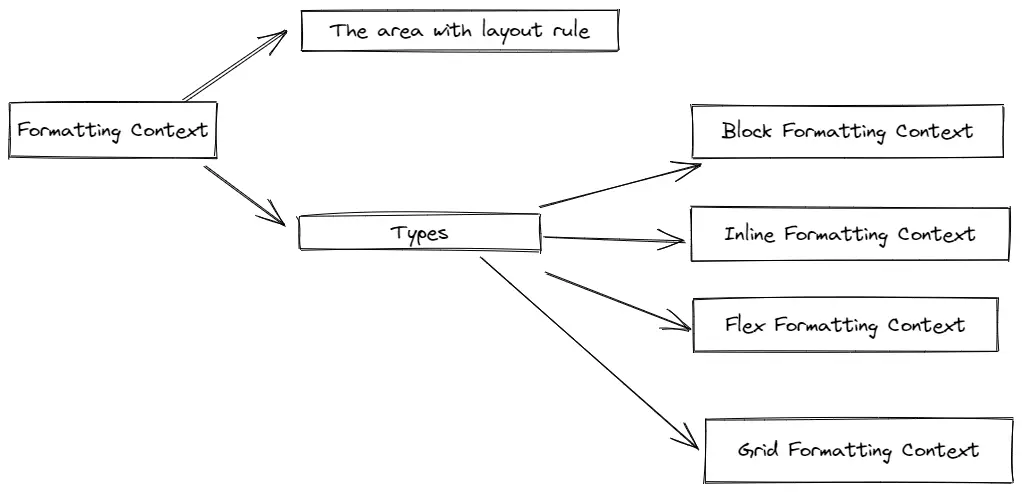
Formatting Context簡單理解,就是定義了佈局規則的一片區域。它的類型包括:
- Block Formatting Context,簡稱BFC
- Inline Formatting Context,簡稱IFC
- Flex Formatting Context,簡稱FFC
- Grid Formatting Context,簡稱GFC
Block Formatting Context(BFC)
A block formatting context is a part of a visual CSS rendering of a web page. It's the region in which the layout of block boxes occurs and in which floats interact with other elements.
Block Formatting Context(BFC) 是web頁面可視化CSS渲染的一部分,它是塊級盒佔據和float與其他元素相互作用的區域。
從定義來看,BFC是一塊area、region,也就是頁面上的一部分區域,這塊區域上有塊級盒、float,並且規定了它們的佈局規則。
Formatting contexts affect layout, but typically, we create a new block formatting context for the positioning and clearing floats rather than changing the layout, because an element that establishes a new block formatting context will:
- contain internal floats.
- exclude external floats.
- suppress margin collapsing.
Formatting context影響佈局,但一般來説,我們會創建一個新的BFC,用於定位和清除float而不是來改變佈局,因為建立了BFC的一個元素會:
- 包含內部float
- 排除外部float
- 阻止外邊距重疊
下面用例子展開説明上面三條規則。
BFC的三條規則
包含內部float
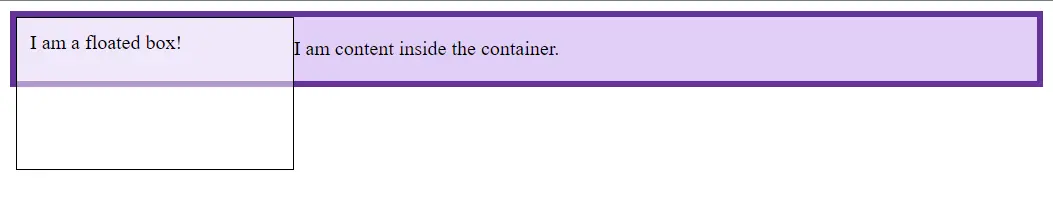
- 當一個元素沒有BFC時:
HTML
<section>
<div class="box">
<div class="float">I am a floated box!</div>
<p>I am content inside the container.</p>
</div>
</section>CSS
section {
height: 150px;
}
.box {
background-color: rgb(224, 206, 247);
border: 5px solid rebeccapurple;
}
.float {
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, .5);
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 10px;
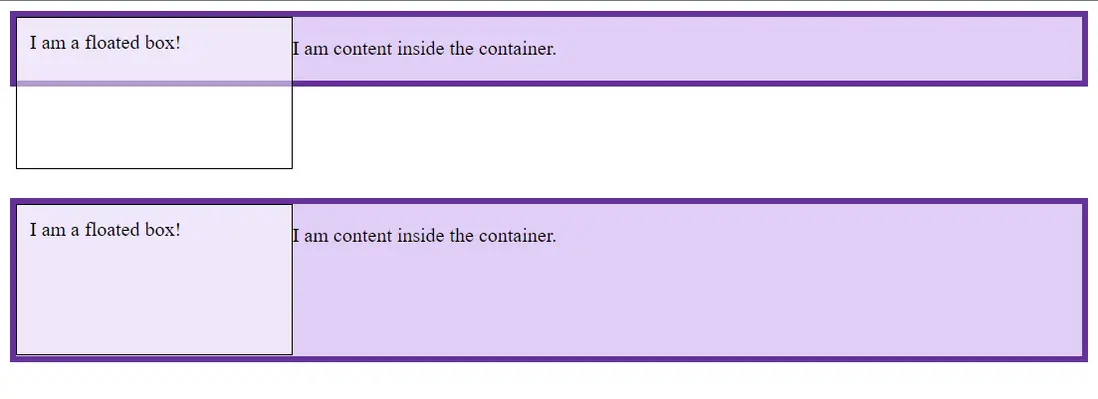
}- 當元素的屬性
overflow不等於visible時,該元素會創建BFC:
HTML
<section>
<div class="box">
<div class="float">I am a floated box!</div>
<p>I am content inside the container.</p>
</div>
</section>
<!-- 添加新的section對比 -->
<section>
<div class="box" style="overflow: auto;">
<div class="float">I am a floated box!</div>
<p>I am content inside the container.</p>
</div>
</section>-
使用
display: flow-root創建BFC。雖然塊級元素的
overflow不為visible或clip時可以創建BFC,但是它有很大的缺點——偏離overflow的原意,overflow是用於設定內容超出容器時的動作,如果單純為了創建BFC而使用overflow,那麼最終樣式效果可能出乎意料,並且足夠迷惑誤導未來看這段代碼的小夥伴。使用
display: flow-root的好處:創建BFC並且不會有副作用。
HTML
<section>
<div class="box">
<div class="float">I am a floated box!</div>
<p>I am content inside the container.</p>
</div>
</section>
<section>
<div class="box" style="overflow: auto;">
<div class="float">I am a floated box!</div>
<p>I am content inside the container.</p>
</div>
</section>
<!-- 添加新的section對比 -->
<section>
<div class="box" style="display: flow-root">
<div class="float">I am a floated box!</div>
<p>I am content inside the container.</p>
</div>
</section>排除外部float
當一個元素挨着另外一個float時:
HTML
<section>
<div class="float">I am float</div>
<div class="box">
<p>Normal</p>
</div>
</section>CSS
section {
height: 150px;
}
.box {
background-color: rgb(224, 206, 247);
border: 5px solid rebeccapurple;
}
.float {
float: left;
overflow: hidden;
margin-right: 25px;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, .75);
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 10px;
}通過display: flow-root為元素加上BFC後:
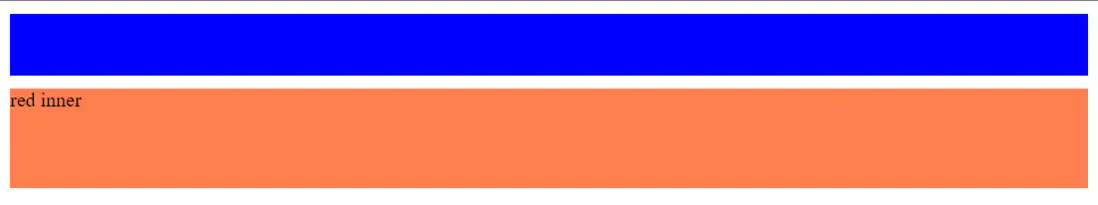
阻止外邊距摺疊
外邊距摺疊指垂直方向的外邊距摺疊,原則上是能夠摺疊就摺疊,主要有三種情況[3]:
- 相鄰元素外邊距摺疊,這是最常見的;
- 父元素和子孫元素沒有分開(被邊框、內邊距、BFC等分開)是外邊距也會摺疊;
- 空元素沒有內容(沒有content,邊框,內邊距時)它的上下邊距會摺疊在一起。
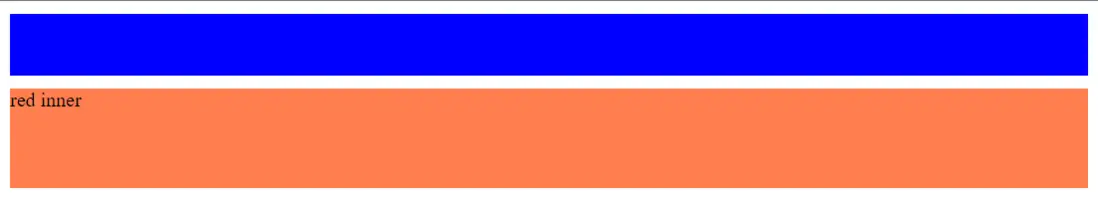
看例子,當沒有BFC時:
HTML
<div class="blue"></div>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner">red inner</div>
</div>CSS
.blue {
height: 50px;
margin: 10px 0;
background: blue;
}
.outer {
background: red;
}
.inner {
height: 80px;
margin: 10px 0;
background-color: coral;
}當創建了BFC後,外邊距的摺疊會被阻止:
創建BFC
A block formatting context is created by at least one of the following:
- The root element of the document (
<html>).- Floats (elements where
floatisn'tnone).- Absolutely positioned elements (elements where
positionisabsoluteorfixed).- Inline-blocks (elements with
display`: inline-block`).- Table cells (elements with
display`: table-cell`, which is the default for HTML table cells).- Table captions (elements with
display`: table-caption`, which is the default for HTML table captions).- Anonymous table cells implicitly created by the elements with
display:table,table-row,table-row-group,table-header-group,table-footer-group(which is the default for HTML tables, table rows, table bodies, table headers, and table footers, respectively), orinline-table.- Block elements where
overflowhas a value other thanvisibleandclip.display:flow-root.- Elements with
contain:layout,content, orpaint.- Flex items (direct children of the element with
display:flexorinline-flex) if they are neither flex nor grid nor table containers themselves.- Grid items (direct children of the element with
display:gridorinline-grid) if they are neither flexnor grid nor table containers themselves.- Multicol containers (elements where
column-countorcolumn-widthisn'tauto, including elements withcolumn-count: 1).column-span:allshould always create a new formatting context, even when thecolumn-span: allelement isn't contained by a multicol container (Spec change Chrome bug[4])
如下情況會創建BFC:
- 文檔的根元素(
<html>)。 - Float(元素的
float屬性值不為none)。 - 絕對定位元素(元素的
position屬性值為absolute或者fix)。 - Inline-block(元素帶有
display:inline-block)。 - 表格單元(元素帶有
display: table-cell,它是HTML表格單元的默認屬性值)。 - 表格標題(元素帶有
display: table-caption,它時HTML表格標題的默認屬性值)。 - 匿名的表格單元,它會隱式地被
display:table, table-row, table-row-group, table-header-group, table-footer-group(它們分別是表格、表格行、表格體、表格腳的默認屬性值),inline-table所創建。 - 塊級元素的
overflow屬性不為visible和clip。 display: flow-root。- 元素有
contain:layout,content或者paint。 - 本身即不是彈性容器、不是網格容器、也不是表格的Flex項目(元素帶有
display:flex或者inline-flex的直接子元素)。 - 本身即不是彈性容器、不是網格容器、也不是表格的Grid項目(元素帶有
display:grid或者inline-grid的直接子元素)。 - 多列容器(元素的
column-count或者column-width不為auto,包括column-count: 1的元素)。 column-span: all應該永遠創建一個新的formatting context,即使column-span: all元素沒有被多行容器所包括(規範改變[4],Chrome Bug[5])。
Inline Formatting Context(IFC)
Inline formatting contexts exist inside other formatting contexts and can be thought of as the context of a paragraph. The paragraph creates an inline formatting context inside which such things as<strong>,<a>, or<span>elements are used on text.
Inline formatting context 存在於其他formatting context裏面,並且可以看作是paragraph的context。paragraph創建一個inline formatting context。paragraph會在用於文本的<strong>,<a>或者<span>的元素上創建IFC。
The box model does not fully apply to items participating in an inline formatting context. In a horizontal writing mode line, horizontal padding, borders and margin will be applied to the element and push the text away left and right. However, margins above and below the element will not be applied. Vertical padding and borders will be applied but may overlap content above and below as, in the inline formatting context, the line boxes will not be pushed apart by padding and borders.
盒模型不會完全應用於帶有IFC的元素。在水平寫模式線、水平內邊距、邊框和外邊距會應用於元素上,並把文字推向左右。然鵝,元素的上邊距和下邊距不會被應用。垂直內邊距和邊框會被應用當可能覆蓋上面或者下面的內容,因為在IFC中,內聯盒子不會被內邊距和邊框所推開。
HTML
<p>Before that night—<strong>a memorable night</strong>, as it was to prove—hundreds of millions of people had watched the rising smoke-wreaths of their fires without drawing any special inspiration from the fact.”</p>CSS
strong {
margin: 20px;
padding: 20px;
border: 5px solid rebeccapurple;
}Flex Formatting Context(FFC) 和 Grid Formatting Context(GFC)
除了包含內部float(因為在彈性容器或者網格容器裏面不存在float子元素),其餘都和BFC一樣:
- 排除外部float
- 阻止外邊距摺疊
總結
Formatting Context可以看作是某塊區域,這塊區域規定了其上元素的佈局規則。Formatting Context主要又4種,BFC、IFC、FFC和GFC。
其中BFC最為重要,當一塊元素伴隨這BFC時,會產生:
- 包含內部float
- 排除外部float
- 組織外邊距摺疊
FFC和GFC除了子孫元素沒有float之外,都和BFC一樣有2和3。
IFC跟內聯元素效果一樣,都是垂直方向外邊距無效[6]。
REFERENCE
[1] https://developer.mozilla.org...
[2] https://developer.mozilla.org...
[3] https://gitee.com/gooder4j/co...
[4] https://github.com/w3c/csswg-...
[5] https://bugs.chromium.org/p/c...
[6] https://gitee.com/gooder4j/co...