synchronized 原理分析
synchronized 是Java 提供的同步源語,它為 共享資源 提供了原子性 和 可見性保障,本文通過原子性 和 可見性 二個維度分析其實現原理
sync 原子性
通過 monitor 保證 原子性,具體表現為 monitorenter 和 monitorexit 或 ACC_SYNCHRONIZED 來實現加鎖
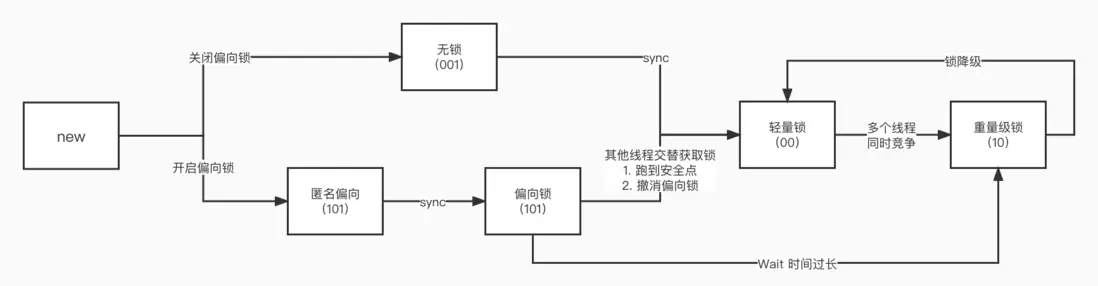
加鎖流程如下
鎖升級流程
-
new 對象時,判斷 是否開啓偏向鎖
- 開啓偏向鎖,構建匿名偏向鎖(101)
- 關閉偏向鎖,構建無鎖對象(001)
- 無鎖(001)遇到 線程加鎖時,直接加自旋鎖/輕量鎖(00)
- 偏向鎖 遇到 一個線程加鎖時,鎖狀態不變,保存線程ID
- 偏向鎖 遇到 多個線程交替加鎖時,線程跑到安全點,撤消偏向鎖,升級為自旋鎖/輕量鎖(00)
- 自旋鎖 是 每個線程通過CAS指令去更新對象頭裏面的markword,如果自旋失敗次數、或自旋等待時間過長,鎖膨脹成重量級鎖(10)
- 重量級鎖 由 ObjectMonitor 實現,需要由用户態切換到內核態
- 當競爭不激烈時,重量級鎖 自動降級為輕量鎖
monitorenter 源碼分析
CASE(_monitorenter): {
// 獲取鎖對象
oop lockee = STACK_OBJECT(-1);
// 在線程棧上找到一個空閒的BasicObjectLock對象
BasicObjectLock* limit = istate->monitor_base();
BasicObjectLock* most_recent = (BasicObjectLock*) istate->stack_base();
BasicObjectLock* entry = NULL;
while (most_recent != limit ) {
if (most_recent->obj() == NULL) entry = most_recent;
else if (most_recent->obj() == lockee) break;
most_recent++;
}
if (entry != NULL) {
// 保存鎖對象,表明當前BasicObjectLock持有鎖對象lockee
entry->set_obj(lockee);
int success = false;
uintptr_t epoch_mask_in_place = (uintptr_t)markOopDesc::epoch_mask_in_place;
markOop mark = lockee->mark(); // 獲取鎖對象的頭部標記信息
// 獲取沒有hash值的標記位值,這裏為0
intptr_t hash = (intptr_t) markOopDesc::no_hash;
// 判斷使用了偏向鎖
if (mark->has_bias_pattern()) {
uintptr_t thread_ident;
uintptr_t anticipated_bias_locking_value;
thread_ident = (uintptr_t)istate->thread(); // 獲取線程id
anticipated_bias_locking_value =
(((uintptr_t)lockee->klass()->prototype_header() | thread_ident) ^ (uintptr_t)mark) &
~((uintptr_t) markOopDesc::age_mask_in_place);
/* anticipated_bias_locking_value為0,表明還沒有批量撤銷偏向鎖,且當前線程
持有了偏向鎖,直接退出 */
if (anticipated_bias_locking_value == 0) {
// already biased towards this thread, nothing to do
if (PrintBiasedLockingStatistics) {
(* BiasedLocking::biased_lock_entry_count_addr())++;
}
success = true;
}
else if ((anticipated_bias_locking_value &
markOopDesc::biased_lock_mask_in_place) != 0) {
/* anticipated_bias_locking_value不為0,可能是批量撤銷偏向鎖,需要繼續判斷是否有
線程持有偏向鎖,如果其他線程持有偏向鎖,判定發生了衝突,就需要撤銷偏向鎖 */
markOop header = lockee->klass()->prototype_header();
if (hash != markOopDesc::no_hash) {
header = header->copy_set_hash(hash);
}
// CAS將對象頭從mark替換為header撤銷偏向鎖
if (lockee->cas_set_mark(header, mark) == mark) {
if (PrintBiasedLockingStatistics)
(*BiasedLocking::revoked_lock_entry_count_addr())++;
}
}
else if ((anticipated_bias_locking_value & epoch_mask_in_place) !=0) {
/* 如果anticipated_bias_locking_value不為0,在批量撤銷偏向鎖時需要更改
epoch的值,這裏如果epoch改變了,當前線程需要重偏向 */
markOop new_header = (markOop) ( (intptr_t) lockee->klass()->prototype_header() | thread_ident);
if (hash != markOopDesc::no_hash) {
new_header = new_header->copy_set_hash(hash);
}
// CAS重偏向
if (lockee->cas_set_mark(new_header, mark) == mark) {
if (PrintBiasedLockingStatistics)
(* BiasedLocking::rebiased_lock_entry_count_addr())++;
}
else {
// CAS失敗,發生了競爭,那麼進入monitorenter
CALL_VM(InterpreterRuntime::monitorenter(THREAD, entry), handle_exception);
}
success = true;
}
else {
/* 以上條件均不滿足,表明開啓了偏向鎖,此時偏向鎖狀態為匿名偏向,嘗試CAS
將其偏向為當前線程*/
markOop header = (markOop) ((uintptr_t) mark &
((uintptr_t)markOopDesc::biased_lock_mask_in_place |
(uintptr_t)markOopDesc::age_mask_in_place |
epoch_mask_in_place));
if (hash != markOopDesc::no_hash) {
header = header->copy_set_hash(hash);
}
markOop new_header = (markOop) ((uintptr_t) header | thread_ident);
// CAS重偏向
if (lockee->cas_set_mark(new_header, header) == header) {
if (PrintBiasedLockingStatistics)
(* BiasedLocking::anonymously_biased_lock_entry_count_addr())++;
}
else {
// CAS失敗,發生了競爭,那麼進入monitorenter
CALL_VM(InterpreterRuntime::monitorenter(THREAD, entry),
handle_exception);
}
success = true;
}
}
// 沒有獲取到鎖,那麼進入傳統的輕量級鎖
if (!success) {
markOop displaced = lockee->mark()->set_unlocked();
entry->lock()->set_displaced_header(displaced);
bool call_vm = UseHeavyMonitors; // 判斷是否直接使用重量級鎖
/* 如果沒有指定直接使用重量級鎖,那麼通過CAS操作嘗試獲取輕量級鎖,即替換
頭部指針,指向entry */
if (call_vm || lockee->cas_set_mark((markOop)entry, displaced) != displaced) {
// 如果失敗,可能是當前線程輕量級鎖重入,那麼判斷是否是鎖重入
if (!call_vm && THREAD->is_lock_owned((address) displaced->clear_lock_bits()))
{
// 輕量級鎖重入,不需要設置displaced_header信息
entry->lock()->set_displaced_header(NULL);
} else {
// 否則調用monitorenter
CALL_VM(InterpreterRuntime::monitorenter(THREAD, entry),
handle_exception);
}
}
}
UPDATE_PC_AND_TOS_AND_CONTINUE(1, -1);
} else {
// 如果未找到,設置more_monitors標誌位,由解釋器分配新的BasicObjectLock並重試
istate->set_msg(more_monitors);
UPDATE_PC_AND_RETURN(0); // Re-execute
}
}
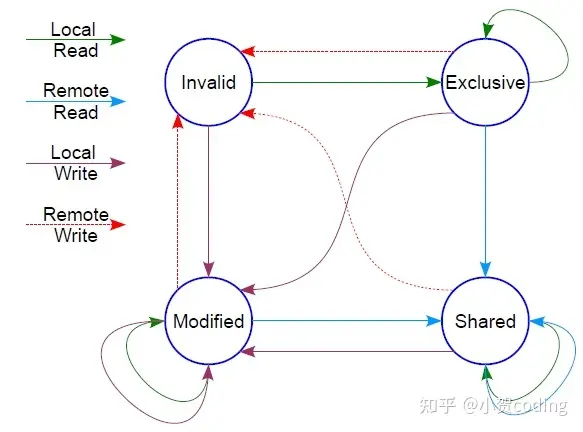
sync 可見性
sync 通過 緩存一致性協議 保證可見性
MESI
M(modified):修改
E(exclusive):獨佔
S(shared):共享
I(invalid):無效
sync 和 Lock 的區別
使用
- sync 自動加鎖、解鎖,Lock 需要手動加鎖、解鎖
功能
- Lock 支持不同的Condition(不同的等待隊列),指定喚醒
-
Lock 可以使用 tryLock 支持超時
- sync鎖 不支持超時
-
Lock 可以使用Lock.lockInterruptibly 響應中斷
- 沒有獲取到 sync鎖 的線程處於 Blocked 狀態不能響應interrupt中斷
- Lock 支持公平鎖 和 非公平鎖 ,sync 只支持非公平鎖
原理
-
sync 底層由4種不同狀態的鎖升級實現, Lock 由 AQS(state + CLH)實現,屬於樂觀鎖
- 無鎖、偏向鎖、輕量鎖都屬於用户態
- 輕量鎖 由CAS實現,屬於樂觀鎖
- 重量級鎖由 Monitor 實現,屬於悲觀鎖