在併發環境下為了解決併發一致性問題保證事務的隔離性,PostgreSQL採用了鎖的機制。當一個事務在進行操作時會對操作的數據進行加鎖,從而限制另一個事務的操作。為保證效率和想,加鎖的粒度不宜太大。加鎖的意義就在於當多個會話同時訪問數據庫的同一數據時,為所有會話提供高效的數據訪問,並同時維護嚴格的數據一致性,從而實現數據的多版本併發控制。
多版本併發控制的英文名稱是Multiversion Concurrency Control,簡稱MVCC。它是指每個SQL語句看到的都只是當前事務開始的數據快照,而不用去關心底層數據的當前狀態。這樣可以保護語句不會看到可能由其他在相同數據行上執行更新的併發事務造成的不一致數據,為每一個數據庫會話提供事務隔離。MVCC避免了傳統的數據庫系統的鎖定方法,將通過鎖爭奪最小化的方法來達到多會話併發訪問時的性能最大化目的。
PostgreSQL提供了多種類型的鎖模式用於控制對錶中數據的併發訪問。在這些鎖當中最主要的是表級鎖與行級鎖,此外還有頁級鎖、諮詢鎖等等。下面將重點介紹表級鎖與行級鎖。視頻講解如下:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1DZSrBtEZJ/?aid=115642531323...
一、 表級鎖
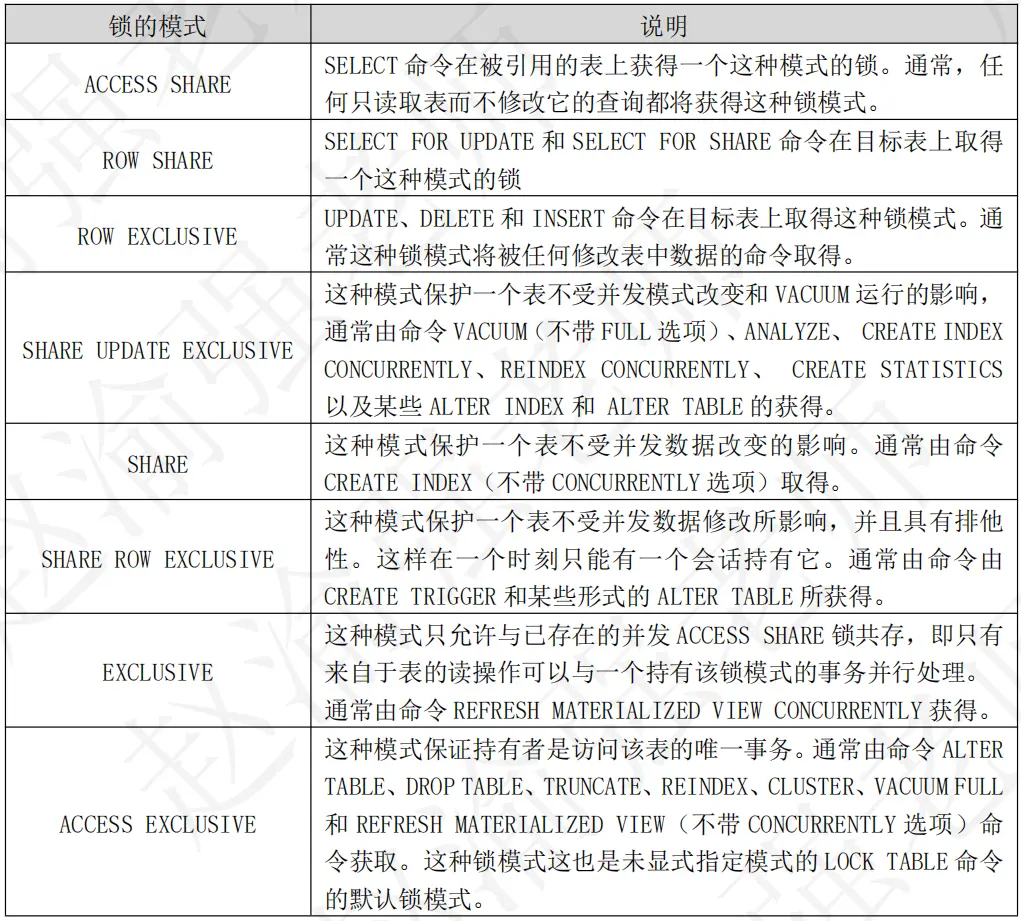
表級鎖通常會在執行各種命令執行時自動獲取,或者通過在事務中使用lock語句顯式獲取,每種表級鎖都有自己的衝突集合。兩個事務在同一時刻不能在同一個表上持有屬於相互衝突模式的鎖,但可以持有不衝突的鎖。PostgreSQL的表級鎖總共有八種模式,並存儲在PostgreSQL的共享內存中。下表詳細説明了這八種PostgreSQL表級鎖。
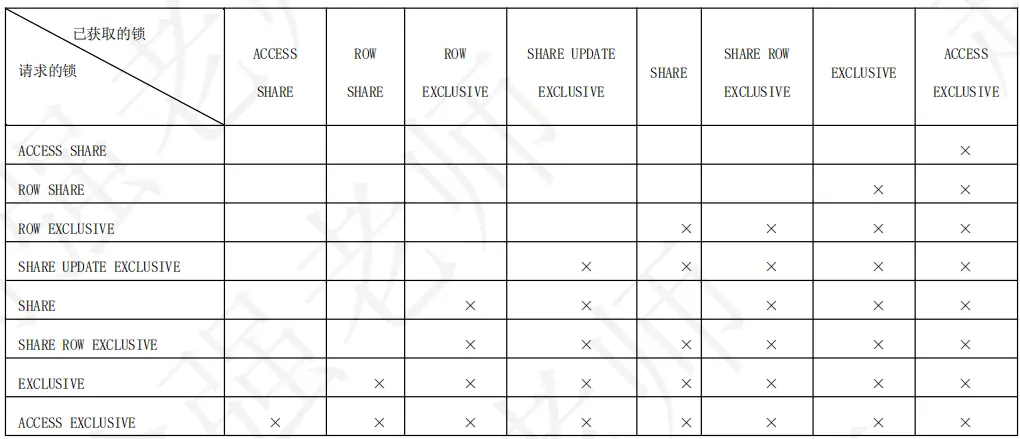
這八種表級鎖彼此之間存在一定的衝突,下表説明了它們之間的衝突關係。
在PostgreSQL數據庫中可以通過pg_locks系統視圖查詢表上已經獲取到的表級鎖信息,下面通過一個具體的示例來説明。
(1)在會話一中查看當前數據庫中的表,並查看錶testtable1的結構。
postgres=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------+-------+----------
public | testtable1 | table | postgres
(1 row)
postgres=# \d testtable1;
Table "public.testtable1"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default
--------+---------+-----------+----------+---------
tid | integer | | not null |
tname | text | | |
Indexes:
"testtable1_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (tid)
Tablespace: "mydemotbs"(2)查看錶testtable1的oid。
postgres=# select oid,relname,relkind,relfilenode from pg_class
postgres-# where relname ='testtable1';
oid | relname | relkind | relfilenode
-------+------------+---------+-------------
16395 | testtable1 | r | 16395
(1 row)(3)在會話一中開啓一個事務並執行一條update語句。
postgres=# start transaction;
postgres=*# update testtable1 set tname='Tom123' where tid=1;
# 這裏執行的事務沒有結束。(4)在會話二中更改表testtable1的結構,如:添加一個新的列。
postgres=# alter table testtable1 add dno int;
# 此時會話二的操作將會被阻塞。(5)在會話三中查看錶testtable1上的鎖信息。
postgres=# \x
postgres=# select * from pg_locks where relation = 16395;
# 這裏的“\x”表示將輸出結果進行豎式顯示。
# 輸出的結果如下:
-[ RECORD 1 ]------+--------------------
locktype | relation
database | 13580
relation | 16395
page |
tuple |
virtualxid |
transactionid |
classid |
objid |
objsubid |
virtualtransaction | 4/401
pid | 41381
mode | AccessExclusiveLock
granted | f
fastpath | f
-[ RECORD 2 ]------+--------------------
locktype | relation
database | 13580
relation | 16395
page |
tuple |
virtualxid |
transactionid |
classid |
objid |
objsubid |
virtualtransaction | 3/644
pid | 40920
mode | RowExclusiveLock
granted | t
fastpath | f
# 從輸出的結果可以看出,此時表testtable1上有兩把表級鎖,
# 分別是:AccessExclusiveLock和RowExclusiveLock。
# 但此時並不能觀察到會話之間的阻塞。(6)執行語句檢查鎖的等待,即:會話之間的阻塞信息。
postgres=# with
t_wait as
(
select
a.mode,a.locktype,a.database,a.relation,a.page,a.tuple,
a.classid,a.granted,a.objid,a.objsubid,a.pid,
a.virtualtransaction,a.virtualxid,a.transactionid,a.fastpath,
b.state,b.query,b.xact_start,b.query_start,b.usename,
b.datname,b.client_addr,b.client_port,b.application_name
from pg_locks a,pg_stat_activity b where a.pid=b.pid and not a.granted
),
t_run as
(
select
a.mode,a.locktype,a.database,a.relation,a.page,a.tuple,
a.classid,a.granted,a.objid,a.objsubid,a.pid,
a.virtualtransaction,a.virtualxid,a.transactionid,a.fastpath,
b.state,b.query,b.xact_start,b.query_start,b.usename,
b.datname,b.client_addr,b.client_port,b.application_name
from pg_locks a,pg_stat_activity b where a.pid=b.pid and a.granted
),
t_overlap as
(
select r.* from t_wait w join t_run r on
(
r.locktype is not distinct from w.locktype and
r.database is not distinct from w.database and
r.relation is not distinct from w.relation and
r.page is not distinct from w.page and
r.tuple is not distinct from w.tuple and
r.virtualxid is not distinct from w.virtualxid and
r.transactionid is not distinct from w.transactionid and
r.classid is not distinct from w.classid and
r.objid is not distinct from w.objid and
r.objsubid is not distinct from w.objsubid and
r.pid <> w.pid
)
),
t_unionall as
(
select r.* from t_overlap r
union all
select w.* from t_wait w
)
select
locktype,datname,relation::regclass,page,tuple,
virtualxid,transactionid::text,classid::regclass,
objid,objsubid,
string_agg(
'Pid: '
||case when pid is null
then 'NULL' else pid::text end||chr(10)||'Lock_Granted: '
||case when granted is null
then 'NULL' else granted::text end||' , Mode: '
||case when mode is null
then 'NULL' else mode::text end||' , FastPath: '
||case when fastpath is null
then 'NULL' else fastpath::text end||' , VirtualTransaction: '
||case when virtualtransaction is null
then 'NULL' else virtualtransaction::text end||' , Session_State: '
||case when state is null
then 'NULL' else state::text end||chr(10)||'Username: '
||case when usename is null
then 'NULL' else usename::text end||' , Database: '
||case when datname is null
then 'NULL' else datname::text end||' , Client_Addr: '
||case when client_addr is null
then 'NULL' else client_addr::text end||' , Client_Port: '
||case when client_port is null
then 'NULL' else client_port::text end||' , Application_Name: '
||case when application_name is null
then 'NULL' else application_name::text end
||chr(10)||'Xact_Start: '
||case when xact_start is null
then 'NULL' else xact_start::text end||' , Query_Start: '
||case when query_start is null
then 'NULL' else query_start::text end||' , Xact_Elapse: '
||case when (now()-xact_start) is null
then 'NULL' else (now()-xact_start)::text end||' , Query_Elapse: '
||case when (now()-query_start) is null
then 'NULL' else (now()-query_start)::text end
||chr(10)||'SQL (Current SQL in Transaction): '||chr(10)
||case when query is null then 'NULL' else query::text end,chr(10)
||'--------'||chr(10)
order by
( case mode
when 'INVALID' then 0
when 'AccessShareLock' then 1
when 'RowShareLock' then 2
when 'RowExclusiveLock' then 3
when 'ShareUpdateExclusiveLock' then 4
when 'ShareLock' then 5
when 'ShareRowExclusiveLock' then 6
when 'ExclusiveLock' then 7
when 'AccessExclusiveLock' then 8
else 0
end ) desc,
(case when granted then 0 else 1 end)
) as lock_conflict
from t_unionall
group by locktype,datname,relation,page,tuple,virtualxid,
transactionid::text,classid,objid,objsubid;
# 輸出的結果如下:
-[ RECORD 1 ]-+------------------------------------------------------
locktype | relation
datname | postgres
relation | testtable1
page |
tuple |
virtualxid |
transactionid |
classid |
objid |
objsubid |
lock_conflict
| Pid: 41381
| Lock_Granted: false , Mode: AccessExclusiveLock , ...
| SQL (Current SQL in Transaction):
| alter table testtable1 add dno int;
| --------
| Pid: 40920
| Lock_Granted: true , Mode: RowExclusiveLock , ...
| SQL (Current SQL in Transaction):
| update testtable1 set tname='Tom123' where tid=1;
# 通過這裏輸出的信息可以看到阻塞的進程ID號,以及發生等待的SQL語句。(7)在會話一執行結束事務操作。
postgres=*# commit;
# 此時會話二將成功執行。(8)重新在會話三中查看錶testtable1上的鎖信息,此時將沒有任何鎖的信息輸出。
postgres=# select * from pg_locks where relation = 16395;二、 行級鎖
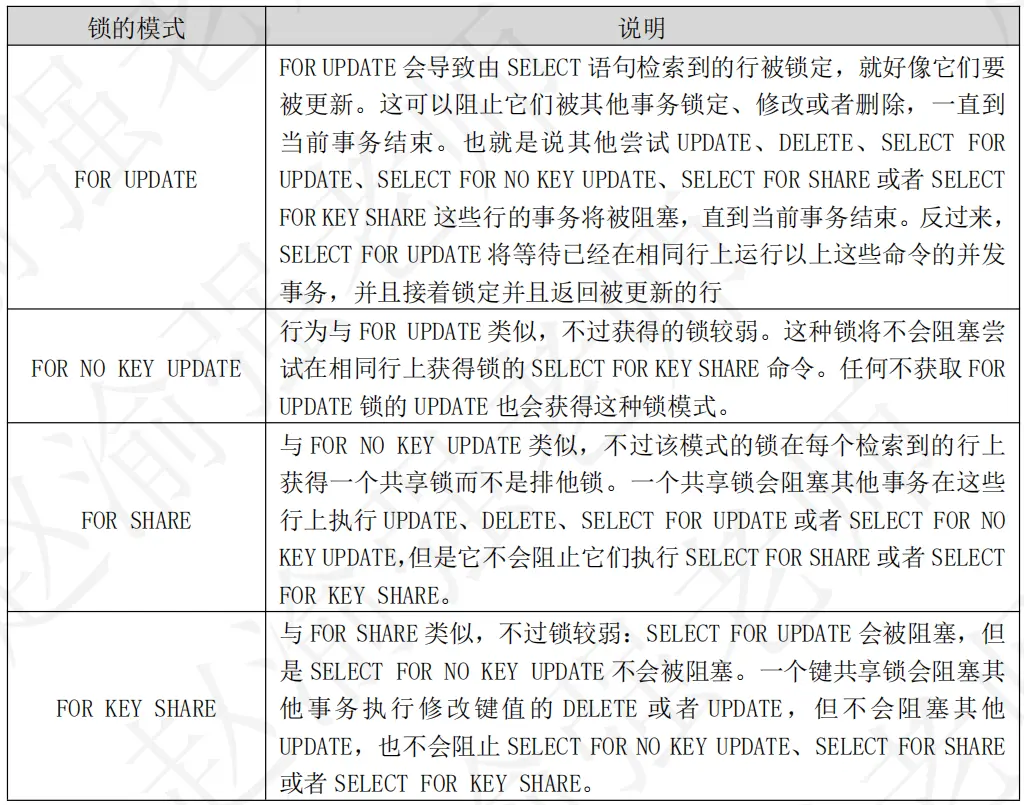
同一個事務可能會在相同的行上保持衝突的鎖。但是除此之外,兩個事務永遠不可能在相同的行上持有衝突的鎖。PostgreSQL行級鎖不影響數據查詢,它們只阻塞對同一行的寫入者和加鎖者。行級鎖在事務結束時或保存點回滾的時候釋放,就像表級鎖一樣。PostgreSQL行級鎖支持以下四種不同的模式,如下表所示。
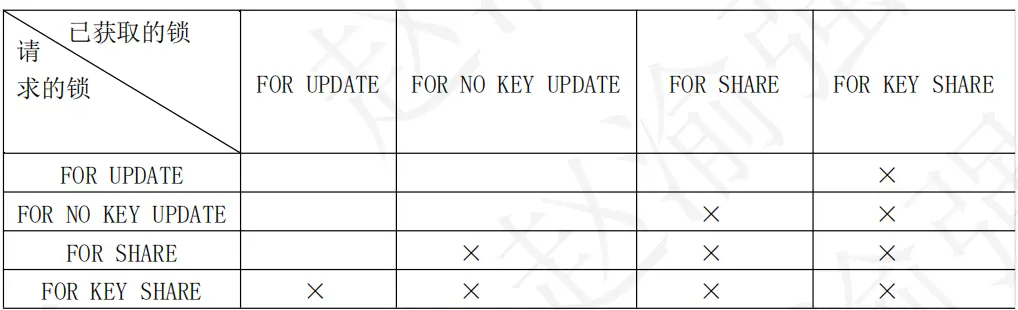
這四種行級鎖彼此之間存在一定的衝突,下表説明了它們之間的衝突關係。
×表示存在相互之間的衝突。
在PostgreSQL中可以通過查詢pg_locks的系統視圖來獲取行級鎖的相關信息。下面展示了該系統視圖的結構。
postgres=# \d pg_locks;
View "pg_catalog.pg_locks"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default
--------------------+----------+-----------+----------+---------
locktype | text | | |
database | oid | | |
relation | oid | | |
page | integer | | |
tuple | smallint | | |
virtualxid | text | | |
transactionid | xid | | |
classid | oid | | |
objid | oid | | |
objsubid | smallint | | |
virtualtransaction | text | | |
pid | integer | | |
mode | text | | |
granted | boolean | | |
fastpath | boolean | | |