React系列
React系列 --- 簡單模擬語法(一)
React系列 --- Jsx, 合成事件與Refs(二)
React系列 --- virtualdom diff算法實現分析(三)
React系列 --- 從Mixin到HOC再到HOOKS(四)
React系列 --- createElement, ReactElement與Component部分源碼解析(五)
React系列 --- 從使用React瞭解Css的各種使用方案(六)
React系列 --- 從零構建狀態管理及Redux源碼解析(七)
React系列 --- 擴展狀態管理功能及Redux源碼解析(八)
完整代碼可查看virtualdom-diff
渲染DOM
經歷過PHP模板開發或者JQuery的洗禮的人都知道,它們實現重新渲染採用最簡單粗暴的辦法就是重新構建DOM替換舊DOM,問題也很明顯
- 性能消耗高
- 無法保存狀態(聚焦,滾動等)
我們先看看創建一個元素所包含的實例屬性有多少個
const div = document.createElement('div');
let num = 0;
for (let k in div) {
num++;
}
console.log(num); // 241然後瀏覽器根據CSS規則查找匹配節點,計算合併樣式佈局,為了避免重新計算一般瀏覽器會保存這些數據.但這是整個過程下來依然會耗費大量的內存和 CPU 資源.
Virtual DOM
實際也是操作Dom樹進行渲染更新,但是它只是針對修改部分進行局部渲染,將影響降到最低,雖然實現方式各有不同,但是大體步驟如下:
- 用Javascript對象結構描述Dom樹結構,然後用它來構建真正的Dom樹插入文檔
- 當狀態發生改變之後,重新構造新的Javascript對象結構和舊的作對比得出差異
- 針對差異之處進行重新構建更新視圖
無非就是利用Js做一層映射比較,操作簡單並且速度遠遠高於直接比較Dom樹
基礎工具函數
無非就是一些類型判斷,循環遍歷的簡化函數
function type(obj) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj).replace(/\[object\s|\]/g, "");
}
function isArray(list) {
return type(list) === "Array";
}
function isObject(obj) {
return type(obj) === "Object";
}
function isString(str) {
return type(str) === "String";
}
function isNotEmptyObj(obj) {
return isObject(obj) && JSON.stringify(obj) != "{}";
}
function objForEach(obj, fn) {
isNotEmptyObj(obj) && Object.keys(obj).forEach(fn);
}
function aryForEach(ary, fn) {
ary.length && ary.forEach(fn);
}
function setAttr(node, key, value) {
switch (key) {
case "style":
node.style.cssText = value;
break;
case "value":
var tagName = node.tagName || "";
tagName = tagName.toLowerCase();
if (tagName === "input" || tagName === "textarea") {
node.value = value;
} else {
// if it is not a input or textarea, use `setAttribute` to set
node.setAttribute(key, value);
}
break;
default:
node.setAttribute(key, value);
break;
}
}
function toArray(data) {
if (!data) {
return [];
}
const ary = [];
aryForEach(data, item => {
ary.push(item);
});
return ary;
}
export {
isArray,
isObject,
isString,
isNotEmptyObj,
objForEach,
aryForEach,
setAttr,
toArray
};相關代碼可以查看util.js
Javascript對象結構描述
我之前講JSX的時候舉過這麼個例子,然後我們就以這個來實現效果吧
<div className="num" index={1}>
<span>123456</span>
</div>"use strict";
React.createElement("div", {
className: "num",
index: 1
}, React.createElement("span", null, "123456"));創建一個Element類負責將Javascript對象結構轉換為Dom樹結構
import {
isObject,
isString,
isArray,
isNotEmptyObj,
objForEach,
aryForEach
} from "./util";
import { NOKEY } from "./common";
class Element {
constructor(tagName, props, children) {
// 解析參數
this.tagName = tagName;
// 字段處理,可省略參數
this.props = isObject(props) ? props : {};
this.children =
children ||
(!isNotEmptyObj(this.props) &&
((isString(props) && [props]) || (isArray(props) && props))) ||
[];
// 無論void後的表達式是什麼,void操作符都會返回undefined
this.key = props ? props.key : void NOKEY;
// 計算節點數
let count = 0;
aryForEach(this.children, (item, index) => {
if (item instanceof Element) {
count += item.count;
} else {
this.children[index] = "" + item;
}
count++;
});
this.count = count;
}
render() {
// 根據tagName構建
const dom = document.createElement(this.tagName);
// 設置props
objForEach(this.props, propName =>
dom.setAttribute(propName, this.props[propName])
);
// 渲染children
aryForEach(this.children, child => {
const childDom =
child instanceof Element
? child.render() // 如果子節點也是虛擬DOM,遞歸構建DOM節點
: document.createTextNode(child); // 如果字符串,只構建文本節點
dom.appendChild(childDom);
});
return dom;
}
}
// 改變傳參方式,免去手動實例化
export default function CreateElement(tagName, props, children) {
return new Element( tagName, props, children );
}
新建示例,調用方式如下
// 1. 構建虛擬DOM
const tree = createElement("div", { id: "root" }, [
createElement("h1", { style: "color: blue" }, ["Tittle1"]),
createElement("p", ["Hello, virtual-dom"]),
createElement("ul", [
createElement("li", { key: 1 }, ["li1"]),
createElement("li", { key: 2 }, ["li2"]),
createElement("li", { key: 3 }, ["li3"]),
createElement("li", { key: 4 }, ["li4"])
])
]);
// 2. 通過虛擬DOM構建真正的DOM
const root = tree.render();
document.body.appendChild(root);運行之後能正常得出結果了,那麼第一步驟算是完成了,具體還有更多不同類型標籤,對應事件狀態先略過.
界面如圖
Javascript結構如圖
結構原型如下
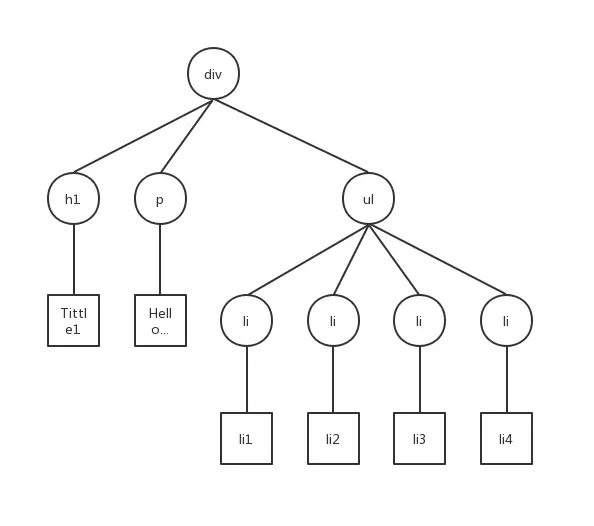
相關代碼可以查看element.js
diff算法
這是整個實現裏面最關鍵的一步,因為這決定了計算的速度和操作Dom的數量
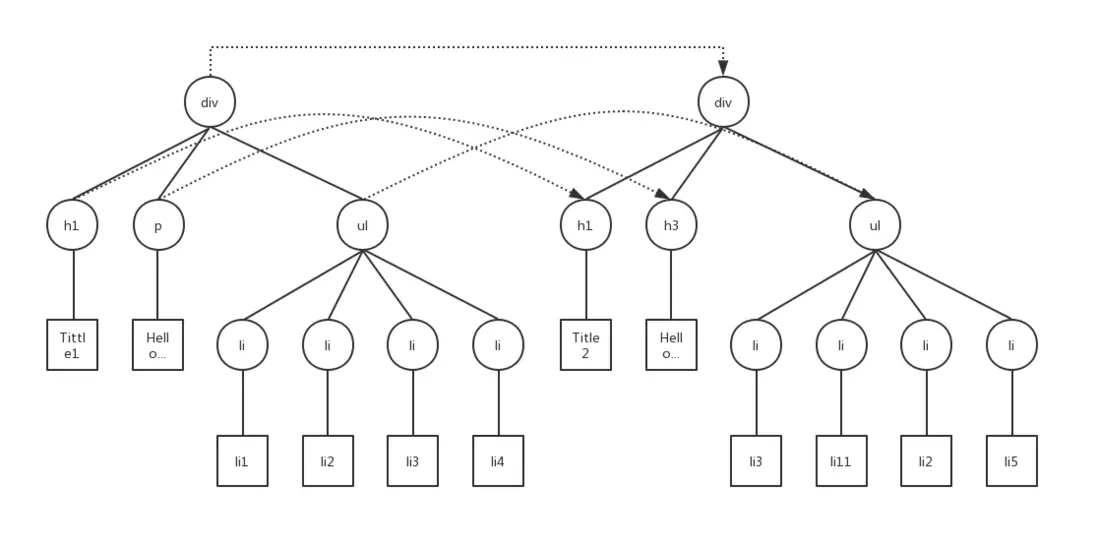
我們創建新的Dom樹作對比
// 3. 生成新的虛擬DOM
const newTree = createElement("div", { id: "container" }, [
createElement("h1", { style: "color: red" }, ["Title2"]),
createElement("h3", ["Hello, virtual-dom"]),
createElement("ul", [
createElement("li", { key: 3 }, ["li3"]),
createElement("li", { key: 1 }, ["li1"]),
createElement("li", { key: 2 }, ["li2"]),
createElement("li", { key: 5 }, ["li5"])
])
]);Javascript結構如圖
tree diff
傳統 diff 算法的複雜度為 O(n^3),但是一般Dom跨層級的情況是非常少見的。所以React 只針對同層級Dom節點做比較,將 O(n^3) 複雜度的問題轉換成 O(n) 複雜度的問題。
比較大的問題就是當節點跨層級移動並不會進行移動而是直接替換整個節點,所以切記這點性能問題
component diff
- 某個組件發生變化,會導致自其從上往下整體替換
- 同一類型組件會進行Virtual DOM進行比較
- React提供了一個
shouldComponentUpdate決定是否更新
儘可能將動態組件往底層節點遷移,有利於提高性能
element diff
元素操作無非就是幾種,我們定義幾個類型做狀態標記
const REPLACE = "replace";
const REORDER = "reorder";
const PROPS = "props";
const TEXT = "text";
const NOKEY = "no_key"
export {
REPLACE,
REORDER,
PROPS,
TEXT,
NOKEY
}其中NOKEY就是專門給那些沒有定義key的組件做默認,React對同一層級的同組子節點,添加唯一 key 進行區分進行位移而不是直接替換,這點對於整體性能尤為關鍵
我們首先針對不同類型做些區分處理
import { isString, objForEach, aryForEach, isNotEmptyObj } from "./util";
import { REPLACE, REORDER, PROPS, TEXT } from "./common";
import listDiff from "list-diff2";
/**
*
* @param {舊Dom樹} oTree
* @param {新Dom樹} nTree
* 返回差異記錄
*/
function diff(oTree, nTree) {
// 節點位置
let index = 0;
// 差異記錄
const patches = {};
dfsWalk(oTree, nTree, index, patches);
return patches;
}
function dfsWalk(oNode, nNode, index, patches) {
const currentPatch = [];
// 首次渲染
if (nNode === null) return;
// 都是字符串形式並且不相同直接替換文字
if (isString(oNode) && isString(nNode)) {
oNode !== nNode &&
currentPatch.push({
type: TEXT,
content: nNode
});
// 同種標籤並且key相同
} else if (oNode.tagName === nNode.tagName && oNode.key === nNode.key) {
// 至少一方有值
if (isNotEmptyObj(oNode.props) || isNotEmptyObj(nNode.props)) {
// 計算props結果
const propsPatches = diffProps(oNode, nNode);
// 有差異則重新排序
propsPatches &&
currentPatch.push({
type: PROPS,
props: propsPatches
});
}
// children對比
if (
!(!isNotEmptyObj(nNode.props) && nNode.props.hasOwnProperty("ignore"))
) {
(oNode.children.length || nNode.children.length) &&
diffChildren(
oNode.children,
nNode.children,
index,
patches,
currentPatch
);
}
} else {
// 都不符合上面情況就直接替換
currentPatch.push({ type: REPLACE, node: nNode });
}
// 最終對比結果
currentPatch.length && (patches[index] = currentPatch);
}新舊節點的props屬性比較
/**
*
* @param {舊節點} oNode
* @param {新節點} nNode
*/
function diffProps(oNode, nNode) {
let isChange = false;
const oProps = oNode.props;
const nProps = nNode.props;
// 節點屬性記錄
const propsPatched = {};
// 替換/新增屬性
objForEach(oProps, key => {
if (nProps[key] !== oProps[key] || !oProps.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
!isChange && (isChange = true);
propsPatched[key] = nProps[key];
}
});
return !isChange ? null : propsPatched;
}新舊節點的子元素對比
/**
* 同級對比
* @param {*} oChildren
* @param {*} nChildren
* @param {*} index
* @param {*} patches
* @param {*} currentPatch
*/
function diffChildren(oChildren, nChildren, index, patches, currentPatch) {
// 得出相對簡化移動路徑
const diffs = listDiff(oChildren, nChildren, "key");
// 保留元素
nChildren = diffs.children;
// 記錄排序位移
diffs.moves.length &&
currentPatch.push({ type: REORDER, moves: diffs.moves });
// 深度遍歷
let leftNode = null;
let currentNodeIndex = index;
aryForEach(oChildren, (_item, _index) => {
const nChild = nChildren[_index];
currentNodeIndex =
leftNode && leftNode.count
? currentNodeIndex + leftNode.count + 1
: currentNodeIndex + 1;
_item !== nChild && dfsWalk(_item, nChild, currentNodeIndex, patches);
leftNode = _item;
});
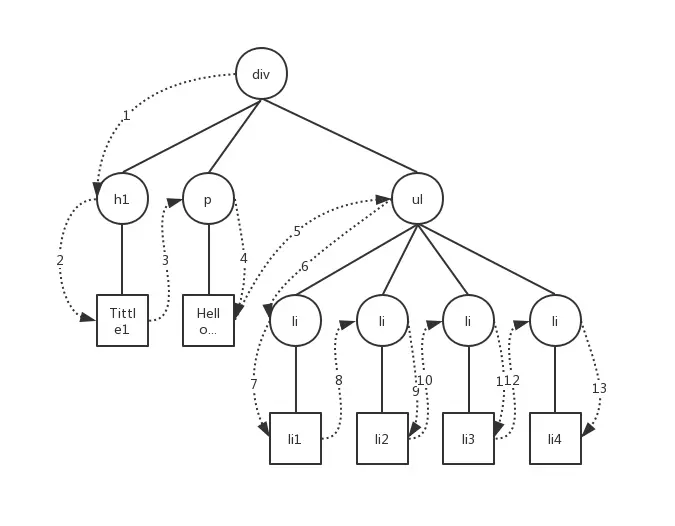
}深度遍歷的原型圖如下
其中的listDiff來自於list-diff,能通過關鍵屬性獲得最小移動量,moves就是給第三步更新視圖做鋪墊指示,官方介紹如下
Diff two lists in time O(n). I The algorithm finding the minimal amount of moves is Levenshtein distance which is O(n*m). This algorithm is not the best but is enougth for front-end DOM list manipulation.
This project is mostly influenced by virtual-dom algorithm.
調用對比方式
// 4. 比較兩棵虛擬DOM樹的不同
const patches = diff(tree, newTree);得出差異如下

相關代碼可以查看diff.js
更新視圖
進行深度遍歷
import {
isString,
isObject,
objForEach,
aryForEach,
setAttr,
toArray
} from "./util";
import { REPLACE, REORDER, PROPS, TEXT, NOKEY } from "./common";
function patch(node, patches) {
const walker = { index: 0 };
dfsWalk(node, walker, patches);
}
// 深度遍歷更新
function dfsWalk(node, walker, patches) {
const currentPatches = patches[walker.index];
node.childNodes &&
aryForEach(node.childNodes, item => {
walker.index++;
dfsWalk(item, walker, patches);
});
currentPatches && applyPatches(node, currentPatches);
}針對不同標誌做對應處理
// 更新類型
function applyPatches(node, currentPatches) {
aryForEach(currentPatches, item => {
switch (item.type) {
case REPLACE:
const nNode = isString(item.node)
? document.createTextNode(item.node)
: item.node.render();
node.parentNode.replaceChild(nNode, node);
break;
case REORDER:
reorderChildren(node, item.moves);
break;
case PROPS:
setProps(node, item.props);
break;
case TEXT:
if (node.textContent) {
// 使用純文本
node.textContent = item.content;
} else {
// 僅僅對CDATA片段,註釋comment,Processing Instruction節點或text節點有效
node.nodeValue = item.content;
}
break;
default:
throw new Error("Unknown patch type " + item.type);
}
});
}先説簡單的屬性替換
// 修改屬性
function setProps(node, props) {
objForEach(props, key => {
if (props[key] === void NOKEY) {
node.removeAttribute(key);
} else {
setAttr(node, key, props[key]);
}
});
}最後就是列表渲染
// 列表排序渲染
function reorderChildren(node, moves) {
const staticNodeList = toArray(node.childNodes);
const maps = {};
aryForEach(staticNodeList, node => {
// Element
if (node.nodeType === 1) {
const key = node.getAttribute("key");
key && (maps[key] = node);
}
});
aryForEach(moves, move => {
const index = move.index;
// 0:刪除 1:替換
if (move.type === 0) {
// 找到對應節點刪除
staticNodeList[index] === node.childNodes[index] &&
node.removeChild(node.childNodes[index]);
staticNodeList.splice(index, 1);
} else if (move.type === 1) {
let insertNode;
if (maps[move.item.key]) {
// 刪除並返回節點
insertNode = node.removeChild(maps[move.item.key]);
// 獲取刪除節點位置
staticNodeList.splice(Array.prototype.indexOf.call(node.childNodes, maps[move.item.key]), 1);
} else {
// 創建節點
insertNode = isObject(move.item)
? move.item.render()
: document.createTextNode(move.item);
}
// 同步staticNodeList信息
staticNodeList.splice(index, 0, insertNode);
// 操作Dom
node.insertBefore(insertNode, node.childNodes[index] || null);
}
});
}
export default patch;當這一步完成以後我們可以直接應用查看效果
// 4. 比較兩棵虛擬DOM樹的不同
const patches = diff(tree, newTree);
// 5. 在真正的DOM元素上應用變更
patch(root, patches);
結果如圖

相關代碼可以查看patch.js
參考
深度剖析:如何實現一個 Virtual DOM 算法