首先感謝兩個恩師,我願稱之為簡體中文互聯網最好的TensorRT教程:
鏈接1
鏈接2
本文的環境是Jetson Orin Nano 安裝的Jetpack版本是6.2.1,包含CUDA12.6,cuDNN 9.3.0,TensorRT 10.3.0,部署的模型是YOLO,對於其他環境,我也會簡單介紹一下如何選擇合適的版本。
1 TensorRT簡介
TensorRT是英偉達推出的一個高性能深度學習推理引擎,專門針對NVIDIA GPU進行了優化,能夠顯著提升深度學習模型在NVIDIA GPU上的推理速度和效率。將模型轉換為TensoRT的engine格式後,藉助TensorRT Runtime,可以實現更快的推理速度,更小的打包體積。TensorRT是以C++閉源構建的,支持以Python和C++以API形式調用。
2 TensorRT版本選擇
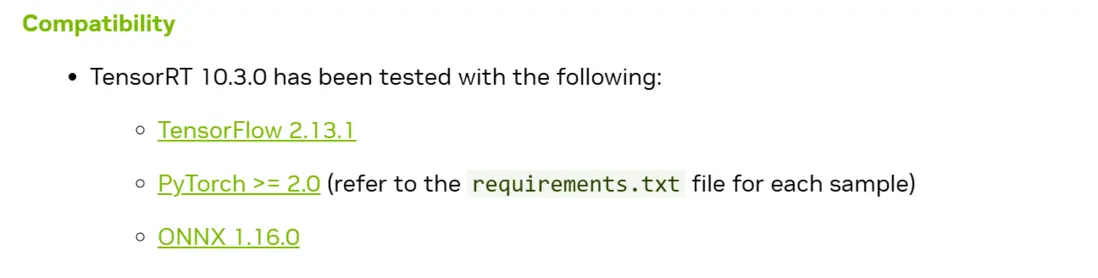
TensorRT和CUDA/cuDNN/ONNX版本有很強的耦合性,由於英偉達官方文檔比較零散,並沒有一個所有版本的對應表格,最新版本的對應信息可以在鏈接中查看,老版本需要藉助搜索引擎搜索了。 我檢索到了10.3.0版本的對應表格如下:
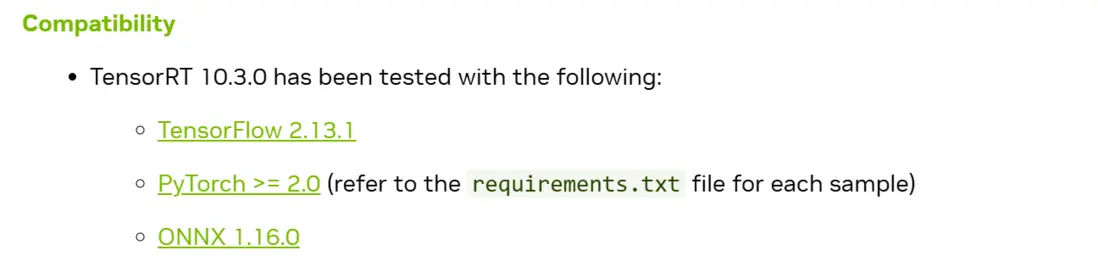
這裏可能有的讀者會疑惑為什麼需要ONNX版本呢,因為TensorRT是不支持直接從Pytorch的pth模型導出的,必須經過中間格式ONNX來導出TensorRT的engine文件。
我的cuda,和cudnn都是Jetpack打包好的,應該不會出現問題,這裏有一個可能出錯的地方就是我服務器端ONNX版本是1.16.3的,ONNX是向下兼容的,所以可能打包的模型出現問題。
3 Engine文件轉換
❕注意事項:TensorRT是硬件相關的,不像ONNX是平台無關的格式,TensorRT生成的plan文件是和具體的GPU型號綁定的,不能跨平台或者跨TensorRT版本使用。如果想在不同GPU上運行,需要重新針對具體GPU進行構建。
The generated plan files are not portable across platforms or TensorRT versions. Plans are specific to the exact GPU model they were built on (in addition to platforms and the TensorRT version) and must be re-targeted to the specific GPU in case you want to run them on a different GPU
也就是説如果我們想在Jetson Nano上運行TensorRT的engine文件,我們必須在Jetson Nano上邊生成這個engine文件,不能在服務器上生成再拷貝過去。
在生成前依然需要配置一些環境,我是通過Python API來生成engine文件的,雖然我們已經安裝了TensorRT的軟件包,但是沒有和我的anaconda虛擬環境綁定起來,需要手動配置一下,配置命令如下:
## 首先找到我們的tensorRT安裝路徑
find /usr -name "tensorrt" -type d 2>/dev/null | head -10
## 將安裝路徑寫入到虛擬環境的pth文件中 這樣python的解釋器就知道去哪裏找我們的TensorRT了
echo "/usr/lib/python3.10/dist-packages" > /home/lzz/miniconda3/envs/yolo310/lib/python3.10/site-packages/tensorrt.pth環境配置好後,可以用YOLO官方的庫去生成Engine,不過都是一樣的需要在Jetson上去運行,我看了他們的實現也是先轉的ONNX在轉Engine,我直接讓Ai寫了個ONNX轉TensorRT Engine的命令,這樣就不需要安裝YOLO的環境了,命令如下:
import tensorrt as trt
import os
def build_engine(onnx_file_path, engine_file_path, fp16_mode=True, max_workspace_size=4):
"""
使用 TensorRT API 將 ONNX 轉換為 Engine
Args:
onnx_file_path: ONNX 模型路徑
engine_file_path: 輸出的 engine 文件路徑
fp16_mode: 是否使用 FP16 精度(Orin Nano 支持,速度更快)
max_workspace_size: 最大工作空間大小(GB)
"""
# 創建 logger
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
# 創建 builder
builder = trt.Builder(logger)
# 創建網絡定義(顯式 batch)
network = builder.create_network(
1 << int(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH)
)
# 創建 ONNX 解析器
parser = trt.OnnxParser(network, logger)
# 解析 ONNX 文件
print(f"Loading ONNX file from path {onnx_file_path}...")
with open(onnx_file_path, 'rb') as model:
if not parser.parse(model.read()):
print('ERROR: Failed to parse the ONNX file.')
for error in range(parser.num_errors):
print(parser.get_error(error))
return None
print(f"ONNX file loaded successfully. Building TensorRT engine...")
# 創建 builder 配置
config = builder.create_builder_config()
# 設置工作空間大小
config.set_memory_pool_limit(
trt.MemoryPoolType.WORKSPACE,
max_workspace_size * (1 << 30) # 轉換為字節
)
# 啓用 FP16 模式(Orin Nano 支持)
if fp16_mode and builder.platform_has_fast_fp16:
config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag. FP16)
print("FP16 mode enabled")
# 構建 engine
print("Building engine... This may take a few minutes.")
serialized_engine = builder.build_serialized_network(network, config)
if serialized_engine is None:
print("Failed to build engine")
return None
# 保存 engine 到文件
print(f"Saving engine to {engine_file_path}")
with open(engine_file_path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(serialized_engine)
print("Engine built and saved successfully!")
return engine_file_path
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
onnx_path = "best.onnx"
engine_path = "best.engine"
build_engine(
onnx_file_path=onnx_path,
engine_file_path=engine_path,
fp16_mode=False # 不使用 FP16 加速
)成功運行,幾分鐘後就產生了Engine文件。
 4 TensorRT推理
4 TensorRT推理
推理也是直接讓Ai寫了個代碼,注意還需要加入Pycuda的包來管理顯存,完整代碼如下:
import tensorrt as trt
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import pycuda.autoinit
import numpy as np
import cv2
def preproc(image, input_size, mean=None, std=None):
"""
預處理圖像:調整大小並歸一化(參考 runtimeOnnx.py)
:param image: 輸入圖像 (RGB格式)
:param input_size: 目標尺寸 (height, width)
:param mean: 均值(未使用)
:param std: 標準差(未使用)
:return: 處理後的圖像和縮放比例
"""
# 直接 resize 到目標尺寸
img = cv2.resize(image, (input_size[1], input_size[0]))
# 歸一化到 [0, 1]
img = img.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
# 轉換為 CHW 格式 (channels, height, width)
img = np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1))
# 添加 batch 維度
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img, dtype=np.float32)
# 計算縮放比例(用於後處理還原座標)
img_h, img_w = image.shape[:2]
ratio_h = input_size[0] / img_h
ratio_w = input_size[1] / img_w
return img, (ratio_h, ratio_w)
def vis(img, boxes, scores, cls_ids, conf=0.25, class_names=None):
"""
可視化檢測結果
:param img: 原始圖像
:param boxes: 邊界框 [[x1, y1, x2, y2], ...]
:param scores: 置信度分數
:param cls_ids: 類別ID
:param conf: 置信度閾值
:param class_names: 類別名稱列表
:return: 繪製了檢測結果的圖像
"""
for i in range(len(boxes)):
box = boxes[i]
cls_id = int(cls_ids[i])
score = scores[i]
if score < conf:
continue
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, box)
# 繪製邊界框
color = (_COLORS[cls_id] * 255).astype(np.uint8).tolist()
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
# 繪製標籤
text = f'{class_names[cls_id] if class_names else cls_id}: {score:.2f}'
txt_color = (0, 0, 0) if np.mean(_COLORS[cls_id]) > 0.5 else (255, 255, 255)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
txt_size = cv2.getTextSize(text, font, 0.5, 2)[0]
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1 - txt_size[1] - 4), (x1 + txt_size[0], y1), color, -1)
cv2.putText(img, text, (x1, y1 - 2), font, 0.5, txt_color, thickness=1)
return img
# 為每個類別生成顏色
np.random.seed(0)
_COLORS = np.random.uniform(0, 1, size=(80, 3))
class BaseEngine(object):
def __init__(self, engine_path, imgsz=(640, 640)):
"""
初始化模型引擎。
:param engine_path: 模型引擎的路徑。
:param imgsz: 圖像的大小,默認為 (640, 640)。
"""
self.imgsz = imgsz
self.mean = None
self.std = None
# 目標類別的名稱列表
self.class_names = [
'person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush'
]
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
# 初始化 TensorRT 插件
trt.init_libnvinfer_plugins(logger, '')
runtime = trt.Runtime(logger)
# 讀取模型引擎
with open(engine_path, "rb") as f:
serialized_engine = f.read()
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(serialized_engine)
self.engine = engine # 保存 engine 引用
self.context = engine.create_execution_context()
self.inputs, self.outputs, self.bindings = [], [], []
self.stream = cuda.Stream()
# 為每個 binding 創建 host 和 device 內存
# 兼容新版 TensorRT API (10.x+)
num_io_tensors = engine.num_io_tensors
for i in range(num_io_tensors):
tensor_name = engine.get_tensor_name(i)
shape = engine.get_tensor_shape(tensor_name)
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_tensor_dtype(tensor_name))
# 計算大小
size = trt.volume(shape)
# 創建 host 和 device 內存
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, dtype)
device_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
self.bindings.append(int(device_mem))
# 判斷是輸入還是輸出
if engine.get_tensor_mode(tensor_name) == trt.TensorIOMode.INPUT:
self.inputs.append({'host': host_mem, 'device': device_mem, 'name': tensor_name})
else:
self.outputs.append({'host': host_mem, 'device': device_mem, 'name': tensor_name})
def infer(self, img):
"""
推理函數,接收一張圖片作為參數
"""
self.inputs[0]['host'] = np.ravel(img) # 將圖片攤平後存入 inputs[0]['host'] 中
# 將數據傳輸到 GPU
for inp in self.inputs:
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(inp['device'], inp['host'], self.stream)
# 為新版 TensorRT API 設置 tensor 地址
for inp in self.inputs:
self.context.set_tensor_address(inp['name'], int(inp['device']))
for out in self.outputs:
self.context.set_tensor_address(out['name'], int(out['device']))
# 執行推理 (新版 API)
self.context.execute_async_v3(stream_handle=self.stream.handle)
# 從 GPU 中獲取輸出
for out in self.outputs:
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(out['host'], out['device'], self.stream)
# synchronize stream 等待傳輸完成
self.stream.synchronize()
# 將輸出數據放入 data 列表中並返回
data = [out['host'] for out in self.outputs]
return data
def inference(self, img_path, conf=0.25):
"""
對圖像進行推理並可視化結果(參考 runtimeOnnx.py)
:param img_path: 圖像路徑
:param conf: 置信度閾值
:return: 繪製了檢測結果的圖像
"""
# 讀取圖像
origin_img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(origin_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 預處理
img, (ratio_h, ratio_w) = preproc(img_rgb, self.imgsz, self.mean, self.std)
# 獲取推理結果
data = self.infer(img)
# 解析輸出: 輸出格式為 1x7x8400
# 參考 runtimeOnnx.py: outputs = np.transpose(np.squeeze(outputs))
outputs = data[0].reshape(1, 7, -1) # (1, 7, 8400)
outputs = np.transpose(np.squeeze(outputs)) # (8400, 7)
boxes = []
scores = []
class_ids = []
# 遍歷所有檢測框,過濾置信度
for i in range(outputs.shape[0]):
# 假設前4個是座標,第5個是置信度,後面是類別(根據實際輸出調整)
x, y, w, h = outputs[i][0], outputs[i][1], outputs[i][2], outputs[i][3]
score = outputs[i][4]
class_id = int(outputs[i][5]) if outputs.shape[1] > 5 else 0
if score >= conf:
# 轉換為左上角座標(YOLO格式轉換)
left = int(x - w / 2)
top = int(y - h / 2)
width = int(w)
height = int(h)
boxes.append([left, top, width, height])
scores.append(float(score))
class_ids.append(class_id)
# NMS 非極大值抑制
if len(boxes) > 0:
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, scores, conf, 0.45)
if len(indices) > 0:
indices = np.array(indices).flatten()
# 繪製檢測結果
for i in indices:
box = boxes[i]
left, top, width, height = box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]
# 還原到原圖尺寸
left = int(left / ratio_w)
top = int(top / ratio_h)
width = int(width / ratio_w)
height = int(height / ratio_h)
# 繪製邊界框
class_id = class_ids[i]
color = (_COLORS[class_id % len(_COLORS)] * 255).astype(np.uint8).tolist()
cv2.rectangle(img_rgb, (left, top), (left + width, top + height), color, 2)
# 繪製標籤
class_name = self.class_names[class_id] if class_id < len(self.class_names) else f'class_{class_id}'
label = f"{class_name}: {scores[i]:.2f}"
cv2.putText(img_rgb, label, (left, top - 10),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2)
# 轉換回BGR用於保存
result_img = cv2.cvtColor(img_rgb, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
return result_img
def get_fps(self):
"""
測試模型推理速度
"""
import time
# warmup
img = np.ones((1, 3, self.imgsz[0], self.imgsz[1]))
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img, dtype=np.float32)
for _ in range(20):
_ = self.infer(img)
t1 = time.perf_counter()
_ = self.infer(img)
print(1 / (time.perf_counter() - t1), 'FPS')
def main():
"""
測試 best.engine 模型(詳細性能測試)
"""
import time
# 初始化引擎
engine_path = "best.engine"
print(f"正在加載模型引擎: {engine_path}")
print("=" * 50)
try:
t1 = time.time()
engine = BaseEngine(engine_path, imgsz=(640, 640))
t2 = time.time()
print(f"模型引擎加載成功!耗時: {(t2-t1)*1000:.2f} ms")
except Exception as e:
print(f"模型引擎加載失敗: {e}")
return
print("\n開始詳細性能測試...")
print("=" * 50)
# 測試圖像推理
img_path = "image.png" # 使用工作區中的圖像
try:
# 1. 圖像讀取
t1 = time.time()
origin_img = cv2.imread(img_path)
t2 = time.time()
print(f"1. 圖像讀取: {(t2-t1)*1000:.2f} ms")
# 2. 顏色轉換
t1 = time.time()
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(origin_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
t2 = time.time()
print(f"2. 顏色轉換 (BGR->RGB): {(t2-t1)*1000:.2f} ms")
# 3. Resize
t1 = time.time()
img_resized = cv2.resize(img_rgb, (640, 640))
t2 = time.time()
print(f"3. 圖像Resize (640x640): {(t2-t1)*1000:.2f} ms")
# 4. 歸一化和轉置
t1 = time.time()
img_processed = img_resized.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
img_processed = np.transpose(img_processed, (2, 0, 1))
img_processed = np.expand_dims(img_processed, axis=0)
img_processed = np.ascontiguousarray(img_processed, dtype=np.float32)
t2 = time.time()
print(f"4. 數據預處理 (歸一化+轉置): {(t2-t1)*1000:.2f} ms")
# 5. GPU推理 (多次測試取平均)
warmup_runs = 3
test_runs = 20
print(f"\n5. GPU推理測試 (預熱{warmup_runs}次, 測試{test_runs}次):")
# 預熱
for _ in range(warmup_runs):
_ = engine.infer(img_processed)
# 測試
inference_times = []
for i in range(test_runs):
t1 = time.time()
output = engine.infer(img_processed)
t2 = time.time()
inference_times.append((t2-t1)*1000)
avg_inference = np.mean(inference_times)
min_inference = np.min(inference_times)
max_inference = np.max(inference_times)
std_inference = np.std(inference_times)
print(f" 平均推理時間: {avg_inference:.2f} ms")
print(f" 最快推理時間: {min_inference:.2f} ms")
print(f" 最慢推理時間: {max_inference:.2f} ms")
print(f" 標準差: {std_inference:.2f} ms")
print(f" 理論最大FPS: {1000/avg_inference:.2f} FPS")
# 運行一次正常推理用於後續處理
data = engine.infer(img_processed)
# 6. 後處理 - 解析輸出
t1 = time.time()
outputs = data[0].reshape(1, 7, -1)
outputs = np.transpose(np.squeeze(outputs))
t2 = time.time()
print(f"\n6. 輸出解析 (轉置): {(t2-t1)*1000:.2f} ms")
# 7. 後處理 - 閾值過濾
t1 = time.time()
boxes = []
scores = []
class_ids = []
conf = 0.25
img_h, img_w = origin_img.shape[:2]
ratio_h = 640 / img_h
ratio_w = 640 / img_w
for i in range(outputs.shape[0]):
x, y, w, h = outputs[i][0], outputs[i][1], outputs[i][2], outputs[i][3]
score = outputs[i][4]
class_id = int(outputs[i][5]) if outputs.shape[1] > 5 else 0
if score >= conf:
left = int(x - w / 2)
top = int(y - h / 2)
width = int(w)
height = int(h)
boxes.append([left, top, width, height])
scores.append(float(score))
class_ids.append(class_id)
t2 = time.time()
print(f"7. 閾值過濾 (遍歷{outputs.shape[0]}個框): {(t2-t1)*1000:.2f} ms")
print(f" 檢測到 {len(boxes)} 個候選框")
# 8. NMS非極大值抑制
t1 = time.time()
indices = []
if len(boxes) > 0:
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, scores, conf, 0.45)
t2 = time.time()
print(f"8. NMS非極大值抑制: {(t2-t1)*1000:.2f} ms")
print(f" 最終保留 {len(indices)} 個框")
# 9. 繪製結果
t1 = time.time()
if len(indices) > 0:
indices = np.array(indices).flatten()
for i in indices:
box = boxes[i]
left, top, width, height = box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]
# 還原到原圖尺寸
left = int(left / ratio_w)
top = int(top / ratio_h)
width = int(width / ratio_w)
height = int(height / ratio_h)
# 繪製邊界框
class_id = class_ids[i]
color = (_COLORS[class_id % len(_COLORS)] * 255).astype(np.uint8).tolist()
cv2.rectangle(img_rgb, (left, top), (left + width, top + height), color, 2)
# 繪製標籤
class_name = engine.class_names[class_id] if class_id < len(engine.class_names) else f'class_{class_id}'
label = f"{class_name}: {scores[i]:.2f}"
cv2.putText(img_rgb, label, (left, top - 10),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2)
t2 = time.time()
print(f"9. 繪製結果: {(t2-t1)*1000:.2f} ms")
# 10. 保存圖像
t1 = time.time()
result_img = cv2.cvtColor(img_rgb, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
output_path = "result_engine.jpg"
cv2.imwrite(output_path, result_img)
t2 = time.time()
print(f"10. 保存圖像: {(t2-t1)*1000:.2f} ms")
print("=" * 50)
print(f"結果已保存到 {output_path}")
print("\n總結: TensorRT 引擎在 GPU 推理階段性能優異")
except Exception as e:
print(f"推理失敗: {e}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()測試結果如下:
模型引擎加載成功!耗時: 154.63 ms
開始詳細性能測試...
==================================================
1. 圖像讀取: 17.45 ms
2. 顏色轉換 (BGR->RGB): 2.93 ms
3. 圖像Resize (640x640): 2.69 ms
4. 數據預處理 (歸一化+轉置): 6.47 ms
5. GPU推理測試 (預熱3次, 測試20次):
平均推理時間: 48.54 ms
最快推理時間: 48.16 ms
最慢推理時間: 49.00 ms
標準差: 0.21 ms
理論最大FPS: 20.60 FPS
6. 輸出解析 (轉置): 0.07 ms
7. 閾值過濾 (遍歷8400個框): 87.68 ms
檢測到 164 個候選框
8. NMS非極大值抑制: 0.28 ms
最終保留 32 個框
9. 繪製結果: 3.44 ms
10. 保存圖像: 14.85 ms
==================================================
結果已保存到 result_engine.jpg