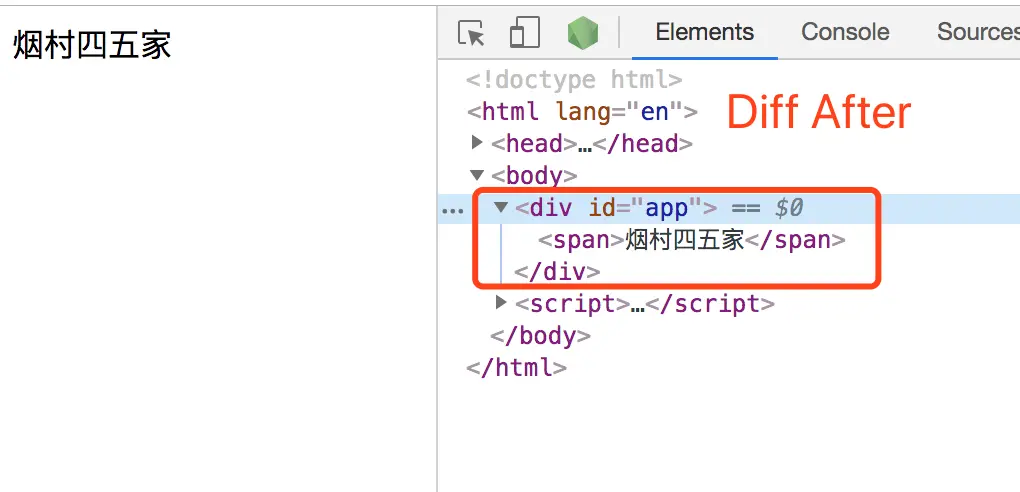
該方法用來真正對新舊節點進行對比,得到最小應該變化的DOM,然後直接更新DOM。下面是需要patch的幾種情況,這幾種情況都會有對應的真實DOM測試用例來驗證。
function patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode) {
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm;
const { children: oldCh } = oldVnode;
const { children: ch } = vnode;
if (!vnode.text) {
if (oldCh && ch) { // 新舊節點都有子節點【子節點就是vnode對象中的 children】
} else if (oldCh) { // 舊節點有子節點,而新節點沒有子節點
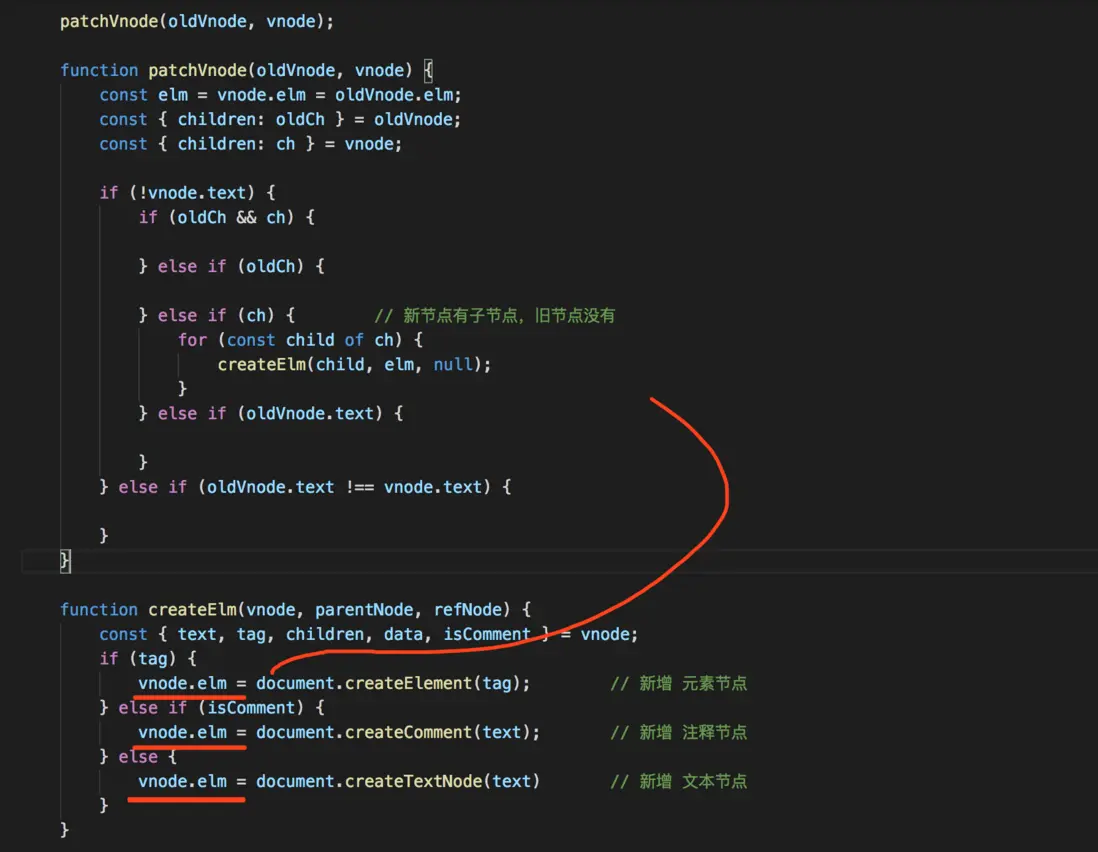
} else if (ch) { // 新節點有子節點,而舊節點沒有子節點
} else if (oldVnode.text) { // 舊節點是一個文本節點,但是新節點的文本為空
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) { // 新舊節點都是文本節點,並且文本不一樣
}
}1. const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm;
vnode表示新節點,此時是沒有elm屬性的。而在經過createElm方法後,vnode.children中的子節點都有了elm屬性,此時只有vnode沒有elm屬性,而能進到 patchVnode 方法來的新舊節點,一定經過了sameVnode方法的判斷,説明他們節點本身幾乎一樣,所以新節點可以用舊節點的elm
if (sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode)
}
2. !vnode.text
能進入到這個條件的,有兩種可能:
- vnode是個文本節點,但是文本節點的text為假值
const vnode = { text: 0/false/'' } - vnode有children子節點
const vnode = { tag: 'div', children: [{...}] }注意: Vnode對象有很多屬性,沒有列出來的屬性,默認值都是undefined, 所以 !vnode.text === !undefined 會進入到這個邏輯來
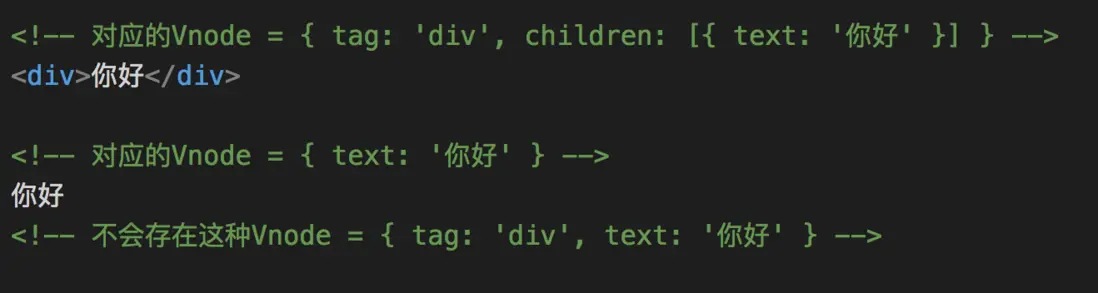
也就是説,文本節點和有children子節點是互斥的。
3. oldCh && ch
新舊節點都有子節點,能進入到 patchVnode 方法,説明新舊節點本身是幾乎一樣的,需要做的就是比較他們的children子節點哪裏不同,從而更新DOM
if (sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode)
}if (oldCh && ch) {
if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch); // updateChildren 方法有點複雜,是Diff的核心方法
}最終的頁面效果對應的DOM結構
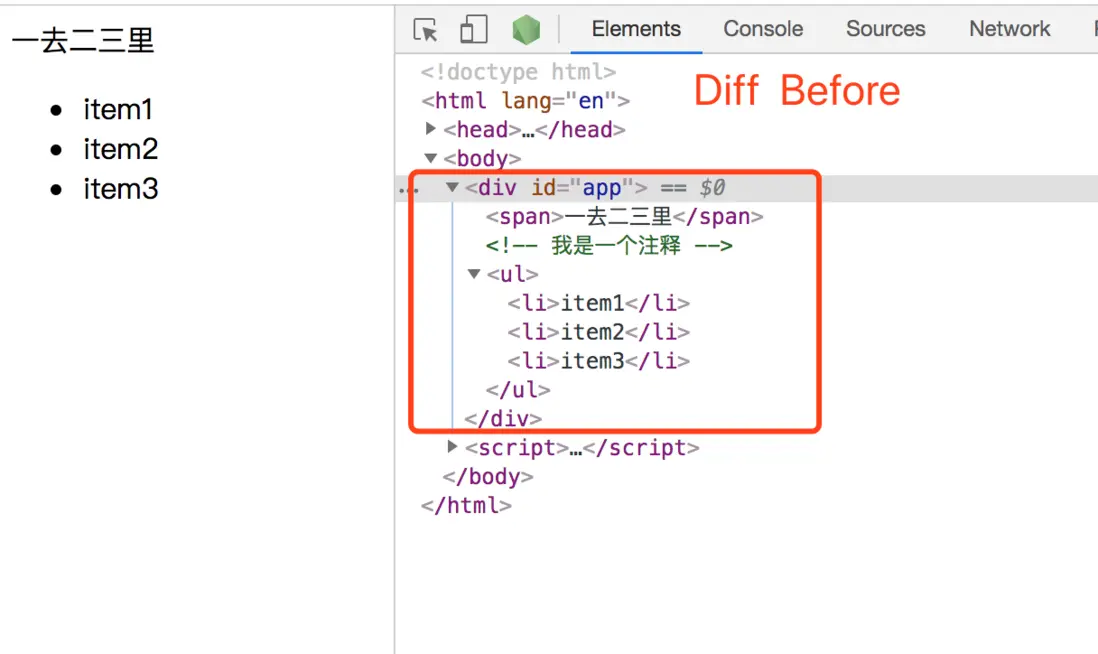
Diff前後對應DOM的Vnode對象
const app = document.getElementById('app');
const span = document.querySelector('span');
const span_text = span.childNodes[0];
const comment = [...app.childNodes].filter(el => el.nodeType === 8)[0]
const ul = document.getElementsByTagName('ul')[0];
const lis = ul.children;
const oldVnode = {
tag: 'div',
data: {
attrs: { id: 'app' }
},
elm: app, // 舊節點的Vnode對象上都會有一個 elm 屬性, 表示該Vnode對應的真實DOM元素
children: [
{
tag: 'span',
elm: span,
children: [{ text: '一去二三裏', elm: span_text }]
},
{
text: '我是一個註釋',
isComment: true,
elm: comment
},
{
tag: 'ul',
elm: ul,
children: [
{
tag: 'li',
elm: lis[0],
children: [{ text: 'item1', elm: lis[0].childNodes[0] }]
},
{
tag: 'li',
elm: lis[1],
children: [{ text: 'item2', elm: lis[1].childNodes[0] }]
},
{
tag: 'li',
elm: lis[2],
children: [{ text: 'item3', elm: lis[2].childNodes[0] }]
},
]
}
]
}// 新節點是沒有 elm 屬性的
const vnode = {
tag: 'div',
data: {
attrs: { id: 'app' }
},
children: [
{
tag: 'span',
children: [{ text: '煙村四五家' }]
},
]
}從圖例和新舊vnode中可以看出,他們都有chidlren子節點,所以這種情況,就會進入到 patchVnode 方法的 oldCh && ch 邏輯中來,下面舉例説一下 updateChildren 方法的邏輯,先放上該方法的一個邏輯框架代碼:
function updateChildren(parentElm, oldCh, newCh) {
let oldStartIdx = 0;
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1;
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0];
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx];
let newStartIdx = 0;
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1;
let newStartVnode = newCh[0];
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx];
let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm;
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) { // 頭頭相同 本身位置不動,只用patch子節點,更新子節點DOM即可
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) { // 尾尾相同 本身位置不動,只用patch子節點,更新子節點DOM即可
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) { // 舊頭 == 新尾 DOM位置需要移動, 從第一個移動到末尾 使用 insertBefore API
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { // 舊尾 == 新頭 DOM位置需要移動,從最後一個移動到第一個
} else { // 上面四種都不符合,單個查找
}
}
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
}
}這就説所有講 Diff 文章中的頭頭相同、尾尾相同、舊頭===新頭....等,剛開始我看到這樣的描述時是迷糊的...每種情況我都會以一個例子來説明
3.1. 新頭 === 舊頭
意思是: 新節點的頭部vnode跟舊節點的頭部vnode是近似相等的,需要做的就是比較他們的子節點有什麼不同,從而更新需要更新的子節點DOM。如圖:
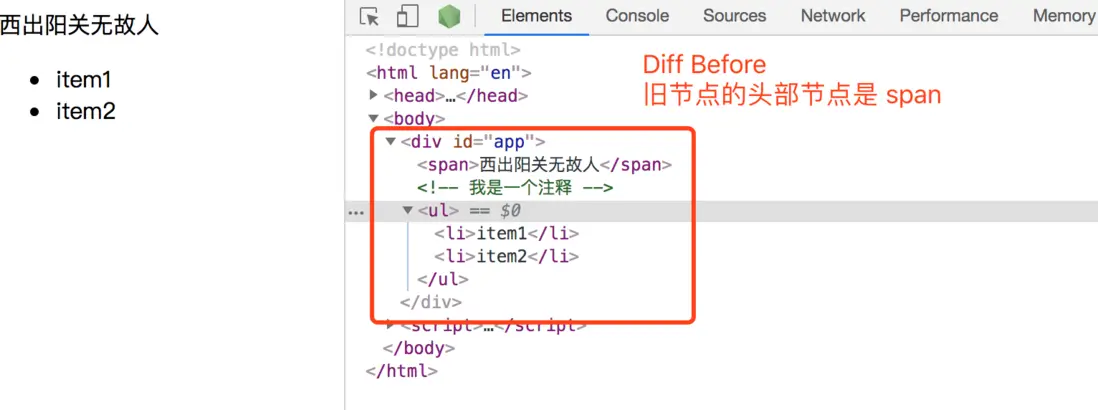
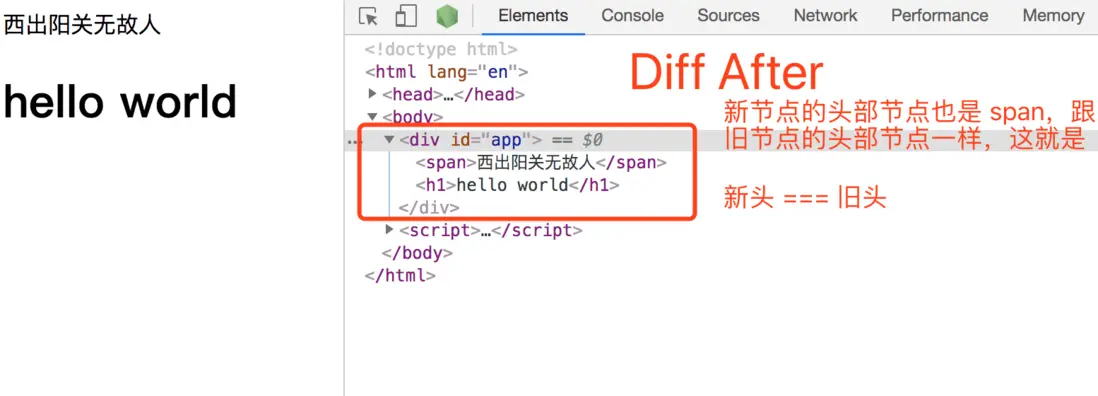
從圖例可以看出,對於頭頭相等的情況,相同的那個節點(span)在DOM中的位置是不用動的,將舊節點中剩餘的子節點(comment、ul)刪除即可。
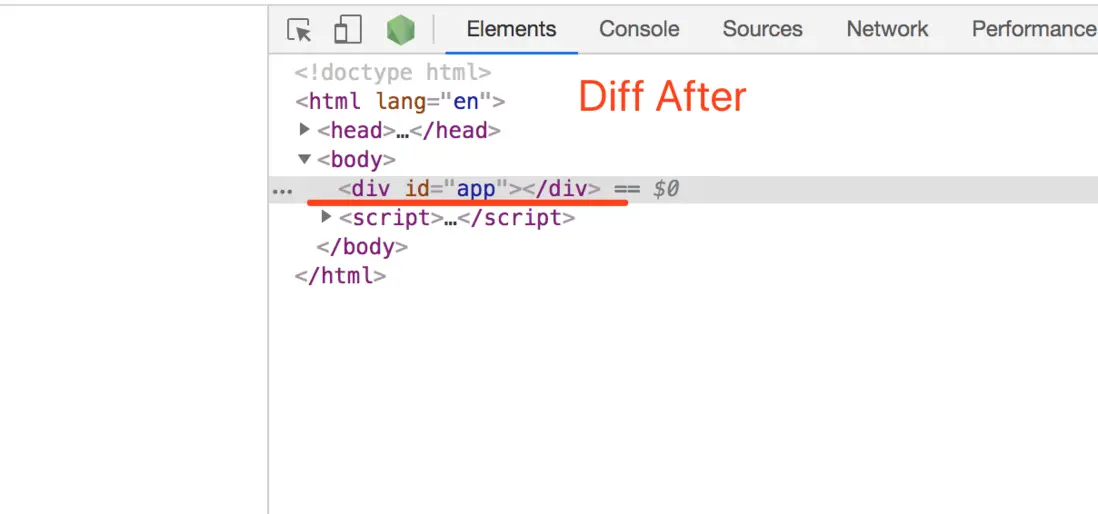
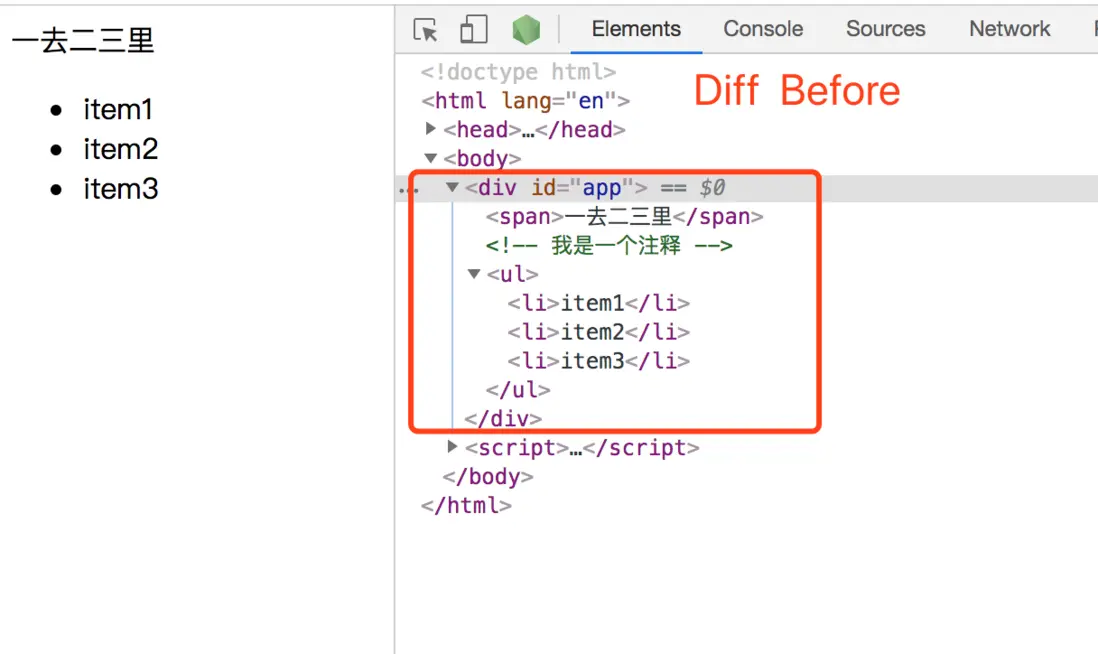
4. oldCh
新節點沒有,而舊節點有的,需要刪除舊節點中的這些DOM元素
最終的頁面效果對應的DOM結構
Diff前後對應DOM的Vnode對象
const oldVnode = {
tag: 'div',
data: {
attrs: { id: 'app' }
},
elm: app,
children: [
{
tag: 'span',
elm: span,
children: [{ text: '一去二三裏', elm: span_text }]
},
{
text: '我是一個註釋',
isComment: true,
elm: comment
},
{
tag: 'ul',
elm: ul,
children: [
{
tag: 'li',
elm: lis[0],
children: [{ text: 'item1', elm: lis[0].childNodes[0] }]
},
{
tag: 'li',
elm: lis[1],
children: [{ text: 'item2', elm: lis[1].childNodes[0] }]
},
{
tag: 'li',
elm: lis[2],
children: [{ text: 'item3', elm: lis[2].childNodes[0] }]
},
]
}
]
}const vnode = {
tag: 'div',
data: {
attrs: { id: 'app' }
},
}patchVnode邏輯
function patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode) {
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm;
const { children: oldCh } = oldVnode;
const { children: ch } = vnode;
if (!vnode.text) {
if (oldCh && ch) {
} else if (oldCh) { // 舊節點有子節點,而新節點沒有子節點
for (const child of oldCh) {
if (child) {
oldVnode.elm.removeChild(child.elm);
}
}
} else if (ch) {
} else if (oldVnode.text) {
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
}
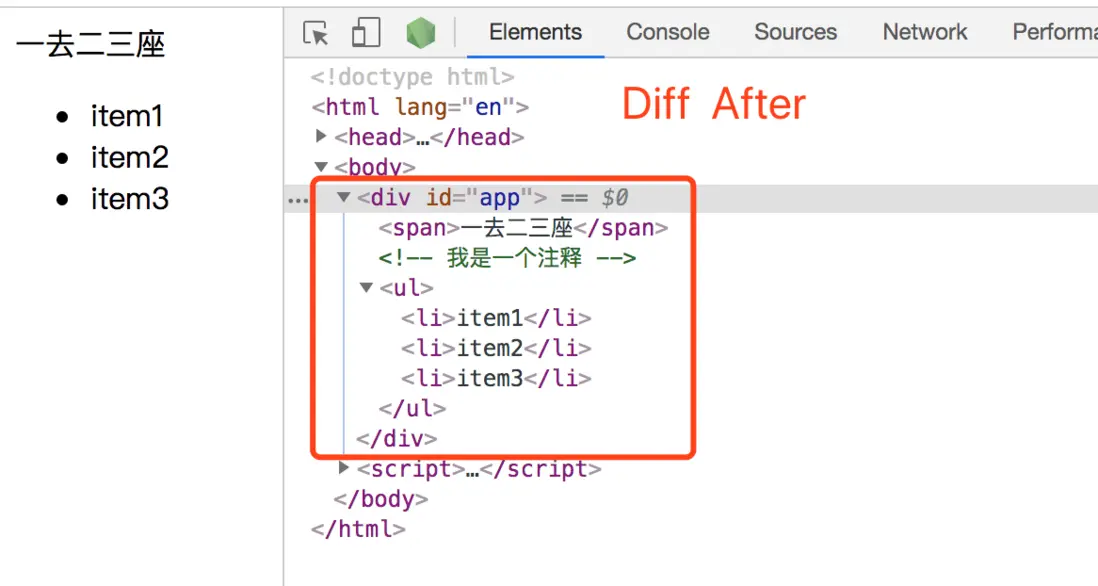
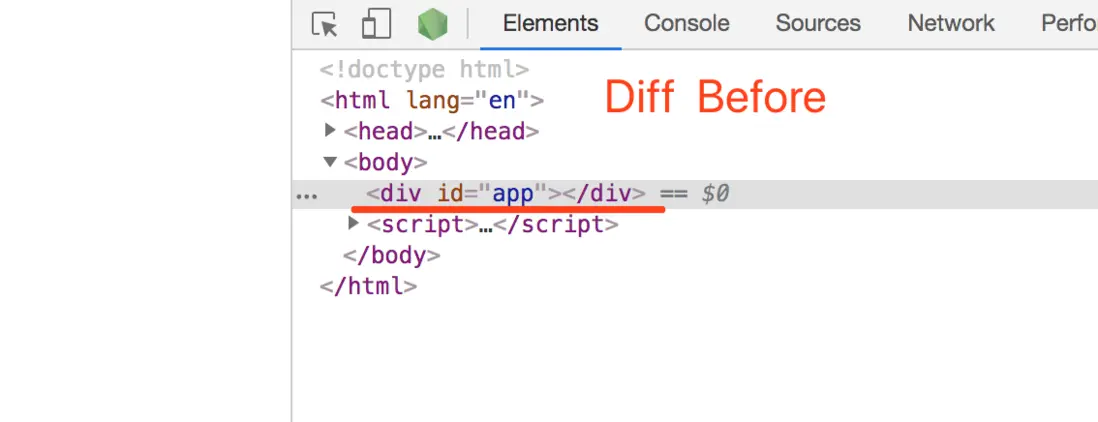
}5. ch
新節點有,而舊節點沒有的,需要創建成節點插入到DOM中
最終的頁面效果對應的DOM結構
Diff前後對應DOM的Vnode對象
const oldVnode = {
tag: 'div',
data: {
attrs: { id: 'app' }
},
elm: app
}const vnode = {
tag: 'div',
data: {
attrs: { id: 'app' }
},
children: [
{
tag: 'span',
data: {
attrs: { class: 'first' }
},
children: [{ text: '一去二三裏' }]
},
{
text: '我是一個註釋',
isComment: true,
},
{
tag: 'ul',
data: {
attrs: { class: 'list' }
},
children: [
{
tag: 'li',
children: [{ text: 'item1' }]
},
{
tag: 'li',
children: [{ text: 'item2' }]
},
{
tag: 'li',
children: [{ text: 'item3' }]
},
]
}
]
}patchVnode邏輯
function patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode) {
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm;
const { children: oldCh } = oldVnode;
const { children: ch } = vnode;
if (!vnode.text) {
if (oldCh && ch) {
} else if (oldCh) {
} else if (ch) { // 新節點有子節點,舊節點沒有
for (const child of ch) {
createElm(child, elm, null); // 創建並插入到父元素中
}
} else if (oldVnode.text) {
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
}
}function createElm(vnode, parentNode, refNode) {
const { text, tag, children, data, isComment } = vnode;
if (tag) {
vnode.elm = document.createElement(tag);
// 生成子節點
createChildren(vnode, children);
// 將屬性添加上去
if (data) {
const { attrs } = data;
if (attrs) {
for (const k in attrs) {
vnode.elm.setAttribute(k, attrs[k]);
}
}
}
// 將子節點插入到父節點
insert(parentNode, vnode.elm, refNode);
} else if (isComment) {
vnode.elm = document.createComment(text); // 新增 註釋節點 並添加到其父元素中
insert(parentNode, vnode.elm, refNode);
} else {
vnode.elm = document.createTextNode(text) // 新增 文本節點 並添加到其父元素中
insert(parentNode, vnode.elm, refNode);
}
}function createChildren(vnode, children) {
if (Array.isArray(children)) {
for (const child of children) {
createElm(child, vnode.elm);
}
}
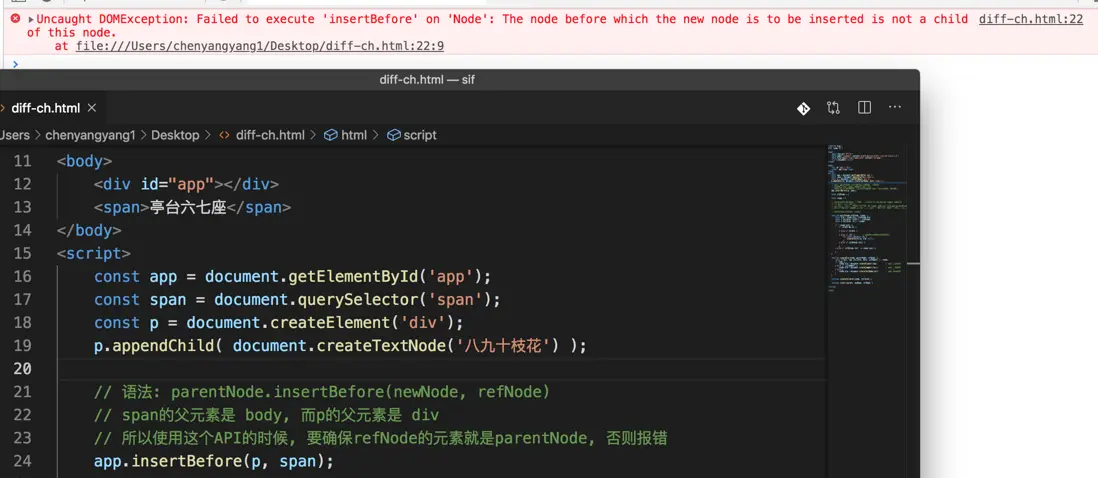
}function insert(parent, newNode, refNode) {
if (parent) {
if (refNode) {
if (refNode.parentNode === parent) { // 看下圖
parent.insertBefore(newNode, refNode);
}
} else {
parent.appendChild(newNode);
}
}
}