在Spring4之後,要使用註解開發,必須要保證aop的包導入了
使用註解需要導入context約束,增加註解的支持
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--指定要掃描的包,這個包下的註解就會生效-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.sunfl.pojo"/>
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>- bean
-
屬性如何注入
//等價於 <bean id="user" class="com.sunfl.pojo.User"/> @Component public class User { public String name; //相當於<property name="name" value="向日葵"> @Value("向日葵") public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } -
衍生的註解
@Component有幾個衍生註解,我們在web開發中,會按照mvc三層架構分層- dao 【@Repository】
- service 【@Service】
- controller 【@Controller】
這四個註解功能都是一樣的,都是代表將某個類註冊到Spring容器中,裝配Bean
-
自動裝配置
- @Autowired:自動裝配通過類型、名字
- @Nullable:字段標記了這個註解,説明這個字段可以為null
- @Resource:自動裝配通過類型、名字
-
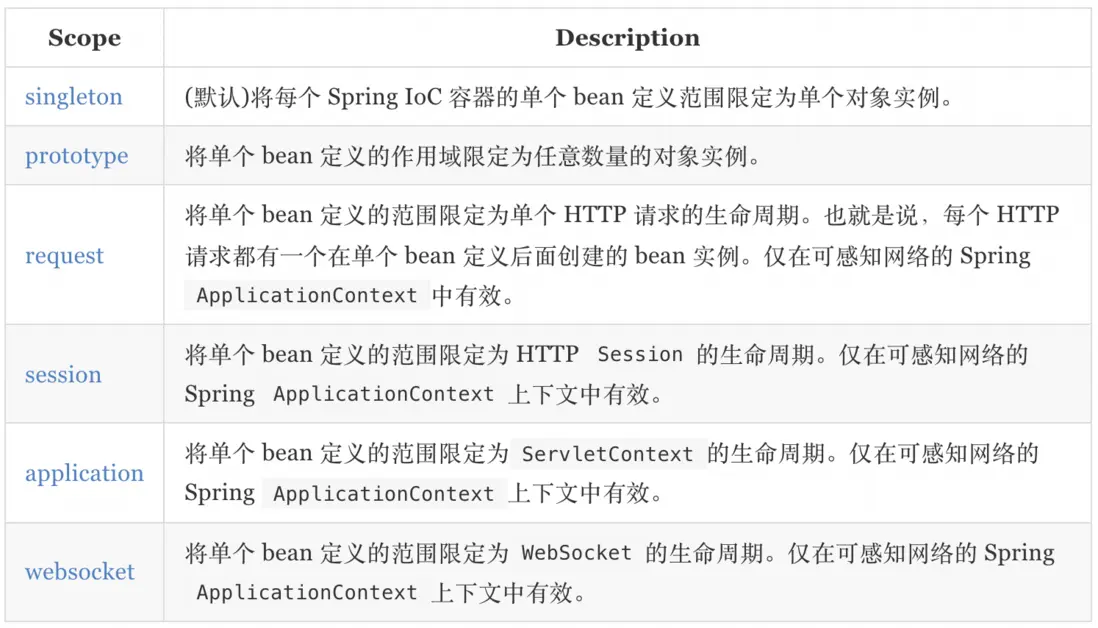
作用域
@Component @Scope("prototype") public class User { } -
小結
xml與註解對比:- xml更加萬能,適用於任何場合!維護簡單方便
- 註解 不是自己類使用不了,維護相對複雜
最佳實踐:
- xml用來管理bean
- 註解只負責完成屬性的注入