在大模型全面走向工程落地的當下,LazyLLM正式與硅基流動(SiliconFlow) 達成深度合作,共同打造面向開發者的下一代智能應用底座。藉助LazyLLM的一鍵接入線上模型API能力,硅基流動的大語言模型、多模態模型、向量與Embedding模型、文生圖模型等已經完整接入,同一套接口即可覆蓋從文本到圖像、從檢索到生成的全鏈路需求。
這次合作帶來的不僅是更強大的RAG選型,還進一步放大了Agent能力:在LazyLLM中,開發者可以基於統一的模型接入層,靈活編排工具調用與工作流,結合對MCP等協議的支持,將檢索、調用外部系統、多模型路由、長程記憶等能力封裝為可協作的智能體網絡。
對於開發者而言,底層模型與算力的複雜度被徹底“藏”在LazyLLM+硅基流動這套組合之下——你只需聚焦業務邏輯,就能搭出既有強RAG能力、又有高擴展Agent能力的AI應用,從原型驗證一路平滑升級到生產級部署。
LazyLLM
LazyLLM是由商湯LazyAGI團隊開發的一款開源低代碼大模型應用開發工具,提供從應用搭建、數據準備、模型部署、微調到評測的一站式工具支持,以極低的成本快速構建AI應用,持續迭代優化效果。
一、API申請和環境配置
(一)賬號註冊
-
註冊硅基流動賬號
(點擊註冊:https://account.siliconflow.cn/zh/login?redirect=https%3A%2F%2Fcloud.siliconflow.cn&invitation=TR9Ym0c4)
-
進入控制枱,獲取APIkey
(獲取方式:https://account.siliconflow.cn/zh/login?redirect=https%3A%2F%2Fcloud.siliconflow.cn%2Faccount%2Fak%3F)
(二)環境配置
參考網頁:快速開始-LazyLLM。
(https://docs.lazyllm.ai/zh-cn/stable/)
二、API使用測試
(一)設置環境變量
可以使用以下命令設置對應的環境變量。或從代碼中顯示給入:
export LAZYLLM_SILICONFLOW_API_KEY=<申請到的api key>
(二)實現對話和圖片識別
1. 文本問答演示
填好api_key後,運行下面代碼可以迅速調用模型並生成一個問答形式的前端界面:
import lazyllm
from lazyllm import OnlineChatModule,WebModule
api_key = 'sk-' #替換成申請的api
# # 測試chat模塊
llm = OnlineChatModule(source='siliconflow', api_key=api_key, stream=False)
w = WebModule(llm, port=8846, title="siliconflow")
w.start().wait()
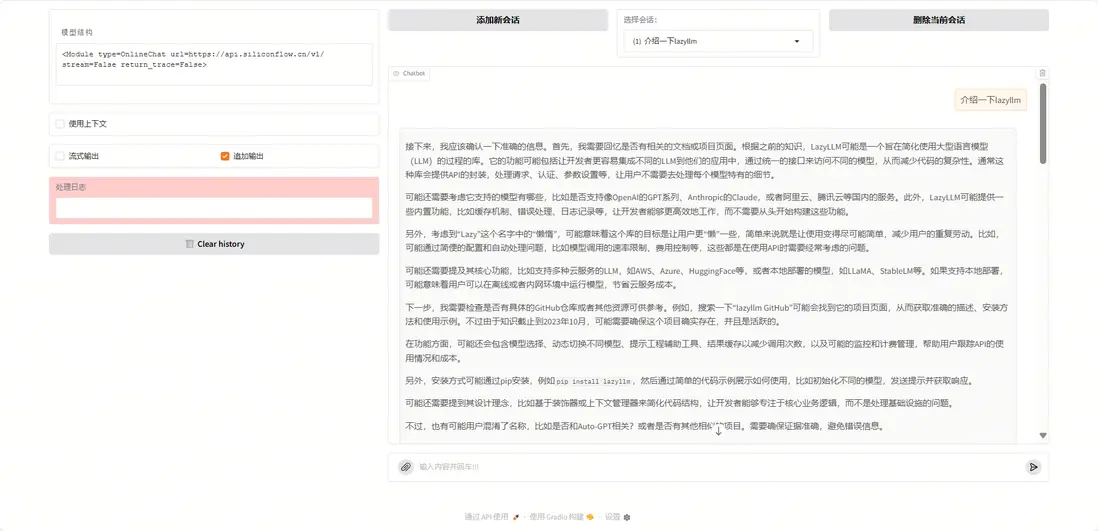
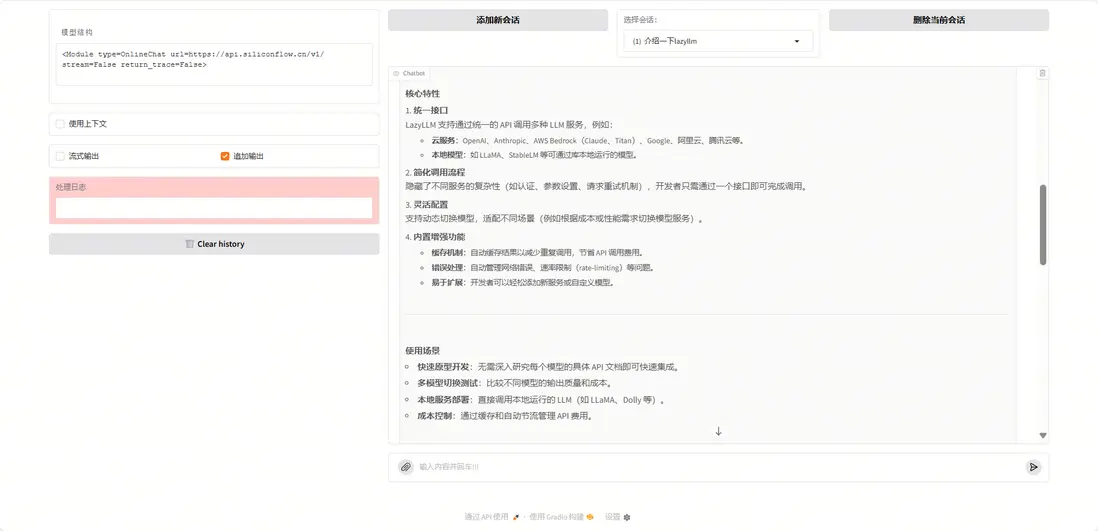
我們詢問“什麼是LazyLLM”,運行結果如下:
2. 多模態問答演示
在輸入中通過lazyllm_files參數傳入一張圖片,並詢問圖片的內容,就可以實現多模態的問答。
import lazyllm
from lazyllm import OnlineChatModule
api_key = 'sk-' #替換成申請的api
llm = OnlineChatModule(source='siliconflow', api_key=api_key, model='Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-72B-Instruct')
print(llm('你好,這是什麼?', lazyllm_files=['your_picture.png']))
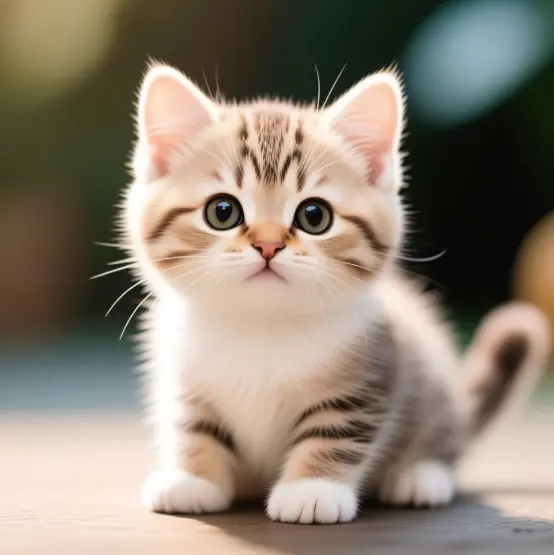
這裏我們使用這個圖片測試多模態問答
命令行中輸出結果:
你好!這是一隻小貓。它看起來非常可愛,毛茸茸的,眼睛大大的,背景是模糊的色彩,突出了小貓的細節。這樣的圖像通常能讓人們感到温暖和愉快。你想了解更多關於小貓的信息嗎?
(lazyllm)→LazyLLMgit:(main)
(三)實現文生圖和文生語音
使用OnlineMultiModalModule進行文生圖和文生語音,運行後會輸出生成的文件路徑
import lazyllm
from lazyllm import OnlineMultiModalModule
api_key = 'sk-xxx'
# 測試文生圖 fuction=text2image
llm = OnlineMultiModalModule(source='siliconflow', api_key=api_key, function='text2image')
print(llm("生成一個可愛的小狗"))
# 測試文生語音 function=tts
llm = OnlineMultiModalModule(source='siliconflow', api_key=api_key, function='tts')
print(llm("你好,你叫什麼名字", voice='fnlp/MOSS-TTSD-v0.5:anna'))
運行結果:
生成的語音如下:
| tmpck44zfds.mp3 | 55.13KB | 2025-10-2723:13 |
(語音鏈接:https://ones.ainewera.com/wiki/#/team/JNwe8qUX/share/7fy5a6mk/page/FUcz8wKs/)
(四)10+行代碼實現知識庫問答
1. 實現Eembed和Rerank功能
運行下面代碼,使用OnlineEmbeddingModule進行向量化嵌入;設置type='rerank'調用重排序模型。
import lazyllm
from lazyllm import OnlineEmbeddingModule
api_key = 'sk-'
#測試embed模塊
llm = OnlineEmbeddingModule(source='siliconflow', api_key=api_key)
print(llm("蘋果"))
#測試rerank模塊
llm = OnlineEmbeddingModule(source='siliconflow', api_key=api_key, type='rerank')
print(llm(["蘋果", ['蘋果','香蕉','橘子']]))
向量化的結果如下:
[-0.0024823144, -0.0075530247, -0.013154144, -0.031351723, -0.024489744, 0.009692847, 0.008086464, -0.037946977, 0.013251133, -0.046675995, -0.011390155, -0.011111312, 0.016779112, 0.054168403, 0.04849454, 0.014742341, 0.02341074, -0.015542501, 0.059939254, -0.024223024, 0.0065467632, -0.041244607, -0.022925794, -0.024804957, 0.006752865, -0.047548898, -0.03685585, 0.0513557....,-0.070656545, -0.01997975, 0.023398615, 0.008735079]
詞相似性分數如下:
[{'index': 0, 'relevance_score': 0.9946065545082092}, {'index': 2, 'relevance_score': 0.014802767895162106}, {'index': 1, 'relevance_score': 0.0004139931406825781}]
2. 知識庫導入
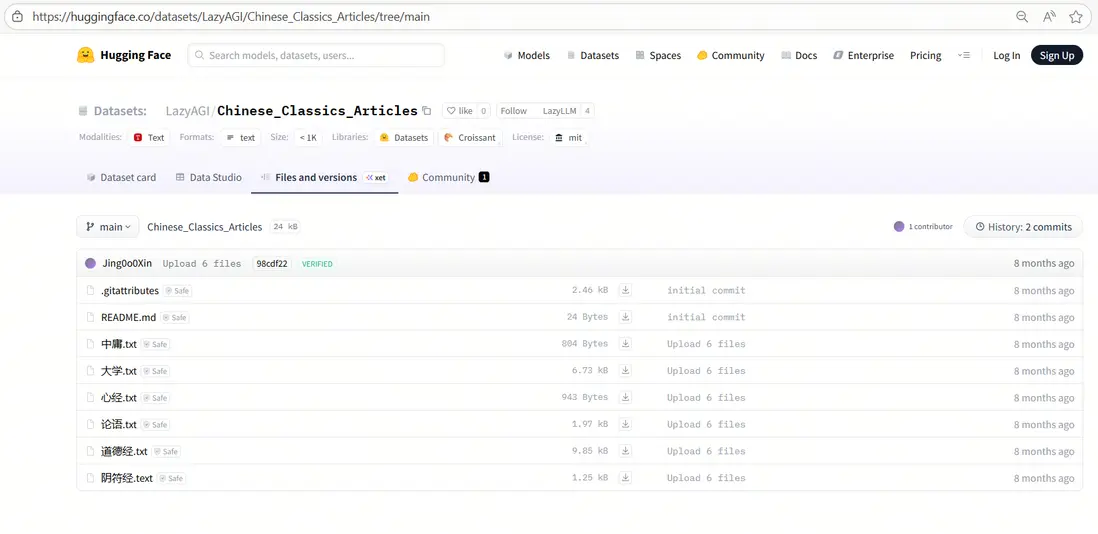
我們使用中國古典文籍作為示例知識庫,下載後放在database文件夾。
(示例數據集下載鏈接:https://huggingface.co/datasets/LazyAGI/Chinese\_Classics\_Articles/tree/main)
首先定義embed模型,然後使用LazyLLM的Document組件創建文檔管理模塊,以實現知識庫的導入。
import lazyllm
api_key='sk-'
embed_model = lazyllm.OnlineEmbeddingModule(source="siliconflow", api_key=api_key)
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path="database", embed=embed_model)
3. 知識庫檢索
現在有了外部知識庫,LazyLLM中使用Retriever組件可以實現檢索知識庫並召回相關內容。使用示例:
import lazyllm
from lazyllm.tools import Retriever, Document, SentenceSplitter
api_key='sk-'
embed_model = lazyllm.OnlineEmbeddingModule(source="siliconflow", api_key=api_key)
documents = Document(dataset_path='database', embed=embed_model, manager=False)
rm = Retriever(documents, group_name='CoarseChunk', similarity='bm25', similarity_cut_off=0.01, topk=6)
rm.start()
print(rm("user query"))
4. 知識庫問答
結合上述模型、文檔管理和檢索模塊,搭配LazyLLM內置的Flow組件進行完整的數據流搭建,完整代碼如下:
import lazyllm
from lazyllm import (
OnlineEmbeddingModule, OnlineChatModule, Document, SentenceSplitter,
Retriever, Reranker, ChatPrompter, pipeline
)
# 初始化api key和提示詞
api_key = 'sk-'
prompt = """
You will play the role of an AI Q&A assistant and complete a dialogue task.
In this task, you need to provide your answer based on the given context and question.
"""
# 初始化模型
embed_model = OnlineEmbeddingModule(source="siliconflow", api_key=api_key)
rerank_model = OnlineEmbeddingModule(source="siliconflow", api_key=api_key, type="rerank")
llm = OnlineChatModule(source="siliconflow", api_key=api_key)
# 定義文檔管理模塊,並創建節點組
doc = Document(dataset_path="/home/xxx/database", manager=False, embed=embed_model)
doc.create_node_group(name="block", transform=SentenceSplitter, chunk_size=1024, chunk_overlap=100)
doc.create_node_group(name="line", transform=SentenceSplitter, chunk_size=128, chunk_overlap=20, parent="block")
# 構建RAG pipeline(多路召回--重排--提示詞拼接--大模型回答)
with pipeline() as ppl:
with lazyllm.parallel().sum as ppl.prl:
prl.r1 = Retriever(doc, group_name='line', similarity="cosine", topk=6, target='block')
prl.r2 = Retriever(doc, group_name='block', similarity="cosine", topk=6)
ppl.reranker = Reranker('ModuleReranker', model=rerank_model, output_format='content',
join=True) | bind(query=ppl.input)
ppl.formatter = (lambda context, query: dict(context_str=str(context), query=query)) | bind(query=ppl.input)
ppl.llm = llm.prompt(lazyllm.ChatPrompter(prompt, extra_keys=["context_str"]))
ppl.start()
query = "何為天道"
print(ppl(query))
可以看到RAG很好地從《道德經》等中取回了有關天道的內容,並傳給大模型進行回答。
更多技術內容,歡迎移步 "LazyLLM" 討論!