經常使用 Java 的 HashMap,但你有了解過其內部的實現原理麼?數據是如何存儲的?哈希衝突是如何處理的?
本篇文章將帶你深入源碼探究 HashMap 的實現原理。
文檔註釋
HashMap 是 Map 接口的實現類,實現了所有可選的操作,並且允許 null key 和 null value。(可以簡單的理解與 HashTable 功能相同,除了它是不同步的,以及支持空值。)
存取效率:在存儲的元素均勻分佈在桶中時,get 和 put 元素的時間不變。遍歷的效率與 capacity 相關,因此如果注重遍歷的效率,不要把 capacity 初始值設的很大,或把負載係數設的很小。
非同步:不要用多線程同時修改。
一、類定義
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {繼承自 AbstractMap,並實現 Map、Cloneable、Serializable 接口。
一)實現的接口
Cloneable和 Serializabel 都是標識接口,裏面沒有方法定義。實現這種接口僅用於標識這個類應該有這中功能。
Map接口中定義了要實現的方法,並且給出了部分方法的實現。
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44203158/article/details/109340113
Q:接口裏面可以實現方法麼?
A:是可以的!
從 Java8 之後添加了這個功能,主要考慮的是若接口發生變化,所有的實現類都要跟着進行修改。但有了接口可以實現方法後,就不用再改實現類了。
Q:接口中實現方法有default和static兩種修飾?
A:用default修飾的叫默認方法,用static修飾的叫靜態方法。default可以被重寫,但是static不行。
Q:實現多個接口的默認方法衝突怎麼辦?
A:在實現類中重寫,且可調用接口中默認的方法。
Q:那為什麼不用抽象類?
A:抽象類不能多繼承。
二)繼承的類
AbstractMap 抽象類提供對 Map 接口的基本實現,以減輕實現 Map 接口的工作量。
對於不可變的 Map 實現類,只需要實現 entrySet() 方法。
對於可變的 Map 實現類,還需要實現 put()、remove() 等方法。
二、成員變量
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
/**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
/**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts
* between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;從變量和註釋中能看出 HashMap 類的部分特性
- 定義容量需要是 2 的次方數。因此表示的時候也用位運算來定義的
- 默認負載達到 75% 時會擴容
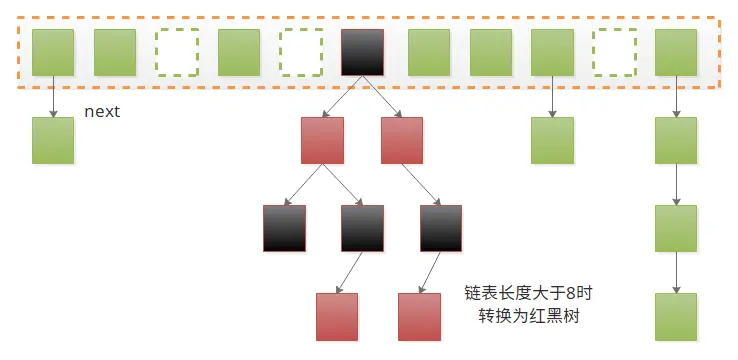
- 單個桶存的元素數大於 8 會變為樹形存儲,小於 6 改回列式存儲
- 當 capacity 大於 64 時,才會觸發單節點的樹形轉換
容量為什麼使用 2 的次方數?
在HashMap中採用的是除留餘數法,即table[hash % length]
在現代CPU中求餘是最慢的操作,所以人們想到一種巧妙的方法來優化它,即length為2的指數冪時,hash % length = hash & (length-1)
如何做到的?
https://www.cnblogs.com/sanzao/p/10245212.html
https://blog.csdn.net/u014540814/article/details/88354793
// 下面的代碼用於調整容量,將容量調為下一個 2 次方數
// 簡單來説使用了位運算的方式,將這個數第一個 1 後面的所有位都換為 1
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}被標記為 transient 的變量
Q:transient 關鍵字是做什麼的?
A:防止屬性被序列化
Q:為什麼要用 transient 修飾?
A:出於安全問題考慮
transient Node<K,V>[] table;三、重要內部類
一)Node
最重要的內部類 Node,定義了 HashMap 中的節點。
/**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
// ......
}注意到使用了泛型類
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000002646193
Q:什麼是泛型類?
A:類名 + 一對尖括號。 person<X>。在 JDK 5 中出現。
Q:為什麼要用泛型類?
A:其中一個重要原因是為了創建容器類。假設沒有泛型,為了支持不同類型的容器,可能需要定義多個類來支持。但有了泛型可以只用定義一個。減少了編碼的冗餘。
Q:泛型定義寫在什麼位置?
A:泛型類寫到類名後面,泛型方法寫到返回類型之前。
Q:泛型的類型是何時確定的?
A:應該是在編譯時確定的。
有 4 個成員變量
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;hashCode() 計算方式有些奇怪?
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); // 為什麼要用異或運算符?
}四、重要函數
hash()
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}getNode()
這個裏面體現了很多設計思想
-
first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]從這裏可以猜出來- hash 底層放到了一個數組裏面
- 容量設計為 2 的指數,在這裏
n-1二進制全是 1,方便做 & 運算
-
在節點衝突時,會有兩種檢索衝突的方式。先判斷是不是樹節點,不是才順序遍歷
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } return null; }
putVal()
插入數據
- 表的空容量判斷
- 桶上如果沒有元素,直接新建
-
桶上如果已有元素
- 先判斷 key 值是否存在,如果存在則將要替換 value
- 如果是樹結構,按照樹的方式處理
- 如果是列表結構,遍歷看是否有 key 相同的
-
若需要新建 Node 節點
- 樹轉換的計數 + 1
- table 存儲量 + 1,若大於 threshold 則 resize()
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }resize()在擴容時會調用的函數
// 擴容時會按照 2 倍的方式擴容 else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold // 重新整理數據 for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { oldTab[j] = null; if (e.next == null) // 如果該節點沒有 hash 衝突,則放到原位或者2倍的位置 newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; else if (e instanceof TreeNode) // 如果有 hash 衝突,且衝突很多(用樹狀存儲),會進行拆分 ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); else { // preserve order // 有 hash 衝突,用列表存放,整體放到 [j + oldCap] 位置上 Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { if (loTail == null) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } else { if (hiTail == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null); if (loTail != null) { loTail.next = null; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null) { hiTail.next = null; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } }treeifyBin()final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { int n, index; Node<K,V> e; // 如果 table 本身容量還很小,先使用擴容 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) resize(); else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; do { // 其實是調用 LinkedHashMap 構造方法,TreeNode 也是 LinkedHashMap 擴展而來 TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); // 這裏是串成一個雙向鏈表 if (tl == null) hd = p; else { p.prev = tl; tl.next = p; } tl = p; } while ((e = e.next) != null); if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) // 將鏈表轉換成樹(紅黑樹),暫不具體研究了 hd.treeify(tab); } }後面函數大同小異,可自己探究。