一、前言
Java性能優化之影響性能的那些細節 - 續來了。打算把這個標題整個系列文章,後面慢慢積累慢慢寫。這是第一篇入口。這次內容主要來源於《Java程序性能優化實戰》這本書,算是一份讀書筆記,感興趣的小夥伴可以閲讀下這本書。
二、List接口
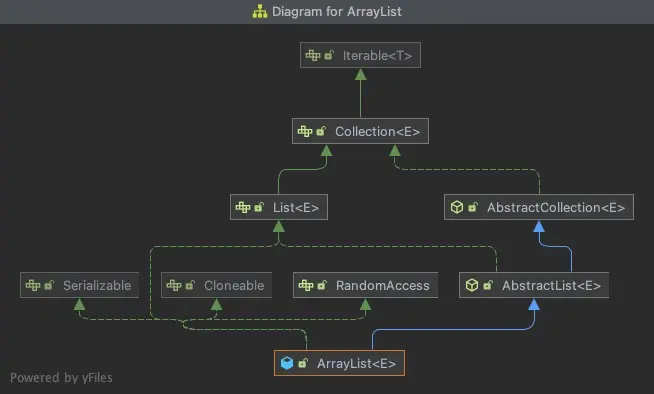
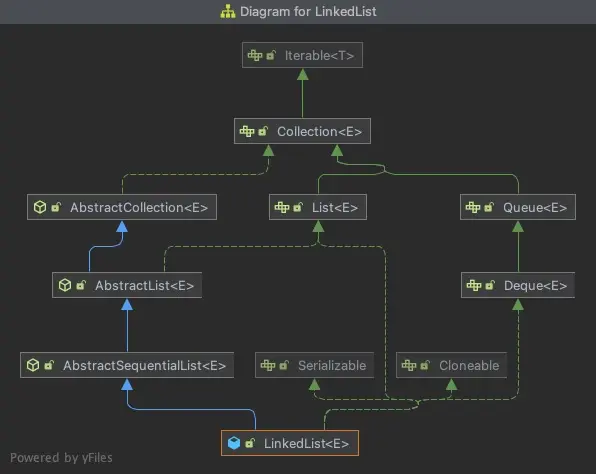
先來看下這幾個List的類圖:
ArrayList
Vector
LinkedList
ArrayList、Vector以及LinkedList3種List均來自AbstractList的實現,而AbstractList直接實現了List接口,並擴展自AbstractCollection。
1. ArrayList和Vector
ArrayList和Vector基本差不多,所以就把這兩放一塊了。這兩個實現類幾乎使用了相同的算法,它們的 唯一區別 可以認為是對多線程的支持。ArrayList沒有對任何一個方法做線程同步,因此不是線程安全的; Vector中的絕大部分方法都做了線程同步,是一種線程安全的實現方式;
ArrayList和Vector使用了數組。可以認為ArrayList或者Vector封裝了對內部數組的操作,例如向數組中添加、刪除、插入新的元素或者數組的擴展和重定義。(對於ArrayList和Vector的一些優化方式其實都是基於數組的來的,因此一般情況同樣適用於底層使用數組的其他情況)
ArrayList的當前容量足夠大【默認初始化長度為10】,add()操作的效率就非常高,ArrayList擴容【默認擴容原本的1.5倍】過程中會進行大量的數組複製操作,相對來説頻繁的擴容會有性能影響;擴容的核心源碼如下:
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 這裏用位運算來實現的。相當於newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity / 2)
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}從源碼中我們又能get一個細節:代碼中的整數乘除使用位運算實現,可以大大提高計算效率。
- 從尾部刪除元素時效率很高,從頭部刪除元素時相當費時,原因是每次刪除後都要進行數組的重組;
- 插入操作都會進行一次數組複製【除尾端插入情況】,而這個操作在增加元素到
List尾端的時候是不存在的。大量的數組重組操作會導致系統性能低下,並且插入的元素在List中的位置越靠前,數組重組的開銷也越大;
- 儘量直接訪問內部元素,而不要調用對應的接口。因為函數調用是需要消耗系統資源的,而直接訪問元素會更高效,比如直接使用List數組下標索引,而不用get接口。
2. LinkedList
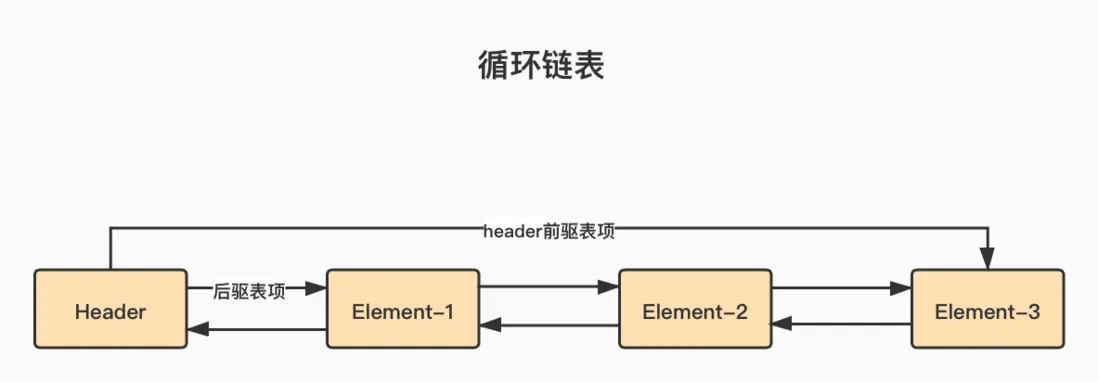
LinkedList使用了循環雙向鏈表數據結構。與基於數組的List相比,這是兩種截然不同的實現技術,這也決定了它們將適用於完全不同的工作場景。LinkedList鏈表由一系列表項連接而成。一個表項包含3部分,即元素內容、前驅表項和後驅表項。
- 無論
LinkedList是否為空,鏈表內都有一個header表項,它既表示鏈表的開始,也表示鏈表的結尾。循環鏈表 示意圖如下:
LinkedList對堆內存和GC要求較高,原因是每次添加元素都要new Entry(),及每次都要封裝數據,因為必須設置前指針和後指針,才能加入到鏈表中;
LinkedList從頭、尾刪除元素時效率相差無幾級,但是從List中間刪除元素時性能非常糟糕,原因是每次都要遍歷半個鏈表;
(下面是前一篇文章中提到過的關於LinkedList的注意點)- 使用ListIterator(forEach,利用指針遍歷)遍歷LinkedList【鏈表特性】;
- 避免任何接受或返回列表中元素索引的LinkedList方法【類似獲取index的操作】,性能很差,遍歷列表實現;
三、Map接口
先來看下這幾個Map的類圖:
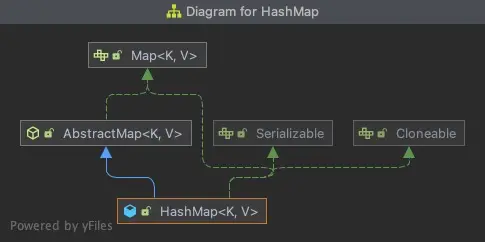
HashMap
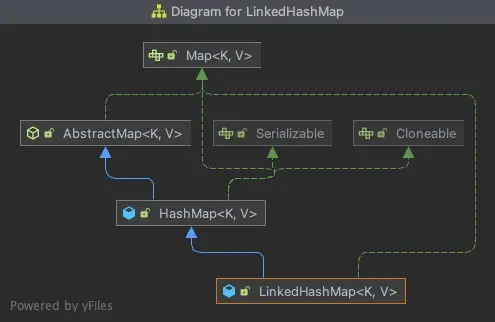
LinkedHashMap
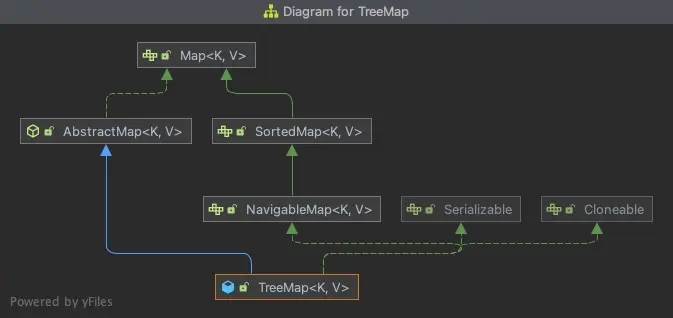
TreeMap
這3個Map都是實現Map接口,繼承AbstractMap類。HashMap和LinkedHashMap直接繼承AbstractMap類,而LinkedHashMap繼承了HashMap。
1. HashMap
HashMap的性能在一定程度上取決於hashCode()的實現。一個好的hashCode()算法,可以儘可能減少衝突,從而提高HashMap的訪問速度。另外,一個較大的負載因子意味着使用較少的內存空間,而空間越小,越可能引起Hash衝突。
HashMap初始化默認數組大小16,在創建的時候指定大小【默認使用達到75%進行自動擴容,每次擴容為原來的2倍,最大長度2^30】,參數必須是2的指數冪(不是的話強行轉換);擴容部分源碼如下:
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
// 這裏也是用的位運算,相當於乘2
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}HashMap擴容大體流程(jdk8):
i. new一個新的數組
ii. 藉助二進制的高低位指針進行數據遷移(最高位是0則座標不變,最高位是1則座標為原位置+新數組長度,如果是樹結構有額外的邏輯)【這裏不過多的解釋HashMap的擴容機制】;
iii. 鏈表長度大於8,且hash table長度大於等於64,則會將鏈表轉紅黑樹(一般情況不使用紅黑樹,優先擴容) ;
2. LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap可以保持元素輸入時的順序;底層使用循環鏈表,在內部實現中,LinkedHashMap通過繼承HashMap.Entry類,實現了LinkedHashMap.Entry,為HashMap.Entry增加了before和after屬性,用於記錄某一表項的前驅和後繼。
- 一些注意點參照
LinkedList(鏈表)
3. TreeMap
TreeMap,實現了SortedMap接口,這意味着它可以對元素進行排序,然而TreeMap的性能卻略微低於HashMap;
TreeMap的內部實現是基於紅黑樹的。紅黑樹是一種平衡查找樹,它的統計性能要優於平衡二叉樹。它具有良好的最壞情況運行時間,可以在O(logn)時間內做查找、插入和刪除操作。
- 如果需要對
Map中的數據進行排序,可以使用TreeMap,而不用自己再去實現很多代碼,而且性能不一定很高;
四、關於List的測試demo
package com.allen.list;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Vector;
/**
* 1、ArrayList,Vector:尾部添加元素性能高,頭部插入元素每次插入都會涉及元素的複製和移動,性能較低
* 2、LinkedList:每次添加元素都要new Entry(),對堆內存和GC要求較高【-Xmx512M -Xms512M 使用這個參數對測試結果有一定影響】
*/
public class TestList {
private static final int CIRCLE1 = 50000;
protected List list;
protected void testAddTail(String funcname){
Object obj=new Object();
long starttime=System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<CIRCLE1;i++){
list.add(obj);
}
long endtime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(funcname+": "+(endtime-starttime));
}
protected void testDelTail(String funcname){
Object obj=new Object();
for(int i=0;i<CIRCLE1;i++){
list.add(obj);
}
long starttime=System.currentTimeMillis();
while(list.size()>0){
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
long endtime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(funcname+": "+(endtime-starttime));
}
protected void testDelFirst(String funcname){
Object obj=new Object();
for(int i=0;i<CIRCLE1;i++){
list.add(obj);
}
long starttime=System.currentTimeMillis();
while(list.size()>0){
list.remove(0);
}
long endtime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(funcname+": "+(endtime-starttime));
}
protected void testDelMiddle(String funcname){
Object obj=new Object();
for(int i=0;i<CIRCLE1;i++){
list.add(obj);
}
long starttime=System.currentTimeMillis();
while(list.size()>0){
list.remove(list.size()>>1);
}
long endtime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(funcname+": "+(endtime-starttime));
}
protected void testAddFirst(String funcname){
Object obj=new Object();
long starttime=System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<CIRCLE1;i++){
list.add(0, obj);
}
long endtime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(funcname+": "+(endtime-starttime));
}
// 測試ArrayList尾部添加
@Test
public void testAddTailArrayList() {
list=new ArrayList();
testAddTail("testAddTailArrayList");
}
//@Test
public void testAddTailVector() {
list=new Vector();
testAddTail("testAddTailVector");
}
// 測試LinkedList尾部添加
@Test
public void testAddTailLinkedList() {
list=new LinkedList();
testAddTail("testAddTailLinkedList");
}
// 測試ArrayList頭部添加
@Test
public void testAddFirstArrayList() {
list=new ArrayList();
testAddFirst("testAddFirstArrayList");
}
// @Test
public void testAddFirstVector() {
list=new Vector();
testAddFirst("testAddFirstVector");
}
// 測試LinkedList頭部添加
@Test
public void testAddFirstLinkedList() {
list=new LinkedList();
testAddFirst("testAddFirstLinkedList");
}
// 測試ArrayList尾部刪除
@Test
public void testDeleteTailArrayList() {
list=new ArrayList();
testDelTail("testDeleteTailArrayList");
}
// @Test
public void testDeleteTailVector() {
list=new Vector();
testDelTail("testDeleteTailVector");
}
// 測試LinkedList尾部刪除
@Test
public void testDeleteTailLinkedList() {
list=new LinkedList();
testDelTail("testDeleteTailLinkedList");
}
// 測試ArrayList頭部刪除
@Test
public void testDeleteFirstArrayList() {
list=new ArrayList();
testDelFirst("testDeleteFirstArrayList");
}
// @Test
public void testDeleteFirstVector() {
list=new Vector();
testDelFirst("testDeleteFirstVector");
}
// 測試LinkedList頭部刪除
@Test
public void testDeleteFirstLinkedList() {
list=new LinkedList();
testDelFirst("testDeleteFirstLinkedList");
}
// 測試LinkedList中間刪除
@Test
public void testDeleteMiddleLinkedList() {
list=new LinkedList();
testDelMiddle("testDeleteMiddleLinkedList");
}
// 測試ArrayList中間刪除
@Test
public void testDeleteMiddleArrayList() {
list=new ArrayList();
testDelMiddle("testDeleteMiddleArrayList");
}
}