第十一篇:加載外部模型:GLTF/OBJ格式解析
引言
在現代3D開發中,90%的複雜模型來自專業建模工具。Three.js提供了強大的模型加載能力,支持20+種3D格式。本文將深入解析GLTF和OBJ格式,並通過Vue3實現模型預覽編輯器,讓你掌握專業3D資產的導入、優化和控制技術。
1. 模型格式對比
1.1 主流格式特性
|
格式
|
類型
|
優勢
|
侷限性
|
適用場景
|
|
GLTF |
開放標準
|
全特性支持、體積小
|
需要轉換工具
|
通用3D內容
|
|
OBJ+MTL |
傳統格式
|
廣泛支持、簡單
|
無動畫、大文件
|
靜態模型
|
|
FBX |
私有格式
|
完整動畫支持
|
需授權、體積大
|
角色動畫
|
|
STL |
工業標準
|
簡單幾何
|
無材質、顏色
|
3D打印
|
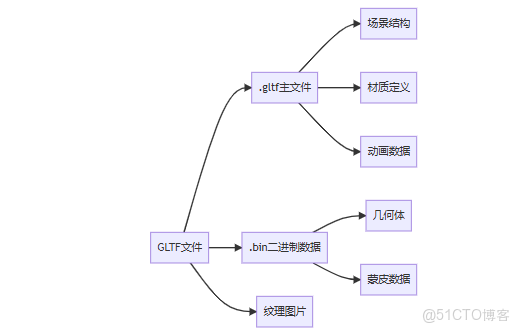
1.2 GLTF結構解析
2. GLTF加載全流程
2.1 基礎加載
<script setup>
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/addons/loaders/GLTFLoader.js';
import { DRACOLoader } from 'three/addons/loaders/DRACOLoader.js';
const modelRef = ref(null);
const loadingProgress = ref(0);
// 初始化加載器
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
const dracoLoader = new DRACOLoader();
dracoLoader.setDecoderPath('libs/draco/');
loader.setDRACOLoader(dracoLoader);
// 加載模型
function loadModel(url) {
loadingProgress.value = 0;
loader.load(
url,
(gltf) => {
const model = gltf.scene;
modelRef.value = model;
// 自動縮放和居中
normalizeModel(model);
scene.add(model);
},
(xhr) => {
loadingProgress.value = (xhr.loaded / xhr.total) * 100;
},
(error) => {
console.error('模型加載失敗:', error);
showFallbackModel();
}
);
}
// 初始加載
onMounted(() => loadModel('models/robot.glb'));
</script>
<template>
<div class="loading" v-if="loadingProgress < 100">
加載中: {{ Math.floor(loadingProgress) }}%
</div>
</template>2.2 模型標準化
function normalizeModel(model) {
const box = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(model);
const size = box.getSize(new THREE.Vector3());
const center = box.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());
// 計算縮放比例(適配高度為2單位)
const scale = 2 / size.y;
// 應用變換
model.position.sub(center);
model.scale.set(scale, scale, scale);
model.position.set(0, -1, 0); // 置於地面
}2.3 動畫處理
const mixer = ref(null);
// 播放所有動畫
function playAnimations(gltf) {
if (gltf.animations.length > 0) {
mixer.value = new THREE.AnimationMixer(gltf.scene);
gltf.animations.forEach((clip) => {
const action = mixer.value.clipAction(clip);
action.play();
});
// 添加到動畫循環
sceneMixers.push(mixer.value);
}
}
// 動畫循環
const sceneMixers = [];
function animate() {
const delta = clock.getDelta();
sceneMixers.forEach(mixer => mixer.update(delta));
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
}3. OBJ/MTL格式處理
3.1 傳統格式加載
<script setup>
import { OBJLoader } from 'three/addons/loaders/OBJLoader.js';
import { MTLLoader } from 'three/addons/loaders/MTLLoader.js';
// 先加載材質
function loadOBJModel(objUrl, mtlUrl) {
const mtlLoader = new MTLLoader();
mtlLoader.load(mtlUrl, (materials) => {
materials.preload();
const objLoader = new OBJLoader();
objLoader.setMaterials(materials);
objLoader.load(objUrl, (object) => {
scene.add(object);
});
});
}
</script>3.2 材質轉換
// 轉換MTL材質為Three.js材質
function convertMaterials(materials) {
Object.values(materials.materials).forEach(mtlMat => {
const threeMat = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({
color: new THREE.Color(mtlMat.diffuse[0], mtlMat.diffuse[1], mtlMat.diffuse[2]),
map: mtlMat.map_diffuse ? loadTexture(mtlMat.map_diffuse) : null,
specular: new THREE.Color(mtlMat.specular[0], mtlMat.specular[1], mtlMat.specular[2]),
shininess: mtlMat.specular_exponent,
transparent: mtlMat.opacity < 1.0,
opacity: mtlMat.opacity
});
mtlMat.userData.threeMat = threeMat;
});
}3.3 格式轉換建議
graph LR
A[原始格式] --> B{需要動畫?}
B -->|是| C[轉換為GLB]
B -->|否| D{需要高質量材質?}
D -->|是| E[轉換為GLTF]
D -->|否| F[轉換為壓縮GLB]4. 模型優化技術
4.1 幾何體壓縮
// 使用Draco壓縮
import { GLTFExporter } from 'three/addons/exporters/GLTFExporter.js';
function exportCompressed(model) {
const exporter = new GLTFExporter();
exporter.parse(model, (gltf) => {
const options = {
binary: true,
dracoOptions: {
compressionLevel: 10
}
};
// 生成壓縮後的GLB
const glb = exporter.packGLB(gltf, options);
downloadFile(glb, 'model.glb');
});
}4.2 紋理優化
// 紋理轉Basis Universal
import { KTX2Exporter } from 'three/addons/exporters/KTX2Exporter.js';
async function convertTexturesToKTX2(materials) {
const exporter = new KTX2Exporter();
for (const material of Object.values(materials)) {
if (material.map) {
const ktx2Data = await exporter.export(material.map);
material.map = new THREE.CompressedTexture(
[ktx2Data],
material.map.image.width,
material.map.image.height,
THREE.RGBAFormat,
THREE.UnsignedByteType
);
}
}
}4.3 模型簡化
// 使用SIMPLIFY修改器
import { SimplifyModifier } from 'three/addons/modifiers/SimplifyModifier.js';
function simplifyModel(mesh, ratio) {
const modifier = new SimplifyModifier();
const simplifiedGeometry = modifier.modify(
mesh.geometry,
Math.floor(mesh.geometry.attributes.position.count * ratio)
);
mesh.geometry.dispose();
mesh.geometry = simplifiedGeometry;
}5. Vue3模型預覽編輯器
5.1 項目結構
src/
├── components/
│ ├── ModelViewer.vue // 模型查看器
│ ├── ModelLibrary.vue // 模型庫
│ ├── AnimationControl.vue // 動畫控制
│ └── MaterialEditor.vue // 材質編輯
└── App.vue5.2 模型查看器
<!-- ModelViewer.vue -->
<template>
<div class="model-viewer">
<canvas ref="canvasRef"></canvas>
<div class="controls">
<button @click="toggleAutoRotate">
{{ autoRotate ? '停止旋轉' : '自動旋轉' }}
</button>
<button @click="resetCamera">重置視圖</button>
<button @click="toggleWireframe">線框模式</button>
</div>
<div class="loading" v-if="loading">
加載中: {{ progress }}%
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue';
import * as THREE from 'three';
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js';
import { GLTFLoader } from 'three/addons/loaders/GLTFLoader.js';
// 狀態管理
const canvasRef = ref(null);
const autoRotate = ref(true);
const loading = ref(false);
const progress = ref(0);
// 場景初始化
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.background = new THREE.Color(0xeeeeee);
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, 1, 0.1, 1000);
camera.position.set(0, 1, 3);
const renderer = ref(null);
const controls = ref(null);
onMounted(() => {
renderer.value = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
canvas: canvasRef.value,
antialias: true
});
renderer.value.setSize(800, 600);
// 添加軌道控制
controls.value = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.value.domElement);
controls.value.autoRotate = autoRotate.value;
// 添加基礎燈光
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.5);
scene.add(ambientLight);
const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 0.8);
directionalLight.position.set(5, 10, 7);
scene.add(directionalLight);
// 啓動渲染循環
animate();
});
// 加載模型方法
function loadModel(url) {
loading.value = true;
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load(
url,
(gltf) => {
// 清除舊模型
clearScene();
const model = gltf.scene;
scene.add(model);
// 標準化模型
normalizeModel(model);
// 處理動畫
if (gltf.animations.length > 0) {
emit('animations-loaded', gltf.animations);
}
loading.value = false;
},
(xhr) => {
progress.value = Math.round((xhr.loaded / xhr.total) * 100);
},
(error) => {
console.error('加載失敗:', error);
loading.value = false;
emit('load-error', error);
}
);
}
// 暴露方法
defineExpose({ loadModel });
</script>5.3 模型庫組件
<!-- ModelLibrary.vue -->
<template>
<div class="model-library">
<h3>模型庫</h3>
<div class="categories">
<button
v-for="category in categories"
:key="category"
:class="{ active: currentCategory === category }"
@click="currentCategory = category"
>
{{ category }}
</button>
</div>
<div class="model-list">
<div
v-for="model in filteredModels"
:key="model.id"
class="model-card"
@click="selectModel(model)"
>
<img :src="model.thumbnail" :alt="model.name">
<div class="info">
<h4>{{ model.name }}</h4>
<p>{{ formatSize(model.size) }}</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
// 模型數據
const models = ref([
{
id: 1,
name: '科幻機器人',
category: '角色',
path: 'models/robot.glb',
thumbnail: 'thumbnails/robot.jpg',
size: 1024 * 1024 * 2.5 // 2.5MB
},
// 更多模型...
]);
const currentCategory = ref('所有');
const categories = computed(() => [
'所有',
...new Set(models.value.map(m => m.category))
]);
const filteredModels = computed(() => {
if (currentCategory.value === '所有') return models.value;
return models.value.filter(m => m.category === currentCategory.value);
});
function selectModel(model) {
emit('select', model);
}
function formatSize(bytes) {
if (bytes < 1024) return bytes + ' B';
if (bytes < 1024 * 1024) return (bytes / 1024).toFixed(1) + ' KB';
return (bytes / 1024 / 1024).toFixed(1) + ' MB';
}
</script>5.4 動畫控制器
<!-- AnimationControl.vue -->
<template>
<div class="animation-control" v-if="animations.length > 0">
<h3>動畫控制</h3>
<select v-model="currentAnimation">
<option v-for="(anim, index) in animations" :key="index" :value="index">
{{ anim.name || `動畫 ${index+1}` }}
</option>
</select>
<div class="timeline">
<input type="range" v-model="animationProgress" min="0" max="1" step="0.01">
<span>{{ formatTime(currentTime) }} / {{ formatTime(duration) }}</span>
</div>
<div class="controls">
<button @click="playAnimation">播放</button>
<button @click="pauseAnimation">暫停</button>
<button @click="stopAnimation">停止</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, watch } from 'vue';
const props = defineProps(['animations', 'mixer']);
const emit = defineEmits(['update']);
const currentAnimation = ref(0);
const animationProgress = ref(0);
const isPlaying = ref(false);
const currentTime = ref(0);
const duration = ref(0);
let currentAction = null;
// 當動畫改變時更新
watch(() => props.animations, (anims) => {
if (anims.length > 0) {
setupAnimation(currentAnimation.value);
}
});
// 設置動畫
function setupAnimation(index) {
if (currentAction) {
currentAction.stop();
}
const clip = props.animations[index];
currentAction = props.mixer.clipAction(clip);
duration.value = clip.duration;
currentTime.value = 0;
// 播放動畫
playAnimation();
}
function playAnimation() {
if (!currentAction) return;
currentAction.play();
isPlaying.value = true;
}
function pauseAnimation() {
if (!currentAction) return;
currentAction.paused = !currentAction.paused;
isPlaying.value = !currentAction.paused;
}
function stopAnimation() {
if (!currentAction) return;
currentAction.stop();
isPlaying.value = false;
currentTime.value = 0;
animationProgress.value = 0;
}
// 更新動畫進度
watch(animationProgress, (value) => {
if (currentAction) {
currentAction.time = value * duration.value;
currentAction.play();
currentAction.paused = true;
}
});
// 監聽mixer更新
props.mixer.addEventListener('loop', (e) => {
currentTime.value = e.time % duration.value;
animationProgress.value = currentTime.value / duration.value;
});
function formatTime(seconds) {
const mins = Math.floor(seconds / 60);
const secs = Math.floor(seconds % 60);
return `${mins}:${secs.toString().padStart(2, '0')}`;
}
</script>5.5 材質編輯器
<!-- MaterialEditor.vue -->
<template>
<div class="material-editor" v-if="materials.length > 0">
<h3>材質編輯</h3>
<select v-model="currentMaterial">
<option v-for="(mat, index) in materials" :key="index" :value="mat">
{{ mat.name || `材質 ${index+1}` }}
</option>
</select>
<div v-if="currentMaterial" class="material-properties">
<ColorPicker label="基礎色" v-model="currentMaterial.color" />
<div class="slider-group">
<label>金屬度</label>
<input type="range" v-model.number="currentMaterial.metalness" min="0" max="1" step="0.01">
<span>{{ currentMaterial.metalness.toFixed(2) }}</span>
</div>
<div class="slider-group">
<label>粗糙度</label>
<input type="range" v-model.number="currentMaterial.roughness" min="0" max="1" step="0.01">
<span>{{ currentMaterial.roughness.toFixed(2) }}</span>
</div>
<button @click="applyChanges">應用更改</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, watch } from 'vue';
const props = defineProps(['model']);
const emit = defineEmits(['update']);
const materials = ref([]);
const currentMaterial = ref(null);
// 收集模型中的所有材質
watch(() => props.model, (model) => {
if (!model) return;
materials.value = [];
model.traverse((obj) => {
if (obj.isMesh && obj.material) {
// 處理材質數組
const mats = Array.isArray(obj.material) ? obj.material : [obj.material];
mats.forEach(mat => {
if (!materials.value.includes(mat)) {
materials.value.push(mat);
}
});
}
});
if (materials.value.length > 0) {
currentMaterial.value = materials.value[0];
}
});
function applyChanges() {
materials.value.forEach(mat => {
mat.needsUpdate = true;
});
emit('update');
}
</script>6. 錯誤處理與回退
6.1 錯誤處理策略
function handleModelError(error, modelPath) {
console.error('模型加載失敗:', modelPath, error);
// 1. 嘗試加載低質量版本
if (!modelPath.includes('-lowpoly')) {
const fallbackPath = modelPath.replace('.glb', '-lowpoly.glb');
loadModel(fallbackPath);
return;
}
// 2. 顯示佔位模型
showPlaceholderModel();
// 3. 報告錯誤到服務器
reportErrorToServer({
error: error.message,
model: modelPath,
browser: navigator.userAgent
});
}
function showPlaceholderModel() {
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1);
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0xff0000,
wireframe: true
});
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
scene.add(cube);
}6.2 模型驗證
function validateModel(model) {
const issues = [];
// 檢查幾何體
model.traverse(obj => {
if (obj.isMesh) {
// 驗證UV座標
if (!obj.geometry.attributes.uv) {
issues.push(`模型 ${obj.name} 缺少UV座標`);
}
// 驗證法線
if (!obj.geometry.attributes.normal) {
issues.push(`模型 ${obj.name} 缺少法線`);
}
// 檢查材質設置
if (obj.material.roughness === 0 && obj.material.metalness === 1) {
issues.push(`材質 ${obj.material.name} 可能設置錯誤 (全反射金屬)`);
}
}
});
return issues;
}7. 高級技巧
7.1 模型分塊加載
// 使用GLTF tiles擴展
import { GLTFTiles } from 'three/addons/loaders/GLTFTiles.js';
const tilesLoader = new GLTFTiles();
tilesLoader.loadBoundingVolume('models/tileset.json', (tileset) => {
// 只加載視野內的區塊
const visibleTiles = tileset.getVisibleTiles(camera);
visibleTiles.forEach(tile => {
tilesLoader.loadTile(tile.url, (gltf) => {
scene.add(gltf.scene);
});
});
});
// 相機移動時更新
cameraControls.addEventListener('change', () => {
const newVisibleTiles = tileset.getVisibleTiles(camera);
// 加載新塊,卸載不可見塊...
});7.2 模型差異更新
// 使用JSON差異更新模型
function updateModel(oldModel, newModel) {
const diff = calculateModelDiff(oldModel, newModel);
diff.changedMaterials.forEach(matDiff => {
const material = findMaterialById(matDiff.id);
Object.assign(material, matDiff.properties);
material.needsUpdate = true;
});
diff.addedObjects.forEach(objData => {
const obj = createObjectFromData(objData);
scene.add(obj);
});
diff.removedObjects.forEach(id => {
const obj = scene.getObjectByProperty('uuid', id);
if (obj) scene.remove(obj);
});
}7.3 模型版本控制
// 模型版本管理
const modelVersions = {
'robot': {
v1: 'models/robot_v1.glb',
v2: 'models/robot_v2.glb',
latest: 'v2'
}
};
function loadModelVersion(modelName, version = 'latest') {
const versionInfo = modelVersions[modelName];
if (!versionInfo) throw new Error(`Unknown model: ${modelName}`);
const actualVersion = version === 'latest' ?
versionInfo.latest : version;
const path = versionInfo[actualVersion];
if (!path) throw new Error(`Invalid version: ${version}`);
loadModel(path);
}8. 最佳實踐
- 模型預處理:
- 使用Blender進行三角化處理
- 刪除無用頂點組和形狀鍵
- 合併相同材質網格
- 資源管理:
graph TD
A[模型加載] --> B{是否常用?}
B -->|是| C[加入預加載隊列]
B -->|否| D[按需加載]
C --> E[資源池緩存]
D --> F[使用後釋放]- 移動端優化:
- 最大模型尺寸<5MB
- 最大紋理尺寸1024x1024
- 使用Draco壓縮幾何體
- 禁用非必要動畫
9. 常見問題解答
Q1:GLB和GLTF有什麼區別?
- GLTF:JSON格式文本文件 + 外部二進制/紋理
- GLB:單文件格式,包含所有數據
- 建議:使用GLB簡化部署,GLTF便於調試
Q2:模型顯示為黑色怎麼辦?
- 檢查光源是否添加
- 確認材質是否需要光照(MeshBasicMaterial不受光)
- 驗證法線方向是否正確
- 檢查紋理是否加載失敗
Q3:如何減小模型體積?
- 使用Draco幾何壓縮(減少50-70%)
- 轉換紋理為Basis Universal(減少80%)
- 簡化幾何體(減少面數)
- 量化頂點數據(減少精度)
10. 總結
通過本文,你已掌握:
- GLTF/OBJ格式結構與加載技術
- 模型標準化與動畫處理方法
- 模型壓縮與優化策略
- Vue3模型預覽編輯器實現
- 錯誤處理與驗證技術
- 高級技巧:分塊加載、差異更新
- 模型管理最佳實踐
核心價值:Three.js的模型加載系統將專業3D內容無縫集成到Web環境,結合Vue3的響應式管理,實現影視級3D資產的實時交互體驗。
下一篇預告
第十二篇:粒子系統:海量點渲染
你將學習:
- Points與PointsMaterial核心API
- GPU加速粒子計算
- 動態粒子效果(火焰/煙霧/魔法)
- 粒子碰撞與物理模擬
- 百萬級粒子優化策略
- Vue3實現粒子編輯器
準備好創造令人驚歎的粒子效果了嗎?讓我們進入微觀世界的視覺盛宴!