點擊上方“程序員蝸牛g”,選擇“設為星標”
跟蝸牛哥一起,每天進步一點點
程序員蝸牛g
大廠程序員一枚 跟蝸牛一起 每天進步一點點
33篇原創內容
公眾號
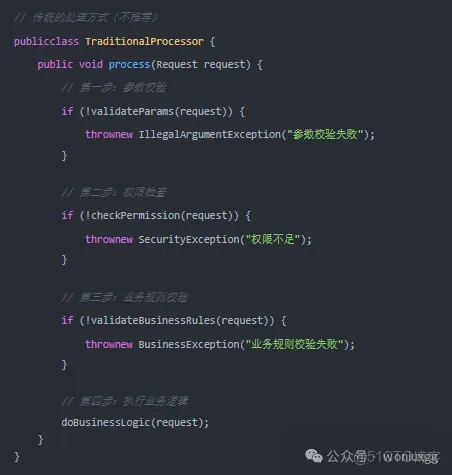
思考一個問題:當一個複雜的業務請求需要經過多個處理節點時,我們通常會怎麼做?
這種方式有什麼問題呢?
二、什麼是責任鏈模式?
三、什麼是策略模式?
四、兩種模式如何結合?
五、實現思路詳解
5.1 定義統一的處理接口
首先我們需要定義一個統一的處理器接口:
// 處理器接口
public interface RequestHandler {
/**
* 處理請求
* @param context 請求上下文
* @return 是否繼續處理
*/
boolean handle(RequestContext context);
/**
* 獲取處理器名稱
*/
String getName();
}5.2 定義請求上下文
為了在處理鏈中傳遞數據,我們需要一個上下文對象:
// 請求上下文
public class RequestContext {
private Map<String, Object> attributes = new HashMap<>();
private Object requestData;
private Object responseData;
private List<String> processLog = new ArrayList<>();
// getter/setter方法...
public void addProcessLog(String log) {
processLog.add(log);
}
}5.3 實現責任鏈接口
接下來實現責任鏈的核心邏輯:
// 責任鏈接口
publicabstractclass AbstractHandlerChain implements RequestHandler {
protected RequestHandler nextHandler;
public void setNextHandler(RequestHandler handler) {
this.nextHandler = handler;
}
@Override
public boolean handle(RequestContext context) {
// 當前處理器處理
boolean result = doHandle(context);
// 如果處理成功且有下一個處理器,則繼續處理
if (result && nextHandler != null) {
return nextHandler.handle(context);
}
return result;
}
// 子類需要實現的具體處理邏輯
protected abstract boolean doHandle(RequestContext context);
}5.4 實現具體的處理器
現在我們可以實現各種具體的處理器了:
// 參數校驗處理器
@Component
publicclass ParameterValidationHandler extends AbstractHandlerChain {
@Override
public String getName() {
return"參數校驗處理器";
}
@Override
protected boolean doHandle(RequestContext context) {
// 獲取請求數據
Object requestData = context.getRequestData();
// 執行參數校驗邏輯
if (requestData == null) {
context.addProcessLog("參數為空,校驗失敗");
returnfalse;
}
// 更多校驗邏輯...
context.addProcessLog("參數校驗通過");
returntrue;
}
}
// 權限檢查處理器
@Component
publicclass PermissionCheckHandler extends AbstractHandlerChain {
@Override
public String getName() {
return"權限檢查處理器";
}
@Override
protected boolean doHandle(RequestContext context) {
// 獲取用户信息
String userId = (String) context.getAttribute("userId");
// 執行權限檢查邏輯
if (!hasPermission(userId)) {
context.addProcessLog("用户權限不足");
returnfalse;
}
context.addProcessLog("權限檢查通過");
returntrue;
}
private boolean hasPermission(String userId) {
// 實際的權限檢查邏輯
returntrue; // 簡化示例
}
}5.5 策略模式的應用
對於同一類型的處理器,我們可以用策略模式來實現不同的處理策略:
// 業務規則校驗策略接口
publicinterface BusinessRuleStrategy {
boolean validate(RequestContext context);
String getRuleName();
}
// 訂單金額校驗策略
@Component
publicclass OrderAmountRuleStrategy implements BusinessRuleStrategy {
@Override
public boolean validate(RequestContext context) {
// 獲取訂單信息
OrderInfo orderInfo = (OrderInfo) context.getRequestData();
// 校驗金額是否合理
if (orderInfo.getAmount().compareTo(BigDecimal.valueOf(100000)) > 0) {
context.addProcessLog("訂單金額過大");
returnfalse;
}
returntrue;
}
@Override
public String getRuleName() {
return"訂單金額校驗";
}
}
// 庫存校驗策略
@Component
publicclass InventoryRuleStrategy implements BusinessRuleStrategy {
@Override
public boolean validate(RequestContext context) {
// 獲取商品信息
ProductInfo productInfo = (ProductInfo) context.getRequestData();
// 校驗庫存是否充足
if (productInfo.getStock() < productInfo.getQuantity()) {
context.addProcessLog("庫存不足");
returnfalse;
}
returntrue;
}
@Override
public String getRuleName() {
return"庫存校驗";
}
}
// 業務規則校驗處理器(使用策略模式)
@Component
publicclass BusinessRuleHandler extends AbstractHandlerChain {
@Autowired
private List<BusinessRuleStrategy> strategies;
@Override
public String getName() {
return"業務規則校驗處理器";
}
@Override
protected boolean doHandle(RequestContext context) {
// 依次執行所有業務規則策略
for (BusinessRuleStrategy strategy : strategies) {
if (!strategy.validate(context)) {
context.addProcessLog("業務規則校驗失敗: " + strategy.getRuleName());
returnfalse;
}
context.addProcessLog("業務規則校驗通過: " + strategy.getRuleName());
}
returntrue;
}
}5.6 鏈的組裝和管理
為了讓責任鏈更加靈活,我們需要一個鏈的管理器:
// 處理鏈管理器
@Component
publicclass HandlerChainManager {
@Autowired
private List<RequestHandler> handlers;
// 根據配置組裝處理鏈
public RequestHandler buildChain(List<String> handlerNames) {
if (handlerNames == null || handlerNames.isEmpty()) {
returnnull;
}
RequestHandler head = null;
RequestHandler current = null;
for (String handlerName : handlerNames) {
RequestHandler handler = findHandlerByName(handlerName);
if (handler != null) {
if (head == null) {
head = handler;
current = handler;
} else {
((AbstractHandlerChain) current).setNextHandler(handler);
current = handler;
}
}
}
return head;
}
private RequestHandler findHandlerByName(String name) {
return handlers.stream()
.filter(h -> h.getName().equals(name))
.findFirst()
.orElse(null);
}
}六、使用示例
現在讓我們看看如何使用這套機制:
// 服務類
@Service
publicclass RequestProcessingService {
@Autowired
private HandlerChainManager chainManager;
public ProcessResult processRequest(Object requestData) {
// 創建請求上下文
RequestContext context = new RequestContext();
context.setRequestData(requestData);
context.setAttribute("userId", getCurrentUserId());
// 定義處理鏈順序
List<String> handlerSequence = Arrays.asList(
"參數校驗處理器",
"權限檢查處理器",
"業務規則校驗處理器",
"業務邏輯處理器"
);
// 組裝處理鏈
RequestHandler chain = chainManager.buildChain(handlerSequence);
// 執行處理
boolean success = chain != null && chain.handle(context);
// 返回處理結果
return ProcessResult.builder()
.success(success)
.processLogs(context.getProcessLog())
.responseData(context.getResponseData())
.build();
}
private String getCurrentUserId() {
// 獲取當前用户ID的邏輯
return"USER001";
}
}為了避免每次都重新組裝處理鏈,我們可以加入緩存機制:
// 帶緩存的處理鏈管理器
@Component
public class CachedHandlerChainManager {
private final Map<String, RequestHandler> chainCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public RequestHandler getOrCreateChain(String chainKey, List<String> handlerNames) {
return chainCache.computeIfAbsent(chainKey, k -> buildChain(handlerNames));
}
}// 帶異常處理的責任鏈接口
public abstract class ExceptionSafeHandlerChain extends AbstractHandlerChain {
@Override
public boolean handle(RequestContext context) {
try {
boolean result = doHandle(context);
if (result && nextHandler != null) {
return nextHandler.handle(context);
}
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 記錄異常日誌
context.addProcessLog("處理器執行異常: " + getName() + ", 錯誤: " + e.getMessage());
// 根據業務需求決定是否繼續執行下一個處理器
return handleException(e, context);
}
}
protected boolean handleException(Exception e, RequestContext context) {
// 默認情況下,異常會導致處理鏈中斷
return false;
}
}在實際項目中,我們可以根據具體的業務需求來調整這種模式的實現細節,但核心思想是一致的:通過合理的抽象和組合,讓複雜的業務邏輯變得清晰可控。
如果這篇文章對您有所幫助,或者有所啓發的話,求一鍵三連:點贊、轉發、在看。
關注公眾號:woniuxgg,在公眾號中回覆:筆記 就可以獲得蝸牛為你精心準備的java實戰語雀筆記,回覆面試、開發手冊、有超讚的粉絲福利