文章目錄
- 字符串轉整型
- 整型轉字符串
- 字符串轉布爾值
- 布爾值轉字符串
- 轉換成 Go 字符串
- 字符串轉浮點數
- 浮點數轉字符串
- 字符串轉複數
- 複數轉字符串
- 字符串追加數據
字符串轉整型
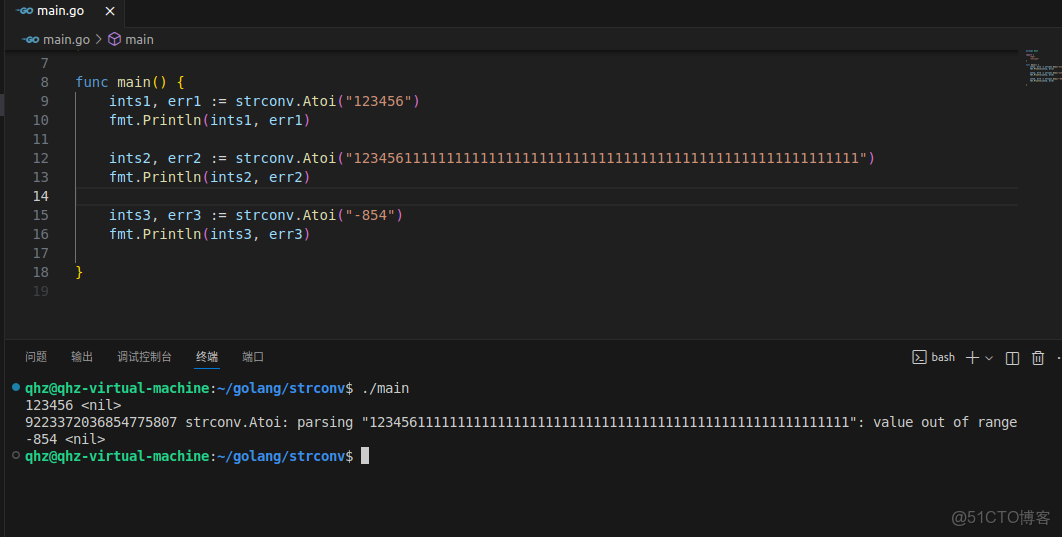
func Atoi(s string) (int, error)s是要轉換的字符串,返回值一個是轉換後的int值,一個是錯誤,當轉換成功的話error為nil。
正數負數都可以轉換,超過範圍、或者無法轉換可以通過返回值error來分辨。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
ints1, err1 := strconv.Atoi("123456")
fmt.Println(ints1, err1)
ints2, err2 := strconv.Atoi("123456111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111")
fmt.Println(ints2, err2)
ints3, err3 := strconv.Atoi("-854")
fmt.Println(ints3, err3)
}整型轉字符串
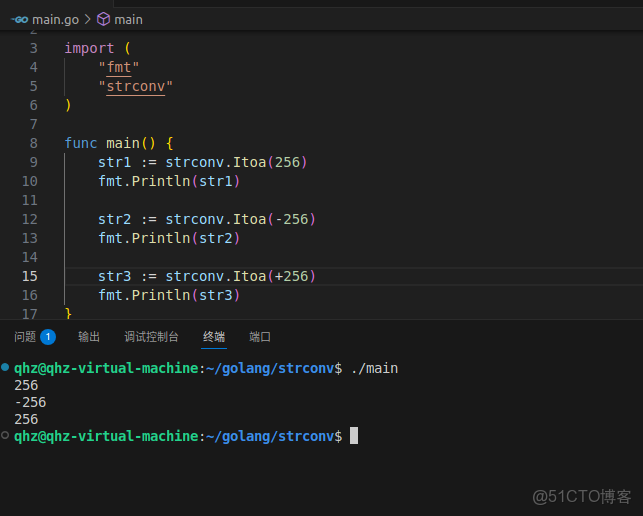
func Itoa(i int) string一個返回值類型為string,和Atoi不一樣,Atoi有倆返回值,Itoa只有一個
正數負數都可轉換
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
str1 := strconv.Itoa(256)
fmt.Println(str1)
str2 := strconv.Itoa(-256)
fmt.Println(str2)
str3 := strconv.Itoa(+256)
fmt.Println(str3)
}字符串轉布爾值
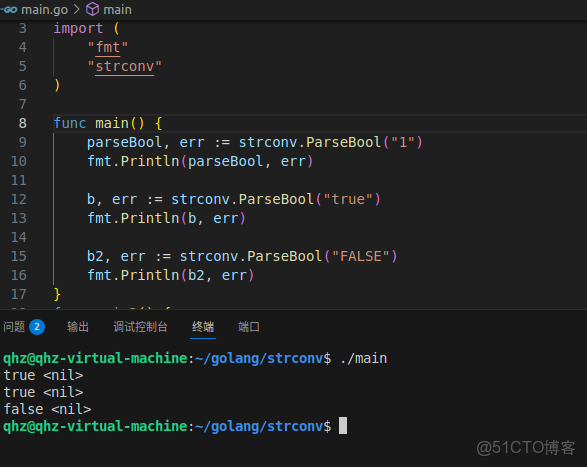
func ParseBool(str string) (bool, error)作用是把下面的字符串轉換為bool值,比如傳入個1,會返回個bool類型的true,傳入個0,會返回個bool類型的false
“1”, “t”, “T”, “true”, “TRUE”, “True” // true
“0”, “f”, “F”, “false”, “FALSE”, “False” // false
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
parseBool, err := strconv.ParseBool("1")
fmt.Println(parseBool, err)
b, err := strconv.ParseBool("true")
fmt.Println(b, err)
b2, err := strconv.ParseBool("FALSE")
fmt.Println(b2, err)
}布爾值轉字符串
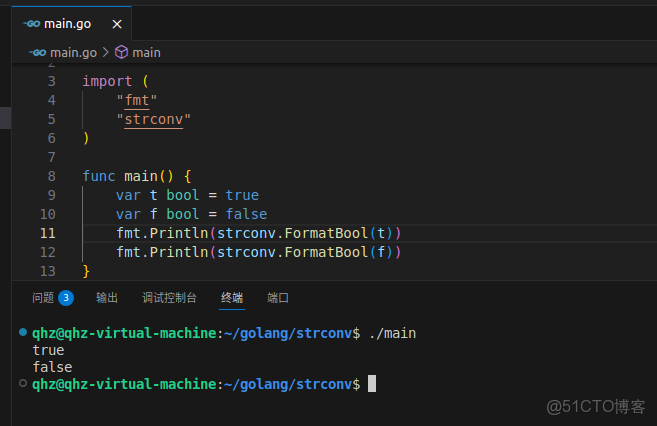
func FormatBool(b bool) string傳入一個bool值,返回一個全小寫無引號的true或者false字符串
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
var t bool = true
var f bool = false
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatBool(t))
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatBool(f))
}轉換成 Go 字符串
func Quote(s string) string
func QuoteToASCII(s string) stringQuote 保留原始字符,非 ASCII 字符(如中文)直接輸出。
QuoteToASCII 將非 ASCII 字符(如中文)轉義為 Unicode 轉義序列(\uXXXX)。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(strconv.Quote("hello 世界")) // 輸出: "hello 世界"
fmt.Println(strconv.QuoteToASCII("hello 世界")) // 輸出: "hello \u4e16\u754c"
}字符串轉浮點數
func ParseFloat(s string, bitSize int) (float64, error)s是要轉換的字符串
bitsize是位數,必須是32或者64其中一個,表示轉為為32位精度還是64位精度。
32位精度在6-7位,64位精度在15-16位
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
float, err := strconv.ParseFloat("3.1415926", 32)
fmt.Println(float, err)
float, err = strconv.ParseFloat("1.14576247456852556", 64)
fmt.Println(float, err)
}- 第一行輸出:3.141592502593994(bitSize=32)
輸入字符串:“3.1415926”(7 位有效數字)。
實際解析:
字符串被解析為 float32 精度(約 6-7 位有效數字),但返回的是 float64 類型。
float32 無法精確表示 3.1415926,因此發生了舍入:
原始值 3.1415926 的二進制表示在 float32 中會被舍入為最接近的可表示值 3.141592502593994。
為什麼返回 float64?
Go 的 ParseFloat 統一返回 float64,但數值範圍受 bitSize 限制。若需 float32,需顯式轉換:float32(float)。 - 第二行輸出:1.14576247456852556(bitSize=64)
輸入字符串:“1.14576247456852556”(17 位有效數字)。
實際解析:
字符串被解析為 float64 精度(約 15-16 位有效數字)。
float64 能精確表示前 15-16 位,因此輸出與輸入幾乎一致(末尾數字可能因二進制浮點表示略有差異)。
浮點數轉字符串
func FormatFloat(f float64, fmt byte, prec int, bitSize int) stringf float64:要格式化的浮點數(類型必須是 float64)。
fmt byte:格式化方式,取值範圍:
'f'(-ddd.dddd):普通小數格式。'e'(-d.dddde±dd):科學計數法(小寫e)。'E'(-d.ddddE±dd):科學計數法(大寫E)。'g'('e'或'f'的緊湊形式):根據情況自動選擇'e'或'f',以生成更短的字符串。'b'(-ddddp±dd):二進制指數格式(如-123456p-78)。
prec int:控制精度(小數點後的位數或科學計數法的有效數字):
- 對於
'f'、'e'、'E':表示小數點後的位數。 - 對於
'g':表示最大有效數字(尾部的0會被省略)。 - 對於
'b':忽略prec。
bitSize int: 指定 f 的原始類型(32 或 64),影響解析時的舍入行為:
32:f是float32轉換來的float64,格式化時會按float32精度處理。64:f是原始float64值,按完整精度處理。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
f := 3.141592653589793
// 1. 普通小數格式 ('f')
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatFloat(f, 'f', 2, 64)) // 3.14
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatFloat(f, 'f', 5, 64)) // 3.14159
// 2. 科學計數法 ('e')
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatFloat(f, 'e', 3, 64)) // 3.142e+00
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatFloat(f, 'E', 3, 64)) // 3.142E+00
// 3. 自動選擇 'e' 或 'f' ('g')
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatFloat(f, 'g', 4, 64)) // 3.142
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatFloat(123456.0, 'g', 4, 64)) // 1.235e+05
// 4. 二進制指數格式 ('b')
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatFloat(f, 'b', 0, 64)) // 7074237752068736p-51
// 5. bitSize 的影響(模擬 float32 的精度)
f32 := float32(f)
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatFloat(float64(f32), 'f', 5, 32)) // 3.14159 (float32 的精度)
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatFloat(float64(f32), 'f', 10, 32)) // 3.1415927410 (float32 的精度限制)
}字符串轉複數
func ParseComplex(s string, bitSize int) (complex128, error)s - 要轉換的字符串
bitSize - 位數,必須是64或128其中之一
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(strconv.ParseComplex("1+2i", 128))
fmt.Println(strconv.ParseComplex("1+2j", 128))//只支持 i 作為虛部單位
}複數轉字符串
func FormatComplex(c complex128, fmt byte, prec, bitSize int) stringc- 複數
fmt - 格式化類型,參考浮點數格式化類型
prec - 參考浮點數精度
bitsize - 位數,必須是64或128之一
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatComplex(complex(1.1, 12), 'f', 2, 128))
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatComplex(complex(5.6, 2.8), 'b', 2, 128))
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatComplex(complex(18.88999, 89.7), 'g', 2, 128))
}字符串追加數據
在 Java 中,字符串與其他類型(如數字)進行拼接時,會自動將非字符串類型轉換為字符串。例如:
String result = "1" + 1; // 結果為 "11",Java 自動將數字 1 轉換為字符串 "1"但在 go 裏,這種隱式類型轉換是不允許的。如果嘗試直接拼接字符串和數字,編譯器會報錯:
result := "1" + 1 // 編譯錯誤:invalid operation: "1" + 1 (mismatched types string and int)go 要求顯式處理類型轉換。如果需要將數字(如 int、float64 等)拼接到字符串中,可以使用 strconv包提供的函數(如 FormatInt、FormatFloat 等),或直接使用 fmt.Sprintf`進行格式化。
但如果高效拼接字符串和數字(避免額外分配內存),Go 的 strconv包還提供了 Append系列函數,可以直接將數字的字符串表示追加到現有的 []byte切片中,減少內存分配。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
bytes := []byte("這裏有一些數據:")
bytes = strconv.AppendInt(bytes, 10, 10)
bytes = strconv.AppendFloat(bytes, 1.2222, 'f', 2, 64)
bytes = strconv.AppendBool(bytes, false)
fmt.Println(string(bytes))
}