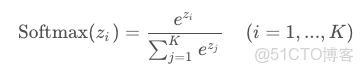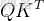Softmax函數
Softmax函數用於將值變成一個概率分佈(和為1)。
softmax 的核心作用可以概括為三個方面:
1. 把一組實數轉換成概率分佈
softmax 會把任意向量轉成非負且總和為 1 的結果,常用來表示概率。
這樣模型輸出可以被解釋為不同類別的概率。
2. 放大差異
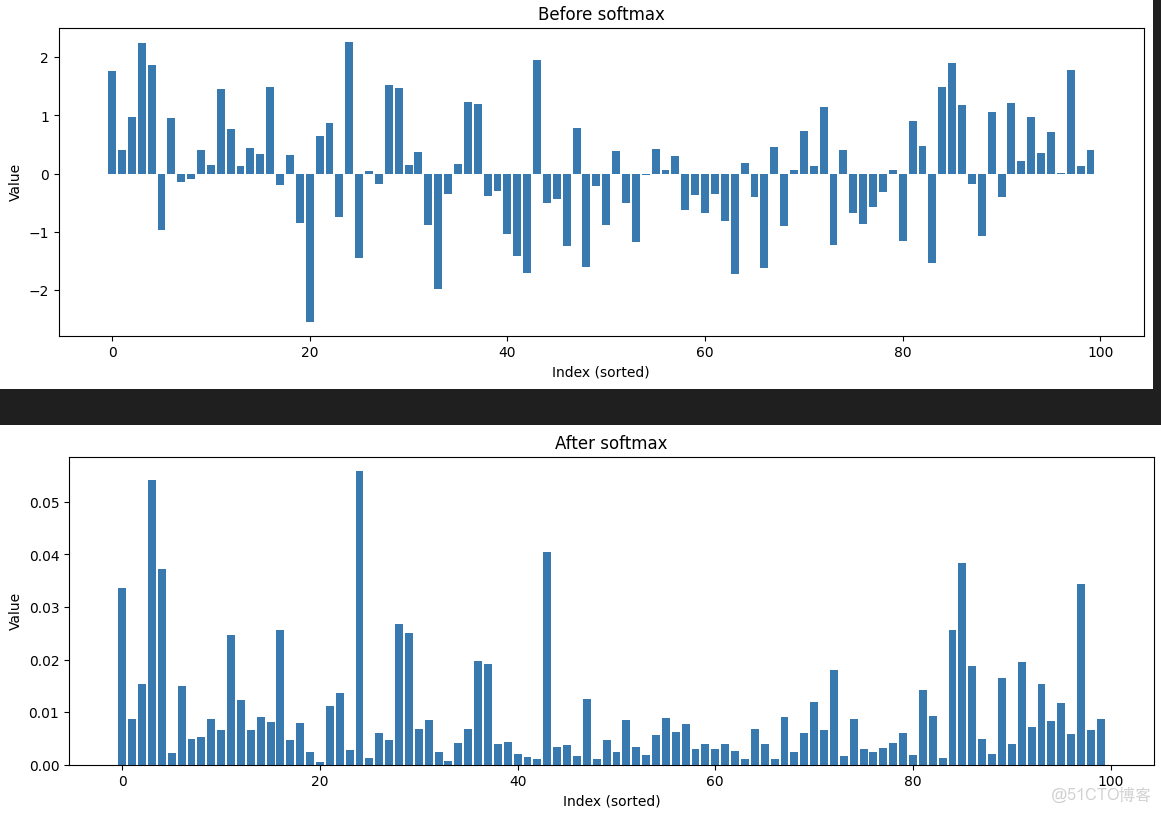
softmax 對大的值更敏感,小的值會被壓得更小,大的值會更突出。
這讓模型更容易做出明確選擇。
3. 在訓練中提供可微分的概率輸出
分類任務通常用交叉熵損失,而交叉熵需要概率分佈,softmax 剛好提供了連續可微的概率。
這讓模型可以通過梯度下降訓練。
# numpy生成矩陣
np.random.randn(2, 3, 4)
# softmax函數示例
# Generate 100 dimensional vector
np.random.seed(0)
x = np.random.randn(100)
# Compute softmax
x_max = np.max(x)
e_x = np.exp(x - x_max)
softmax_x = e_x / np.sum(e_x)實際使用時的函數:
def softmax(x, axis=-1):
x_max = np.max(x, axis=axis, keepdims=True)
e_x = np.exp(x - x_max)
return e_x / np.sum(e_x, axis=axis, keepdims=True)Attention的示意圖
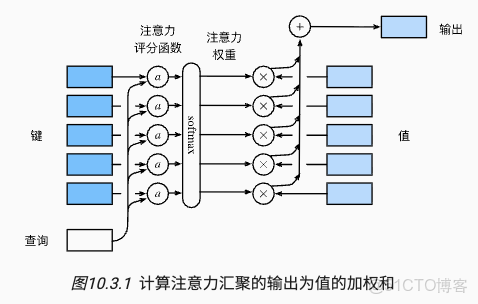
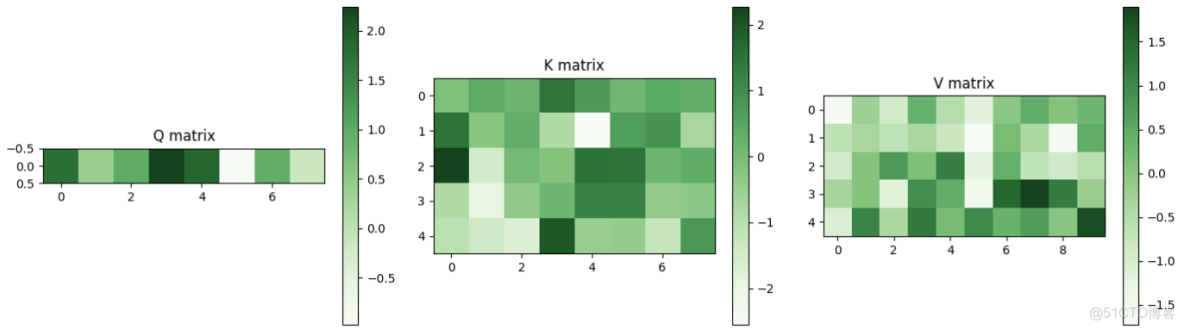
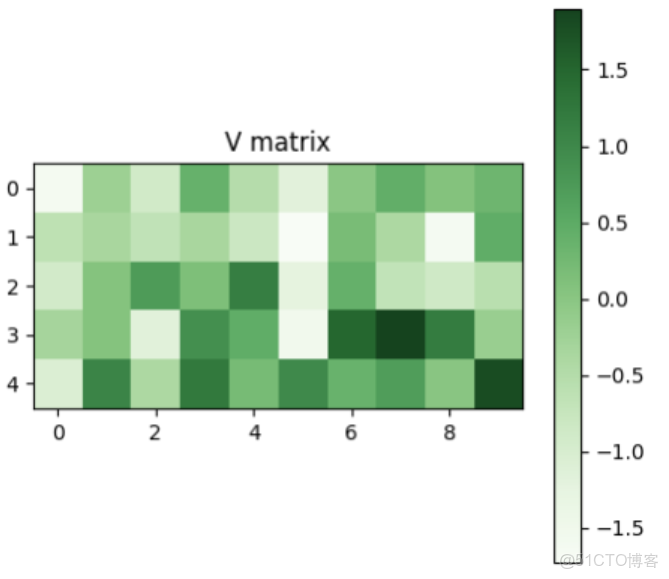
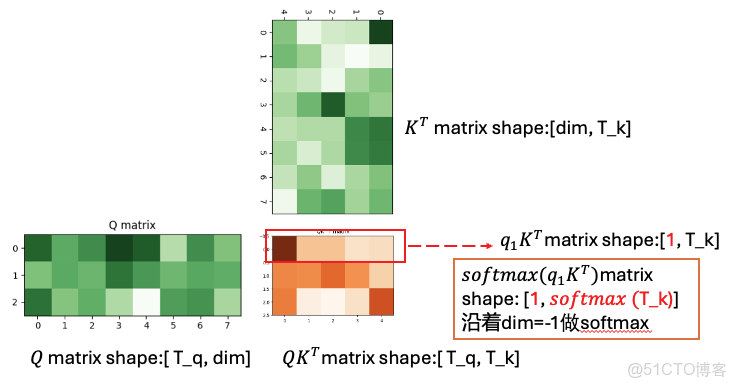
假設有一個query Q,維度是8,
5個key:維度也是8,其對應的5個value,維度是10
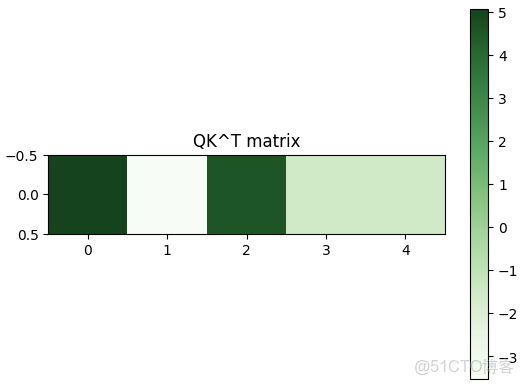
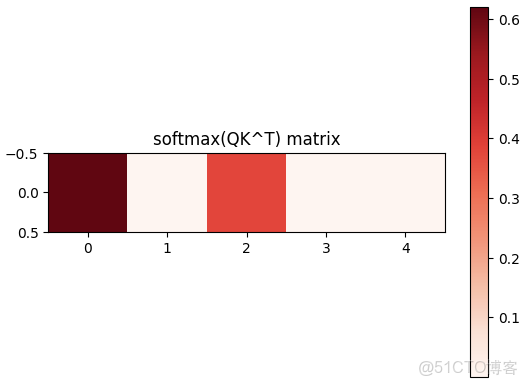
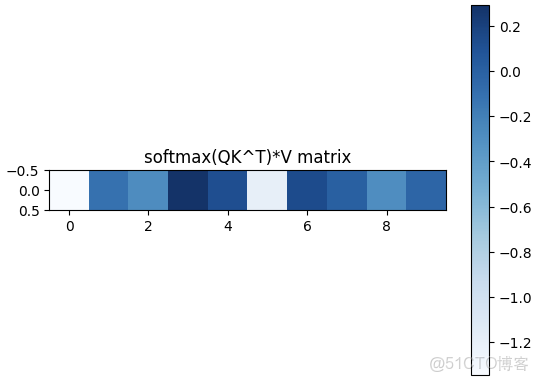
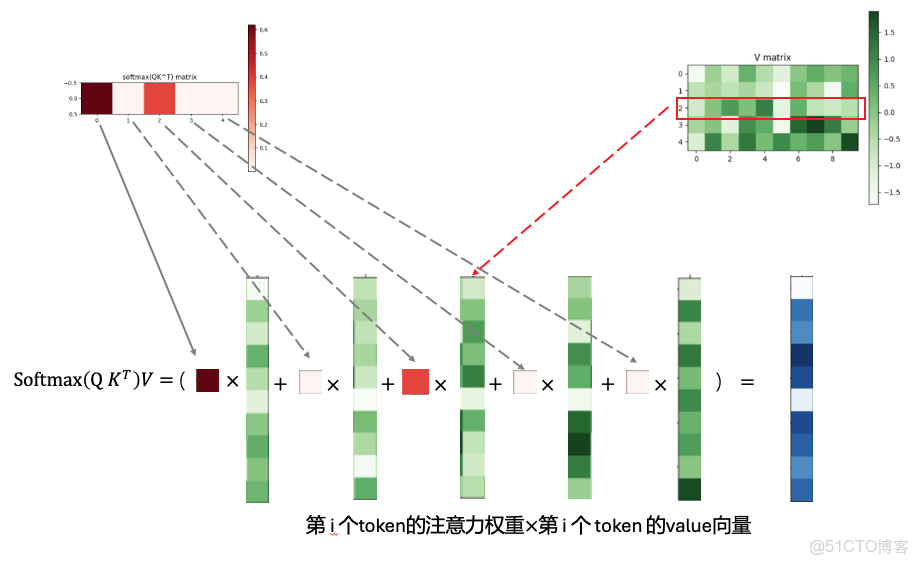
首先Q會和每個key算內積,得到的值經過softmax就是attention的概率分佈(注意力權重,是概率分佈)
經過softmax之後,就是這個query對5個key的注意力權重分佈。
根據這個權重,將其分配到每個value上,就得到了query最終的結果。
最後,這個計算的可視化展示如下:
對於多個query(比如有三個),其和五個keys計算attention時(
)的計算方式如下:
由上面的過程可以看出,廣義的attention計算中:
- KV的個數必須一樣(實際體現在KV都是由同一組token得到)
- Q的個數可以和KV不一樣,但是Q和K的維度要一樣(計算內積,用於Q對於每個key的計算注意力權重)
- V的維度是自由的,其維度為最後的到的token的維度。同時,最後的到的token的數量為Q的數量
單頭注意力機制的numpy代碼實現:
numpy函數用法:
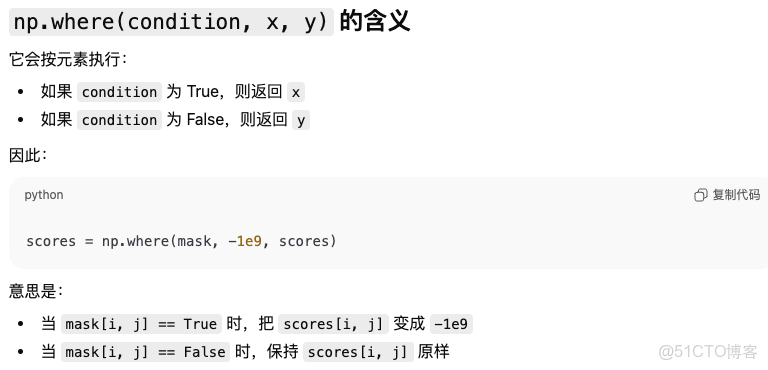
np.where
np.matmul()
批量矩陣乘法。當輸入是三維或更高維,會對前面的維度廣播(batch dim 不參與乘法,只逐個對應計算)
np.transpose()
import numpy as np
def softmax(x, axis=-1):
x_max = np.max(x, axis=axis, keepdims=True)
e_x = np.exp(x - x_max)
return e_x / np.sum(e_x, axis=axis, keepdims=True)
def scaled_dot_product_attention(Q, K, V, mask=None):
"""
Q: (batch, seq_q, d_k)
K: (batch, seq_k, d_k)
V: (batch, seq_k, d_v)
mask: (batch, seq_q, seq_k) or None. mask entries True means masked (ignore)
returns: output (batch, seq_q, d_v), attention_weights (batch, seq_q, seq_k)
"""
d_k = Q.shape[-1]
# 1) Q @ K^T
scores = np.matmul(Q, K.transpose(0, 2, 1)) # (batch, seq_q, seq_k)
# 2) scale
scores = scores / np.sqrt(float(d_k))
# 3) apply mask if present
if mask is not None:
# set masked positions to large negative value so softmax ~ 0
scores = np.where(mask, -1e9, scores)
# 4) softmax to get attention weights
attn = softmax(scores, axis=-1) # 在seq_k的維度上做softmax,(batch, seq_q, seq_k)
# 5) weighted sum with V
output = np.matmul(attn, V) # (batch, seq_q, d_v)
return output, attn
# example
if __name__ == "__main__":
np.random.seed(0)
B, Tq, Tk, d = 2, 3, 4, 8 # d是dimension
Q = np.random.randn(B, Tq, d)
K = np.random.randn(B, Tk, d)
V = np.random.randn(B, Tk, d)
out, weights = scaled_dot_product_attention(Q, K, V)
print("out shape:", out.shape) # (2, 3, 8)
print("attn shape:", weights.shape) # (2, 3, 4)多頭注意力的pytorch實現:
tensor.transpose():用於交換兩個維度
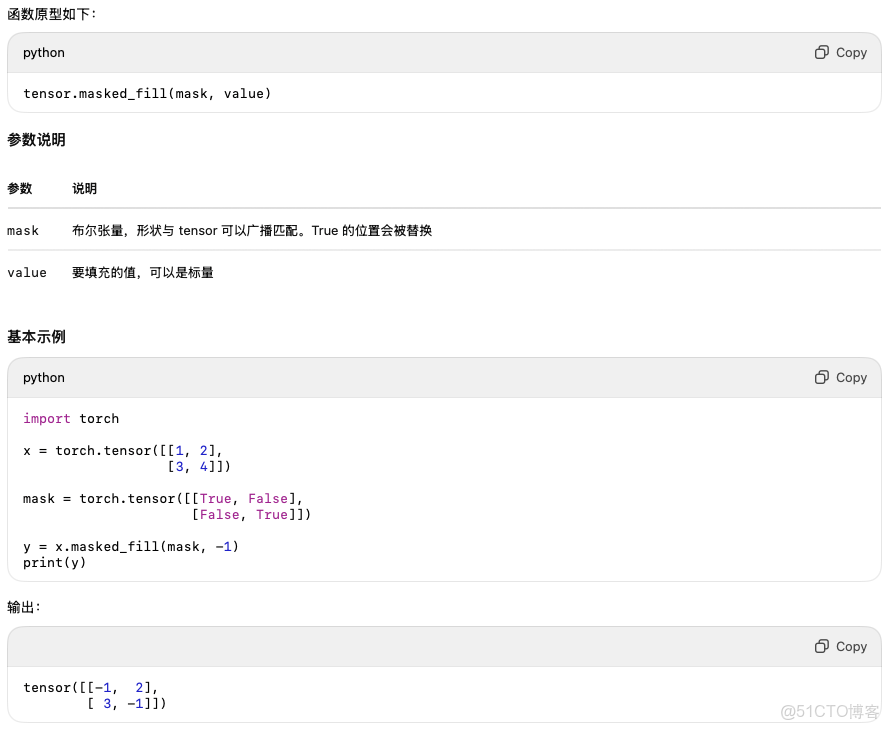
tensor.masked_fill()
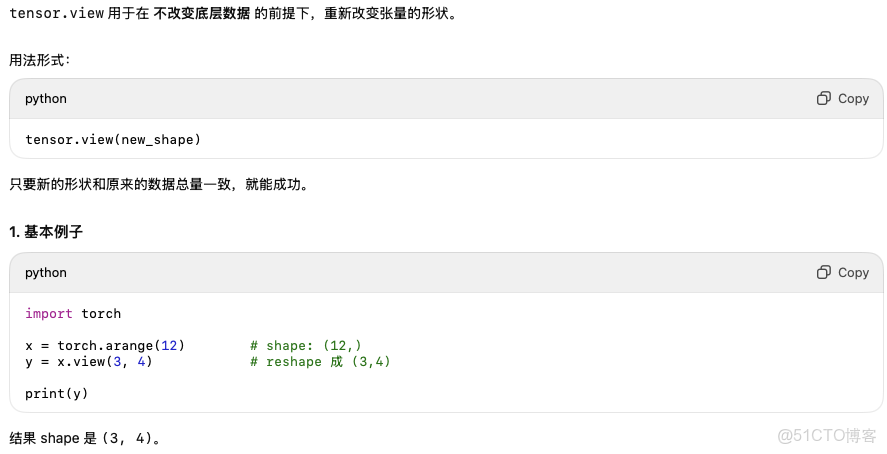
tensor.view()
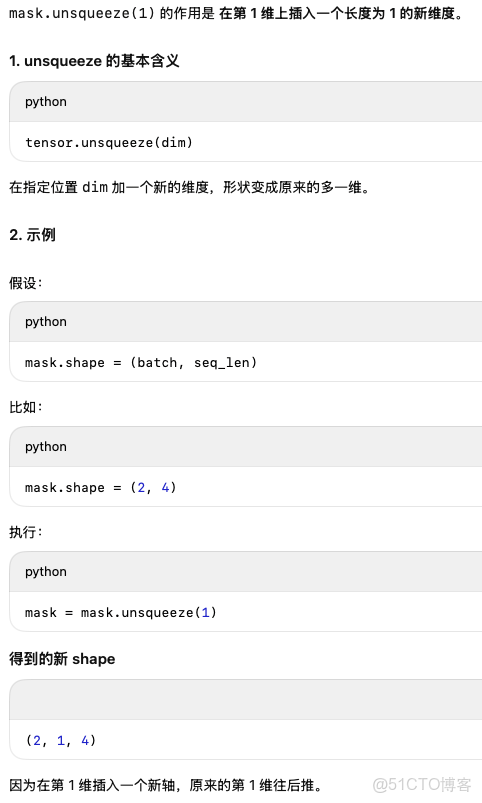
tensor.unsqueeze()
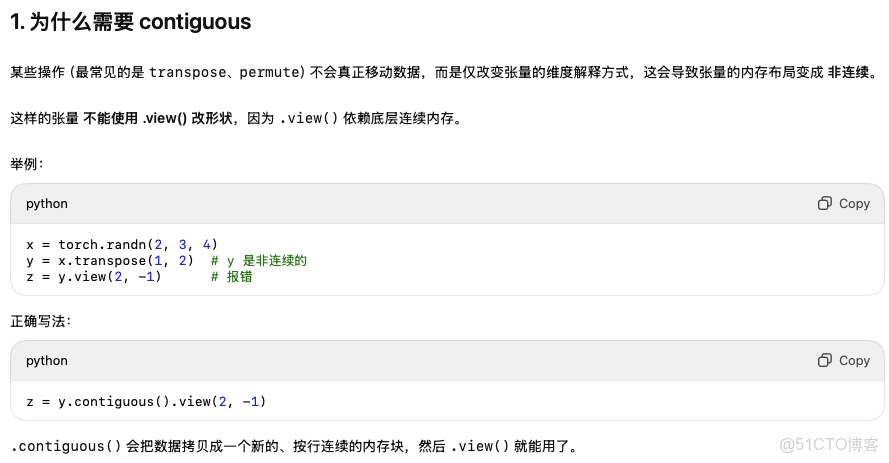
.contiguous()
如果一個tensor在transpose之後還需要進一步合併或者分裂維度時,就需要用contiguous
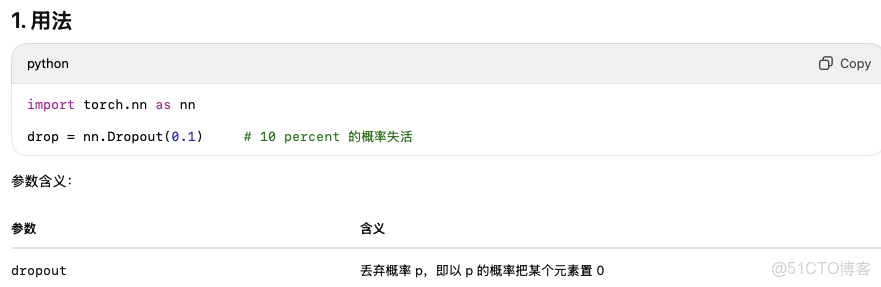
nn.Dropout()
代碼實現
單個頭的注意力計算代碼,基於Q,K,V
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
def scaled_dot_product_attention_torch(Q, K, V, mask=None, dropout=None):
"""
Q: (batch, heads, seq_q, d_k)
K: (batch, heads, seq_k, d_k)
V: (batch, heads, seq_k, d_v)
mask: (batch, 1, seq_q, seq_k) or (batch, heads, seq_q, seq_k) or None
returns: output (batch, heads, seq_q, d_v), attn (batch, heads, seq_q, seq_k)
"""
d_k = Q.size(-1)
scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-2, -1)) / torch.sqrt(torch.tensor(d_k, dtype=Q.dtype, device=Q.device))
if mask is not None:
# mask entries should be True for positions to mask
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask, float("-1e9"))
attn = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1) # softmax 從 torch.nn.functional.F中得到
if dropout is not None:
attn = dropout(attn)
output = torch.matmul(attn, V)
return output, attn
# quick test
if __name__ == "__main__":
torch.manual_seed(0)
B, H, Tq, Tk, d_k = 2, 2, 3, 4, 16
Q = torch.randn(B, H, Tq, d_k)
K = torch.randn(B, H, Tk, d_k)
V = torch.randn(B, H, Tk, d_k)
# no mask
out, att = scaled_dot_product_attention_torch(Q, K, V)
print(out.shape, att.shape) # (2, 2, 3, 16), (2, 2, 3, 4)完整代碼:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
'''
multihead,對不同的維度,有不同的head
'''
def __init__(self, d_model, num_heads, dropout=0.0):
super().__init__()
assert d_model % num_heads == 0
self.d_model = d_model
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.d_k = d_model // num_heads
self.w_q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_k = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_v = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_o = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) if dropout > 0 else None
def _split_heads(self, x):
# x: (batch, seq, d_model) -> (batch, heads, seq, d_k)
B, T, _ = x.size()
x = x.view(B, T, self.num_heads, self.d_k) # d_k 是每一小份的維度
return x.transpose(1, 2)
def _combine_heads(self, x):
# x: (batch, heads, seq, d_k) -> (batch, seq, d_model)
x = x.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
B, T, _, _ = x.size()
return x.view(B, T, self.d_model)
def forward(self, query, key, value, mask=None):
"""
query/key/value: (batch, seq, d_model)
mask: (batch, seq_q, seq_k) boolean where True means masked
returns: outputs (batch, seq_q, d_model), attn_weights (batch, heads, seq_q, seq_k)
"""
Q = self.w_q(query)
K = self.w_k(key)
V = self.w_v(value)
Q = self._split_heads(Q)
K = self._split_heads(K)
V = self._split_heads(V)
# adapt mask shape: (batch, seq_q, seq_k) -> (batch, 1, seq_q, seq_k)
if mask is not None:
mask = mask.unsqueeze(1)
out, attn = scaled_dot_product_attention_torch(Q, K, V, mask=mask, dropout=self.dropout)
# out: (batch, heads, seq_q, d_k)
out = self._combine_heads(out) # (batch, seq_q, d_model)
out = self.w_o(out) # 對拼接在一起之後的token再進行一個線性變換
return out, attn
# example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
B, T, S, d_model, heads = 2, 5, 6, 64, 8
mha = MultiHeadAttention(d_model, heads, dropout=0.1)
x_q = torch.randn(B, T, d_model) # query length T
x_kv = torch.randn(B, S, d_model) # key/value length S
# optional mask: mask padded positions in key (True = mask)
mask = torch.zeros(B, T, S, dtype=torch.bool) # no mask here
out, attn = mha(x_q, x_kv, x_kv, mask=mask)
print("out", out.shape) # (B, T, d_model)
print("attn", attn.shape) # (B, heads, T, S)