20.1打開pytorch官網
1.打開torch.nn-Normalization Layers
找到BatchNorm2d:
點擊查看代碼
class torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True, device=None, dtype=None)其中num_features是num_features (int) – C from an expected input of size (N,C,H,W);
Normalization層用於加快神經網絡的運行速度
2.打開torch.nn-Linear Layers(常用)
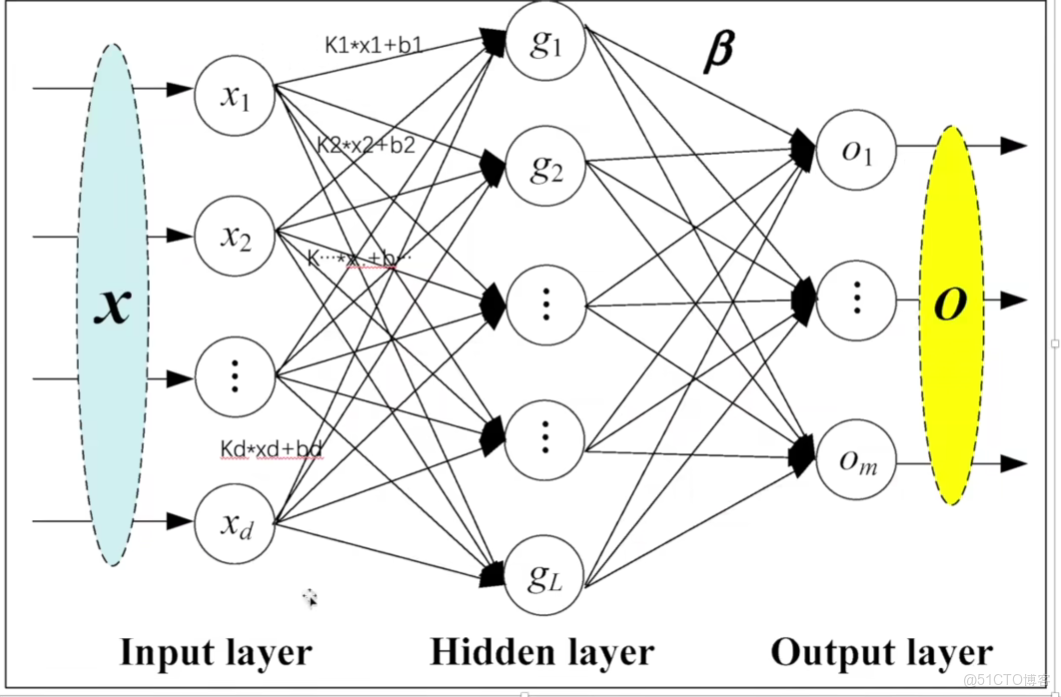
(1)線性層
class torch.nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=True, device=None, dtype=None
(2)Linear的Parameters:
in_features:x1-xd的個數
out_features:g1-gl的個數
bias=True就加b,bias=False就不加b
(3)Linear的Variables:
weight相當於下圖的k,bias相當於下圖的b
Linear Layers的weight和bias的初始化是正態分佈
20.2打開pycharm
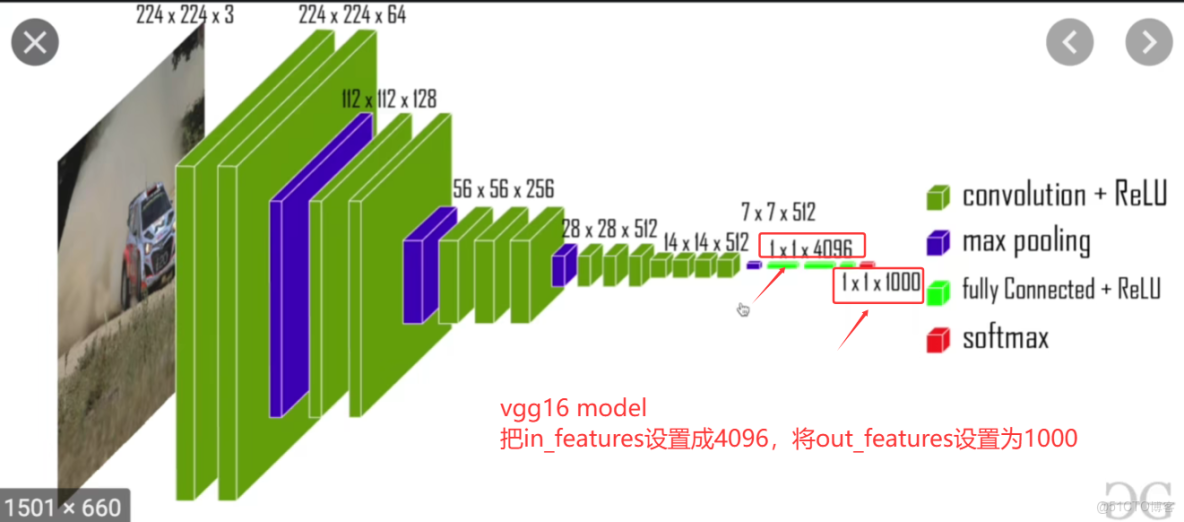
1.vgg16 model
vgg16 model中的in_features和out_features
2.代碼實戰
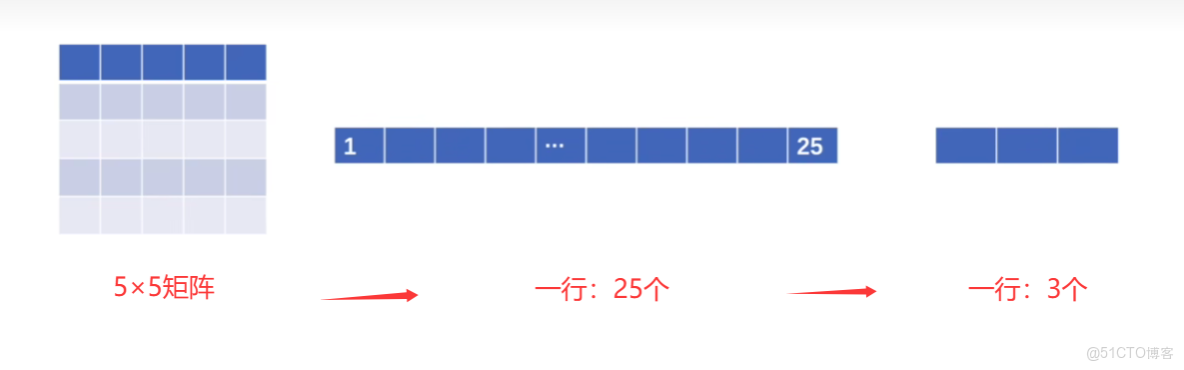
(1)想實現:5×5矩陣展成一行:1×25,然後想通過線性層把25個變成3個
(2)使用CIFAR10數據集進行線性變換
點擊查看代碼
import torchvision
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("./dataset",train=False,transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset,batch_size=64)
for data in dataloader:
imgs,targets = data
print(imgs.shape)運行如下:
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
(3)其中運行成果中的torch.size的四個參數:
B 代表批量大小(batch size),即一次處理的圖像數量;
C 代表通道數(channel),對於彩色RGB圖像來説,這個值通常是3;
H 代表圖像的高度(height);
W 代表圖像的寬度(width)。
(4)要將[64,3,32,32]變成[1,1,1,對應的數(讓其自己算就可以記作-1)]即[1,1,1,-1]
點擊查看代碼
output = torch.reshape(imgs,(1,1,1,-1))
print(output.shape)輸出如下: 點擊查看代碼
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 196608])可見,他自動算出我們的in_features就是196608
(5)創建我們的神經網絡
點擊查看代碼
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Linear
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("./dataset",train=False,transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset,batch_size=64)
class Dyl(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Dyl,self).__init__()
self.linear1 = Linear(196608,10)
def forward(self,input):
output = self.linear1(input)
return output
dyl = Dyl()
for data in dataloader:
imgs,targets = data
print(imgs.shape)
output = torch.reshape(imgs,(1,1,1,-1))
print(output.shape)
#現在要將output送到dyl神經網絡的linear線性層,再返回給output:output=dyl(output)
output = dyl(output)
print(output.shape)輸出: 點擊查看代碼
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 196608])
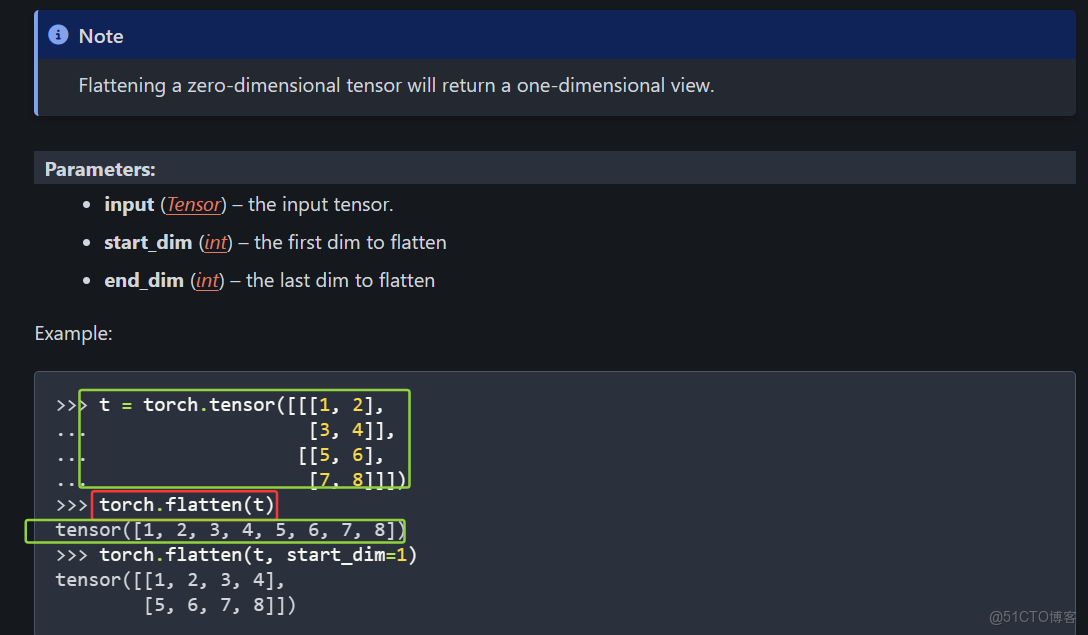
torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 10])(6)torch.flatten()可以展平數據
faltten將多維數據變成一行
上圖就是將 三維數據展平為一行數據
將reshape換成flatten:reshape指定尺寸大小,
點擊查看代碼
for data in dataloader:
imgs,targets = data
print(imgs.shape)
#output = torch.reshape(imgs,(1,1,1,-1))
output = torch.flatten(imgs)
print(output.shape)
#現在要將output送到dyl神經網絡的linear線性層,再返回給output:output=dyl(output)
output = dyl(output)
print(output.shape)輸出:
點擊查看代碼
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
torch.Size([196608])
torch.Size([10])