一、多窗口通信方式
C# WinForms 多窗口通信的方式有:
- 構造函數傳遞
- 屬性傳遞
- 接口
- 事件通信
- 委託回調
- 靜態消息中心
二、示例代碼
C# WinForms中多窗口之間各種通信方式的示例。示例包含一個主窗口和多個子窗口,測試開發中常用的幾種通信方式。
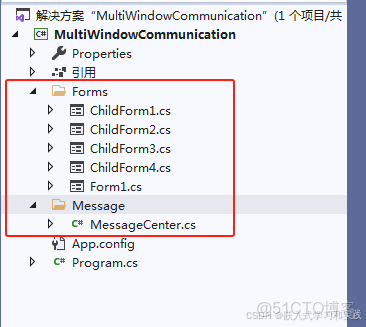
項目結構如下:
2.1 MessageCenter.cs 代碼
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication.Message
{
//class MessageCenter
//{
//}
// 4. 使用靜態類作為消息中心
public static class MessageCenter
{
// 定義消息接收事件
public static event Action<string, string> MessageReceived;
// 發送消息的方法
public static void SendMessage(string sender, string message)
{
// 觸發所有訂閲者的事件
MessageReceived?.Invoke(sender, message);
}
}
}2.2 ChildForm1.cs 代碼
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication.Forms
{
// 定義接口用於子窗口向主窗口通信
public interface IMainForm
{
void ReceiveMessageFromChild1(string message);
}
public partial class ChildForm1 : Form
{
public ChildForm1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// 2. 使用屬性傳遞數據
private string _receivedMessage;
public string ReceivedMessage
{
get => _receivedMessage;
set
{
_receivedMessage = value;
txtReceived.Text = $"收到主窗口消息: {value}";
}
}
// 保存主窗口引用
private readonly IMainForm _mainForm;
// 1. 使用構造函數傳遞數據
public ChildForm1(string initialMessage, IMainForm mainForm)
{
InitializeComponent();
_mainForm = mainForm;
txtReceived.Text = initialMessage;
}
private void btnSendToMain_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtMessage.Text) && _mainForm != null)
{
// 通過接口向主窗口發送消息
_mainForm.ReceiveMessageFromChild1(txtMessage.Text);
txtMessage.Clear();
}
}
}
}2.3 ChildForm2.cs 代碼
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication.Forms
{
public partial class ChildForm2 : Form
{
// 定義事件用於向主窗口發送消息
public event EventHandler<string> SendMessageToMain;
public ChildForm2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// 供主窗口調用的方法,接收主窗口消息
public void ReceiveMessage(string message)
{
txtReceived.Text = $"收到主窗口消息: {message}";
}
private void btnSendToMain_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtMessage.Text))
{
// 觸發事件,向主窗口發送消息
SendMessageToMain?.Invoke(this, txtMessage.Text);
txtMessage.Clear();
}
}
}
}2.4 ChildForm3.cs 代碼
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication.Forms
{
public partial class ChildForm3 : Form
{
// 定義委託
private Action<string> _callback;
public ChildForm3()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// 設置回調函數
public void SetCallback(Action<string> callback)
{
_callback = callback;
}
private void btnSendToMain_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtMessage.Text) && _callback != null)
{
// 通過委託向主窗口發送消息
_callback(txtMessage.Text);
txtMessage.Clear();
}
}
}
}2.5 ChildForm4.cs 代碼
using MultiWindowCommunication.Message;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication.Forms
{
public partial class ChildForm4 : Form
{
public ChildForm4()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 訂閲消息中心事件
MessageCenter.MessageReceived += OnMessageReceived;
}
private void btnSendToAll_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtMessage.Text))
{
// 通過消息中心發送消息
MessageCenter.SendMessage("ChildForm4", txtMessage.Text);
txtMessage.Clear();
}
}
// 接收消息中心的消息
private void OnMessageReceived(string sender, string message)
{
// 過濾掉自己發送的消息
if (sender != "ChildForm4")
{
txtReceived.Text = $"從{sender}收到消息: {message}";
}
}
private void ChildForm4_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
// 取消訂閲
MessageCenter.MessageReceived -= OnMessageReceived;
}
}
}2.6 MainForm.cs 代碼
using MultiWindowCommunication.Forms;
using MultiWindowCommunication.Message;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication
{
public partial class MainForm : Form, IMainForm
{
// 子窗口實例
private ChildForm1 _childForm1;
private ChildForm2 _childForm2;
private ChildForm3 _childForm3;
private ChildForm4 _childForm4;
public MainForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 初始化消息中心事件
MessageCenter.MessageReceived += OnMessageFromMessageCenter;
}
#region 打開子窗口的方法
private void btnOpenForm1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm1 == null || _childForm1.IsDisposed)
{
// 1. 使用構造函數傳遞數據
_childForm1 = new ChildForm1("來自主窗口的初始消息", this);//(IMainForm)this
_childForm1.Show();
}
else
{
_childForm1.BringToFront();
}
}
private void btnOpenForm2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm2 == null || _childForm2.IsDisposed)
{
_childForm2 = new ChildForm2();
// 2. 使用事件進行通信(子窗口到主窗口)
_childForm2.SendMessageToMain += OnMessageFromChildForm2;
_childForm2.Show();
}
else
{
_childForm2.BringToFront();
}
}
private void btnOpenForm3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm3 == null || _childForm3.IsDisposed)
{
// 3. 使用委託進行通信(子窗口回調主窗口)
_childForm3 = new ChildForm3();
_childForm3.SetCallback(OnMessageFromChildForm3);
_childForm3.Show();
}
else
{
_childForm3.BringToFront();
}
}
private void btnOpenForm4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm4 == null || _childForm4.IsDisposed)
{
// 4. 使用靜態類消息中心進行通信
_childForm4 = new ChildForm4();
_childForm4.Show();
}
else
{
_childForm4.BringToFront();
}
}
#endregion
#region 接收來自子窗口的消息
// 處理來自ChildForm1的消息(通過接口)
public void ReceiveMessageFromChild1(string message)
{
AddMessageToLog($"從ChildForm1收到: {message}");
}
// 處理來自ChildForm2的消息(通過事件)
private void OnMessageFromChildForm2(object sender, string e)
{
AddMessageToLog($"從ChildForm2收到: {e}");
}
// 處理來自ChildForm3的消息(通過委託)
private void OnMessageFromChildForm3(string message)
{
AddMessageToLog($"從ChildForm3收到: {message}");
}
// 處理來自消息中心的消息
private void OnMessageFromMessageCenter(string sender, string message)
{
AddMessageToLog($"從{sender}通過消息中心收到: {message}");
}
#endregion
#region 向子窗口發送消息
private void btnSendToForm1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm1 != null && !_childForm1.IsDisposed)
{
// 使用屬性傳遞數據(主窗口到子窗口)
_childForm1.ReceivedMessage = txtMessage.Text;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("請先打開ChildForm1");
}
}
private void btnSendToForm2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm2 != null && !_childForm2.IsDisposed)
{
// 直接調用子窗口方法
_childForm2.ReceiveMessage(txtMessage.Text);
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("請先打開ChildForm2");
}
}
private void btnSendToALL_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 通過消息中心向所有窗口廣播消息
MessageCenter.SendMessage("MainForm", txtMessage.Text);
}
#endregion
// 添加消息到日誌
private void AddMessageToLog(string message)
{
txtLog.AppendText($"[{DateTime.Now:HH:mm:ss}] {message}{Environment.NewLine}");
txtLog.ScrollToCaret();
}
private void MainForm_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
// 清理事件訂閲
MessageCenter.MessageReceived -= OnMessageFromMessageCenter;
// 關閉所有子窗口
if (_childForm1 != null && !_childForm1.IsDisposed)
_childForm1.Close();
if (_childForm2 != null && !_childForm2.IsDisposed)
{
_childForm2.SendMessageToMain -= OnMessageFromChildForm2;
_childForm2.Close();
}
if (_childForm3 != null && !_childForm3.IsDisposed)
_childForm3.Close();
if (_childForm4 != null && !_childForm4.IsDisposed)
_childForm4.Close();
}
}
}2.7 通信方式詳解
WinForms中的幾種常用的多窗口通信方式:
- 構造函數傳遞(ChildForm1)
- 適用於初始化時需要傳遞數據的場景
- 優點:簡單直接,適合初始化數據
- 缺點:只能在創建窗口時傳遞一次
- 屬性傳遞(ChildForm1)
- 適用於需要多次傳遞數據的場景
- 優點:可以在窗口生命週期內隨時設置
- 缺點:需要手動檢查窗口是否已釋放
- 事件通信(ChildForm2)
- 適用於子窗口主動向父窗口發送消息
- 優點:解耦性好,子窗口不需要知道父窗口具體類型
- 缺點:需要手動管理事件訂閲和取消訂閲
- 委託回調(ChildForm3)
- 適用於父窗口需要對子窗口消息做出響應的場景
- 優點:靈活,可以傳遞複雜參數
- 缺點:需要維護委託引用
- 靜態消息中心(ChildForm4)
- 適用於多個窗口之間需要互相通信的複雜場景
- 優點:完全解耦,任意窗口間可通信
- 缺點:需要管理事件訂閲,可能導致內存泄漏
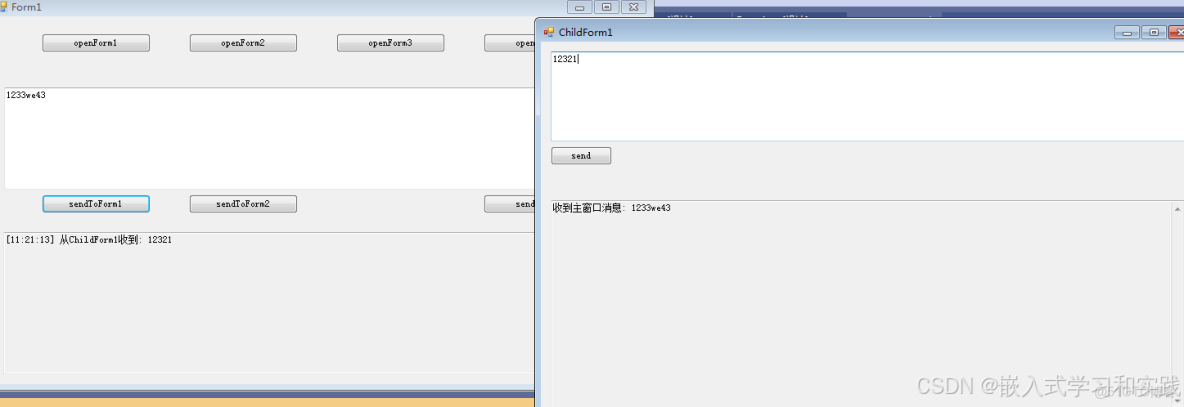
三、測試結果
四、建議
- 簡單的父子窗口通信,優先使用事件或委託
- 初始化數據傳遞,使用構造函數
- 複雜的多窗口通信場景,使用靜態消息中心
- 無論使用哪種方式,都要注意在窗口關閉時清理事件訂閲,避免內存泄漏
可以根據實際項目需求選擇合適的通信方式,也可以結合多種方式使用。