Rust Slint實現炫酷鎖屏源碼分享
- 一、源碼分享
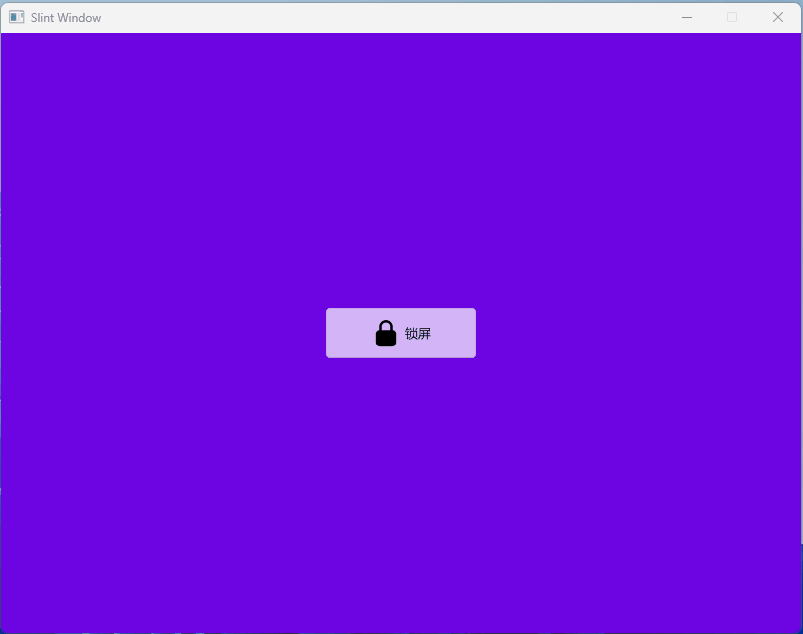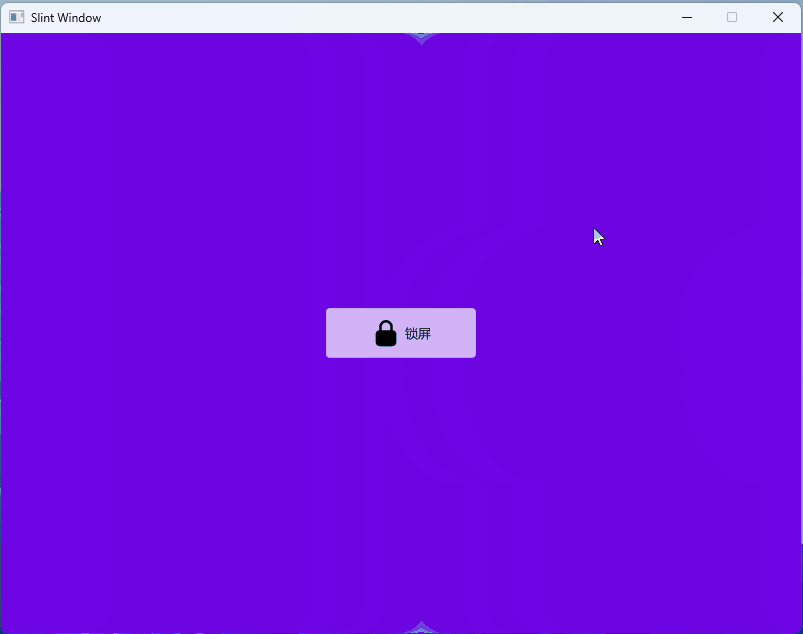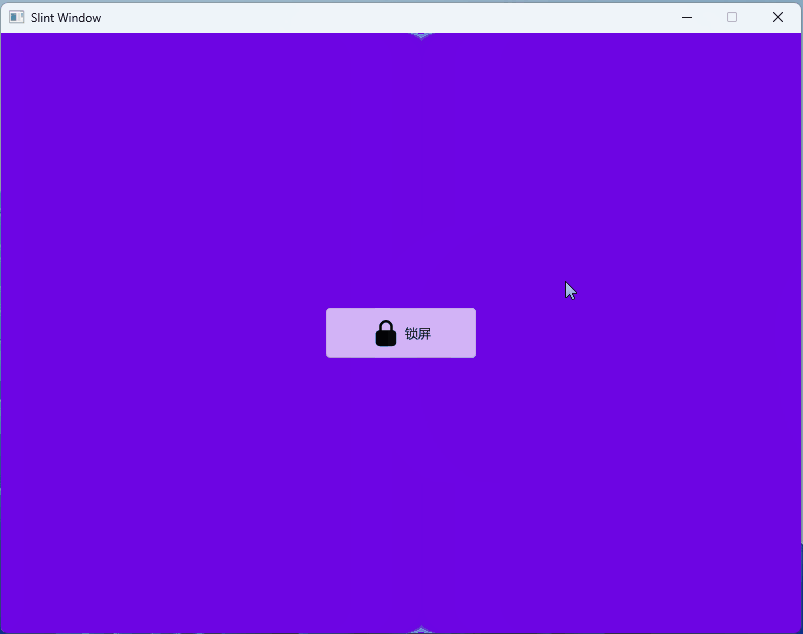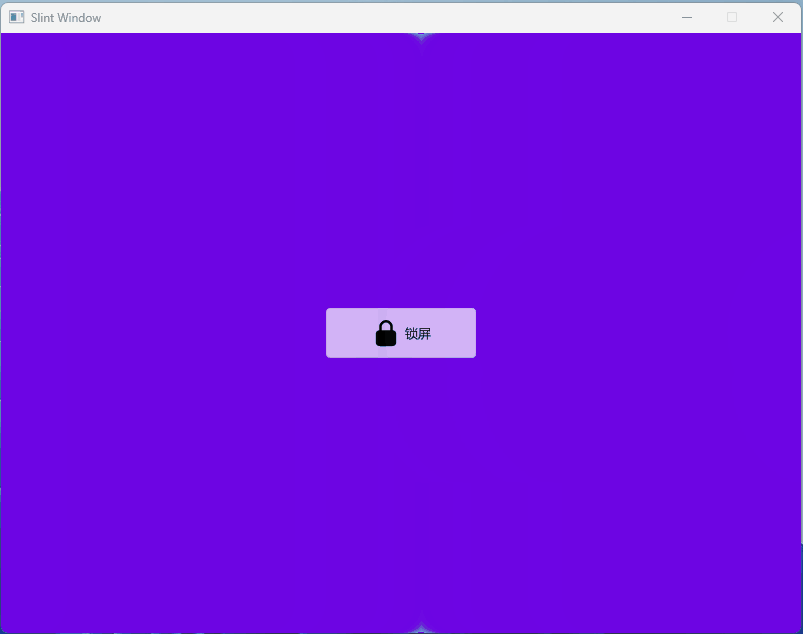
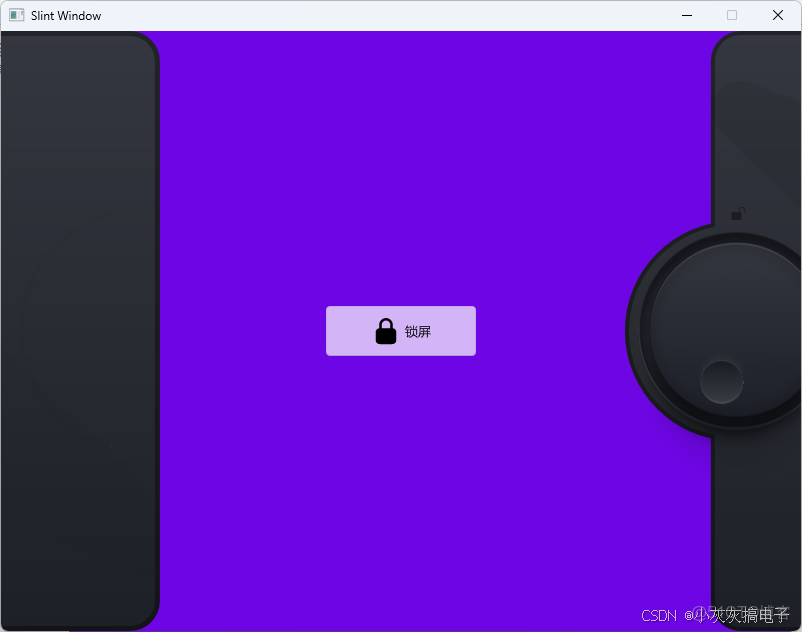
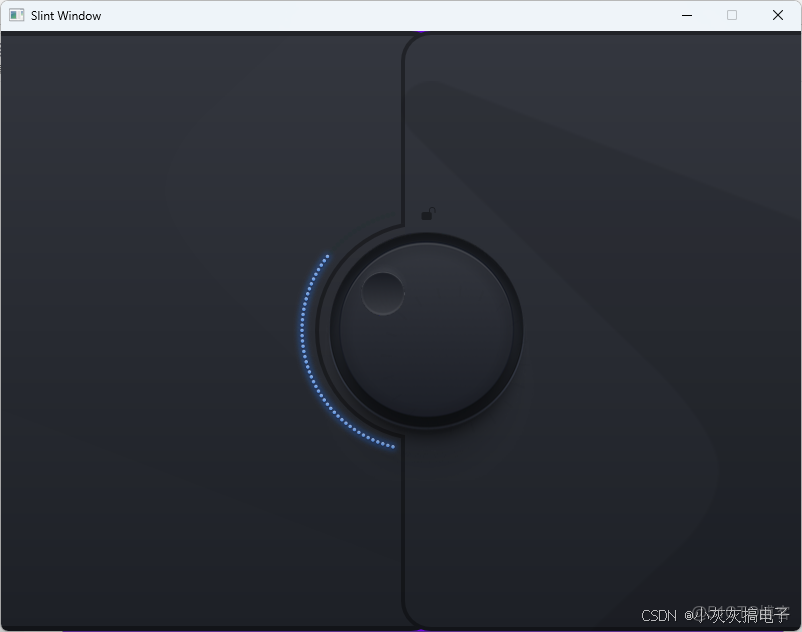
- 1、效果展示
- 2、源碼分享
- 2.1、工程搭建
- 2.2、工程結構
- 2.3、main.rs
- 2.4、main.slint
- 2.5、models.slint
- 2.6、Cargo.toml
- 2.7、源碼資源下載
- 二、Slint詳解
- 1、核心特性
- 2、架構模式 (MVU)
- 3、優勢
- 4、適用場景
- 5、總結
一、源碼分享
1、效果展示
2、源碼分享
2.1、工程搭建
參考我這篇博文:【Rust 使用Slint庫開發UI界面工程搭建詳細教程】
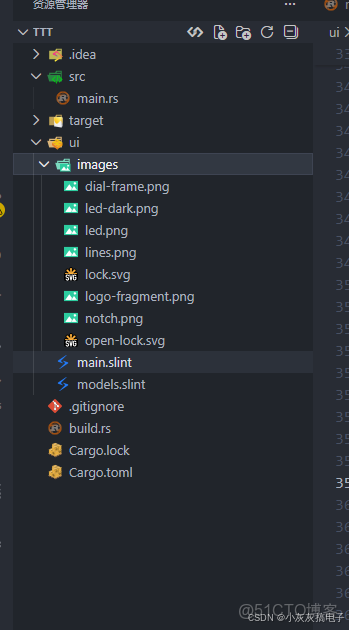
2.2、工程結構
2.3、main.rs
use slint::{PlatformError};
slint::include_modules!();
fn main() ->Result<(), PlatformError>{
let app: MainWindow = MainWindow::new()?;
let weak: slint::Weak<MainWindow> = app.as_weak();
app.global::<DataAdapter>().on_btn_clicked({
let weak: slint::Weak<MainWindow> = weak.clone();
move ||{
if let Some(strong) = weak.upgrade(){
let _adapter: DataAdapter<'_> = strong.global::<DataAdapter>();
}
}
});
let _ = app.run();
Ok(())
}2.4、main.slint
import { AboutSlint, VerticalBox, LineEdit, HorizontalBox, Button, GroupBox, GridBox,
ComboBox, Spinner, Slider, ListView, Palette, ProgressIndicator, CheckBox, Switch } from "std-widgets.slint";
import { DataAdapter} from "models.slint";
export { DataAdapter}
export global DialState {
out property <int> totalLights: 60;
out property <angle> degreesFilledWithLights: 360deg - (startAngle - endAngle);
out property <angle> startAngle: 104deg;
out property <angle> endAngle: -startAngle;
in-out property <length> elementRadius: 120px;
}
component Dial {
pure public function normalizeAngle(angle: angle) -> angle {
return (angle + 360deg).mod(360deg);
}
in property <bool> interactive: true;
property <bool> moving: ta.firstTouch;
in-out property <angle> dialAngle: DialState.startAngle;
out property <int> volume: ((dialAngle - DialState.startAngle) / DialState.degreesFilledWithLights) * DialState.totalLights;
width: 212px;
height: 213px;
knob := Rectangle {
base := Rectangle {
Image {
x: 0px;
y: 9px;
source: @image-url("images/dial-frame.png");
}
Image {
source: @image-url("images/lines.png");
colorize: #000;
transform-rotation: root.dialAngle;
width: self.source.width * 0.55 * 1px;
height: self.source.height * 0.55 * 1px;
opacity: 0.03;
}
ta := TouchArea {
property <length> centerX: self.width / 2;
property <length> centerY: self.height / 2;
property <length> relativeX;
property <length> relativeY;
property <angle> newAngle;
property <angle> deltaDegrees;
property <bool> firstTouch: false;
width: parent.width;
height: parent.height;
enabled: root.interactive;
changed pressed => {
if !self.pressed {
firstTouch = false;
}
}
moved => {
relativeX = ta.mouse-x - centerX;
relativeY = ta.mouse-y - centerY;
newAngle = normalizeAngle(atan2(relativeY / 1px, relativeX / 1px));
if !firstTouch {
firstTouch = true;
deltaDegrees = normalizeAngle(root.dialAngle - newAngle);
} else {
root.dialAngle = normalizeAngle(deltaDegrees + newAngle).clamp(DialState.startAngle, 260deg);
}
}
}
}
}
Rectangle {
width: 1px;
height: 1px;
x: 106px;
y: 105px;
Rectangle {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
x: 55px * root.dialAngle.cos();
y: 55px * root.dialAngle.sin();
Image {
source: @image-url("images/notch.png");
}
}
}
}
component Light {
function pulseAnimation(duration: duration) -> float {
return 1 * (1 - abs(sin(360deg * animation-tick() / duration)));
}
in property <int> index;
in property <int> volume;
property <angle> gap: (360deg - (DialState.startAngle - DialState.endAngle)) / DialState.totalLights;
property <angle> angle: (index * gap) + DialState.startAngle;
property <bool> lightOn: index <= volume;
property <float> pulse: index == 0 && lightOn && volume <= 1 ? pulseAnimation(5s) : 1.0;
x: DialState.elementRadius * angle.cos();
y: DialState.elementRadius * angle.sin();
width: 0;
height: 0;
states [
lightOff when !root.lightOn: {
dialLed.opacity: 0;
}
lightOn when root.lightOn: {
dialLed.opacity: pulse;
in {
animate dialLed.opacity {
duration: 100ms;
easing: ease-in-sine;
}
}
out {
animate dialLed.opacity {
duration: 600ms;
easing: ease-out-sine;
}
}
}
]
Rectangle {
Rectangle {
width: 5px;
height: self.width;
border-radius: self.width / 2;
background: #00331a;
opacity: 0.1;
}
dialLed := Image {
source: @image-url("images/led-dark.png");
width: self.source.width * 0.5 * 1px;
height: self.source.height * 0.5 * 1px;
}
}
}
component DialLights {
width: 212px;
height: 213px;
in property <int> volume;
Rectangle {
width: 1px;
height: 1px;
x: 106px;
y: 105px;
lightHolder := Rectangle {
x: 0px;
y: 1px;
for i in DialState.totalLights + 1: Light {
index: i;
volume: root.volume;
}
}
}
}
enum DoorState { closed, open }
component Doors {
property <brush> notch-border-color: #0000005d;
in-out property <bool> demo-locked: true;
in-out property <DoorState> initial-door-state: closed;
property <DoorState> target-door-state: initial-door-state;
callback unlockDemo();
callback doorsOpened();
callback doorsOpening();
callback doorsClosed();
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
unlockDemo => {
demo-locked = false;
target-door-state = DoorState.open;
doorsOpening();
}
Timer {
interval: 1ms;
triggered => {
if initial-door-state == DoorState.open && demo-locked {
target-door-state = DoorState.closed;
initial-door-state = DoorState.closed;
}
self.running = false;
}
}
touch-catcher := Rectangle {
TouchArea { }
}
leftDoor := Rectangle {
x: -30px;
width: parent.width / 2 + 70px;
height: 100%;
background: @linear-gradient(180deg, #34373F, #1D2026);
border-width: 5px;
border-color: notch-border-color;
border-radius: 30px;
clip: true;
changed x => {
if root.initial-door-state == DoorState.closed && self.x <= -leftDoor.width {
root.doorsOpened();
}
if self.x == -60px {
root.doorsClosed();
}
}
Image {
x: 0;
y: 0;
width: self.source.width * 2 * 1px;
height: self.source.height * 2 * 1px;
source: @image-url("images/logo-fragment.png");
opacity: 0.02;
}
DialLights {
x: parent.width - 125px;
volume: dial.volume;
}
}
states [
doorsOpen when target-door-state == DoorState.open: {
leftDoor.x: -leftDoor.width;
rightDoor.x: root.width + 85px;
dial.dialAngle: DialState.startAngle;
in {
animate rightDoor.x, leftDoor.x {
duration: 800ms;
easing: ease-in-expo;
}
}
}
doorsClosed when target-door-state == DoorState.closed: {
leftDoor.x: -30px;
rightDoor.x: root.width / 2;
in {
animate rightDoor.x, leftDoor.x {
duration: 800ms;
easing: ease-in-expo;
}
}
}
]
rightDoor := Rectangle {
property <length> notch-width: 220px;
property <length> notch-border: 4px;
property <length> notch-indent: 20px;
x: parent.width / 2;
width: parent.width / 2 + 30px;
height: 100%;
Rectangle {
background: @linear-gradient(180deg, #34373F, #1D2026);
clip: true;
border-radius: 30px;
Image {
x: parent.width - self.width;
y: parent.height - self.height;
width: self.source.width * 2 * 1px;
height: self.source.height * 2 * 1px;
source: @image-url("images/logo-fragment.png");
transform-rotation: 180deg;
opacity: 0.08;
}
}
Rectangle {
border-width: notch-border;
border-color: notch-border-color;
border-radius: 30px;
}
Rectangle {
x: -(notch-width / 2) + notch-border;
width: (notch-width / 2);
// - notch-indent ;
height: notch-width;
clip: true;
Rectangle {
x: notch-indent;
y: 0;
width: notch-width;
height: self.width;
Rectangle {
width: notch-width;
height: self.width;
border-radius: self.width / 2;
background: @linear-gradient(180deg, #2e3037, #25272c);
border-width: notch-border;
border-color: notch-border-color;
}
}
}
Image {
x: 20px;
y: (parent.height / 2) - 125px;
source: @image-url("images/open-lock.svg");
colorize: #000;
width: 15px;
height: self.width;
opacity: 0.4;
}
dial := Dial {
x: -82px;
y: (parent.height - self.height) / 2 - 1px;
interactive: root.demo-locked;
changed volume => {
if self.volume >= 60 {
root.unlockDemo()
}
}
}
}
}
export component MainWindow inherits Window {
width: 800px;
height: 600px;
background: #6d05e4;
in-out property <bool> door-component-loaded: false;
in-out property <DoorState> initial-door-state: open;
property <bool> demo-locked: true;
Button {
width: 150px;
height: 50px;
icon: @image-url("images/lock.svg");
text: "鎖屏";
icon-size: 30px;
clicked => {
door-component-loaded = true;
}
}
if door-component-loaded: door := Doors{
doorsOpened => {
door-component-loaded = false;
initial-door-state = DoorState.open;
}
demo-locked: demo-locked;
initial-door-state: initial-door-state;
}
}2.5、models.slint
export global DataAdapter {
callback btn_clicked();
}2.6、Cargo.toml
[package]
name = "ttt"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2024"
author = "<peng.xu@sf-express.com>"
[dependencies]
slint = "1.14.1"
[build-dependencies]
slint-build = "1.14.1"2.7、源碼資源下載
文章頂部下載。
二、Slint詳解
Slint 是一個用於創建本地用户界面的聲明式框架,特別為 Rust 設計,但也支持 C++。它的目標是提供一個輕量級、高效且易於使用的解決方案,用於構建具有現代外觀和感覺的桌面和嵌入式應用程序的 UI。Slint 的核心思想是使用一種聲明式的語言來描述用户界面,並將其與 Rust 的業務邏輯代碼緊密結合。
1、核心特性
- 聲明式 UI 語言 (.slint):
- Slint 定義了自己的領域特定語言(DSL),通常寫在
.slint文件中。 - 這種語言語法簡潔,專注於描述 UI 的結構、佈局、屬性、狀態和交互。
- 示例
.slint片段:
import { Button } from "std-widgets.slint";
export component MainWindow {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
VerticalLayout {
Button {
text: "Click Me!";
clicked => { // 處理點擊事件的邏輯 }
}
Text {
text: "Hello Slint!";
}
}
}- 響應式數據綁定:
- Slint 支持聲明式響應式編程模型。
- 使用
:=運算符綁定屬性值,當依賴項(如其他屬性或狀態變量)發生變化時,綁定會自動更新。 - 例如:
export component MainWindow {
in property <int> count: 0; // 輸入屬性
out property <string> label_text: "Count: " + count; // 輸出屬性,綁定到 count
...
}- 當
count改變時,label_text會自動更新。
- 狀態管理:
- 使用
state關鍵字定義組件的內部狀態。 - 狀態變化會觸發 UI 的重新渲染。
- 例如:
export component ToggleButton {
out property <bool> checked;
state property <bool> is_checked: false;
// 點擊切換狀態
clicked => {
is_checked = !is_checked;
checked = is_checked;
}
// UI 根據狀態變化
background: is_checked ? @linear-gradient(...) : @solid-color(...);
...
}- 與 Rust 集成:
- 使用
slint-build或slint-interpreter庫將.slint文件編譯或解釋成 Rust 代碼。 - 編譯後,UI 組件在 Rust 中變成結構體,其屬性、回調函數和函數都可以在 Rust 代碼中訪問和操作。
- 在 Rust 中實例化和運行 UI 的典型代碼:
use slint::ComponentHandle;
slint::slint! { // 這裏可以內聯 .slint 代碼,或使用路徑指向文件
// ... .slint 內容 ...
}
fn main() {
let ui = MainWindow::new();
// 設置 Rust 回調
let ui_weak = ui.as_weak();
ui.on_button_clicked(move || {
let ui = ui_weak.unwrap();
// 處理點擊事件,更新 UI 狀態等
ui.set_some_property(new_value);
});
ui.run();
}- 跨平台:
- Slint 支持 Windows, macOS, Linux (X11/Wayland), 以及嵌入式平台(如通過 OpenGL ES 或軟件渲染)。
- 其渲染後端是可插拔的。
- 輕量級與高性能:
- 設計之初就考慮了資源受限的環境(如嵌入式設備)。
- 渲染引擎高效,避免了不必要的重繪。
- 生成的代碼量相對較小。
- 內置組件庫:
- 提供了一套基礎組件(如
Button,Slider,TextInput,ListView等),稱為 “std-widgets”。 - 用户可以基於這些基礎組件構建自己的自定義組件。
2、架構模式 (MVU)
Slint 鼓勵一種類似於 Model-View-Update (MVU) 或 Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) 的模式:
- View: 在
.slint文件中聲明式定義。 - Model/ViewModel/State: 在
.slint文件中通過property,state和回調函數定義,或者在 Rust 中定義並通過綁定暴露給 UI。 - Update/Logic: 在 Rust 中實現,處理用户交互、業務邏輯,並更新 Model/State,進而通過綁定驅動 View 更新。
3、優勢
- 開發效率: 聲明式語法簡化了 UI 構建和佈局。
.slint文件清晰地將 UI 描述與邏輯分離。 - 性能: 高效渲染和輕量級設計。
- 跨平台: 一套代碼支持多個目標平台。
- Rust 集成: 與 Rust 語言深度集成,利用 Rust 的安全性和性能。
- 熱重載 (部分支持): 在開發過程中,某些工具鏈支持修改
.slint文件後無需重新編譯整個 Rust 項目即可看到 UI 變化。
4、適用場景
- 桌面應用程序 (Windows, macOS, Linux)
- 嵌入式設備 GUI
- 需要輕量級、原生 UI 的 Rust 應用
5、總結
Slint 為 Rust 開發者提供了一個現代、聲明式且高效的 UI 框架。它通過自定義的 .slint 語言描述界面,結合強大的響應式數據綁定和狀態管理,並與 Rust 代碼無縫集成。其輕量級和高性能的特點使其成為桌面和嵌入式應用 UI 開發的強有力候選方案。如果你正在尋找一個 Rust 生態下的原生 GUI 解決方案,Slint 絕對值得一試。
建議查閲 Slint 官方文檔 和示例以獲取更詳細的信息和上手教程。