目錄
引言
一. 源碼及框架分析
二. 模擬實現set/map
2.1 實現出複用紅黑樹的框架
2.1.1 實現仿函數KeyOfT
2.1.2 調整insert
2.1.3 紅黑樹模板複用結構的設計
2.2 迭代器的實現
2.2.1 iterator實現思路分析
2.2.2 Iterator代碼實現
2.2.3 迭代器類型的傳遞關係
2.3 map中的operator[ ]
2.3.1 operator[ ]的實現思路
2.3.2 operator[ ]的執行流程
2.4 set的完整封裝實現
2.5 map的完整封裝實現
2.6 完整的紅黑樹模板類
結語
引言
在C++標準模板庫(STL)中,std::set 和 std::map 是兩個常用的關聯容器,它們提供了高效的元素存儲、查找和插入操作。這些容器的底層實現通常基於紅黑樹(Red-Black Tree),一種自平衡的二叉搜索樹,能夠保證操作的時間複雜度為O(log N)。
一. 源碼及框架分析
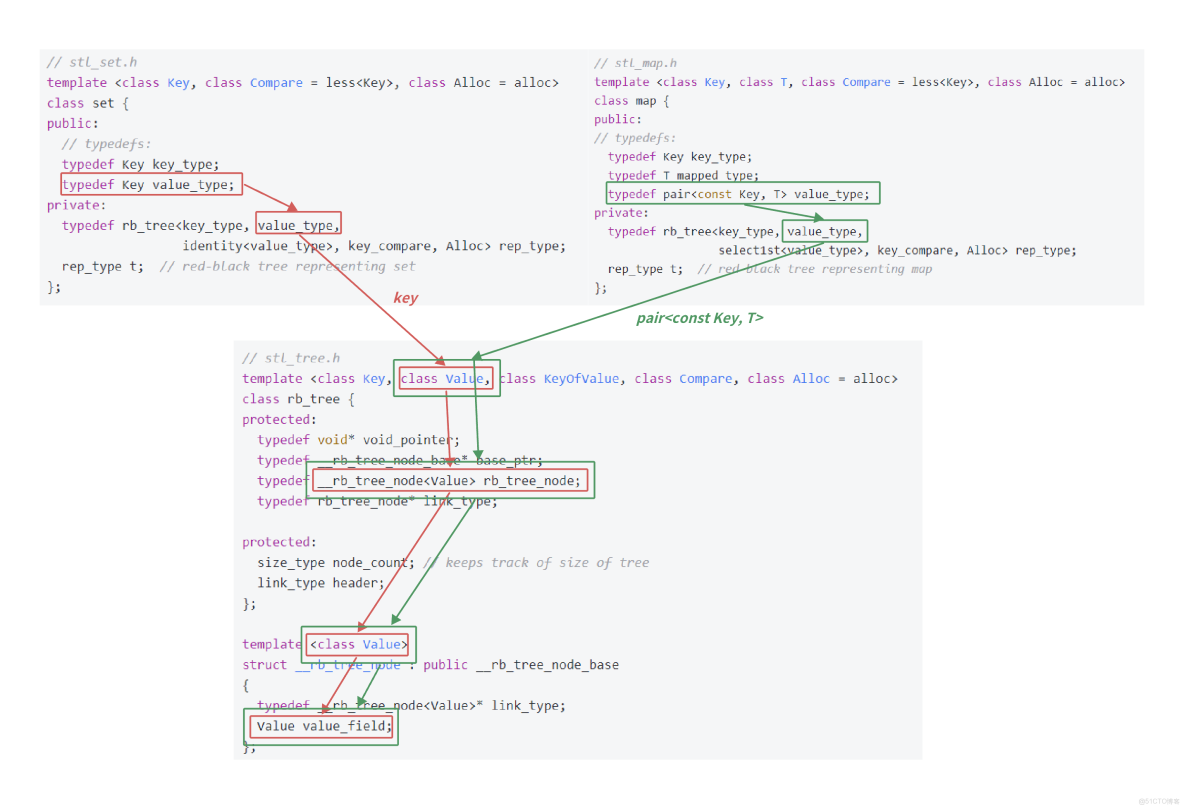
SGI-STL的map和set源代碼主要分佈在stl_map.h、stl_set.h和stl_tree.h等頭文件中。核心框架如下:
- set 和 map 都複用了一個紅黑樹模板類 rb_tree。
- 對於 set,它存儲的元素是鍵(Key),因此實例化 rb_tree 時,第二個模板參數為 Key,使用 identity 仿函數提取鍵。
- 對於 map,它存儲鍵值對(pair<Key, T>),第二個模板參數為 pair<const Key, T>,使用 select1st 仿函數提取鍵。
源碼片段:
// stl_set.h
template <class Key, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class set {
public:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Key value_type;
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type, identity<value_type>, Compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t; // red-black tree representing set
};
// stl_map.h
template <class Key, class T, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class map {
public:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef T mapped_type;
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type, select1st<value_type>, Compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t; // red-black tree representing map
};
// stl_tree.h
struct __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type;
typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;
color_type color;
base_ptr parent;
base_ptr left;
base_ptr right;
};
// stl_tree.h
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc
= alloc>
class rb_tree {
protected:
typedef void* void_pointer;
typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;
typedef rb_tree_node* link_type;
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Value value_type;
public:
// insert⽤的是第⼆個模板參數左形參
pair<iterator,bool> insert_unique(const value_type& x);
// erase和find⽤第⼀個模板參數做形參
size_type erase(const key_type& x);
iterator find(const key_type& x);
protected:
size_type node_count; // keeps track of size of tree
link_type header;
};
template <class Value>
struct __rb_tree_node : public __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type;
Value value_field;
};- rb_tree 的模板參數包括 Key(用於find/erase的參數)、Value(結點存儲的數據類型)、KeyOfValue(鍵提取仿函數)。
- insert 使用 Value 類型參數,find 和 erase 使用 Key 類型參數。
- 這種設計允許紅黑樹既支持純鍵搜索(set),也支持鍵值對搜索(map)。
- 通過分析,我們可以看到STL使用泛型編程巧妙地實現了代碼複用。Value 決定了結點存儲類型:對於set是Key,對於map是pair<const Key, T>。
問:rb_tree第二個模板參數Value已經控制了紅黑樹結點中存儲的數據類型,為什麼還要傳第一個模板參數Key呢?尤其是set,兩個模板參數是一樣的
答:對於 map和set,find/erase時的函數參數都是Key,所以第一個模板參數是傳給find/erase等函數做形參的類型的。對於set而言兩個參數是一樣的,但是對於map而言就完全不一樣了,map insert的是pair對象,但是find和ease的是Key對象。
這樣設計的意義:
- 將"用於查找的關鍵字類型"與"實際存儲的數據類型"分離
- 使得同一個紅黑樹模板可以同時適配 set(T=K)和 map(T=pair<K,V>)
- 提供類型安全的查找接口
- 通過下圖對框架的分析,我們可以看到源碼中rb_tree用了一個巧妙的泛型思想實現,rb_tree是實 現key的搜索場景,還是key/value的搜索場景不是直接寫死的,而是由第二個模板參數Value決定 _rb_tree_node中存儲的數據類型。
- set實例化rb_tree時第二個模板參數給的是key,map實例化rb_tree時第二個模板參數給的是 pair,這樣一顆紅黑樹既可以實現key搜索場景的set,也可以實現key/value搜索場景的map。
二. 模擬實現set/map
set/map模擬實現主要以下面的幾個步驟完成:
- 實現紅黑樹
- 封裝set/map框架,解決KeyOfT
- 迭代器Iterator的實現
- cosnt_iterator的實現
- key不支持修改的問題
- operator[ ]
2.1 實現出複用紅黑樹的框架
- 參考源碼框架,map和set複用之前實現的紅黑樹。
- 這裏相比源碼調整一下,key參數就用K,value參數就用V,紅黑樹中的數據類型使用T。
- 其次因為RBTree實現了泛型不知道T參數導致是K,還是pair,那麼insert內部進行插入邏輯比較時,就沒辦法進行比較,因為pair的默認支持的是key和value一起參與比較,我們需要的是任何時候只比較key,所以我們在map和set層分別實現⼀個MapKeyOfT和SetKeyOfT的仿函數傳給 RBTree的KeyOfT,然後RBTree中通過KeyOfT仿函數取出T類型對象中的key,再進行比較,具體細節參考如下代碼實現。
2.1.1 實現仿函數KeyOfT
namespace MySet
{
template<class K>
class set
{
// 內部類(把key取出來)
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
// key的迭代器不能支持修改,把第二個模板參數改為const K
RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}namespace MyMap
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
// 內部類(把key取出來)
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}2.1.2 調整insert
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
T _data;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _col(RED)
{}
};
// RBTree<K, K> _t; // set
// RBTree<K, pair<K, V>> _t; // map
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
~RBTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK; // 根節點必須為黑色
return { Iterator(_root), true }; // 插入成功
}
KeyOfT kot; // 通過kot,把T類型的數據中的key取出來,然後在下面比較大小
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)) // 如果data是key就用key比較大小可以;如果data是pair,用pair比較大小,不一定是我們想要的
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return { Iterator(cur), false }; // 已經有這個值,插入失敗
}
}
// 新增節點必須為紅色
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur; // cur在旋轉時可能會變,用newnode保存一下
cur->_col = RED;
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
// g
// p u
//c
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
// 叔叔存在且為紅
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
// 變色+繼續往上處理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 叔叔不存在或者叔叔存在且為黑
{
// g
// p u
//c
// 單旋+變色
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
// 雙旋+變色
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
// 叔叔存在且為紅
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
// 變色+繼續往上處理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 叔叔不存在或者叔叔存在且為黑
{
// g
// p u
// c
// 單旋+變色
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
// 雙旋+變色
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
// 無論最後根節點是否為黑,就直接置為黑
_root->_col = BLACK;
return { Iterator(newnode), true };
}
private:
void Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
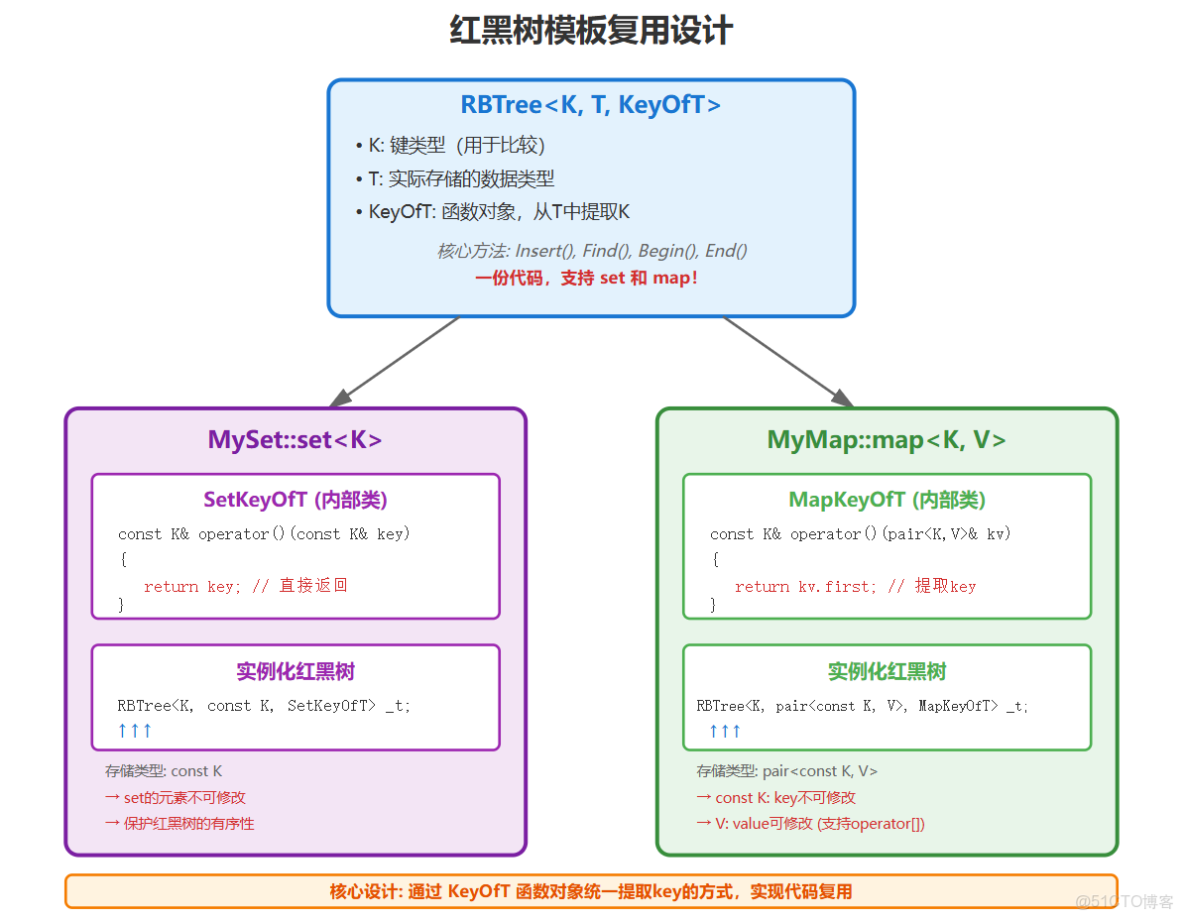
};2.1.3 紅黑樹模板複用結構的設計
2.2 迭代器的實現
2.2.1 iterator實現思路分析
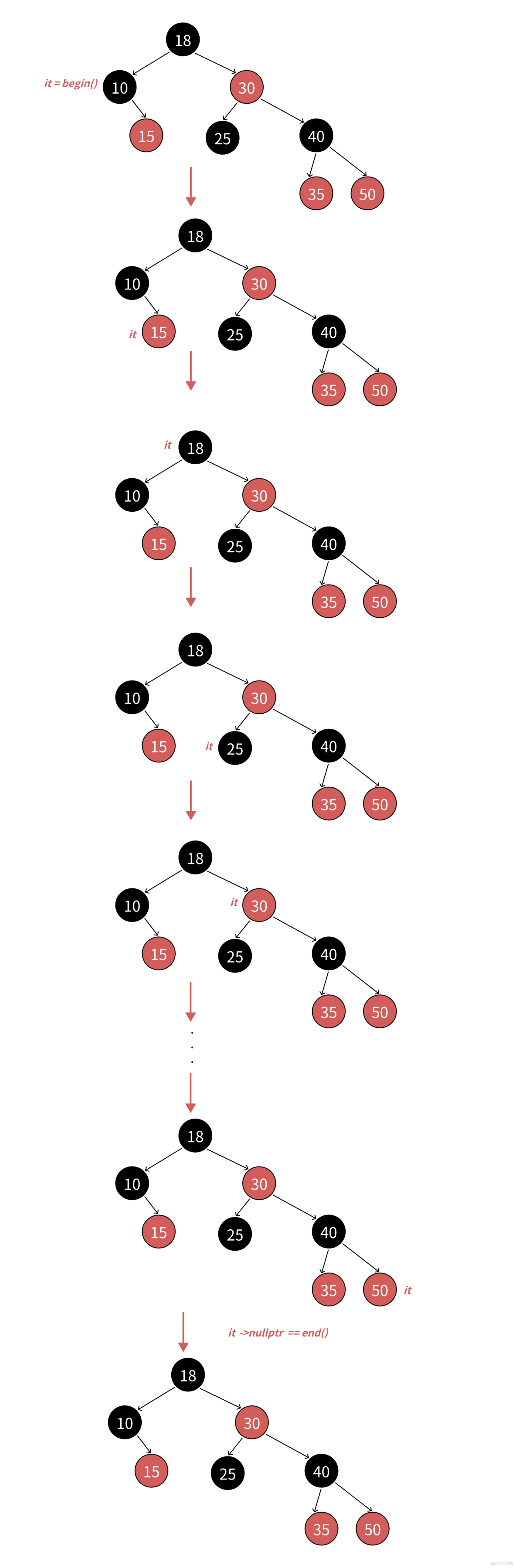
- iterator實現的大框架跟list的iterator思路是一致的,用一個類型封裝結點的指針,再通過重載運算符實現,迭代器像指針一樣訪問的行為。
- 這裏的難點是operator++和operator--的實現。之前使用部分,我們分析了,map和set的迭代器走的是中序遍歷,即左子樹->根結點->右子樹,那麼begin()會返回中序第一個結點的iterator也就是10 所在結點的迭代器。
- 迭代器++的核心邏輯就是不看全局,只看局部,只考慮當前中序局部要訪問的下一個結點。
- 迭代器++時,如果it指向的結點的子樹不為空,代表當前結點已經訪問完了,要訪問下一個結點是右子樹的中序第一個,一棵樹中序第一個是最左結點,所以直接找右子樹的最左結點即可。
- 迭代器++時,如果it指向的結點的右子樹空,代表當前結點已經訪問完了且當前結點所在的子樹也 訪問完了,要訪問的下一個結點在當前結點的祖先裏面,所以要沿着當前結點到根的祖先路徑向上 找。
- 如果當前結點是父親的左,根據中序左子樹->根結點->右子樹,那麼下一個訪問的結點就是當前結 點的父親;如下圖:it指向25,25右為空,25是30的左,所以下一個訪問的結點就是30。
- 如果當前結點是父親的右,根據中序左子樹->根結點->右子樹,當前當前結點所在的子樹訪問完 了,當前結點所在父親的子樹也訪問完了,那麼下一個訪問的需要繼續往根的祖先中去找,直到找 到孩子是父親左的那個祖先就是中序要遍歷的下一個結點。如下圖:it指向15,15右為空,15是10 的右,15所在⼦樹話訪問完了,10所在子樹也訪問完了,繼續往上找,10是18的左,那麼下⼀個 訪問的結點就是18。
- end()如何表示呢?如下圖:當it指向50時,++it時,50是40的右,40是30的右,30是18的右,18 到根沒有父親,沒有找到孩子是父親左的那個祖先,這時父親為空了,那我們就把it中的結點指針 置為nullptr,我們用nullptr去充當end。需要注意的是stl源碼空,紅黑樹增加了一個哨兵位頭結點 做為end(),這哨兵位頭結點和根互為父親,左指向最左結點,右指向最右結點。相比我們用nullptr作為end(),差別不大,他能實現的,我們也能實現。只是--end()判斷到結點時空,特殊處理一下,讓迭代器結點指向最右結點。具體參考迭代器--實現。
- 迭代器--的實現跟++的思路完全類似,邏輯正好反過來即可,因為他訪問順序是右子樹->根結點-> 左子樹,具體參考下面代碼實現。
- set的iterator也不支持修改,我們把set的第二個模板參數改成const K即可, RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
- map的iterator不支持修改key但是可以修改value,我們把map的第二個模板參數pair的第一個參數改成const K即可, RBTree<K,pair<const K,V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
2.2.2 Iterator代碼實現
紅黑樹底層封裝:
// 迭代器
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
// map常用->訪問數據
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
// 返回類型依舊是迭代器
Self& operator++()
{
// 右孩子不為空,找右孩子的最左節點
if (_node->_right)
{
Node* minRight = _node->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
_node = minRight;
}
// 右為空,找孩子是父親左的祖先
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};set封裝:
namespace MySet
{
template<class K>
class set
{
public:
// 沒有實例化,編譯器無法確定這是類型還是靜態成員變量
// 前面要加一個typename,告訴編譯器這時一個類型
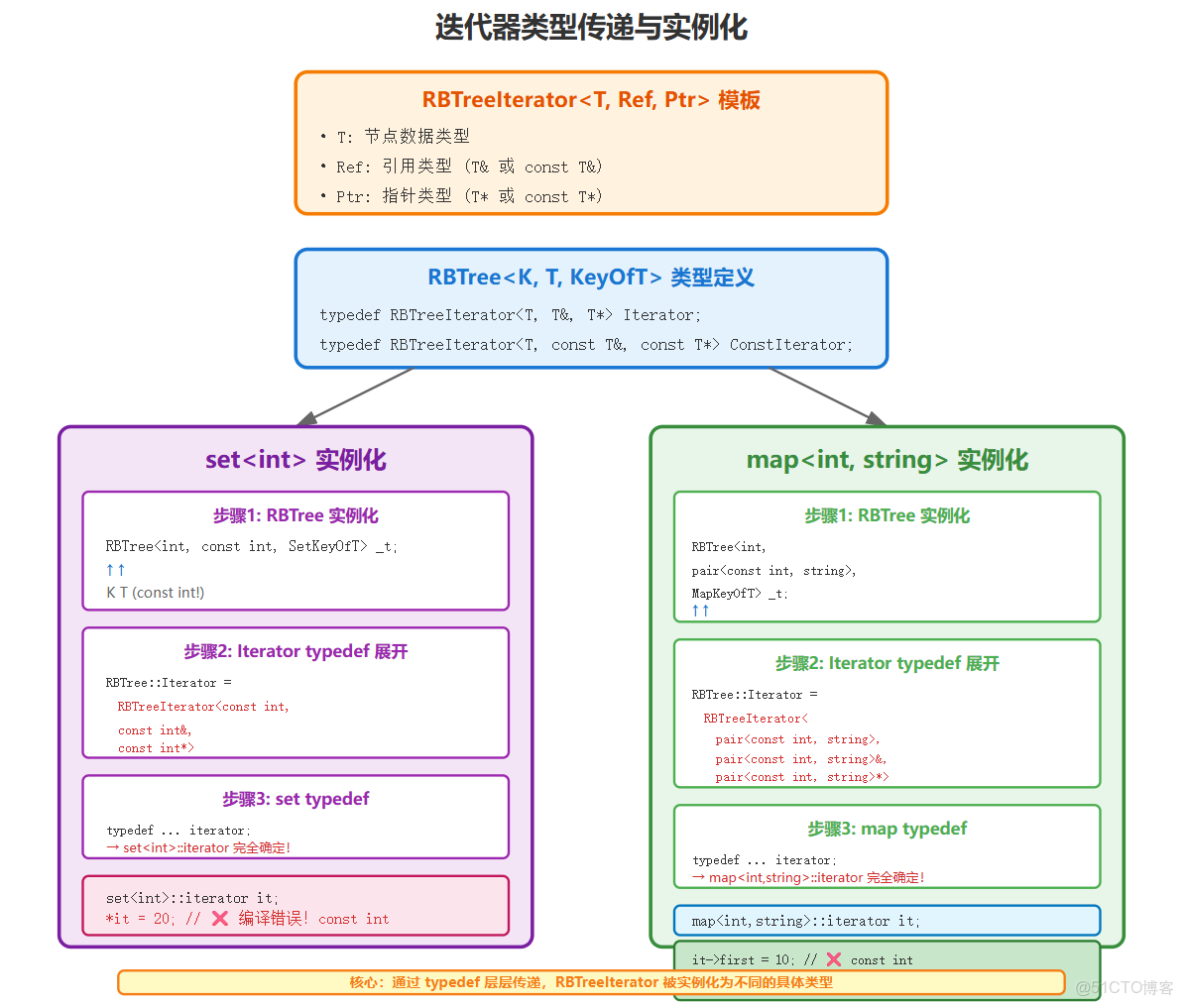
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
private:
// key的迭代器不能支持修改,把第二個模板參數改為const K
RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}map封裝:
namespace MyMap
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}2.2.3 迭代器類型的傳遞關係
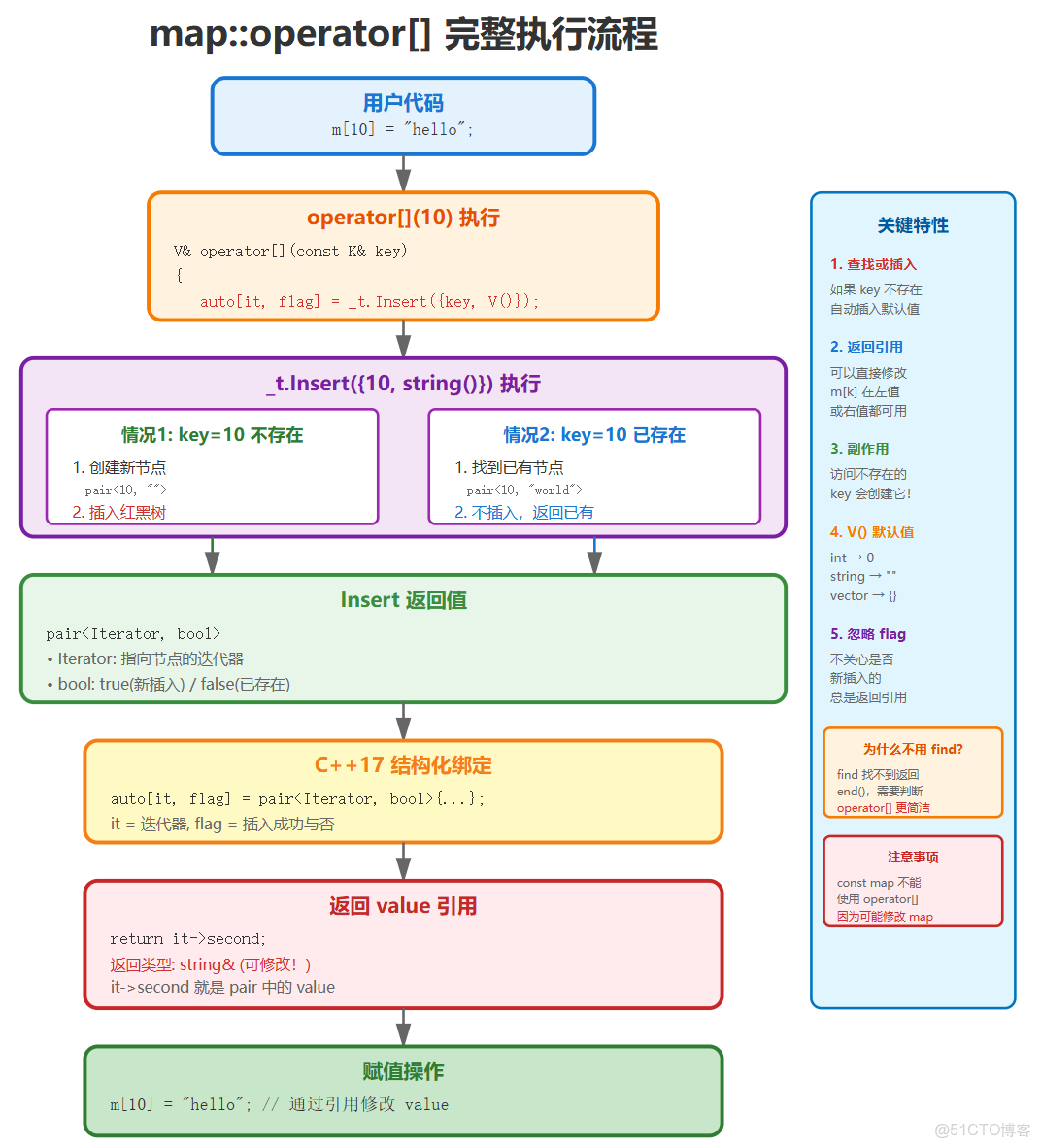
2.3 map中的operator[ ]
2.3.1 operator[ ]的實現思路
map 支持下標訪問 dict["key"],其底層邏輯非常巧妙。它依賴於 insert 函數的返回值 。
insert 返回的是 pair<iterator, bool>:
- 如果 Key 存在,返回
{指向該元素的迭代器, false}。 - 如果 Key 不存在,插入新節點,返回
{指向新節點的迭代器, true}。
利用這個特性,operator[] 的實現如下 :
V& operator[](const K& key) {
// 1. 調用 insert,無論 key 是否存在,ret.first 都會指向該節點
// pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
auto[it, flag] = _t.Insert({ key, V() }); // 結構化綁定 C++17
// 2. 返回該節點 value 的引用,以便用户讀寫
return ret.first->second;
}2.3.2 operator[ ]的執行流程
2.4 set的完整封裝實現
set的特點
- 存儲的是Key值,用於快速查找
- 不允許重複元素
- 底層是紅黑樹,按Key有序存儲
namespace MySet
{
template<class K>
class set
{
// 內部類(把key取出來)
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
// 沒有實例化,編譯器無法確定這是類型還是靜態成員變量
// 前面要加一個typename,告訴編譯器這時一個類型
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
private:
// key的迭代器不能支持修改,把第二個模板參數改為const K
RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}2.5 map的完整封裝實現
map的特點
- 存儲鍵值對(Key-Value)
- 通過Key快速查找Value
- Key不允許重複,Value可以重複
- 支持通過operator[]訪問元素
namespace MyMap
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
// 內部類(把key取出來)
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
// 插入+修改(因為返回的是引用,所以可以修改)
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
// pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert({ key, V() });
auto[it, flag] = _t.Insert({ key, V() });
return it->second;
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}2.6 完整的紅黑樹模板類
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
T _data;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _col(RED)
{}
};
// RBTree<K, K> _t; // set
// RBTree<K, pair<K, V>> _t; // map
// 迭代器
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
// map常用->訪問數據
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
// 返回類型依舊是迭代器
Self& operator++()
{
// 右孩子不為空,找右孩子的最左節點
if (_node->_right)
{
Node* minRight = _node->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
_node = minRight;
}
// 右為空,找孩子是父親左的祖先
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> ConstIterator;
~RBTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
Iterator Begin()
{
// 最左節點
Node* minLeft = _root;
while (minLeft && minLeft->_left)
{
minLeft = minLeft->_left;
}
return Iterator(minLeft); // 用minLeft構造了一個迭代器
}
Iterator End()
{
return Iterator(nullptr); // 用nullptr充當end
}
ConstIterator Begin() const
{
// 最左節點
Node* minLeft = _root;
while (minLeft && minLeft->_left)
{
minLeft = minLeft->_left;
}
return ConstIterator(minLeft); // 用minLeft構造了一個迭代器
}
ConstIterator End() const
{
return ConstIterator(nullptr); // 用nullptr充當end
}
pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK; // 根節點必須為黑色
return { Iterator(_root), true }; // 插入成功
}
KeyOfT kot; // 通過kot,把T類型的數據中的key取出來,然後在下面比較大小
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)) // 如果data是key就用key比較大小可以;如果data是pair,用pair比較大小,不一定是我們想要的
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return { Iterator(cur), false }; // 已經有這個值,插入失敗
}
}
// 新增節點必須為紅色
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur; // cur在旋轉時可能會變,用newnode保存一下
cur->_col = RED;
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
// 叔叔存在且為紅
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
// 變色+繼續往上處理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 叔叔不存在或者叔叔存在且為黑
{
// 單旋+變色
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// 雙旋+變色
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
// 叔叔存在且為紅
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
// 變色+繼續往上處理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 叔叔不存在或者叔叔存在且為黑
{
// 單旋+變色
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// 雙旋+變色
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
// 無論最後根節點是否為黑,就直接置為黑
_root->_col = BLACK;
return { Iterator(newnode), true };
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parentParent->_left == parent)
{
parentParent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parentParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent == parentParent->_left)
{
parentParent->_left = subR;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
// 返回類型為迭代器,既可以查找也可以修改
Iterator Find(const K& key)
{
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return Iterator(cur);
}
}
return End();
}
private:
void Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};