1.首先創建twosortfile1.txt,並在此文件中輸入內容
cd /usr/local/hadoop
vim twosortfile1.txttwosortfile1.txt文件內容如下:
a 20
b 20
a 5
c 10
c 8
b 15
a 10
b 18
c 29
b 52編寫twosortfile2.txt的內容
vim twosortfile2.txttwosortfile2.txt文件內容如下:
a 21
b 21
a 6
c 11
c 9
b 16
a 11
b 19
c 30
b 532.啓動hadoop
./sbin/start-dfs.sh
jps3.在HDFS中新建與當前Linux用户hadoop對應的input2目錄,即“/user/hadoop/input2”目錄,不用創建output2文件,程序運行完成後,會自動創建,創建input2目錄的具體命令如下:
cd /usr/local/hadoop
./bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir input2然後,把之前在第上面在Linux本地文件系統中新建的兩個文件twosortfile1.txt和twosortfile2.txt(這兩個文件位於“/usr/local/hadoop”目錄下,並且裏面包含了一些數據),上傳到HDFS中的“/user/hadoop/input2”目錄下,命令如下:
cd /usr/local/hadoop
./bin/hdfs dfs -put ./twosortfile1.txt input2
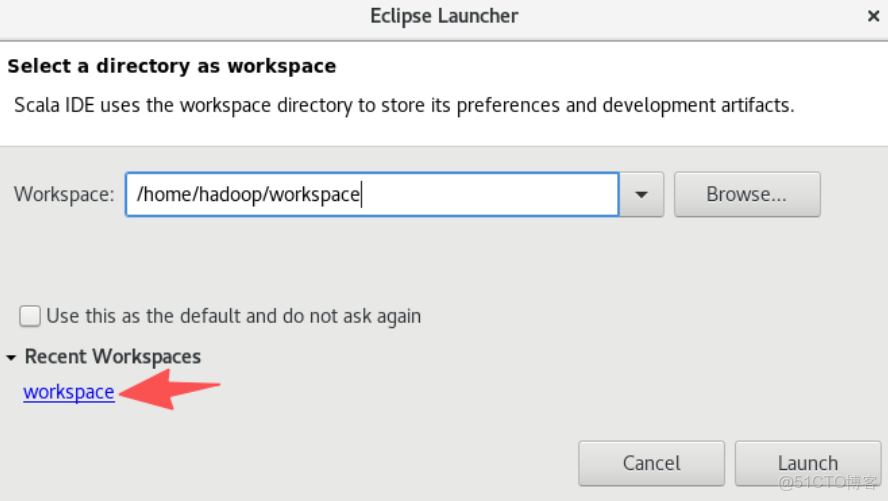
./bin/hdfs dfs -put ./twosortfile2.txt input24.打開eclipse,因為之前實驗創建過workspace,因為在下面的界面點擊我們之前創建的workspace即可
cd /usr/local/eclipse
./eclipse
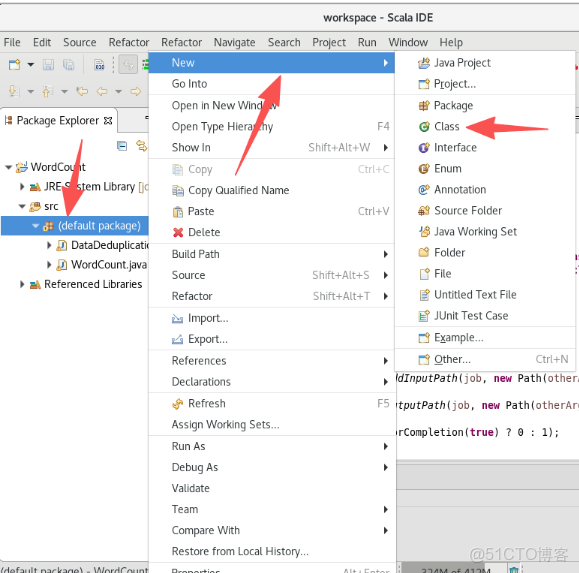
5.按照下圖從左到右創建.java文件
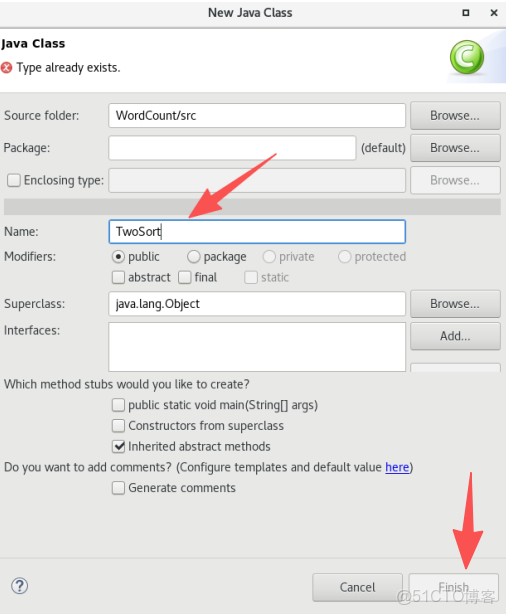
6.給.java文件命名
7.將以下代碼放在TwoSort.java文件中
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class TwoSort{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = (new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args)).getRemainingArgs();
if(otherArgs.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: datadedup <in> [<in>...] <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(TwoSort.class);
job.setMapperClass(TwoSort.TemplateMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(TwoSort.TemplateReducer.class);
//設置輸出類型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
//設置輸入和輸出目錄
for(int i = 0; i < otherArgs.length - 1; ++i) {
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[i]));
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[otherArgs.length - 1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
public static class TemplateMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,Text, IntWritable>{
// 創建map輸出的對象
private static final Text mapOutKey = new Text();
private static final IntWritable mapOutValue = new IntWritable();
@Override
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 將每一行數據按空格拆開
String[] values = value.toString().split(" ");
// 數據預處理,將數組超過2的過濾掉
if (values.length != 2){
return;
}
mapOutKey.set(values[0]);
mapOutValue.set(Integer.valueOf(values[1]));
context.write(mapOutKey,mapOutValue);
}
}
public static class TemplateReducer extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable>{
// 創建reduceout端的對象
private static final IntWritable outputValue = new IntWritable();
@Override
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
List<Integer> valueList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 取出value
for (IntWritable value:values){
valueList.add(value.get());
}
// 打印出reduce輸入的key和valueList
System.out.println("Reduce in == KeyIn: "+key+" ValueIn: "+valueList);
// 進行排序
Collections.sort(valueList);
/*
valueList:表示上面已經排序好的列表,即需要遍歷列表中的值作為reduce的輸出
key不需要改變,即可作為reduce的輸出
*/
for (Integer value : valueList){
outputValue.set(value);
context.write(key,outputValue);
}
}
}
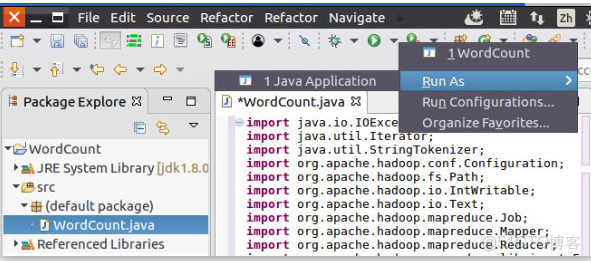
}8.現在就可以編譯上面編寫的代碼。可以直接點擊Eclipse工作界面上部的運行程序的快捷按鈕,當把鼠標移動到該按鈕上時,在彈出的菜單中選擇“Run as”,繼續在彈出來的菜單中選擇“Java Application”,如下圖所示。
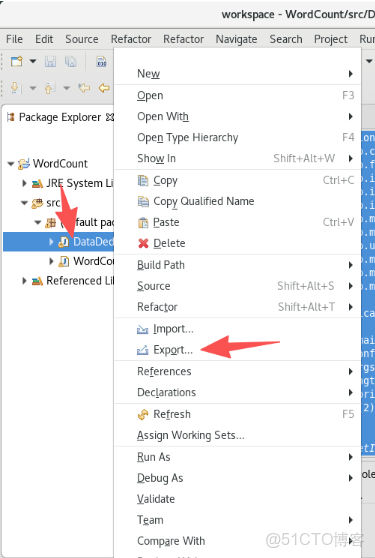
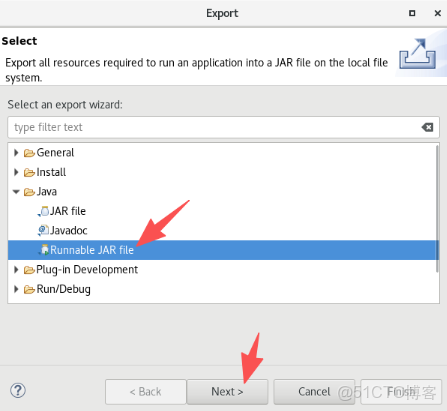
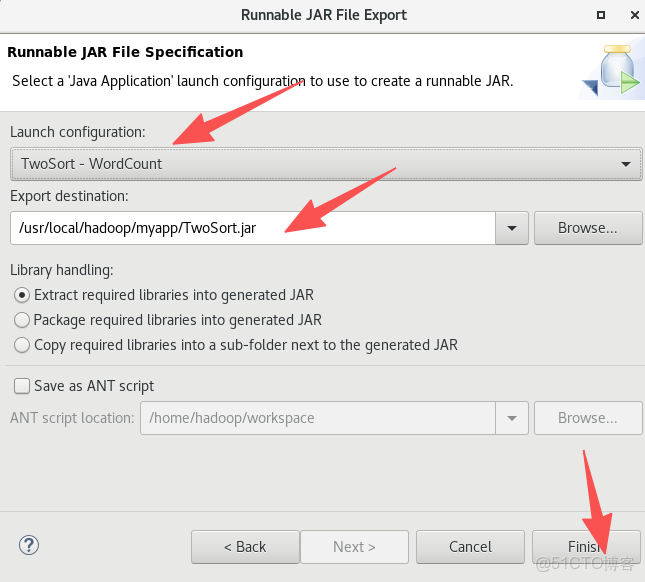
9.將TwoSort.java文件按照下面圖片的操作打包成jar包
10.現在,就可以在Linux系統中,使用hadoop jar命令運行程序,命令如下:
cd /usr/local/hadoop
./bin/hadoop jar ./myapp/TwoSort.jar input2 output2二次排序結果已經被寫入了HDFS的“/user/hadoop/output2”目錄中,可以執行如下命令查看去重結果:
cd /usr/local/hadoop
./bin/hdfs dfs -cat output2/*