使用優先級
ID → Name → CSS Selector → XPath → Class Name → Link Text → Partial Link Text → Tag Name
ID
唯一,同一頁面內不會重複。有ID優先用ID
d.find_element(By.ID, "searchKey")name
次優選擇,可能不唯一。
d.find_element(By.NAME, "searchKey")class
類名定位;不唯一,一般不用
el = d.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, "s_input")
els = d.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "s_input")
print(len(els)) # 2tag_name
通過HTML標籤名,不唯一且重複性最高,一般不單獨用
# 根據HTML的標籤名查詢
el = d.find_element(By.TAG_NAME, "input")
els = d.find_elements(By.TAG_NAME, "input") # 查詢頁面上所有的input標籤
print(len(els)) # 5link_text
只有A標籤能用,根據a標籤的文本內容精準匹配
partial_link_text
同Link_text,區別在於partial_link_text是模糊匹配,link_text是精準匹配
el = d.find_element(By.LINK_TEXT, "首頁") # 查找頁面上所有A標籤中,文本內容等於"首頁"字的元素
el = d.find_element(By.PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT, "首") # 查找頁面上所有A標籤中,文本內容包含"首"字的元素xpath
通過XML路徑語言定位,功能最強大,幾乎可以定位任何元素,用的最多。缺點:性能較差,語法複雜
// 文檔中的任意位置 //div - 文檔中所有div
. 當前節點 .//input - 當前節點下的input
.. 父節點 ../div - 父節點的div
@ 屬性 @id - id屬性
* 通配符 //* - 所有元素1. 路徑定位
絕對路徑
絕對路徑從文檔根節點開始,通過依次指定每個層級的節點來定位目標節點。
el = d.find_element(By.XPATH, "/html/body/div[2]/div/div[1]/form/ul/li[2]/input")相對路徑:
相對路徑是相對於當前上下文節點來定位目標節點的路徑表達式。
el = d.find_element(By.XPATH, "//a[@href='/book/bookclass.html']") # 找任意位置的a標籤中屬性href='/'的元素2. 屬性定位
語法
//*[@屬性名='值']
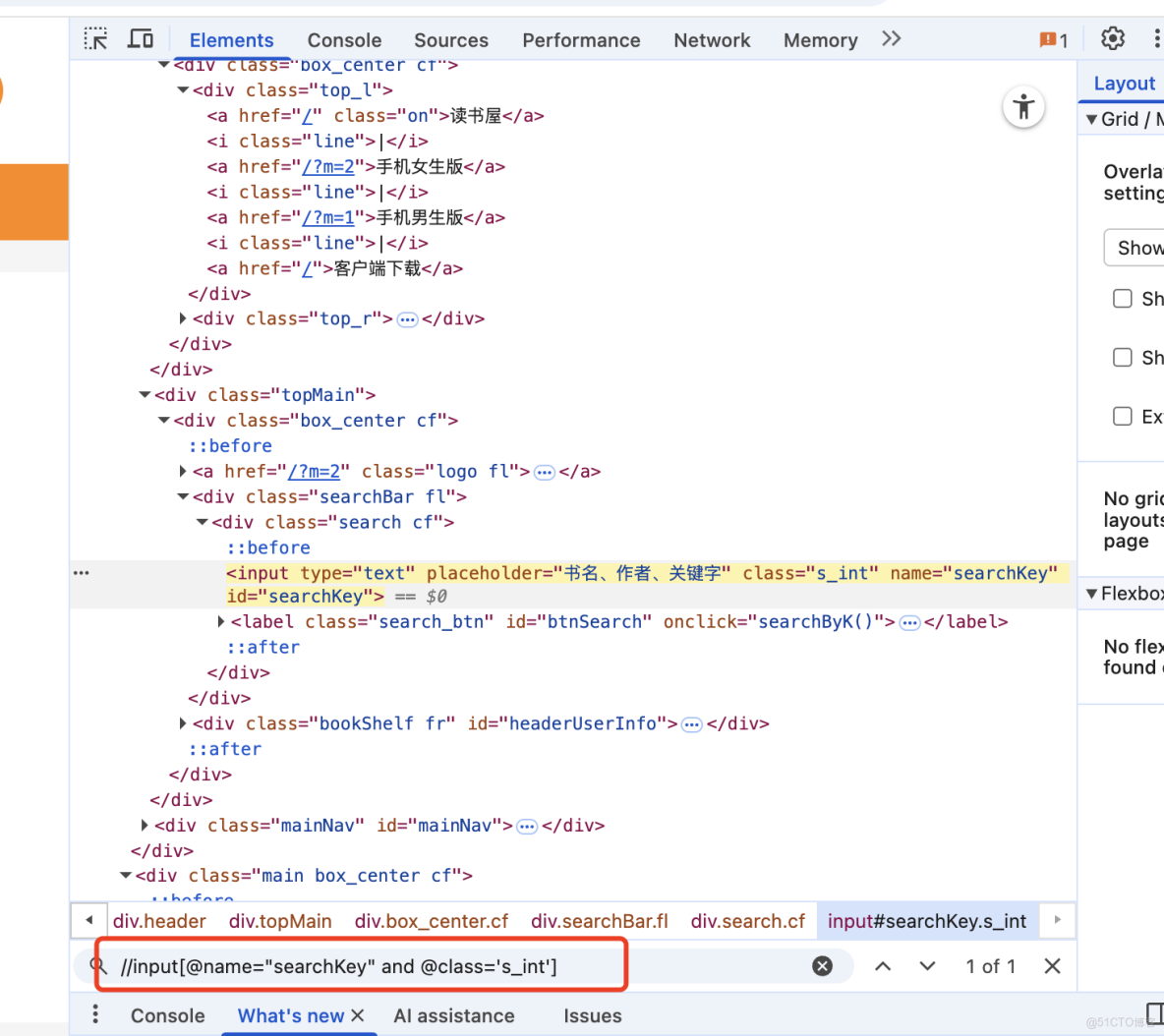
//input[@name='searchKey'] # 找任意位置的input標籤,並且name屬性為searchKey
//input[@name="searchKey" and @class="s_int"] # 從整個頁面中查找name="searchKey" 並且 @class="s_int"]的元素模糊匹配
語法
//標籤名[contains(@屬性, '值')] 找包含xx元素
//*[starts-with(@placeholder,'手機')] # 找placeholder屬性以手機開頭的元素//標籤名[starts-with(@屬性, '值')] 以xx開頭的元素
//*[contains(@class, 's_input icon_name')] # 找class屬性包含s_input icon_name的元素
//input[contains(@class, 's_input icon_name')] # 找input標籤中class屬性包含s_input icon_name的元素3.文本定位
文本跟屬性不同,文本是text(),與屬性的@有區別
//*[text()='我的書架'] # 找任意位置文本為 我的書架 的元素模糊搜索同樣適用
//*[contains(text(),'我的')]
//*[starts-with(text(),'我的')]css
通過CSS選擇器語法定位。性能好,語法簡潔;缺點:某些複雜定位不如XPath
.代表class
.s_input # 找class=s_input的元素
input[class='s_input'] # input標籤中class=s_input的元素
input. s_input # 同上#代表id
#txtUName # 找ID=txtUName的元素
input#txtPassword>直接子元素,只能找一層父子關係
div.search>input # 找class=search的div標籤,並且子元素標籤為input的元素空格 後代元素 子孫後代,不限層級
div.search input # 找class=search的div標籤,並且後代元素標籤為input的元素
div.search i+ 同級元素
div.search input+label # 選擇所有 class 為 "search" 的 div 元素內部、緊跟在 input 元素後面的第一個同級 label 元素。css-網格定位
#在name=txtPassword的上方找一個input元素
driver.find_element(locate_with(By.TAG_NAME,"input").above({By.XPATH:'//*[@name="txtPassword"]'}))locate_with() # 用於創建相對定位策略。
.above # 在參考元素的上方查找,above裏面是參考元素,locate_with是要找的元素
.below # 在參考元素的下方查找
d.find_element(locate_with(By.TAG_NAME, 'input').below({By.CSS_SELECTOR:'input.s_input'})) #