鴻蒙學習實戰之路:狀態管理最佳實踐
狀態管理是 HarmonyOS 開發中非常重要的一部分,它用於管理應用程序的數據狀態和界面交互。本文將結合華為開發者聯盟的官方最佳實踐,介紹 HarmonyOS 中的狀態管理方案和最佳實踐。
關於本文
本文基於華為開發者聯盟官方文檔《狀態管理最佳實踐》整理而成,旨在幫助開發者快速掌握 HarmonyOS 中的狀態管理技巧。
官方文檔傳送門永遠是你的好夥伴,請收藏!
- 本文不能代替官方文檔,所有內容均基於官方文檔+個人實踐經驗總結
- 基本所有章節都會附上對應的文檔鏈接,強烈建議你點擊查看
- 所有代碼示例建議自己動手嘗試一下
- 如果英文水平不是很好,善用瀏覽器翻譯功能
狀態管理概述
在聲明式 UI 編程範式中,UI 是應用程序狀態的函數,應用程序狀態的修改會更新相應的 UI 界面。ArkUI 採用了 MVVM 模式,其中 ViewModel 將數據與視圖綁定在一起,更新數據的時候直接更新視圖。
在 HarmonyOS 中,狀態管理用於管理應用程序的數據狀態和界面交互。有效的狀態管理可以幫助開發者:
- 提高代碼的可維護性和可測試性
- 減少組件間的耦合度
- 優化應用程序的性能
- 提供更好的用户體驗
HarmonyOS 提供了多種狀態管理方案,包括:
- 組件級狀態管理:使用
@State、@Prop、@Link等裝飾器 - 父子組件間狀態傳遞:使用
@Provide和@Consume裝飾器 - 全局狀態管理:使用
AppStorage和LocalStorage
組件級狀態管理
1. @State 裝飾器
功能説明:@State 裝飾器用於定義組件內部的狀態變量,當狀態變量的值發生變化時,組件會自動重新渲染。被@State 裝飾器修飾後狀態的修改只會觸發當前組件實例的重新渲染。
實現步驟:
- 在組件中定義
@State裝飾的狀態變量 - 在組件的
build方法中使用該狀態變量 - 當狀態變量的值發生變化時,組件會自動重新渲染
代碼示例:
import { State, Component, Entry, Text, Button, Column, FlexAlign, FontSize, FontWeight } from '@kit.ArkUI'
@Entry
@Component
struct StateExample {
// 使用@State裝飾器定義狀態變量
@State count: number = 0
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center,
justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text(`當前計數: ${this.count}`)
.fontSize(FontSize.Large)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Row() {
Button('增加')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.margin({ right: 10 })
.onClick(() => {
// 修改狀態變量的值,組件會自動重新渲染
this.count++
})
Button('減少')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.onClick(() => {
this.count--
})
}
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}2. @Prop 裝飾器
功能説明:@Prop 裝飾器用於實現父組件向子組件的單向數據傳遞。子組件可以使用父組件傳遞的數據,但不能直接修改它。
實現步驟:
- 在子組件中定義
@Prop裝飾的屬性 - 在父組件中使用子組件時,傳遞對應的屬性值
- 子組件可以使用該屬性值,但不能直接修改
代碼示例:
import { State, Prop, Component, Entry, Text, Button, Column, FlexAlign, FontSize, FontWeight } from '@kit.ArkUI'
// 子組件
@Component
struct ChildComponent {
// 使用@Prop裝飾器定義從父組件接收的屬性
@Prop message: string
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text(`子組件接收到的消息: ${this.message}`)
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
}
.width('100%')
.padding(20)
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.borderRadius(12)
}
}
// 父組件
@Entry
@Component
struct PropExample {
// 父組件的狀態變量
@State parentMessage: string = 'Hello from Parent'
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center,
justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text('父組件')
.fontSize(FontSize.Large)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
// 使用子組件並傳遞屬性值
ChildComponent({ message: this.parentMessage })
Button('修改消息')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.margin({ top: 20 })
.onClick(() => {
// 修改父組件的狀態變量,子組件會自動更新
this.parentMessage = 'Updated Message'
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}3. @Link 裝飾器
功能説明:@Link 裝飾器用於實現父組件與子組件之間的雙向數據綁定。子組件可以直接修改父組件傳遞的數據,並且修改後會自動同步回父組件。
實現步驟:
- 在子組件中定義
@Link裝飾的屬性 - 在父組件中使用子組件時,使用
$符號傳遞狀態變量的引用 - 子組件可以直接修改該屬性值,並且修改會自動同步回父組件
代碼示例:
import { State, Link, Component, Entry, Text, Button, Column, FlexAlign, FontSize, FontWeight } from '@kit.ArkUI'
// 子組件
@Component
struct ChildComponent {
// 使用@Link裝飾器定義雙向綁定的屬性
@Link count: number
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text(`子組件中的計數: ${this.count}`)
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Button('子組件增加計數')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.onClick(() => {
// 直接修改@Link裝飾的屬性,父組件的狀態變量會自動更新
this.count++
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding(20)
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.borderRadius(12)
}
}
// 父組件
@Entry
@Component
struct LinkExample {
// 父組件的狀態變量
@State parentCount: number = 0
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center,
justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text(`父組件中的計數: ${this.parentCount}`)
.fontSize(FontSize.Large)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
// 使用子組件並傳遞狀態變量的引用(使用$符號)
ChildComponent({ count: $parentCount })
Button('父組件增加計數')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.margin({ top: 20 })
.onClick(() => {
this.parentCount++
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}父子組件間狀態傳遞
組件間需要共享的狀態
組件間需要共享的狀態,按照共享範圍從小到大依次有三種場景:父子組件間共享狀態,不同子樹上組件間共享狀態和不同組件樹間共享狀態。
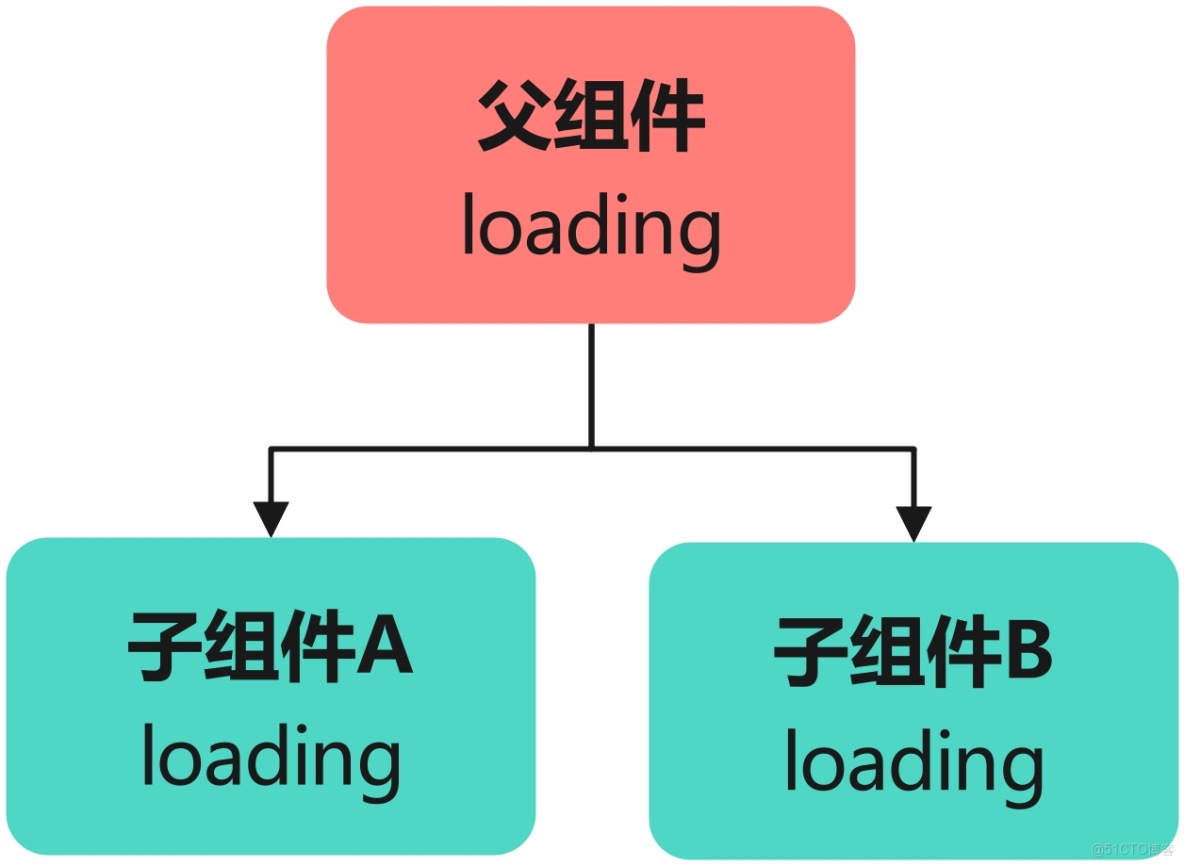
父子組件間共享狀態
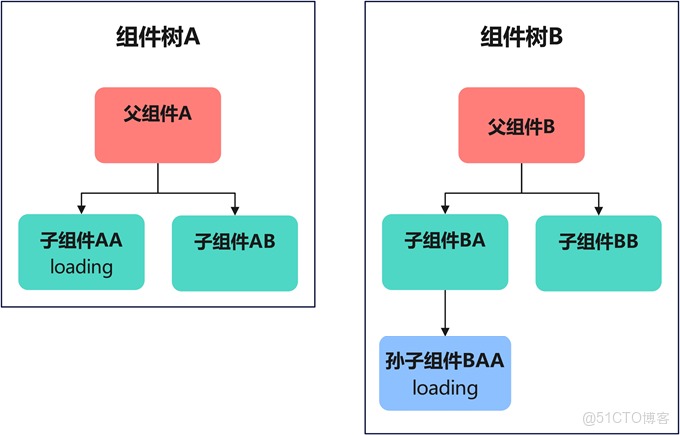
不同子樹上組件間共享狀態
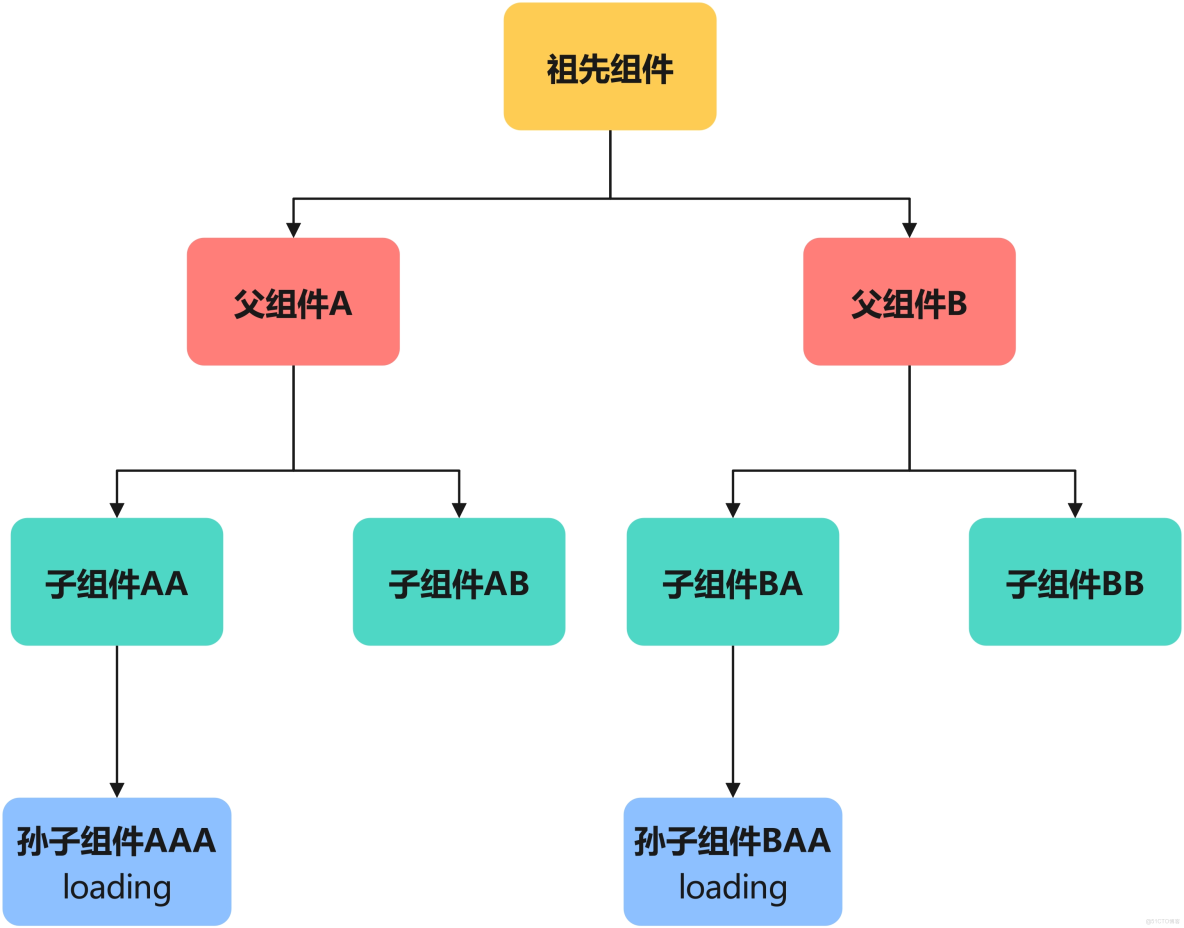
不同組件樹間共享狀態
@Provide 和 @Consume 裝飾器
功能説明:@Provide 和 @Consume 裝飾器用於實現跨層級組件間的狀態共享,父組件使用 @Provide 提供狀態,子組件使用 @Consume 消費狀態。
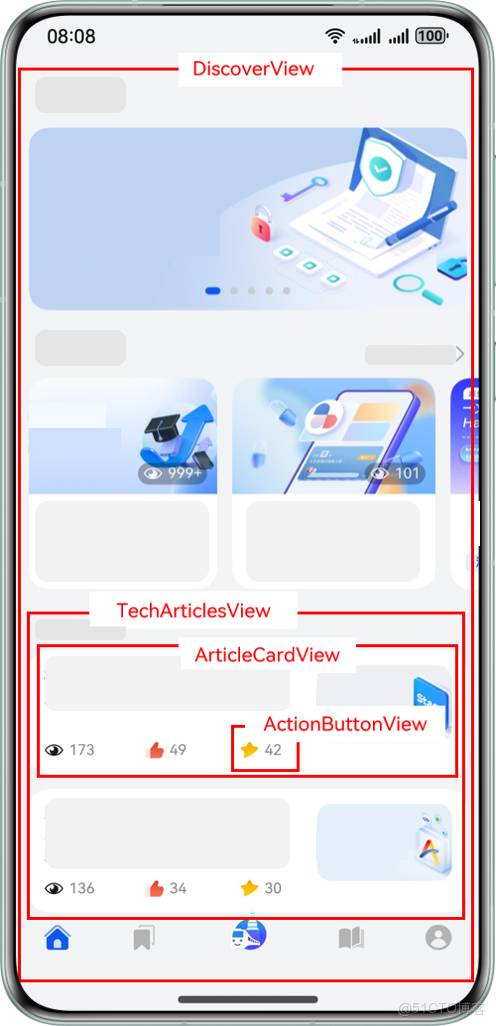
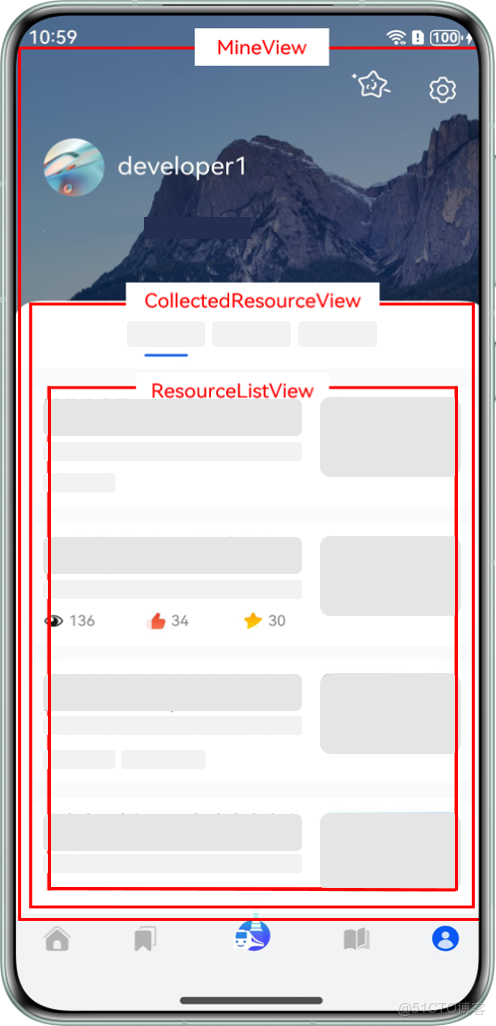
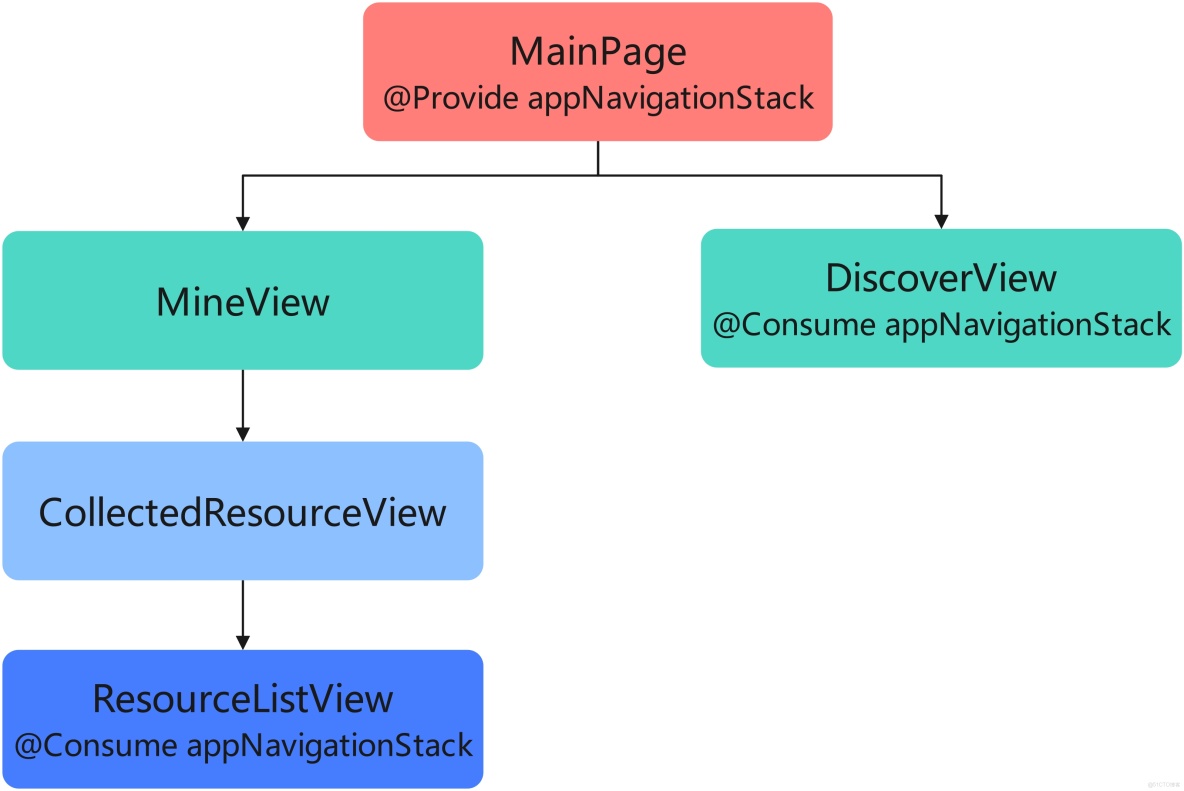
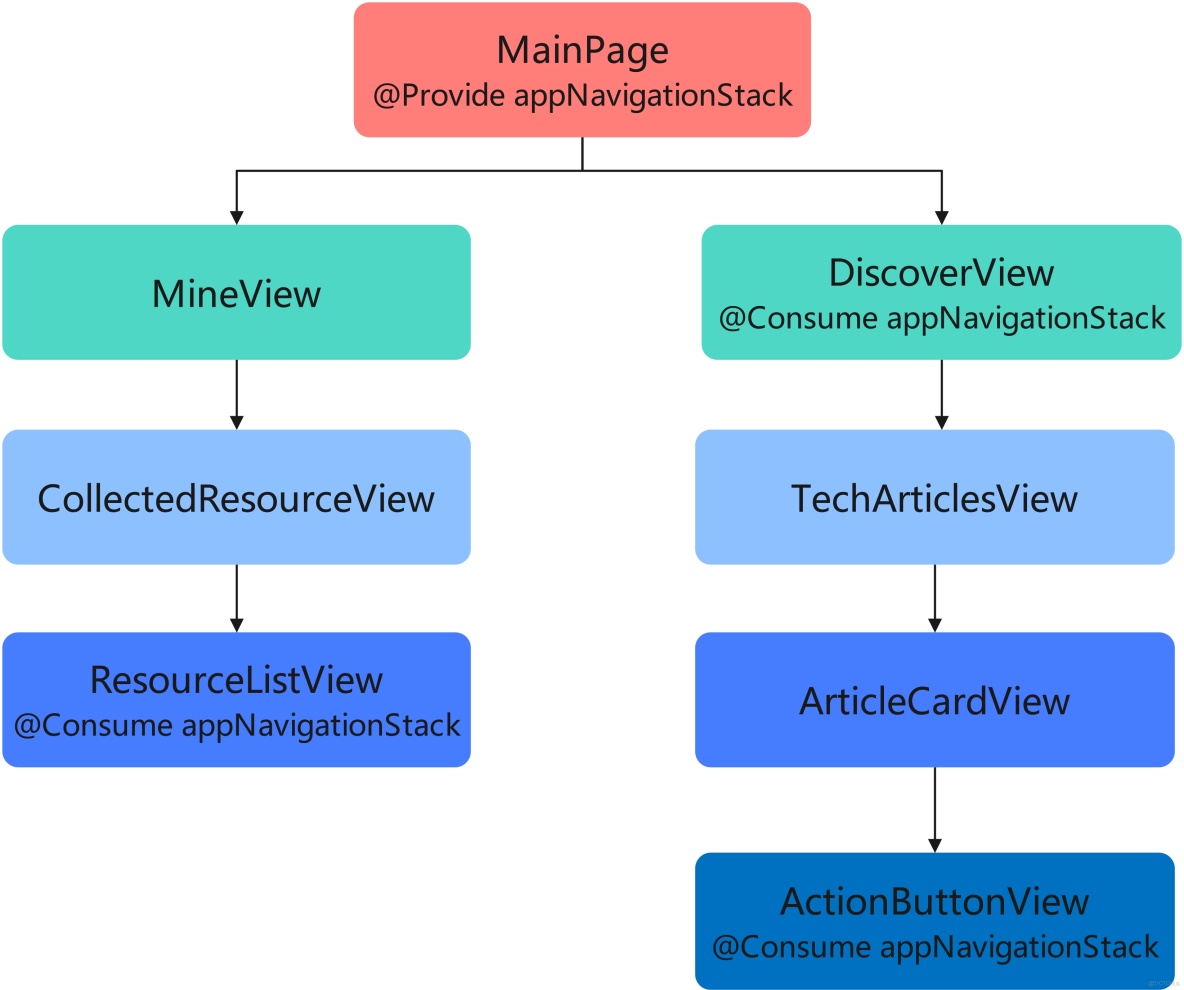
以 HMOS 世界 App 為例,其“探索”Tab 和“我的”Tab 界面組件示意圖如下:
組件結構説明:
- "MainPage"是主頁面,該頁面有 2 個子組件"MineView"和"DiscoverView"。
- "MineView"是"我的"Tab 對應的內容視圖組件,"CollectedResourceView"是該組件內展示收藏列表的視圖組件,"ResourceListView"是"CollectedResourceView"的子組件。
- "DiscoverView"是"探索"Tab 對應的內容視圖組件,"TechArticlesView"是該組件內展示文章列表的視圖組件,"ArticleCardView"是列表上單個卡片視圖組件,"ActionButtonView"是卡片上交互視圖組件。
若使用@State+@Prop 方式實現組件間狀態共享,當前組件設計圖如下:
存在的問題:為了實現"ResourceListView"組件和"DiscoverView"組件共享狀態,需要將狀態定義在兩者的最近公共祖先"MainPage"組件上,並通過@Prop 裝飾器層層傳遞,直到兩個需要共享狀態的組件。
若新增功能要求在"DiscoverView"組件的後代"ActionButtonView"組件上新增對路由信息的判斷邏輯,需要修改多個組件:
問題分析:新功能的邏輯原本只是在"ActionButtonView"這一個組件中使用,卻需要修改從"DiscoverView"組件到"ActionButtonView"組件路徑上 3 個組件的結構。
使用@Provide+@Consume 方案更為合理,組件設計圖如下:
優勢:通過在最頂部組件"MainPage"中注入路由信息狀態,其後代組件均可以通過@Consume 裝飾器獲取該狀態值,無需修改中間組件結構。
當業務變動需要"DiscoverView"的後代"ActionButtonView"組件也共享路由信息時,只需在"ActionButtonView"組件上使用@Consume 裝飾器直接獲取路由信息狀態,無需修改其他組件:
總結:當共享狀態的組件間跨層級較深時,或共享的信息對於整個組件樹是"全局"的存在時,選擇@Provide+@Consume 的裝飾器組合代替層層傳遞的方式,能夠提升代碼的可維護性和可拓展性。
實現步驟:
- 在父組件中使用
@Provide裝飾器定義共享狀態 - 在子組件或孫組件中使用
@Consume裝飾器消費該狀態 - 當共享狀態的值發生變化時,所有消費該狀態的組件都會自動重新渲染
代碼示例:
import { Provide, Consume, Component, Entry, Text, Button, Column, Row, FlexAlign, FontSize, FontWeight } from '@kit.ArkUI'
// 孫子組件
@Component
struct GrandChildComponent {
// 使用@Consume裝飾器消費共享狀態
@Consume themeColor: string
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text('孫子組件')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 10 })
Text(`當前主題顏色: ${this.themeColor}`)
.fontSize(FontSize.Small)
.margin({ bottom: 10 })
Button('紅色主題')
.fontSize(FontSize.Small)
.margin({ right: 5 })
.onClick(() => {
// 直接修改@Consume裝飾的狀態,所有消費該狀態的組件都會更新
this.themeColor = 'red'
})
Button('藍色主題')
.fontSize(FontSize.Small)
.onClick(() => {
this.themeColor = 'blue'
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding(20)
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.borderRadius(12)
}
}
// 子組件
@Component
struct ChildComponent {
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text('子組件')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
// 孫子組件會自動繼承父組件提供的狀態
GrandChildComponent()
}
.width('100%')
.padding(20)
.backgroundColor('#E5E5E5')
.borderRadius(12)
}
}
// 父組件
@Entry
@Component
struct ProvideConsumeExample {
// 使用@Provide裝飾器提供共享狀態
@Provide themeColor: string = 'green'
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center,
justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text('父組件')
.fontSize(FontSize.Large)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Text(`當前主題顏色: ${this.themeColor}`)
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
// 子組件和孫子組件可以消費父組件提供的狀態
ChildComponent()
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}全局狀態管理
1. AppStorage
功能説明:AppStorage 是應用級別的全局狀態存儲,用於存儲整個應用程序共享的狀態數據,如用户信息、主題設置等。
以 HMOS 世界 App 為例,其點贊高亮狀態和用户信息組件視圖如下:
應用場景:
- “我的”模塊頂部有展示用户信息的組件“UserInfoView”,底部有展示用户收藏列表,列表卡片上需要高亮展示用户是否點讚了當前文章。
- “探索”模塊首頁展示技術文章列表,列表卡片上同樣需要展示用户是否點讚了當前文章。
- 當兩個模塊中任一模塊的卡片有點贊交互時,需要同步用户是否對文章點讚的狀態給另一個模塊。
實現步驟:
- 在應用程序的入口文件中初始化
AppStorage - 在組件中使用
@StorageProp或@StorageLink裝飾器訪問AppStorage中的數據 - 當
AppStorage中的數據發生變化時,所有訪問該數據的組件都會自動重新渲染
代碼示例:
import { StorageProp, StorageLink, Component, Entry, Text, Button, Column, FlexAlign, FontSize, FontWeight } from '@kit.ArkUI'
// 組件A
@Entry
@Component
struct ComponentA {
// 使用@StorageLink裝飾器訪問AppStorage中的數據(雙向綁定)
@StorageLink('globalCount') count: number = 0
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center,
justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text('組件A')
.fontSize(FontSize.Large)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Text(`全局計數: ${this.count}`)
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Button('增加計數')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.onClick(() => {
this.count++
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('50%')
}
}
// 組件B
@Component
struct ComponentB {
// 使用@StorageProp裝飾器訪問AppStorage中的數據(單向綁定)
@StorageProp('globalCount') count: number = 0
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center,
justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text('組件B')
.fontSize(FontSize.Large)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Text(`全局計數: ${this.count}`)
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Button('減少計數')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.onClick(() => {
// 使用AppStorage的API修改數據
AppStorage.setOrCreate('globalCount', this.count - 1)
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('50%')
}
}
// 應用入口
@Entry
@Component
struct AppStorageExample {
build() {
Column() {
ComponentA()
ComponentB()
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}2. LocalStorage
功能説明:LocalStorage 是頁面級別的全局狀態存儲,用於存儲單個頁面內多個組件共享的狀態數據。
實現步驟:
- 創建
LocalStorage實例並初始化數據 - 在組件中使用
@LocalStorageProp或@LocalStorageLink裝飾器訪問LocalStorage中的數據 - 當
LocalStorage中的數據發生變化時,所有訪問該數據的組件都會自動重新渲染
代碼示例:
import { LocalStorageProp, LocalStorageLink, Component, Entry, Text, Button, Column, FlexAlign, FontSize, FontWeight } from '@kit.ArkUI'
// 初始化LocalStorage
const localStorage = new LocalStorage({
'localCount': 0
})
// 組件A
@Component
struct LocalComponentA {
// 使用@LocalStorageLink裝飾器訪問LocalStorage中的數據(雙向綁定)
@LocalStorageLink('localCount', localStorage) count: number = 0
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center,
justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text('本地存儲組件A')
.fontSize(FontSize.Large)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Text(`本地計數: ${this.count}`)
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Button('增加計數')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.onClick(() => {
this.count++
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('50%')
}
}
// 組件B
@Component
struct LocalComponentB {
// 使用@LocalStorageProp裝飾器訪問LocalStorage中的數據(單向綁定)
@LocalStorageProp('localCount', localStorage) count: number = 0
build() {
Column({
alignItems: FlexAlign.Center,
justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center
}) {
Text('本地存儲組件B')
.fontSize(FontSize.Large)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Text(`本地計數: ${this.count}`)
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
Button('減少計數')
.fontSize(FontSize.Medium)
.onClick(() => {
// 使用LocalStorage的API修改數據
localStorage.set('localCount', this.count - 1)
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('50%')
}
}
// 頁面入口
@Entry
@Component
struct LocalStorageExample {
build() {
Column() {
LocalComponentA()
LocalComponentB()
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}狀態管理最佳實踐
按照狀態複雜度選擇裝飾器
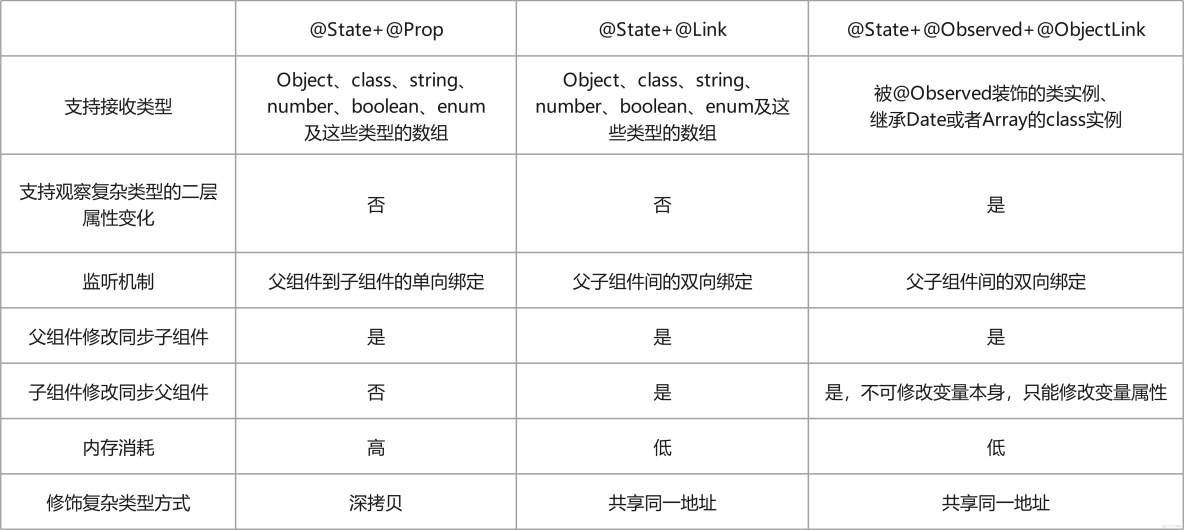
對於具有相同優先級的裝飾器選擇方案@State+@Prop、@State+@Link 和@State+@Observed+@ObjectLink,在選擇方案時,需要結合具體的業務場景和狀態數據結構的複雜度。這三種不同的裝飾器組合方案在內存消耗、性能消耗和對數據類型的支持能力都不相同:
1. 選擇合適的狀態管理方案
根據應用程序的規模和複雜度選擇合適的狀態管理方案:
- 組件內部狀態:使用@State
- 父子組件間狀態:根據複雜度選擇@Prop、@Link 或@Observed+@ObjectLink
- 跨層級組件狀態:使用@Provide+@Consume
- 全局共享狀態:使用 AppStorage 或 LocalStorage
2. 最小化狀態範圍
將狀態變量的範圍限制在必要的最小範圍內,避免不必要的狀態共享和組件重新渲染。
3. 避免過度使用全局狀態
全局狀態應該用於真正需要在多個組件間共享的數據,如用户信息、主題設置等,避免將所有狀態都放入全局存儲。
4. 使用不可變數據
儘量使用不可變數據來管理狀態,避免直接修改對象或數組,這樣可以提高應用程序的性能和可預測性。
5. 合理使用生命週期函數
在適當的生命週期函數中初始化和清理狀態,如 onPageShow、onPageHide 等。
6. 優化性能
避免不必要的狀態更新和組件重新渲染:
- 使用條件渲染避免不必要的組件創建
- 合理使用@Watch 裝飾器監聽狀態變化
- 對於大型列表,使用 VirtualList 等高性能組件
常見問題與解決方案
1. 狀態更新後組件沒有重新渲染
問題:當狀態變量的值發生變化時,組件沒有自動重新渲染。
解決方案:
- 確保狀態變量使用了正確的裝飾器(如
@State、@Link等) - 確保狀態變量的類型是可觀察的(如基本類型、數組、對象等)
- 對於對象或數組,確保創建了新的引用而不是直接修改原對象
2. 組件間狀態傳遞複雜
問題:當應用程序的組件層級較深時,狀態傳遞變得複雜。
解決方案:
- 使用
@Provide和@Consume裝飾器實現跨層級狀態共享 - 使用全局狀態管理方案(如
AppStorage或LocalStorage) - 考慮使用狀態管理庫(如
Redux或MobX)
3. 性能問題
問題:頻繁的狀態更新導致應用程序性能下降。
解決方案:
- 避免不必要的狀態更新
- 使用
memo或shouldComponentUpdate優化組件渲染 - 合理使用
debounce或throttle限制狀態更新的頻率 - 考慮使用
VirtualList等組件優化長列表的性能
參考文檔
- HarmonyOS 官方文檔:狀態管理
- HarmonyOS 官方文檔:狀態管理概述
- HarmonyOS 官方文檔:AppStorage
- HarmonyOS 官方文檔:LocalStorage
總結
狀態管理是 HarmonyOS 開發中非常重要的一部分,本文介紹了 HarmonyOS 提供的多種狀態管理方案,包括組件級狀態管理、父子組件間狀態傳遞和全局狀態管理。通過合理使用這些狀態管理方案,可以提高代碼的可維護性、可測試性和性能,提供更好的用户體驗。
希望本文能夠幫助你快速掌握 HarmonyOS 中的狀態管理技巧,如果你想了解更多關於狀態管理的內容,建議查看華為開發者聯盟的官方文檔。