python中學物理實驗模擬:凸透鏡成像和凹透鏡成像
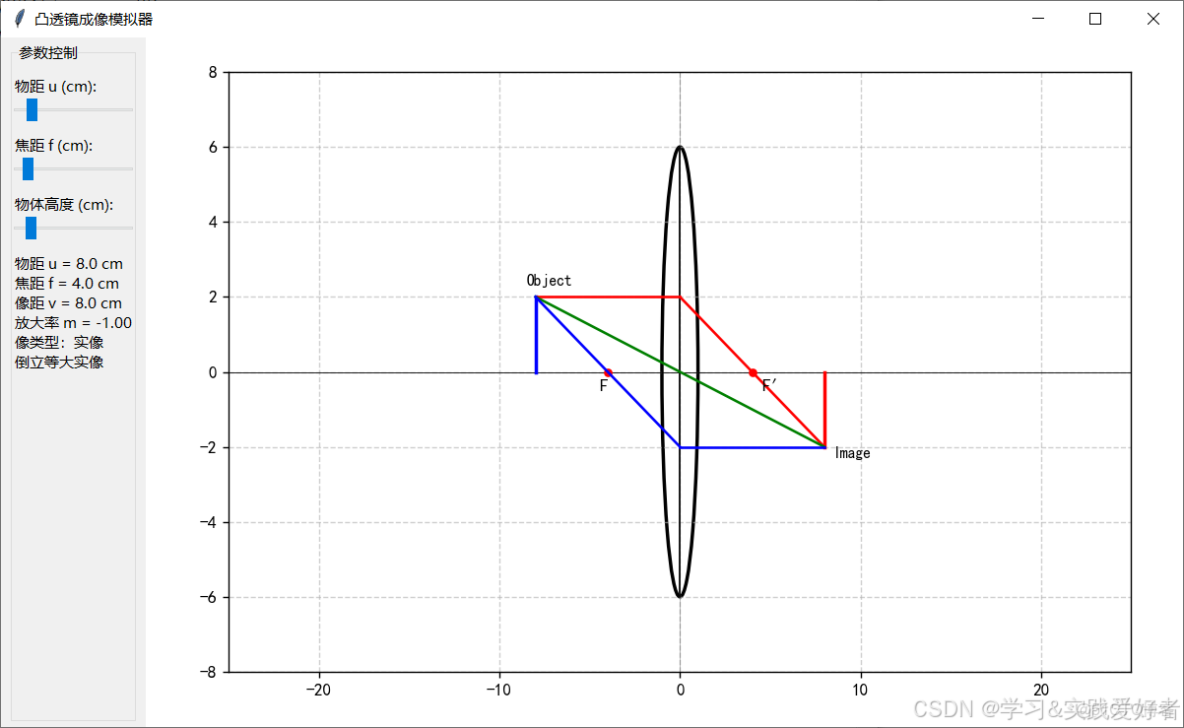
凸透鏡成像
凸透鏡是指中間厚、邊緣薄的透鏡。它對光線有會聚作用,即光線通過凸透鏡後會向主光軸方向偏折。
成像原理
基於光的折射,平行於主光軸的光線經凸透鏡折射後會聚於焦點(F),過光心的光線傳播方向不變。
焦點 (F) 和焦距 (f): 平行於主光軸的光線經凸透鏡折射後實際會聚的點稱為實焦點(在透鏡的另一側)。焦點到透鏡光心的距離稱為焦距 (f)。凸透鏡有兩個對稱的實焦點(物方焦點和像方焦點)。
成像規律: 凸透鏡成像的性質(大小、正倒、虛實)和位置主要取決於物體到透鏡光心的距離(物距 u)與透鏡焦距 (f) 的關係。
成像規律(物距 u、像距 v、焦距 f):
|
物距u範圍 |
像距 (v) 範圍 |
像的性質 |
應用實例 |
|
u > 2f |
f < v < 2f |
倒立、縮小的實像 |
照相機、監控攝像頭 |
|
u = 2f |
v = 2f |
倒立、等大的實像 |
測焦距 |
|
f < u < 2f |
v > 2f |
倒立、放大的實像 |
投影儀、幻燈機 |
|
u = f |
不成像(光線平行射出) |
- |
- |
|
u < f |
像與物同側,v > u |
正立、放大的虛像 |
放大鏡、老花鏡 |
關鍵點理解:
實像: 由實際光線會聚而成,可以用光屏接收(如投影在牆上)。像與物位於透鏡異側。
虛像: 是光線反向延長線的交點,不能用光屏直接接收,只能通過透鏡觀察到。像與物位於透鏡同側。
像距 (v): 像到透鏡光心的距離。實像時 v 為正值;虛像時 v 為負值(在公式計算中體現)。
透鏡公式: 1/f = 1/u + 1/v (符號規定:實物距 u 為正,實像距 v 為正,虛像距 v 為負,凸透鏡焦距 f 為正)。
放大率 (m): m = |v/u| = 像高 / 物高。m > 1 表示放大,m < 1 表示縮小。
運行截圖:
源碼如下:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg import FigureCanvasTkAgg
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
# 配置中文字體
def find_chinese_font():
fonts = ['SimHei', 'Microsoft YaHei', 'SimSun', 'STSong', 'KaiTi']
existing_fonts = []
for f in fonts:
if any([f.lower() in font.lower() for font in fm.findSystemFonts(fontpaths=None)]):
existing_fonts.append(f)
return existing_fonts[0] if existing_fonts else None
chinese_font = find_chinese_font()
if chinese_font:
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = [chinese_font, 'sans-serif']
else:
print("警告: 找不到中文字體,將使用英文")
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 正確顯示負號
class ConvexLensSimulator:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("凸透鏡成像模擬器")
# 物理常量
self.focal_length = 4 # 默認焦距8cm
self.object_height = 2 # 物體高度4cm
# 設置UI
self.setup_ui()
self.root.update() # 強制佈局更新,處理Matplotlib 區域顯示不完整
def setup_ui(self):
"""設置用户界面"""
# 主界面佈局
self.main_frame = ttk.Frame(self.root)
self.main_frame.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
# 控制面板
self.control_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(self.main_frame, text="參數控制")
self.control_frame.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10, pady=5, fill=tk.Y)
# 可視化區域
self.viz_frame = ttk.Frame(self.main_frame)
self.viz_frame.pack(side=tk.RIGHT, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
# 創建控制組件
self.create_controls()
# 初始化繪圖區域
self.init_plot()
# 首次更新
self.update_display()
def create_controls(self):
"""創建控制組件"""
# 物距滑塊
ttk.Label(self.control_frame, text="物距 u (cm):").grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="w", pady=(10,0))
self.u_value = tk.DoubleVar(value=8)
self.u_slider = ttk.Scale(self.control_frame, from_=5, to=30,
variable=self.u_value,
command=lambda _: self.update_display())
self.u_slider.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky="ew")
# 焦距滑塊,焦距允許的範圍 from_=3, to=15,
ttk.Label(self.control_frame, text="焦距 f (cm):").grid(row=2, column=0, sticky="w", pady=(10,0))
self.f_value = tk.DoubleVar(value=self.focal_length)
self.f_slider = ttk.Scale(self.control_frame, from_=3, to=15,
variable=self.f_value,
command=lambda _: self.update_display())
self.f_slider.grid(row=3, column=0, sticky="ew")
# 物體高度滑塊
ttk.Label(self.control_frame, text="物體高度 (cm):").grid(row=4, column=0, sticky="w", pady=(10,0))
self.height_value = tk.DoubleVar(value=self.object_height)
self.height_slider = ttk.Scale(self.control_frame, from_=1, to=10,
variable=self.height_value,
command=lambda _: self.update_display())
self.height_slider.grid(row=5, column=0, sticky="ew")
# 信息顯示
self.info_text = tk.StringVar()
ttk.Label(self.control_frame, textvariable=self.info_text, wraplength=200).grid(row=6, column=0, sticky="w", pady=10)
def init_plot(self):
"""初始化繪圖區域"""
self.fig = plt.Figure(figsize=(10, 6))
self.ax = self.fig.add_subplot(111)
self.ax.set_xlim(-25, 25)
self.ax.set_ylim(-8, 8)
self.ax.axhline(0, color='black', lw=0.5) # 主光軸
# 設置固定的邊距,避免tight_layout問題
self.fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.08, right=0.95, top=0.95, bottom=0.08)
self.canvas = FigureCanvasTkAgg(self.fig, master=self.viz_frame)
self.canvas.get_tk_widget().pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
def calculate_image(self):
"""計算像的位置和性質"""
f = self.f_value.get()
u = self.u_value.get()
# 特殊情況:u = f
if abs(u - f) < 0.01: # 使用小的容差值
return np.inf, np.inf, "不成像"
v = u*f/(u-f) # 高斯成像公式 1/u + 1/v = 1/f
magnification = -v/u # 放大率 m = -v/u
image_type = "實像" if v > 0 else "虛像"
return v, magnification, image_type
def draw_optical_elements(self, u, v):
"""繪製光學元件和光線"""
self.ax.clear()
self.ax.set_xlim(-25, 25)
self.ax.set_ylim(-8, 8)
self.ax.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.6)
self.ax.axhline(0, color='black', lw=0.5) # 主光軸
self.ax.axvline(0, color='black', lw=0.5, alpha=0.3) # 光心垂線
# 標記焦點
f = self.f_value.get()
self.ax.plot([-f, f], [0, 0], 'ro', markersize=4)
self.ax.text(-f-0.5, -0.5, 'F', fontsize=10)
self.ax.text(f+0.5, -0.5, 'F′', fontsize=10)
# 繪製透鏡
self.draw_lens()
# 繪製物體
object_height = self.height_value.get()
self.ax.plot([-u, -u], [0, object_height], 'b-', lw=2) # 物體
self.ax.text(-u-0.5, object_height+0.3, 'Object', fontsize=9)
# 繪製像 - 添加對無窮大的檢查
if v not in [np.inf, -np.inf] and v is not None and not np.isinf(v):
image_height = object_height * (-v/u) # 像的高度, 負號表示倒立
style = 'r-' if v > 0 else 'r--'
self.ax.plot([v, v], [0, image_height], style, lw=2)
self.ax.text(v+0.5, image_height-0.3, 'Image', fontsize=9)
# 繪製光線 - 只有當v不是無窮大時才繪製
if v not in [np.inf, -np.inf] and not np.isinf(v):
self.draw_rays(u, v, object_height)
else:
# 當u=f時,繪製特殊的平行光線
self.draw_parallel_rays(u, object_height)
def draw_parallel_rays(self, u, object_height):
"""繪製u=f時的平行光線"""
f = self.f_value.get()
# 光線1:平行於主光軸入射,經過透鏡後仍然平行
self.ax.plot([-u, 0], [object_height, object_height], 'r-', lw=1.5)
self.ax.plot([0, 25], [object_height, object_height], 'r-', lw=1.5)
# 光線2:通過光心,不發生偏折 - 這條光線應該是直線
self.ax.plot([-u, 25], [object_height, object_height], 'g-', lw=1.5)
# 光線3:從物體頂端指向左焦點,經過透鏡後平行於主光軸射出
lens_height = object_height / 2 # 當u=f時,lens_height = object_height * f / (f + u) = object_height/2
self.ax.plot([-u, 0], [object_height, lens_height], 'b-', lw=1.5)
self.ax.plot([0, 25], [lens_height, lens_height], 'b-', lw=1.5)
def draw_lens(self):
"""繪製凸透鏡"""
# 垂直線
self.ax.plot([0, 0], [-6, 6], 'black', lw=1)
# 凸出部分
arc_left = plt.matplotlib.patches.Arc((0, 0), 2, 12,
theta1=90, theta2=270,
color='black', lw=2)
arc_right = plt.matplotlib.patches.Arc((0, 0), 2, 12,
theta1=270, theta2=90,
color='black', lw=2)
self.ax.add_patch(arc_left)
self.ax.add_patch(arc_right)
def draw_rays(self, u, v, object_height):
"""繪製光線"""
try:
f = self.f_value.get()
if v > 0: # 實像
image_height = -object_height * v / u
# 光線1:平行於主光軸入射 -> 經過右焦點
self.ax.plot([-u, 0], [object_height, object_height], 'r-', lw=1.5)
self.ax.plot([0, v], [object_height, image_height], 'r-', lw=1.5)
# 光線2:通過光心,不發生偏折
self.ax.plot([-u, v], [object_height, image_height], 'g-', lw=1.5)
# 光線3:【修正】從物體頂端經過左焦點到透鏡,然後平行射出
# 第一段:從物體頂端(-u, object_height)經過左焦點(-f, 0)到透鏡(0, y)
# 計算這條直線與透鏡的交點
# 直線斜率 = (0 - object_height) / (-f - (-u)) = -object_height / (u - f)
# 從左焦點到透鏡的延伸:y = 0 + 斜率 * (0 - (-f)) = 斜率 * f
lens_y = -object_height * f / (u - f)
# 繪製:物體頂端 -> 左焦點 -> 透鏡
self.ax.plot([-u, -f, 0], [object_height, 0, lens_y], 'b-', lw=1.5)
# 從透鏡平行於主光軸射出到像點
self.ax.plot([0, v], [lens_y, image_height], 'b-', lw=1.5)
else: # 虛像 (u < f)
image_height = -object_height * v / u # 虛像高度(正值,正立)
# 光線1:平行於主光軸入射 -> 折射後反向延長經過右焦點
self.ax.plot([-u, 0], [object_height, object_height], 'r-', lw=1.5)
self.ax.plot([0, 25], [object_height, object_height - (object_height/f)*25], 'r-', lw=1.5)
self.ax.plot([0, v], [object_height, image_height], 'r--', lw=1.5, alpha=0.7)
# 光線2:通過光心,不發生偏折
self.ax.plot([-u, 25], [object_height, object_height], 'g-', lw=1.5)
self.ax.plot([0, v], [object_height, image_height], 'g--', lw=1.5, alpha=0.7)
# 光線3:【修正】從物體頂端指向右焦點到透鏡,然後平行射出
# 第一段:從物體頂端(-u, object_height)指向右焦點(f, 0),延伸到透鏡(0, y)
# 直線斜率 = (0 - object_height) / (f - (-u)) = -object_height / (f + u)
# 從物體到透鏡:y = object_height + 斜率 * (0 - (-u)) = object_height + 斜率 * u
lens_y = object_height - object_height * u / (f + u)
# 繪製:物體頂端 -> 透鏡(指向右焦點方向)
self.ax.plot([-u, 0], [object_height, lens_y], 'b-', lw=1.5)
# 從透鏡平行於主光軸射出
self.ax.plot([0, 25], [lens_y, lens_y], 'b-', lw=1.5)
# 反向延長線到虛像
self.ax.plot([0, v], [lens_y, image_height], 'b--', lw=1.5, alpha=0.7)
except Exception as e:
print(f"繪製光線錯誤: {str(e)}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
def update_display(self, event=None):
"""更新整個界面"""
try:
self.focal_length = self.f_value.get()
self.object_height = self.height_value.get()
u = self.u_value.get()
v, magnification, image_type = self.calculate_image()
# 更新信息顯示
info = f"物距 u = {u:.1f} cm\n"
info += f"焦距 f = {self.focal_length:.1f} cm\n"
if v is not None:
if not np.isinf(v):
info += f"像距 v = {v:.1f} cm\n"
else:
info += "像距 v = ∞\n"
if not np.isinf(magnification):
info += f"放大率 m = {magnification:.2f}\n"
else:
info += "放大率 m = ∞\n"
info += f"像類型:{image_type}"
# 改進的成像規律判斷 - 使用統一的容差值
tolerance = 0.05 # 合適的容差值
if abs(u - self.focal_length) < tolerance: # u ≈ f
info += "\n不成像"
elif u > 2*self.focal_length + tolerance:
info += "\n倒立縮小實像"
elif abs(u - 2*self.focal_length) < tolerance: # u ≈ 2f
info += "\n倒立等大實像"
elif u > self.focal_length + tolerance and u < 2*self.focal_length - tolerance:
info += "\n倒立放大實像"
elif u < self.focal_length - tolerance:
info += "\n正立放大虛像"
else:
# 邊界情況,根據image_type來判斷
if image_type == "不成像":
info += "\n不成像"
elif image_type == "實像":
if abs(magnification) > 1:
info += "\n倒立放大實像"
elif abs(magnification) < 1:
info += "\n倒立縮小實像"
else:
info += "\n倒立等大實像"
else: # 虛像
info += "\n正立放大虛像"
self.info_text.set(info)
# 重繪光學元件
self.draw_optical_elements(u, v)
self.canvas.draw()
except Exception as e:
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
self.info_text.set(f"更新錯誤: {str(e)}")
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = ConvexLensSimulator(root)
root.geometry("1200x700") # 增大窗口尺寸
root.mainloop()凹透鏡成像
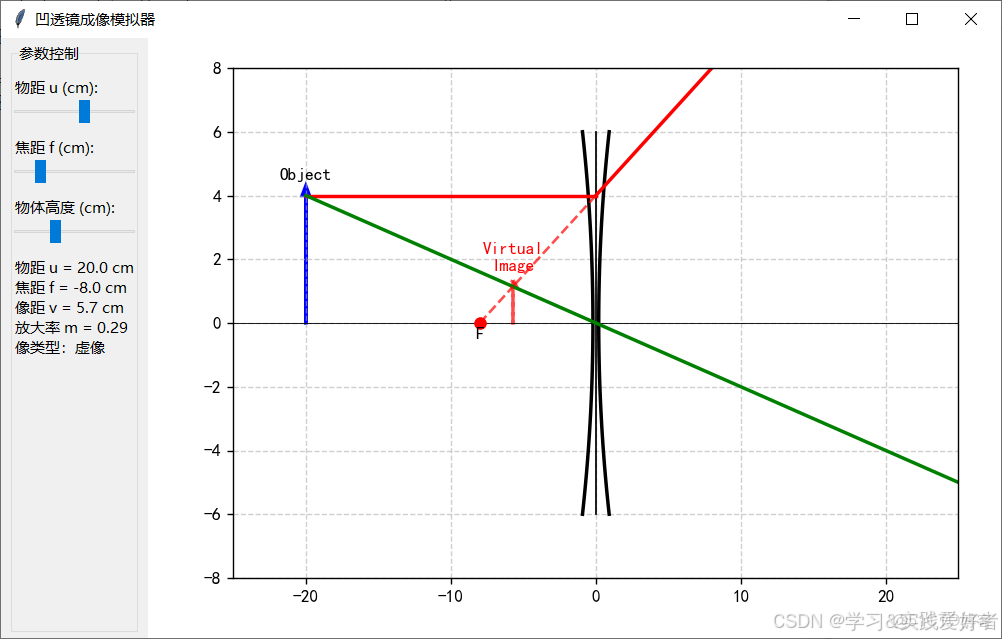
凹透鏡是指中間薄、邊緣厚的透鏡。它對光線有發散作用,即光線通過凹透鏡後會遠離主光軸方向偏折。
成像原理
凹透鏡成像也是基於光線的折射。光線通過凹透鏡時,由於透鏡的形狀,光線會被髮散。發散光線的反向延長線會交於一點,形成虛像。
凹透鏡成像規律:
• 物距 u > 0(任意正值)
• 像距 v < 0(負值,表示虛像)
• 焦距 f < 0(負值)
• 像的性質:正立、縮小、虛像
• 數學關係:f < v < 0,即 |v| < |f| < u
透鏡公式: 同樣適用 1/f = 1/u + 1/v (凹透鏡焦距 f 為負值,實物距 u 為正,虛像距 v 為負)。
應用
近視眼鏡:矯正近視眼時,利用凹透鏡的發散作用,使遠處物體的像成在視網膜上。
門鏡(貓眼):由凹透鏡和凸透鏡組合而成,凹透鏡在外,使室外物體成縮小虛像,便於室內觀察。
運行截圖:
源碼如下:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg import FigureCanvasTkAgg
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
# 配置中文字體
def find_chinese_font():
fonts = ['SimHei', 'Microsoft YaHei', 'SimSun', 'STSong', 'KaiTi']
existing_fonts = []
for f in fonts:
if any([f.lower() in font.lower() for font in fm.findSystemFonts(fontpaths=None)]):
existing_fonts.append(f)
return existing_fonts[0] if existing_fonts else None
chinese_font = find_chinese_font()
if chinese_font:
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = [chinese_font, 'sans-serif']
else:
print("警告: 找不到中文字體,將使用英文")
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 正確顯示負號
class ConcaveLensSimulator:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("凹透鏡成像模擬器")
# 物理常量
self.focal_length = 8 # 凹透鏡焦距為負,取絕對值,單位cm,滑塊顯示為正,內部轉換為負
self.object_height = 4 # 物體高度4cm
# 設置UI
self.setup_ui()
self.root.update() # 強制佈局更新,處理Matplotlib 區域顯示不完整
def setup_ui(self):
"""設置用户界面"""
self.main_frame = ttk.Frame(self.root)
self.main_frame.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
self.control_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(self.main_frame, text="參數控制")
self.control_frame.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10, pady=5, fill=tk.Y)
self.viz_frame = ttk.Frame(self.main_frame)
self.viz_frame.pack(side=tk.RIGHT, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
self.create_controls()
self.init_plot()
self.update_display()
def create_controls(self):
"""創建控制組件"""
# 物距滑塊
ttk.Label(self.control_frame, text="物距 u (cm):").grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="w", pady=(10, 0))
self.u_value = tk.DoubleVar(value=20)
self.u_slider = ttk.Scale(self.control_frame, from_=5, to=30,
variable=self.u_value,
command=lambda _: self.update_display())
self.u_slider.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky="ew")
# 焦距滑塊(顯示正值,內部取負值)
ttk.Label(self.control_frame, text="焦距 f (cm):").grid(row=2, column=0, sticky="w", pady=(10, 0))
self.f_value = tk.DoubleVar(value=self.focal_length)
self.f_slider = ttk.Scale(self.control_frame, from_=5, to=20,
variable=self.f_value,
command=lambda _: self.update_display())
self.f_slider.grid(row=3, column=0, sticky="ew")
# 物體高度滑塊
ttk.Label(self.control_frame, text="物體高度 (cm):").grid(row=4, column=0, sticky="w", pady=(10, 0))
self.height_value = tk.DoubleVar(value=self.object_height)
self.height_slider = ttk.Scale(self.control_frame, from_=1, to=10,
variable=self.height_value,
command=lambda _: self.update_display())
self.height_slider.grid(row=5, column=0, sticky="ew")
# 信息顯示
self.info_text = tk.StringVar()
ttk.Label(self.control_frame, textvariable=self.info_text, wraplength=200).grid(row=6, column=0, sticky="w", pady=10)
def init_plot(self):
"""初始化繪圖區域"""
self.fig = plt.Figure(figsize=(8, 6))
self.ax = self.fig.add_subplot(111)
self.ax.set_xlim(-25, 25)
self.ax.set_ylim(-8, 8)
self.ax.axhline(0, color='black', lw=0.5) # 主光軸
self.fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.1, right=0.95, top=0.95, bottom=0.1)
self.canvas = FigureCanvasTkAgg(self.fig, master=self.viz_frame)
self.canvas.get_tk_widget().pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
def calculate_image(self):
"""計算像的位置和性質, 凹透鏡焦距f為負"""
f = -abs(self.f_value.get()) # 確保焦距為負值
u = self.u_value.get()
# 成像公式 1/v = 1/f - 1/u
v = (u * f) / (u - f)
# 放大率 m = -v/u
magnification = -v / u # 由於v是負值,所以放大率為正(正立像),但小於1(縮小像)
image_type = "虛像" # 凹透鏡始終成虛像
return v, magnification, image_type
def draw_optical_elements(self, u, v):
self.ax.clear()
self.ax.set_xlim(-25, 25)
self.ax.set_ylim(-8, 8)
self.ax.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.6)
self.ax.axhline(0, color='black', lw=0.5) # 主光軸
f = -abs(self.f_value.get()) # 確保焦距為負值
# 保留焦點的紅色圓點
self.ax.plot([f, -abs(f)], [0, 0], 'ro', markersize=6)
#self.ax.text(f, -0.5, "F'", ha='center', fontsize=10)
self.ax.text(-abs(f), -0.5, "F", ha='center', fontsize=10)
self.draw_lens()
object_height = self.height_value.get()
# 保留物體箭頭
self.ax.arrow(-u, 0, 0, object_height, head_width=0.5, head_length=0.3,
fc='blue', ec='blue', lw=2)
self.ax.text(-u, object_height + 0.5, 'Object', fontsize=10, ha='center')
# 保留虛像箭頭
if v not in [np.inf, -np.inf] and v is not None:
magnification = -v / u
image_height = object_height * magnification
# 虛像用虛線箭頭
self.ax.arrow(v, 0, 0, image_height, head_width=0.5, head_length=0.2,
fc='red', ec='red', lw=2, linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)
self.ax.text(v, image_height + 0.5, 'Virtual\nImage', fontsize=10, ha='center', color='red')
self.draw_rays(u, v, object_height)
def draw_lens(self):
"""繪製凹透鏡 - 邊緣厚中間薄"""
# 凹透鏡的形狀 - 雙曲線
h = 6 # 透鏡高度
# 繪製兩條垂直邊線
self.ax.plot([0, 0], [-h, h], 'black', lw=1)
# 繪製透鏡的邊緣輪廓(雙曲線形狀)
t = np.linspace(-h, h, 100)
x_left = -0.2 - 0.02 * t**2 # 左側曲線
x_right = 0.2 + 0.02 * t**2 # 右側曲線
self.ax.plot(x_left, t, 'black', lw=2)
self.ax.plot(x_right, t, 'black', lw=2)
def draw_rays(self, u, v, object_height):
"""繪製凹透鏡成像光路 - 去掉箭頭符號版本"""
try:
f = -abs(self.f_value.get()) # 凹透鏡焦距為負值
left_focus = f # 左焦點位置
magnification = -v / u
image_height = object_height * magnification
# 光路1:平行於x軸的光線
# 從Object頂點平行射到透鏡中心線上的點(0, object_height)
self.ax.plot([-u, 0], [object_height, object_height], 'r-', lw=2)
# 折射後,反向延長線過左焦點,實際光線發散
slope1 = object_height / (-left_focus)
x_end = 25
y_end = object_height + slope1 * x_end
self.ax.plot([0, x_end], [object_height, y_end], 'r-', lw=2)
# 光路2:從Object頂點射向透鏡光心
self.ax.plot([-u, 0], [object_height, 0], 'g-', lw=2)
# 穿過光心後方向不變
slope2 = object_height / u
y_end2 = -slope2 * 25
self.ax.plot([0, 25], [0, y_end2], 'g-', lw=2)
# 繪製反向延長線的交點(虛像)
# 光路1的反向延長線
self.ax.plot([0, v], [object_height, image_height], 'r--', lw=1.5, alpha=0.7)
# 光路2的反向延長線
self.ax.plot([0, v], [0, image_height], 'g--', lw=1.5, alpha=0.7)
# 添加焦點和虛像點之間的紅虛線
self.ax.plot([left_focus, v], [0, image_height], 'r--', lw=1.5, alpha=0.7)
except Exception as e:
print(f"繪製光線錯誤: {str(e)}")
def update_display(self, event=None):
try:
self.focal_length = self.f_value.get()
self.object_height = self.height_value.get()
u = self.u_value.get()
v, magnification, image_type = self.calculate_image()
info = f"物距 u = {u:.1f} cm\n"
info += f"焦距 f = {-self.focal_length:.1f} cm\n" # 負值表示凹透鏡焦距
if v is not None:
if abs(v) != np.inf:
info += f"像距 v = {abs(v):.1f} cm\n"
else:
info += "像距 → ∞\n"
if abs(magnification) != np.inf:
info += f"放大率 m = {magnification:.2f}\n"
else:
info += "放大率 → ∞\n"
info += f"像類型:{image_type}"
self.info_text.set(info)
self.draw_optical_elements(u, v)
self.canvas.draw()
except Exception as e:
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
self.info_text.set(f"更新錯誤: {str(e)}")
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = ConcaveLensSimulator(root)
root.geometry("1000x600")
root.mainloop()