1、http緩存
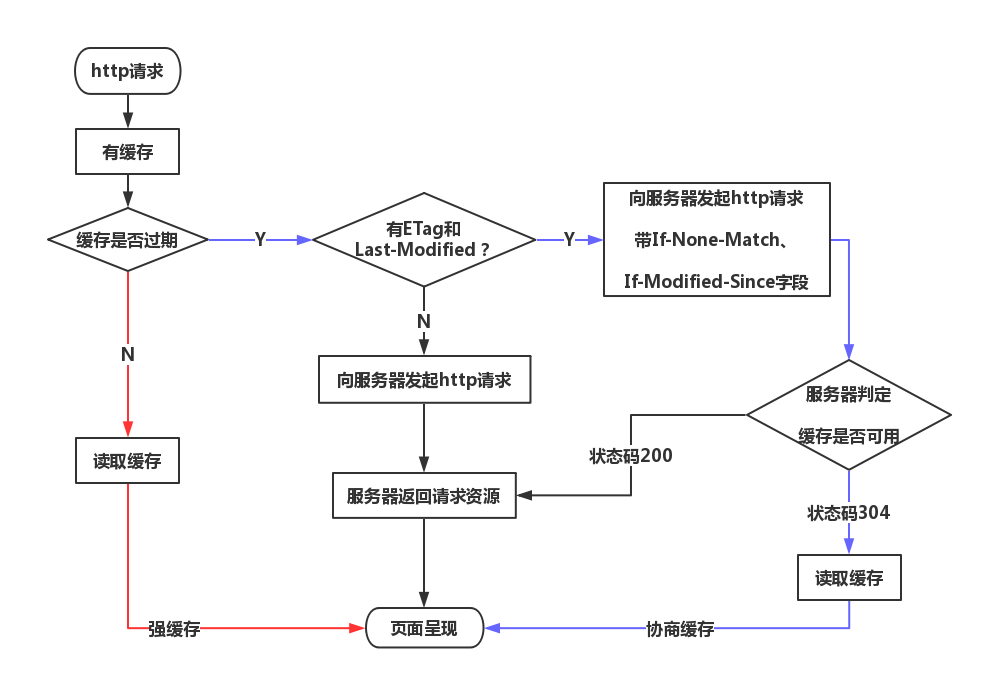
瀏覽器第一次向一個web服務器發起http請求後,服務器會返回請求的資源,並且在響應頭中添加一些有關緩存的字段如:Cache-Control、Expires、Last-Modified、ETag、Date等等。之後瀏覽器再向該服務器請求該資源就可以視情況使用強緩存和協商緩存。
- 強緩存:瀏覽器直接從本地緩存中獲取數據,不與服務器進行交互。
- 協商緩存:瀏覽器發送請求到服務器,服務器判定是否可使用本地緩存。
- 聯繫與區別:兩種緩存方式最終使用的都是本地緩存;前者無需與服務器交互,後者需要。
下面假定瀏覽器已經訪問了服務器,服務器返回了緩存相關的頭部字段且瀏覽器已對相關資源做好緩存。通過下圖來分析強緩存和協商緩存:
1.1、強緩存
強緩存由兩個http響應頭部字段控制,Expires和Cache-Control,其中Cache-Control的優先級比Expires高。
一、Cache-Control:
-
max-age(單位為s)指定設置緩存最大的有效時間,定義的是時間長短。當瀏覽器向服務器發送請求後,在max-age這段時間裏瀏覽器就不會再向服務器發送請求了。max-age>0表示在設置時間內請求直接從瀏覽器緩存中讀取,使用強緩存max-age<=0表示請求到服務器,服務器需要判斷文件是否已更新,進而返回200還是304
-
no-cache:設置了no-cache之後並不代表瀏覽器不緩存,而是在緩存前要向服務器確認資源是否被更改。Cache-Control: no-cache, max-age=2000表示在2000秒內使用強緩存,超過2000秒使用協商緩存
no-store:禁用緩存。public:表明其他用户也可使用緩存,適用於公共緩存服務器的情況。如果沒有指定public還是private,則默認為public。
private:表明只有特定用户才能使用緩存,適用於公共緩存服務器的情況。
s-maxage:適用於多用户使用的公共緩存服務器,比如CDN。比如,當s-maxage=60時,在這60秒中,即使更新了CDN的內容,瀏覽器也不會進行請求。也就是説max-age用於普通緩存,而s-maxage用於代理緩存。如果存在s-maxage,則會覆蓋掉max-age和Expires header。
二、Expires:
緩存過期時間,用來指定資源到期的時間,是服務器端的具體的時間點。也就是説,Expires=max-age + 請求時間,需要和Last-modified結合使用。但在上面我們提到過,cache-control的優先級更高。 Expires是Web服務器響應消息頭字段,在響應http請求時告訴瀏覽器在過期時間前瀏覽器可以直接從瀏覽器緩存取數據,而無需再次請求。
1.2、協商緩存
當瀏覽器發現緩存過期後,緩存並不一定不能使用了,因為服務器端的資源可能仍然沒有改變,所以需要與服務器協商,讓服務器判斷本地緩存是否還能使用。
當第一次請求響應頭中有ETag或Last-Modified字段,那麼第二次請求的請求頭中就會攜帶If-None-Match和If-Modified-Since字段,服務器收到請求後會判斷ETag與If-None-Match以及Last-Modified與If-Modified-Since是否一致,如果一致就表示請求資源沒有被修改,服務器返回304狀態碼,使用瀏覽器緩存資源。如果不一致,則服務器處理請求,返回新資源,狀態碼為200。
一、ETag和If-None-Match
二者的值都是服務器為每份資源分配的唯一標識字符串,相當於hash。
- 瀏覽器請求資源,服務器會在響應報文頭中加入
ETag字段。資源更新時,服務器端的ETag值也隨之更新; - 瀏覽器再次請求資源時,會在請求報文頭中添加
If-None-Match字段,它的值就是上次響應報文中的ETag的值; - 服務器會比對
ETag與If-None-Match的值是否一致,如果不一致,服務器則接受請求,返回更新後的資源;如果一致,表明資源未更新,則返回狀態碼為304的響應,可繼續使用本地緩存,要注意的是,此時響應頭會加上ETag字段,即使它沒有變化。
二、Last-Modified和If-Modified-Since
二者的值都是GMT格式的時間字符串。
- 瀏覽器第一次向服務器請求資源後,服務器會在響應頭中加上
Last-Modified字段,表明該資源最後一次的修改時間; - 瀏覽器再次請求該資源時,會在請求報文頭中添加
If-Modified-Since字段,它的值就是上次服務器響應報文中的Last-Modified的值; - 服務器會比對
Last-Modified與If-Modified-Since的值是否一致,如果不一致,服務器則接受請求,返回更新後的資源;如果一致,表明資源未更新,則返回狀態碼為304的響應,可繼續使用本地緩存,與ETag不同的是:此時響應頭中不會再添加Last-Modified字段。
三、ETag較之Last-Modified的優勢
以下內容引用於:http協商緩存VS強緩存
你可能會覺得使用Last-Modified已經足以讓瀏覽器知道本地的緩存副本是否足夠新,為什麼還需要ETag呢?HTTP1.1中ETag的出現主要是為了解決幾個Last-Modified比較難解決的問題:
- 一些文件也許會週期性的更改,但是他的內容並不改變(僅僅改變的修改時間),這個時候我們並不希望客户端認為這個文件被修改了,而重新
GET; - 某些文件修改非常頻繁,比如在秒以下的時間內進行修改,(比方説1s內修改了N次),
If-Modified-Since能檢查到的粒度是s級的,這種修改無法判斷(或者説UNIX記錄MTIME只能精確到秒); - 某些服務器不能精確的得到文件的最後修改時間。
這時,利用ETag能夠更加準確的控制緩存,因為ETag是服務器自動生成的資源在服務器端的唯一標識符,資源每次變動,都會生成新的ETag值。Last-Modified與ETag是可以一起使用的,但服務器會優先驗證ETag。
2、tomcat服務的靜態資源緩存機制
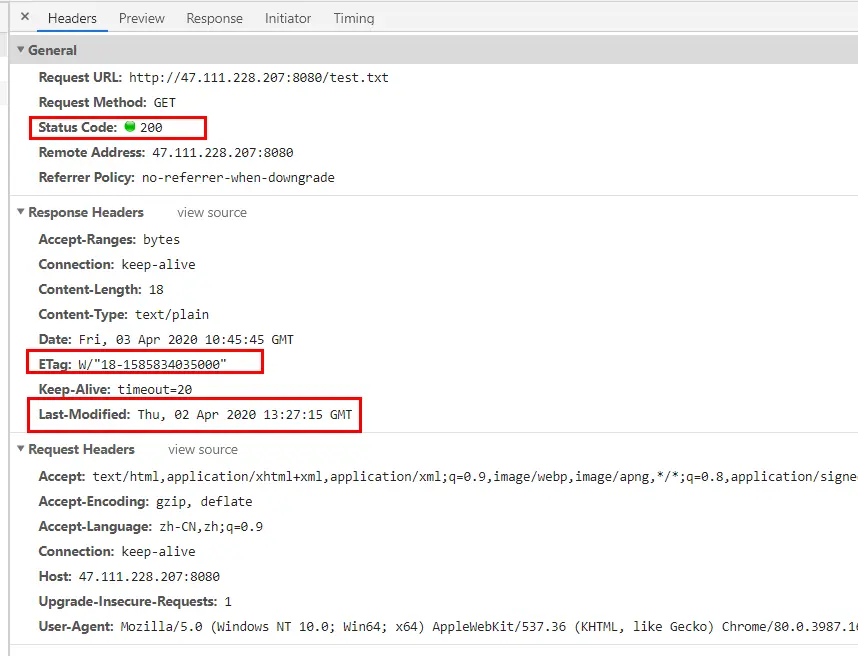
先舉一個例子,先在linux服務器上安裝tomcat,然後上傳一個文件到服務器導航,向服務器請求這個靜態資源
刷新再次請求
我們並沒有配置響應頭ETag和Last-Modified,為什麼會進行協商緩存呢?我們來查看一下tomcat源碼如何處理http緩存的,在servlet-api.jar包中有一個HttpServlet.class字節碼文件,我們用idea打開可以看到反編譯後的源碼。
HttpServlet的功能
HttpServlet 首先必須讀取Http請求的內容。Servlet容器負責創建HttpServlet對象,並把Http請求直接封裝到HttpServlet對象中,大大簡化了HttpServlet解析請求數據的工作量。HttpServlet容器響應Web客户請求流程如下:
Web客户向Servlet容器發出Http請求;Servlet容器解析Web客户的Http請求;Servlet容器創建一個HttpRequest對象,在這個對象中封裝Http請求信息;Servlet容器創建一個HttpResponse對象;Servlet容器調用HttpServlet的service方法,把HttpRequest和HttpResponse對象作為service方法的參數傳給HttpServlet對象;HttpServlet調用HttpRequest的有關方法,獲取HTTP請求信息;HttpServlet調用HttpResponse的有關方法,生成響應數據;Servlet容器把HttpServlet的響應結果傳給Web客户。
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package javax.servlet.http;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import javax.servlet.DispatcherType;
import javax.servlet.GenericServlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private static final String METHOD_DELETE = "DELETE";
private static final String METHOD_HEAD = "HEAD";
private static final String METHOD_GET = "GET";
private static final String METHOD_OPTIONS = "OPTIONS";
private static final String METHOD_POST = "POST";
private static final String METHOD_PUT = "PUT";
private static final String METHOD_TRACE = "TRACE";
private static final String HEADER_IFMODSINCE = "If-Modified-Since";
private static final String HEADER_LASTMOD = "Last-Modified";
private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings";
private static final ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings");
public HttpServlet() {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_get_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
protected long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest req) {
return -1L;
}
protected void doHead(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
if (DispatcherType.INCLUDE.equals(req.getDispatcherType())) {
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
NoBodyResponse response = new NoBodyResponse(resp);
this.doGet(req, response);
response.setContentLength();
}
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_post_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
protected void doPut(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_put_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
protected void doDelete(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_delete_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(405, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(400, msg);
}
}
private static Method[] getAllDeclaredMethods(Class<?> c) {
if (c.equals(HttpServlet.class)) {
return null;
} else {
Method[] parentMethods = getAllDeclaredMethods(c.getSuperclass());
Method[] thisMethods = c.getDeclaredMethods();
if (parentMethods != null && parentMethods.length > 0) {
Method[] allMethods = new Method[parentMethods.length + thisMethods.length];
System.arraycopy(parentMethods, 0, allMethods, 0, parentMethods.length);
System.arraycopy(thisMethods, 0, allMethods, parentMethods.length, thisMethods.length);
thisMethods = allMethods;
}
return thisMethods;
}
}
protected void doOptions(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
Method[] methods = getAllDeclaredMethods(this.getClass());
boolean ALLOW_GET = false;
boolean ALLOW_HEAD = false;
boolean ALLOW_POST = false;
boolean ALLOW_PUT = false;
boolean ALLOW_DELETE = false;
boolean ALLOW_TRACE = true;
boolean ALLOW_OPTIONS = true;
Class clazz = null;
try {
clazz = Class.forName("org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade");
Method getAllowTrace = clazz.getMethod("getAllowTrace", (Class[])null);
ALLOW_TRACE = (Boolean)getAllowTrace.invoke(req, (Object[])null);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | SecurityException | IllegalAccessException | IllegalArgumentException | InvocationTargetException | ClassNotFoundException var14) {
}
for(int i = 0; i < methods.length; ++i) {
Method m = methods[i];
if (m.getName().equals("doGet")) {
ALLOW_GET = true;
ALLOW_HEAD = true;
}
if (m.getName().equals("doPost")) {
ALLOW_POST = true;
}
if (m.getName().equals("doPut")) {
ALLOW_PUT = true;
}
if (m.getName().equals("doDelete")) {
ALLOW_DELETE = true;
}
}
String allow = null;
if (ALLOW_GET) {
allow = "GET";
}
if (ALLOW_HEAD) {
if (allow == null) {
allow = "HEAD";
} else {
allow = allow + ", HEAD";
}
}
if (ALLOW_POST) {
if (allow == null) {
allow = "POST";
} else {
allow = allow + ", POST";
}
}
if (ALLOW_PUT) {
if (allow == null) {
allow = "PUT";
} else {
allow = allow + ", PUT";
}
}
if (ALLOW_DELETE) {
if (allow == null) {
allow = "DELETE";
} else {
allow = allow + ", DELETE";
}
}
if (ALLOW_TRACE) {
if (allow == null) {
allow = "TRACE";
} else {
allow = allow + ", TRACE";
}
}
if (ALLOW_OPTIONS) {
if (allow == null) {
allow = "OPTIONS";
} else {
allow = allow + ", OPTIONS";
}
}
resp.setHeader("Allow", allow);
}
protected void doTrace(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String CRLF = "\r\n";
StringBuilder buffer = (new StringBuilder("TRACE ")).append(req.getRequestURI()).append(" ").append(req.getProtocol());
Enumeration reqHeaderEnum = req.getHeaderNames();
while(reqHeaderEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String headerName = (String)reqHeaderEnum.nextElement();
buffer.append(CRLF).append(headerName).append(": ").append(req.getHeader(headerName));
}
buffer.append(CRLF);
int responseLength = buffer.length();
resp.setContentType("message/http");
resp.setContentLength(responseLength);
ServletOutputStream out = resp.getOutputStream();
out.print(buffer.toString());
out.close();
}
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
long lastModified;
if (method.equals("GET")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1L) {
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException var9) {
ifModifiedSince = -1L;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified / 1000L * 1000L) {
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(304);
}
}
} else if (method.equals("HEAD")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("POST")) {
this.doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("PUT")) {
this.doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("DELETE")) {
this.doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("OPTIONS")) {
this.doOptions(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("TRACE")) {
this.doTrace(req, resp);
} else {
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method};
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(501, errMsg);
}
}
private void maybeSetLastModified(HttpServletResponse resp, long lastModified) {
if (!resp.containsHeader("Last-Modified")) {
if (lastModified >= 0L) {
resp.setDateHeader("Last-Modified", lastModified);
}
}
}
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
try {
request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
response = (HttpServletResponse)res;
} catch (ClassCastException var6) {
throw new ServletException(lStrings.getString("http.non_http"));
}
this.service(request, response);
}
}
可以看到在調用service方法時會處理GET請求(靜態資源都是通過get請求),調用getLastModified來獲取響應內容最後修改時間,service方法可以根據這個返回值在響應消息中自動生成Last-Modified頭字段,所以在向tomcat服務器請求靜態資源時會使用協商緩存。這裏解釋一下為什麼HttpServlet類中getLastModified方法返回-1呢?其實,在HttpServlet子類中可以對這個方法進行覆蓋,以便返回一個代表當前輸出的響應內容的修改時間。參考:https://blog.csdn.net/andydev...
3、客户端處理緩存
其實,在很多業務中都有不需要使用緩存的情況,主要因為緩存會導致資源不是最新的,比如在html頁面中使用script引入第三方插件。在客户端常有以下幾種處理方式:
3.1、使用meta標籤中http-equiv
<meta http-equiv="Cache-Control" content="no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate" />
<meta http-equiv="Pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />3.2、在請求url加上版本號
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./reverse.css?v=2019060301">
<script src="./reverse.js?v=2019060301"></script>3.3、webpack打包後文件帶上hsah
entry: {
main: path.join(__dirname, './main.js'),
vendor: ['react', 'antd']
},
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname,'./dist'),
publicPath: '/dist/',
filname: 'bundle.[chunkhash].js'
}webpack給我們提供了三種哈希值計算方式,分別是hash、chunkhash和contenthash。那麼這三者有什麼區別呢?
hash:跟整個項目的構建相關,構建生成的文件hash值都是一樣的,只要項目裏有文件更改,整個項目構建的hash值都會更改。chunkhash:根據不同的入口文件(Entry)進行依賴文件解析、構建對應的chunk,生成對應的hash值。contenthash:由文件內容產生的hash值,內容不同產生的contenthash值也不一樣。
顯然,我們是不會使用第一種的。改了一個文件,打包之後,其他文件的hash都變了,緩存自然都失效了。這不是我們想要的。
那chunkhash和contenthash的主要應用場景是什麼呢?在實際在項目中,我們一般會把項目中的css都抽離出對應的css文件來加以引用。如果我們使用chunkhash,當我們改了css代碼之後,會發現css文件hash值改變的同時,js文件的hash值也會改變。這時候,contenthash就派上用場了。
參考:
https://juejin.im/entry/56f0e...
https://segmentfault.com/a/11...
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_2995...
https://www.xp.cn/c.php/28750...
https://blog.csdn.net/andydev...
https://juejin.im/post/5c136b...