最新文檔已同步至 : https://book.iamtsm.cn
簡介
tl-ops-manage (tl-openresty-web-manage),基於openresty開發的一款基礎服務管理工具,支持服務動態擴展,自定義路由規則,健康檢查,服務熔斷,服務限流,動態配置,數據統計,日誌記錄,數據版本控制,後台可視化管理,等等...
做這個項目最開始的想法很簡單,只是想在造輪子的過程中瞭解,學習一些新的知識面。到後面完成了大部分基礎功能點後,發現可以整理為一個服務管理工具的項目。於是就有了tl-ops-manage
實現源碼解析
tl-ops-manage-源碼實現解析文檔
體驗demo
安裝
下載項目 : https://github.com/iamtsm/tl-...
或者
git clone https://github.com/iamtsm/tl-...
安裝依賴
首先需要安裝openresty,可以去官網下載對應包, http://openresty.org/cn/downl...
如果需要將數據同步至redis存儲,需要安裝redis,https://redis.io/download/, redis啓用開關在tl_ops_manage_env.lua中
修改配置
tl-ops-manage/conf/tl_ops_manage.conf
location /tlopsmanage/ {
# 管理後台目錄
alias /path/to/tl-ops-manage/web/;
}openresty/conf/nginx.conf
http {
...
# 引入tl_ops_manage.conf
include "/path/to/tl-ops-manage/conf/*.conf;
# 引入lua包
lua_package_path "/path/to/tl-ops-manage/?.lua;;"
...
}tl-ops-manage/tl_ops_manage_env.conf
# 日誌輸出目錄
log_dir = "/path/to/tl-ops-manage/",
# 數據存放目錄
store_dir = "/path/to/tl-ops-manage/store/",啓動nginx/openresty
訪問 http://your-domain/tlopsmanag... 管理後台
以下模塊,將以兩種方式進行説明,一種是在配置文件中填寫配置,另外一種是在管理台填寫配置。
在文件中設置的節點會在啓動時即可生效,在管理後台設置的節點,將會在各模塊依賴的時候同步到其中(稍延時,但最終一致)。
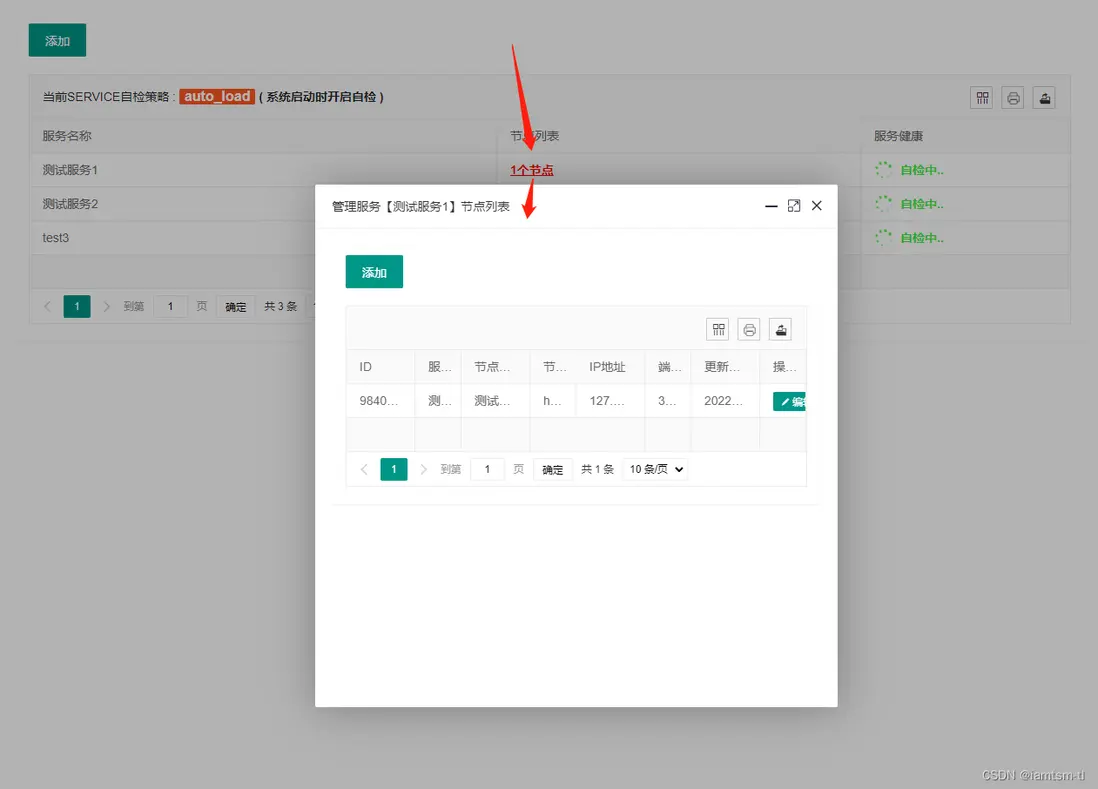
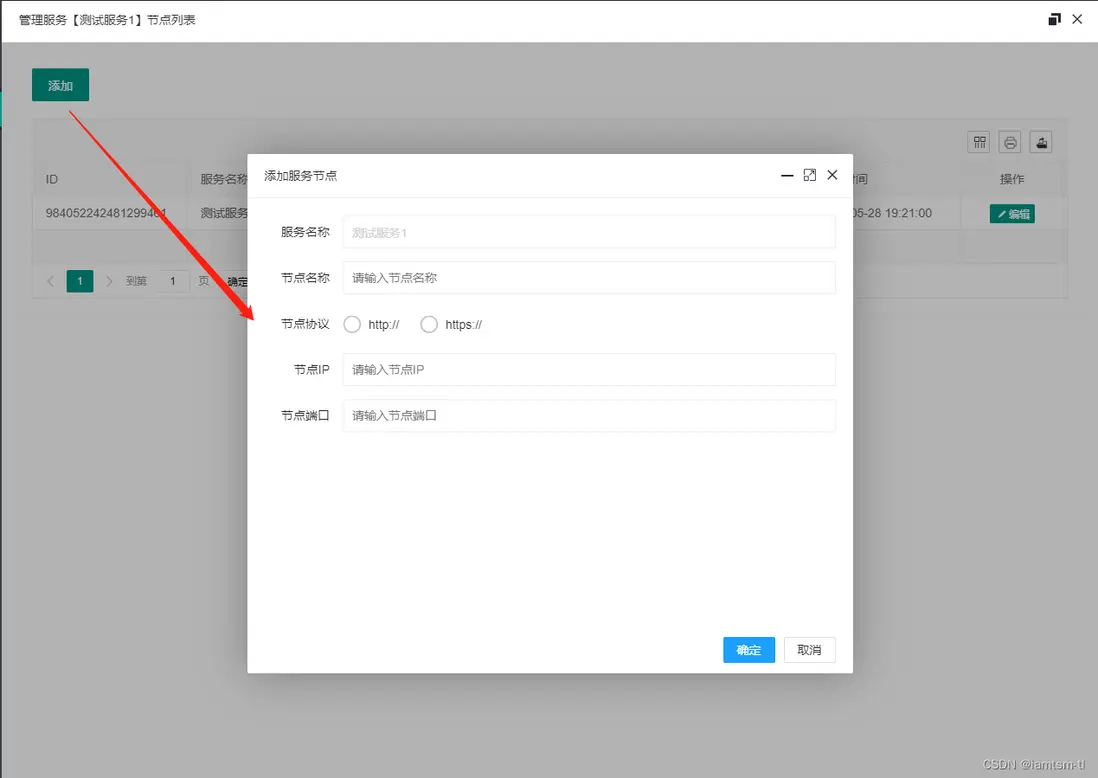
服務節點
服務節點是基礎配置,添加好的節點會被用於健康檢查,節點限流,熔斷降級,路由統計,負載均衡等模塊。節點的基礎數據可以在文件中設置好,或也可以在管理後台中設置。
在文件中配置
配置節點數據對應的文件在 constant/tl_ops_constant_service.lua,在文件中,我提供了demo示例數據,只需要按照對應的格式放入 list 中即可,需要配置多少個,放置多少個即刻。
list = {
{
id = snowflake.generate_id( 100 ), -- default snow id
name = "節點1", -- 當前節點name
service = "測試服務", -- 當前節點所屬service
protocol = "http://", -- 當前節點協議頭
ip = "127.0.0.1", -- 當前節點ip
port = 6666, -- 當前節點port
},
{
id = snowflake.generate_id( 100 ),
name = "節點2",
service = "測試服務",
protocol = "http://",
ip = "127.0.0.1",
port = 6667,
}
....
}在管理台配置
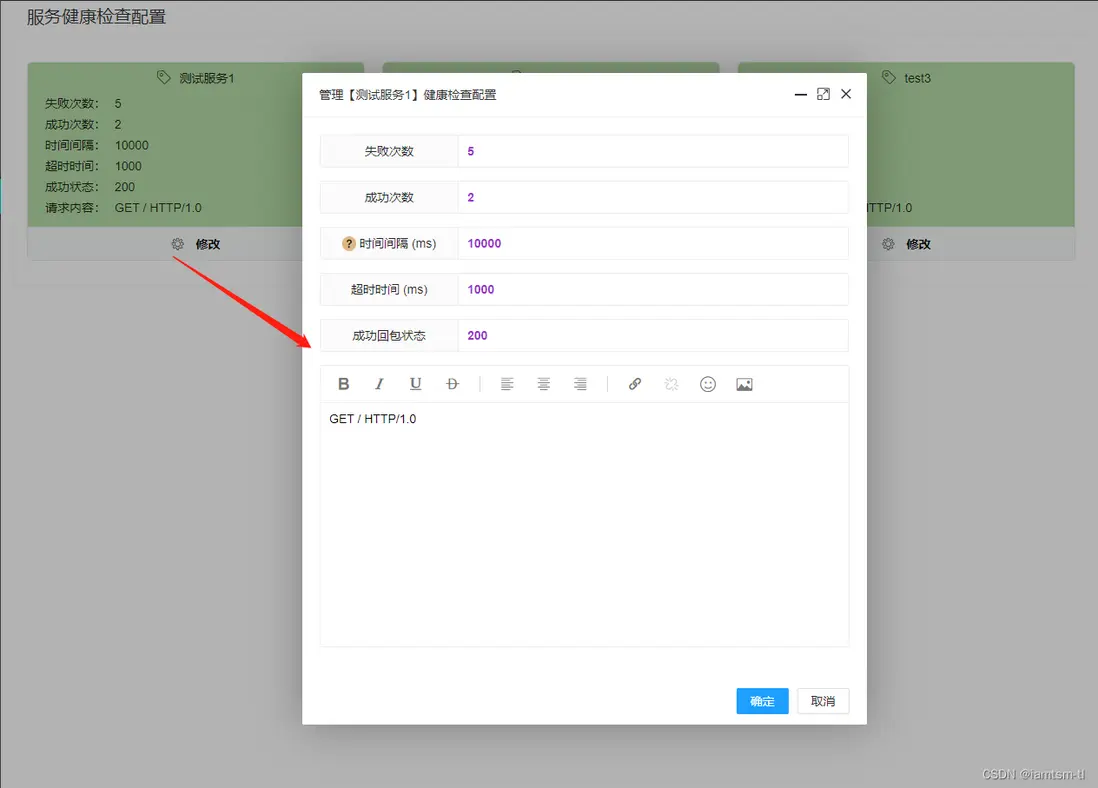
健康檢查
健康檢查依賴設置好的節點,對節點依次進行發包檢查節點狀態,在健康檢查中,如檢查間隔,發包超時時間,週期內請求成功多少次算正常服務狀態,週期內請求失敗多少次才需要轉變服務狀態,接收服務回包時什麼狀態才算成功,等等... ,這些需要數據根據每個服務的不同,可以做到配置化,並實時更新。
在文件中配置
配置節點數據對應的文件在 constant/tl_ops_constant_health.lua,在文件中,我提供了demo示例數據,只需要按照對應的格式放入 options 中即可,需要配置多少個,放置多少個即刻。
options = {
{
check_failed_max_count = 5, -- 自檢週期內失敗次數
check_success_max_count = 2, -- 自檢週期內成功次數
check_interval = 10 * 1000, -- 自檢服務自檢週期 (單位/ms)
check_timeout = 1000, -- 自檢節點心跳包連接超時時間 (單位/ms)
check_content = "GET / HTTP/1.0", -- 自檢心跳包內容
check_success_status = { -- 自檢返回成功狀態, 如 201,202(代表成功)
200
},
check_service_name = "測試服務1" -- 該配置所屬服務
},
{
check_failed_max_count = 5,
check_success_max_count = 2,
check_interval = 10 * 1000
check_timeout = 1000,
check_content = "GET / HTTP/1.0",
check_success_status = {
200
},
check_service_name = "測試服務2"
}
}在管理台配置
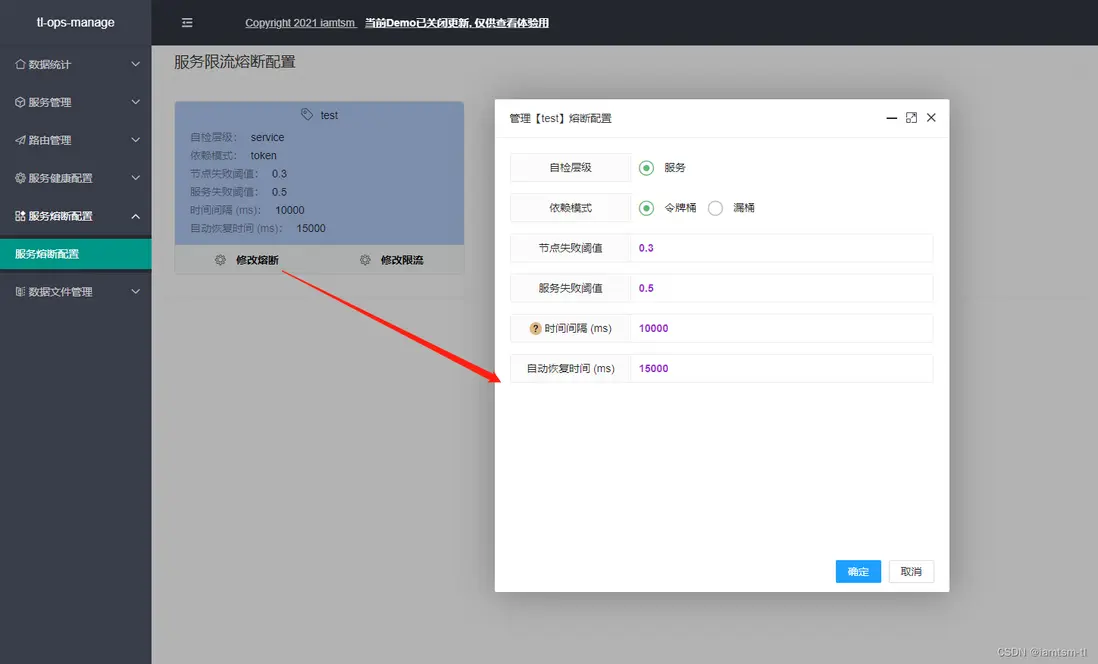
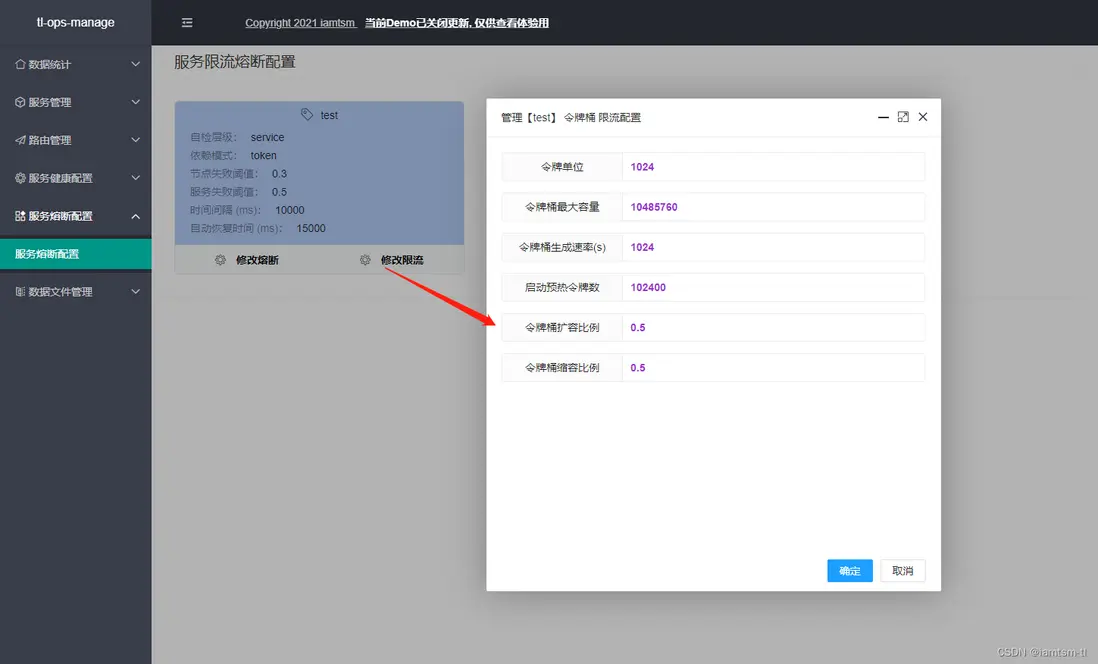
熔斷限流
熔斷限流,其實是自動化熔斷,限流兩種配置的組合。對於服務自動化熔斷來説,其應該是根據節點 ‘狀態’ 來進行一種服務降級的手段。在節點負載過高時,應該對節點減少流量的進入,在服務性能較優時,增加流量的進入,而控制流量的進入就需要用到一些流控手段。所以我將其組合來配置
在文件中配置
熔斷配置
options = {
{
service_name = "測試服務1", -- 該配置所屬服務
interval = 10 * 1000, -- 檢測時間間隔 單位/ms
node_threshold = 0.3, -- 切換狀態閾值 (node失敗佔比)
service_threshold = 0.5, -- 切換狀態閾值 (service切換閾值,取決於node失敗狀態佔比)
recover = 15 * 1000, -- 全熔斷恢復時間 單位/ms
depend = depend.token, -- 默認依賴組件 :token_bucket
level = level.service, -- 默認組件級別,服務層級 [限流熔斷針對的層級]
},
....
},
-- 依賴限流組件
local depend = {
token = "token",
leak = "leak"
}
-- 組件級別
local level = {
service = "service"
}令牌桶限流配置
-- 限流配置
options = {
service_name = "測試服務1", -- 令牌桶配置所屬服務
capacity = 10 * 1024 * 1024, -- 最大容量 10M (按字節為單位,可做字節整型流控)
rate = 1024, -- 令牌生成速率/秒 (每秒 1KB)
warm = 100 * 1024, -- 預熱令牌數量 (預熱100KB)
block = 1024, -- 流控以1024為單位
expand = 0.5, -- 擴容比例
shrink = 0.5, -- 縮容比例
}
漏桶限流配置
-- 限流配置
options = {
service_name = "測試服務1", -- 漏桶配置所屬服務
capacity = 10 * 1024 * 1024, -- 最大容量 10M (按字節為單位,可做字節整型流控)
rate = 1024 * 10, -- 漏桶流速/秒 (每秒 10KB)
block = 1024, -- 流控以1024為單位
expand = 0.5, -- 擴容比例
shrink = 0.5, -- 縮容比例
}
在管理台配置
熔斷配置
限流配置
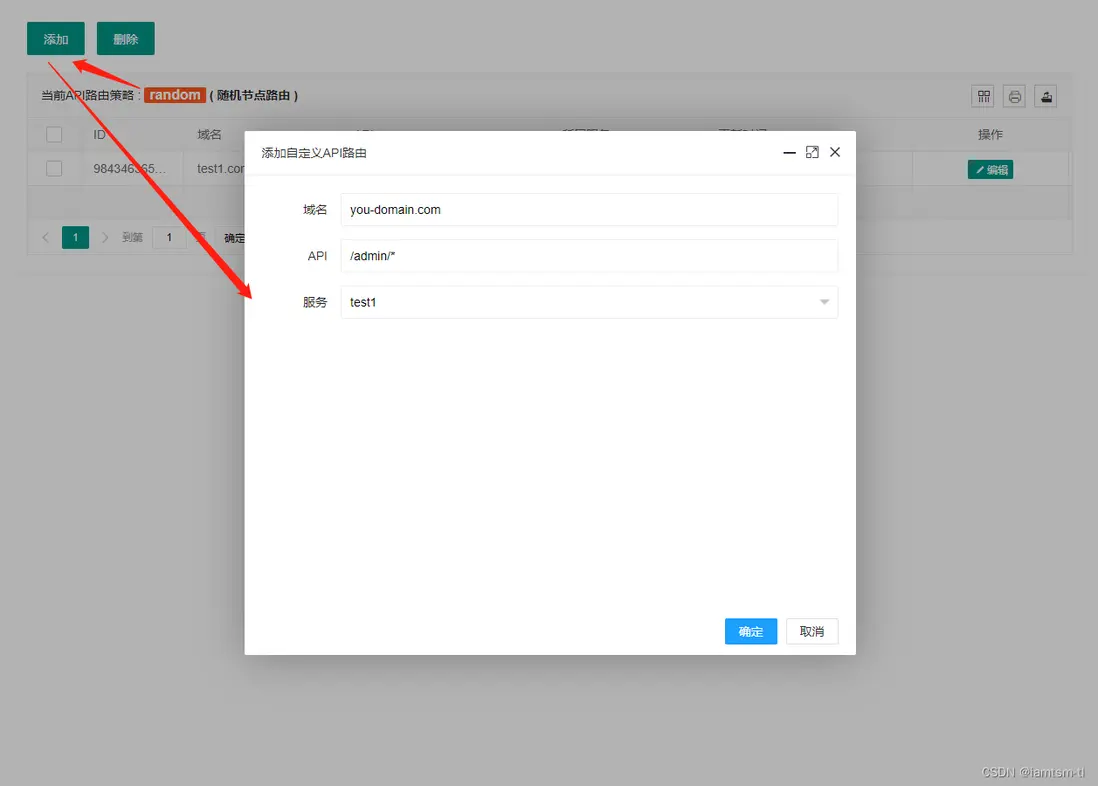
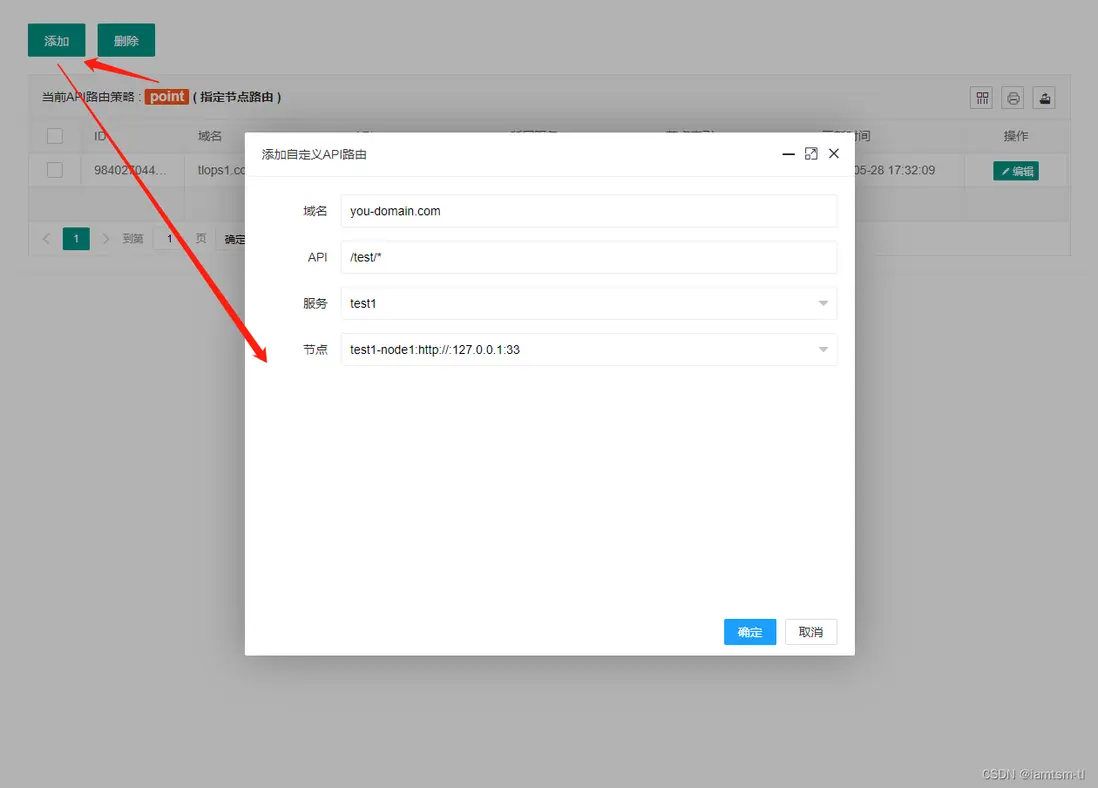
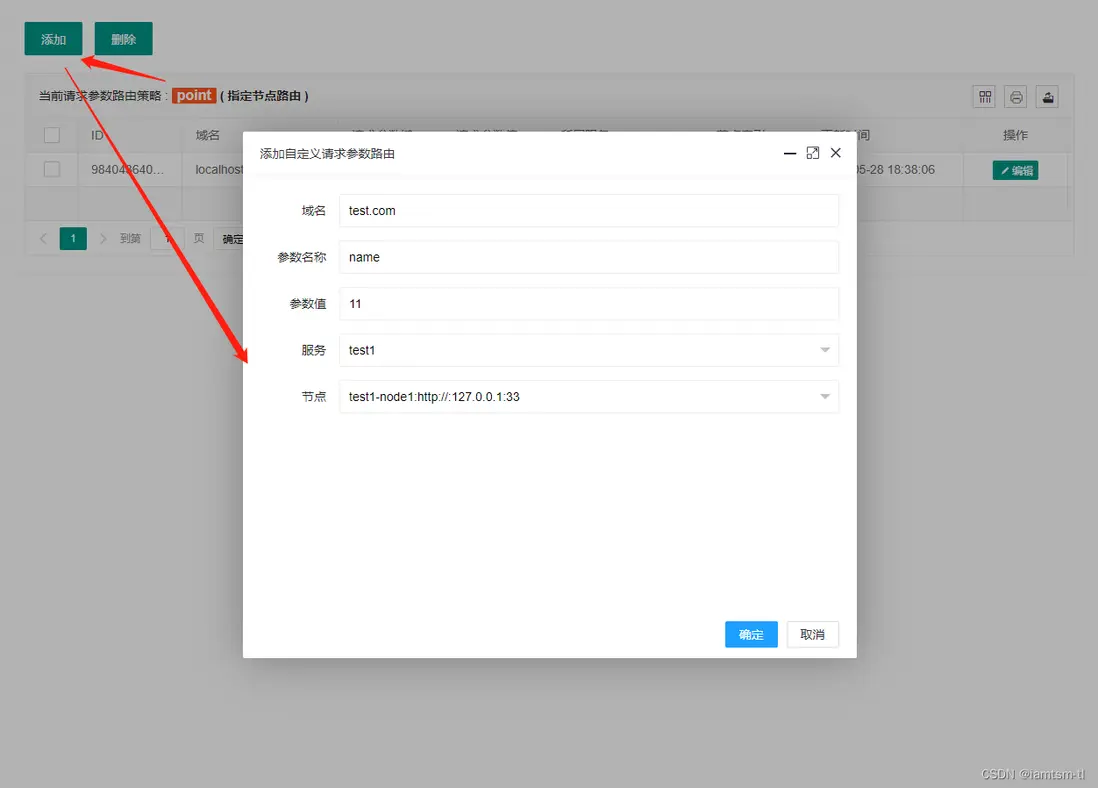
負載均衡
對於負載均衡,目前分為四個負載策略,在負載時,會按照這個順序進行負載,URL負載 > 請求參數負載 > 請求COOKIE負載 > 請求頭負載
而每個策略分為兩種模式 指定路由,隨機路由。
對於指定路由,一旦請求命中三個模式中的任意一條規則,即會路由到具體節點。
對於隨機路由,一旦請求命中三個模式中的任意一條規則,不會路由到具體節點,而是在命中的服務中隨機選取一個節點進行路由。
對於模式的不同,每個隨機方式也是不相同,對於URL隨機負載,隨機模式是根據當前請求url的長度設置隨機種子,得到隨機數進行隨機負載。對於請求參數和請求COOKIE的隨機負載,是根據當前命中的key的長度設置隨機種子,得到隨機數進行隨機負載。
在文件中的配置
API策略
point = {
{
id = snowflake.generate_id( 100 ), -- default snow id
url = "/*", -- 當前url匹配規則
service = "測試服務1", -- 當前url路由到的service
node = 0, -- 當前url路由到的service下的node的索引
host = "tlops1.com", -- 當前url處理的域名範圍
}
},
random = {
{
id = snowflake.generate_id( 100 ), -- default snow id
url = "/*", -- 當前url匹配規則
service = "測試服務1", -- 當前url路由到的service
node = 0, -- 當前url路由到的service下的node的索引
host = "tlops1.com", -- 當前url處理的域名範圍
}
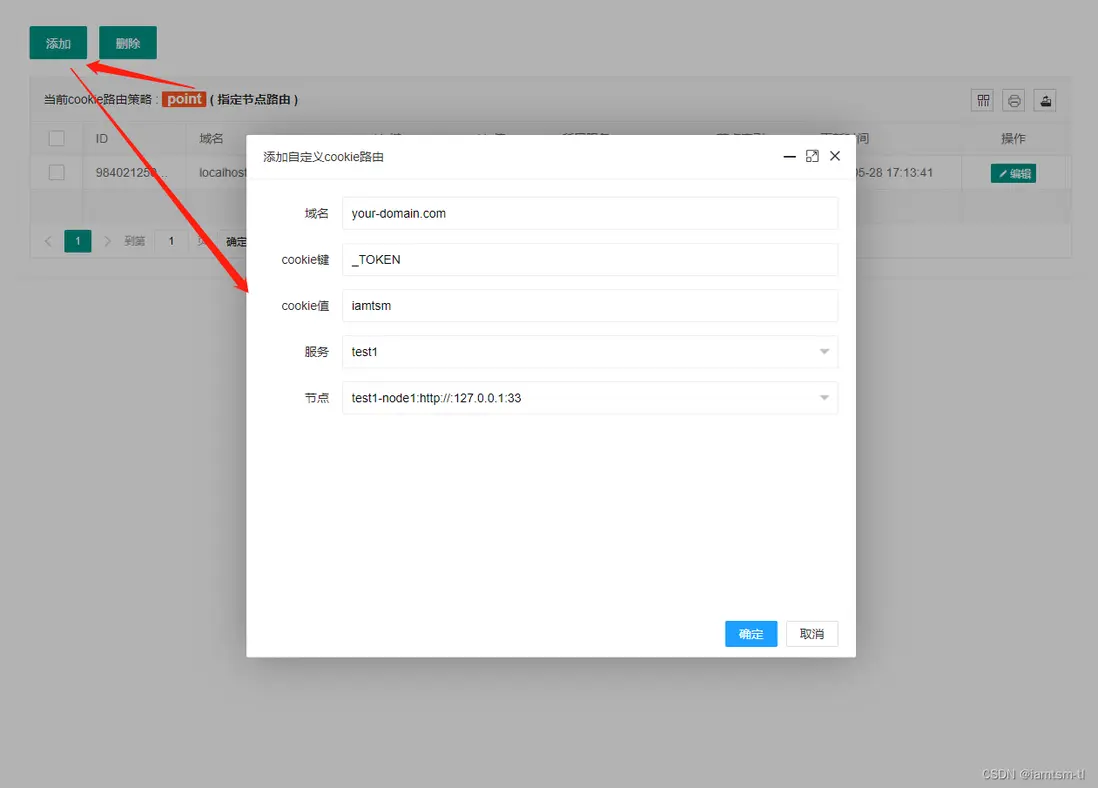
},cookie策略
point = {
{
id = snowflake.generate_id( 100 ), -- default snow id
key = "_tl_session_id", -- 當前cookie匹配名稱
value = "session_iamtsm", -- 當前cookie名稱對應值
service = "測試服務1", -- 當前cookie路由到的service
node = 0, -- 當前cookie路由到的service下的node的索引
host = "tlops1.com", -- 當前cookie處理的域名範圍
}
},
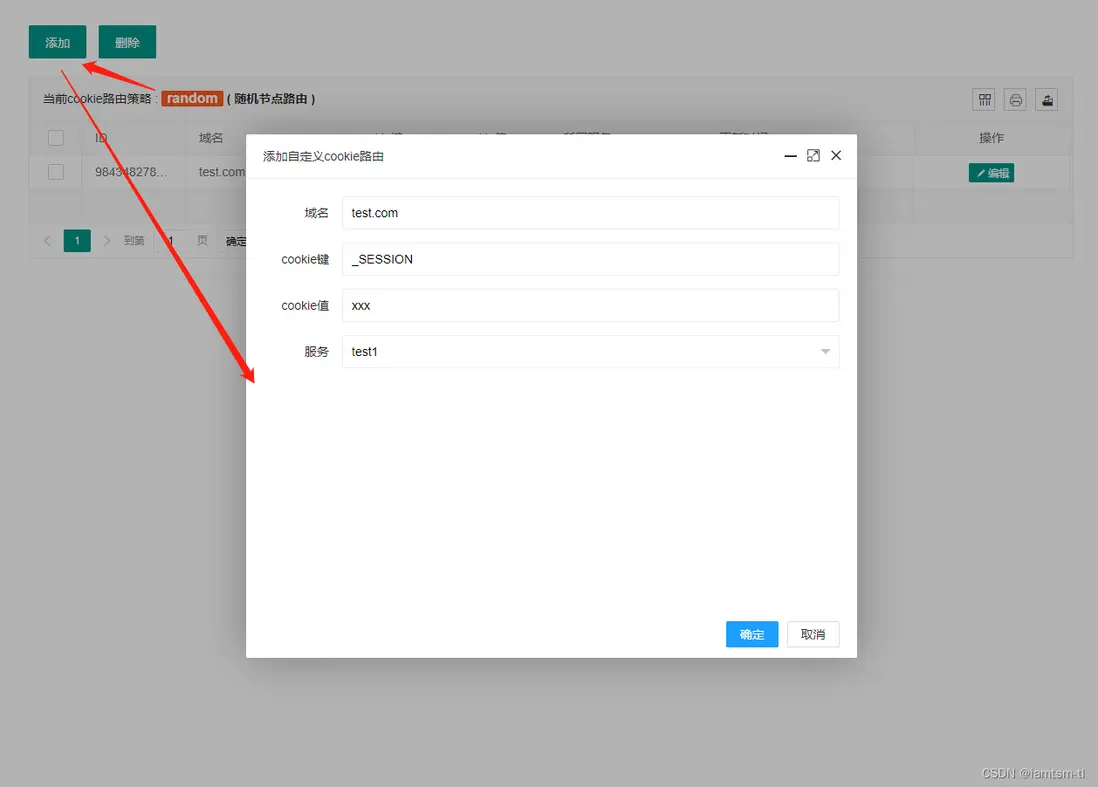
random = {
{
id = snowflake.generate_id( 100 ), -- default snow id
key = "_tl_token_id", -- 當前cookie匹配名稱
value = "token_iamtsm", -- 當前cookie名稱對應值
service = "測試服務1", -- 當前cookie路由到的service
node = 0, -- 當前cookie路由到的service下的node的索引
host = "tlops1.com", -- 當前cookie處理的域名範圍
}
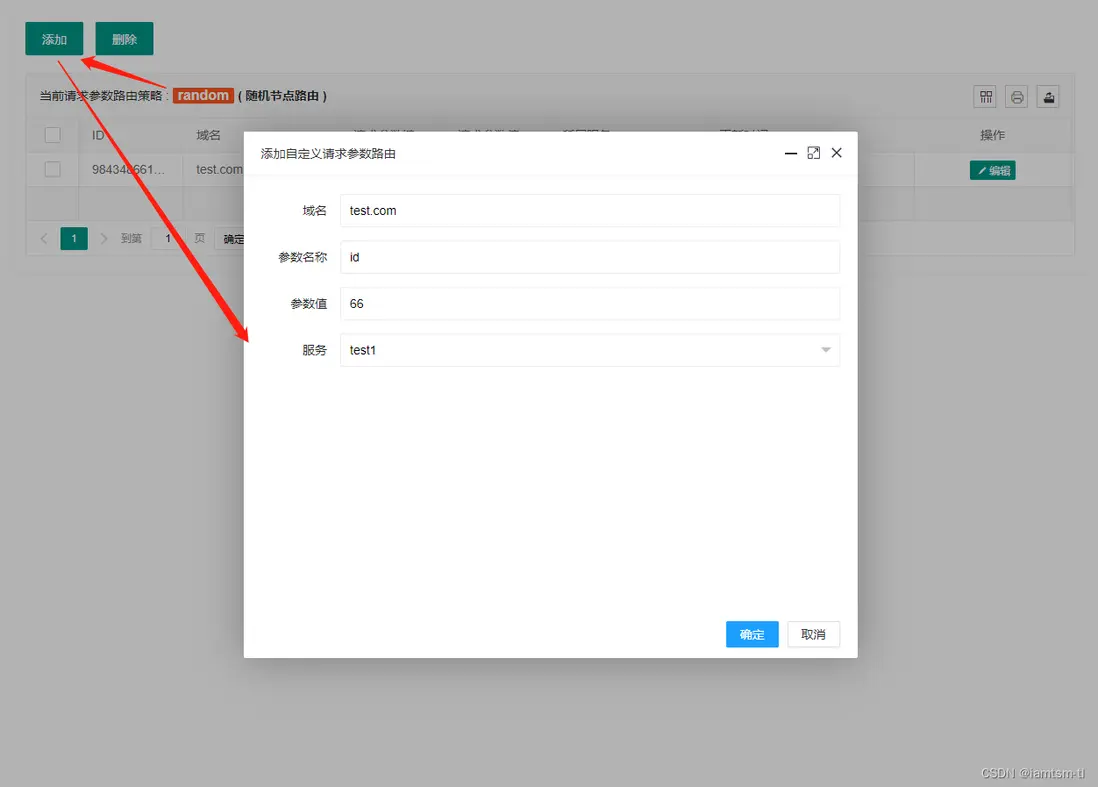
},參數策略
point = {
{
id = snowflake.generate_id( 100 ), -- default snow id
key = "_tl_id", -- 當前請求參數匹配名稱
value = "0", -- 當前請求參數名稱對應值
service = "測試服務1", -- 當前請求參數路由到的service
node = 0, -- 當前請求參數路由到的service下的node的索引
host = "tlops1.com", -- 當前請求參數處理的域名範圍
}
},
random = {
{
id = snowflake.generate_id( 100 ), -- default snow id
key = "_tl_name", -- 當前請求參數匹配名稱
value = "iamtsm", -- 當前請求參數名稱對應值
service = "tlops-demo", -- 當前請求參數路由到的service
node = 0, -- 當前請求參數路由到的service下的node的索引
host = "tlops1.com", -- 當前請求參數處理的域名範圍
}
},在管理台配置
URL模式
請求參數模式
COOKIE模式
路由統計
路由統計,是在負載均衡模塊上擴充的一種功能,在服務進行負載邏輯時,可能存在負載成功,或失敗,有些情況下可能需要統計負載情況進行展示。其對應的配置在 constant/tl_ops_constant_balance.lua中。
在文件中配置
-- 路由統計時間間隔
count = {
interval = 5 * 60 -- 統計週期 單位/s, 默認:5min
}實現源碼説明
服務節點
我將服務劃分為服務與節點,節點隸屬於服務,是一個上下級關係。用如下配置可以展示他們之間的關係
product = { ---- 服務
{ ---- 節點1
id = snowflake.generate_id( 100 ), ---- default snow id
name = "product-node-1", ---- 當前節點name
service = "product", ---- 當前節點所屬service
protocol = "http://", ---- 當前節點協議頭
ip = "127.0.0.1", ---- 當前節點ip
port = 6666, ---- 當前節點port
},
{---- 節點2
id = snowflake.generate_id( 100 ), ---- default snow id
name = "product-node-2", ---- 當前節點name
service = "product", ---- 當前節點所屬service
protocol = "http://", ---- 當前節點協議頭
ip = "127.0.0.1", ---- 當前節點ip
port = 6667, ---- 當前節點port
}
}例如在業務場景中會有產品功能,對於產品功能來説,運行他的應該是有一個或多個機器實例,產品業務對應的就是產品服務,這些機器實例對應的就是產品節點。
對於tl-ops-manage來説,服務-節點是基礎,其他的路由,檢查等模塊都需要依賴服務-節點。所以服務-節點可以理解為公共全局配置,僅有一份,其對應的項目文件在 constant/tl_ops_constant_service.lua
健康檢查
健康檢查的主要邏輯是 定時檢查器 的實現。
定時檢查器根據配置啓動相應定時器執行檢查邏輯。配置加載器根據管理端新增或修改的配置動態同步到定時檢查器中。實現方式都是通過ngx.timer
首先,我們先了解下健康檢查對應的配置,還是以product服務為例
{---- product服務自檢配置
check_failed_max_count = 5, #自檢時心跳包最大失敗次數,達到這個次數會將在線節點置為下線。
check_success_max_count = 2, #自檢時心跳包最大成功次數,達到這個次數會將下線節點置為上線。
check_interval = 5 * 1000, #自檢週期, 默認單位/ms
check_timeout = 1000, #自檢心跳包接收超時時間,默認單位/ms
check_content = "GET / HTTP/1.0", #自檢心跳包內容,可自定義,但是需要被檢方處理兼容。
check_service_name = "product" #自檢服務名稱
}在項目啓動時,會首先執行到 conf/tl_ops_manage.conf 中的 init_worker_by_lua_block邏輯,啓動相應的定時任務
# 代碼位置 : conf/tl_ops_manage.conf
init_worker_by_lua_block {
-- 啓動健康檢查
require("health.tl_ops_health"):init();
...
}進入 require("health.tl_ops_health"):init(); 方法後,我們可以看到一系列的啓動器,如根據配置啓動相應的health-check-timer, 還有配置加載器的啓動,以及服務的版本初始化,以及服務健康檢查配置版本的初始化
# 代碼位置 : health/tl_ops_health.lua
function _M:init( )
--動態加載新增配置
tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf.dynamic_conf_add_start()
--默認初始化一次version
for i = 1, #tl_ops_constant_health.options do
local option = tl_ops_constant_health.options[i]
local service_name = option.check_service_name
if service_name then
tl_ops_health_check_version.incr_service_version(service_name)
end
end
tl_ops_health_check_version.incr_service_option_version()
end
我們先從健康檢查主邏輯開始,可以看到先執行了一段配置初始化邏輯 tl_ops_health_check_default_confs, 初始化配置中,會檢查配置的合法性,以及對服務狀態,節點狀態的初始值進行定義。
緊接着可以看到根據confs的數量,用ngx.timer.at去啓動相應的定時器去執行 tl_ops_health_check 邏輯,而 tl_ops_health_check 也就是執行相應的 tl_ops_health_check_main邏輯, conf 就是每個定時器所需的健康檢查配置
# 代碼位置 : health/tl_ops_health_check.lua
-- 創建健康檢查啓動器
function _M:tl_ops_health_check_start()
if not self.options or not self.services then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_start no default args ")
return nil
end
local confs, _ = tl_ops_health_check_default_confs(self.options, self.services)
if not confs then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_start failed to start , confs nil ", _)
return nil
end
...
for index, conf in ipairs(confs) do
local ok, _ = ngx.timer.at(0, tl_ops_health_check, conf)
if not ok then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_start failed to run check , create timer failed " , _)
return nil
end
...
end
...
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_start check end , timer_list=",timer_list)
return true
end接下來進入核心邏輯tl_ops_health_check,tl_ops_health_check 對應的核心邏輯是 tl_ops_health_check_main, 可以看到tl_ops_health_check_main邏輯主要由兩部分組成,也就是 dynamic_conf_change_start(同步配置),tl_ops_health_check_nodes(心跳包),接下來將對這兩個方法進行詳細解析
# 代碼位置 : health/tl_ops_health_check.lua
-- 健康檢查主邏輯
tl_ops_health_check_main = function (conf)
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_main start")
--同步配置
tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf.dynamic_conf_change_start( conf )
-- 心跳包
if tl_ops_health_check_get_lock(conf) then
-- 是否主動關閉自檢
local uncheck_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.uncheck, conf.check_service_name)
local uncheck, _ = shared:get(uncheck_key)
if uncheck and uncheck == true then
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_main is uncheck check_service_name=",conf.check_service_name)
return
end
tl_ops_health_check_nodes(conf)
end
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_main end")
end心跳包
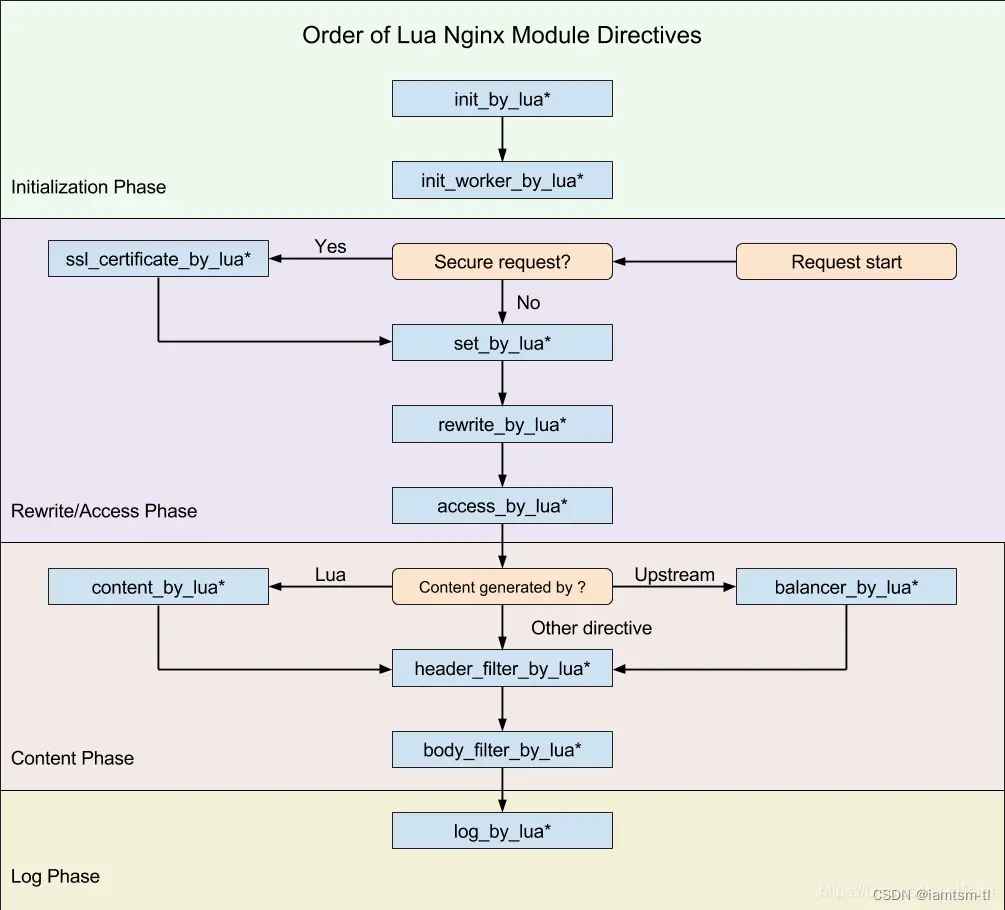
在介紹實現之前,首先有必要鋪墊一下openresty的執行階段相關知識。
由於nginx在啓動時是多woker進程來處理請求,而openresty將nginx處理請求分為七個階段。
健康檢查的啓動應與請求階段無關,所以應該放在 init_by_lua階段或者init_worker_by_lua階段較為合適,但是定時器的生命週期只能在init_worker_by_lua階段(如下圖),所以健康檢查的啓動器就應在init_worker_by_lua階段來做。
由於init_worker_by_lua階段是初始化worker進程階段,所以在此階段是存在多個worker進程,也就是可能存在搶佔執行定時器的情況。而每個定時器有其依賴的配置,多個worker之間數據不共享,就會導致健康檢查數據統計、配置不一致的情況。
所以才會有這樣一段邏輯,tl_ops_health_check_get_lock對應的就是加鎖邏輯,主要方式是通過 ngx.shared 共享內存來實現,有興趣可以查看下具體實現代碼,這裏就不細講了。
---- 心跳包
if tl_ops_health_check_get_lock(conf) then
tl_ops_health_check_nodes(conf)
end
我們繼續看回代碼,在搶佔鎖後,只會有一個worker進程進入鎖內,並執行 tl_ops_health_check_nodes,進行發送心跳包。
對於發送心跳包,我們可以看到是對 服務-節點 依次進行遍歷發送socket包(心跳包內容自定義),如心跳週期正常結束,進入 tl_ops_health_check_node_ok 成功邏輯,否則進入tl_ops_health_check_node_failed 失敗邏輯
# 代碼位置 : health/tl_ops_health_check.lua
-- 對配置的路由機器依次發送心跳包
tl_ops_health_check_nodes = function (conf)
...
for i = 1, #nodes do
repeat
local node = nodes[i]
local node_id = i - 1
local name = node.ip .. ":" .. node.port
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_nodes start connect socket : name=", name)
local sock, _ = nx_socket()
if not sock then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_nodes failed to create stream socket: ", _)
break
end
sock:settimeout(check_timeout)
-- 心跳socket
local ok, _ = sock:connect(node.ip, node.port)
if not ok then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_nodes failed to connect socket: ", _)
tl_ops_health_check_node_failed(conf, node_id, node)
break;
end
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_nodes connect socket ok : ok=", ok)
local bytes, _ = sock:send(check_content .. "\r\n\r\n\r\n")
if not bytes then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_nodes failed to send socket: ", _)
tl_ops_health_check_node_failed(conf, node_id, node)
break
end
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_nodes send socket ok : byte=", bytes)
-- socket反饋
local receive_line, _ = sock:receive()
if not receive_line then
if _ == "check_timeout" then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_nodes socket check_timeout: ", _)
sock:close()
end
tl_ops_health_check_node_failed(conf, node_id, node)
break
end
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_nodes receive socket ok : ", receive_line)
local from, to, _ = ngx.re.find(receive_line, [[^HTTP/\d+\.\d+\s+(\d+)]], "joi", nil, 1)
if not from then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_nodes ngx.re.find receive err: ", from, to, _)
sock:close()
tl_ops_health_check_node_failed(conf, node_id, node)
break
end
-- 心跳狀態
local status = tonumber(string.sub(receive_line, from, to))
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_nodes get status ok ,name=" ,name, ", status=" , status)
local statusPass = false;
for j = 1, #check_success_status do
if check_success_status[j] == status then
statusPass = true
end
end
if statusPass == false then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_nodes status not pass ,name=" ,name, ", status=" , status)
tl_ops_health_check_node_failed(conf, node_id, node)
sock:close()
break
end
-- 心跳成功
tl_ops_health_check_node_ok(conf, node_id, node)
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_nodes node ok")
sock:close()
break
until true
end
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_nodes end ,conf=" , conf, ",nodes=",nodes)
end心跳成功
心跳成功之後,會累加成功的次數,並清空之前累加的失敗次數,當成功累加達到一定的次數後,認為該節點可以用於正常處理請求,即可將改節點狀態變更為 上線節點,由此該節點就可以用於請求路由負載節點中
# 代碼位置 : health/tl_ops_health_check.lua
-- 心跳檢查成功
tl_ops_health_check_node_ok = function (conf, node_id, node)
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_node_ok start ,conf=" , conf, ",node=" , node)
local shared = shared
local check_success_max_count = conf.check_success_max_count
local check_service_name = conf.check_service_name
local key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.success, check_service_name, node_id)
local cur_success_count, _ = shared:get(key)
if not cur_success_count then
cur_success_count = 1
local ok, _ = shared:set(key, cur_success_count)
if not ok then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_node_ok failed to set node ok key: " , key)
end
else
cur_success_count = cur_success_count + 1
local ok, _ = shared:incr(key, 1)
if not ok then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_node_ok failed to incr node ok key: " , key)
end
end
-- 心跳包成功後,重置之前有過累計的失敗次數
if cur_success_count == 1 then
key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.failed, check_service_name, node_id)
local fails, _ = shared:get(key)
if not fails or fails == 0 then
if _ then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_node_ok failed to get node nok key: " , key)
end
else
local ok, _ = shared:set(key, 0)
if not ok then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_node_ok failed to set node nok key: " , key)
end
end
end
-- 該機器當前狀態:下線 && 心跳包成功次數 > 配置的次數,將shareDict中該機器的狀態置為上線,
-- {tl_ops_health_check_donw_state:resin-site0:nil}
if not node.state and cur_success_count >= check_success_max_count then
local name = node.port .. ":" .. node.ip
key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.state, check_service_name, node_id)
local ok, _ = shared:set(key, true)
if not ok then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_node_ok failed to set node down state:", _)
end
node.state = true
...
end
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_node_ok end ,node=" , node)
end心跳失敗
心跳失敗之後,會累加失敗的次數,並清空之前累加的成功次數,當失敗累加達到一定的次數後,認為該節點不可以用於正常處理請求,即可將改節點狀態變更為 下線節點,由此該節點就應該剔除在正常服務中,就不能用於路由負載使用
# 代碼位置 : health/tl_ops_health_check.lua
-- 心跳檢查失敗
tl_ops_health_check_node_failed = function (conf, node_id, node)
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_node_failed start ,conf=" , conf, ",node=" , node)
local check_failed_max_count = conf.check_failed_max_count
local check_service_name = conf.check_service_name
-- key=tl_ops_health_check_failed_count:resin-site0 (health check not ok)
local key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.failed, check_service_name, node_id)
local cur_failed_count, _ = shared:get(key)
if not cur_failed_count then
cur_failed_count = 1
local ok, _ = shared:set(key, cur_failed_count)
if not ok then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_node_failed failed to set node check_failed_max_count key: " , key)
end
else
cur_failed_count = cur_failed_count + 1
local ok, _ = shared:incr(key, 1)
if not ok then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_node_failed failed to incr node check_failed_max_count key: " , key)
end
end
-- 心跳包失敗後,重置之前有過累計的成功次數
if cur_failed_count == 1 then
key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.success, check_service_name, node_id)
local succ, _ = shared:get(key)
if not succ or succ == 0 then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_node_failed failed to get node check_success_max_count key: " , key , " or check_success_max_count = 0")
else
local ok, _ = shared:set(key, 0)
if not ok then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_node_failed failed to set node check_success_max_count key: " .. key)
end
end
end
-- 該機器當前狀態:在線 && 心跳包失敗次數 > 配置的次數,將shareDict中該機器的狀態置為下線,
-- {tl_ops_health_check_donw_state:resin-site0:true}
if node.state and cur_failed_count > check_failed_max_count then
local name = node.ip .. ":" .. node.port
key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.state, check_service_name, node_id)
local ok, _ = shared:set(key, nil)
if not ok then
tlog:err("tl_ops_health_check_node_failed failed to set node down state:", _)
end
node.state = false
...
end
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_health_check_node_failed end ,node=" , node)
end
路由負載
負載均衡的實現是本身nginx是支持配置多種輪詢機制的,如權重,隨機,備份等。tl-ops-manage提供的負載策略是更加細化的負載。目前支持幾種策略 api最長前綴正則匹配負載,cookie鍵值對匹配負載,請求參數鍵值對匹配負載,請求頭部鍵值對匹配負載,以及每種策略下支持兩種模式的動態切換,指定節點負載 ,隨機節點負載。
在服務節點列表中,所有節點是依賴健康檢查動態上下線。上線節點加入負載列表,下線節點剔除負載列表。在負載列表中的所有有效節點,將被用作根據負載策略進行負載。
通過下面代碼,我們可以看到主入口是放置在 conf 文件中的,通過設置一個節點變量 node 在 rewrite_by_lua_block 階段執行balance邏輯後,得到具體的node值,從而通過proxy_pass轉發到具體節點。
# 代碼位置 : conf/tl_ops_manage.conf
location / {
...
set $node '';
rewrite_by_lua_block {
require("balance.tl_ops_balance"):init();
}
proxy_pass $node;
}接下來,我們看回負載核心邏輯代碼 : tl_ops_balance_core_balance,可以看到先獲取當前所有服務節點,然後根據負載策略依次匹配,直到命中規則,得到具體節點。
策略匹配順序為 : api策略 > 請求參數策略 > 請求cookie策略 > 請求頭策略 。
匹配到具體規則後,轉而匹配域名,如果域名匹配也命中,説明當前請求應該被此條規則所配置的節點處理。
當前在實際負載前,應該要考慮當前節點所配置的流控策略,在流控限制下,如果能拿到令牌或正常留出漏桶,説明當前請求已經被允許轉發到上游服務了,當然,如果此時,服務狀態不佳,不能正常處理請求,那麼就無需轉發請求,直接丟棄即可。
# 代碼位置 : balance/tl_ops_balance_core.lua
-- 負載核心流程
function _M:tl_ops_balance_core_balance()
-- 服務節點配置列表
local service_list_str, _ = cache_service:get(tl_ops_constant_service.cache_key.service_list);
if not service_list_str then
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = "";
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "empty"
ngx.exit(503)
end
local service_list_table = cjson.decode(service_list_str);
if not service_list_table and type(service_list_table) ~= 'table' then
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = "";
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "empty"
ngx.exit(503)
end
-- 負載模式
local balance_mode = "api"
-- 先走api負載
local node, node_state, node_id, host = tl_ops_balance_core_api.tl_ops_balance_api_service_matcher(service_list_table)
if not node then
-- api不匹配,走param負載
balance_mode = "param"
node, node_state, node_id, host = tl_ops_balance_core_param.tl_ops_balance_param_service_matcher(service_list_table)
if not node then
-- param不匹配,走cookie負載
balance_mode = "cookie"
node, node_state, node_id, host = tl_ops_balance_core_cookie.tl_ops_balance_cookie_service_matcher(service_list_table)
if not node then
-- cookie不匹配,走header負載
balance_mode = "header"
node, node_state, node_id, host = tl_ops_balance_core_header.tl_ops_balance_header_service_matcher(service_list_table)
if not node then
-- 無匹配
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = "";
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "empty"
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Mode'] = balance_mode
ngx.exit(503)
end
end
end
end
-- 域名負載
if host == nil or host == '' then
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = "";
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "nil"
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Mode'] = balance_mode
ngx.exit(503)
end
-- 域名匹配
if host ~= "*" and host ~= ngx.var.host then
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = "";
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "pass"
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Mode'] = balance_mode
ngx.exit(503)
end
-- 流控介入
local depend = tl_ops_balance_core_get_limiter(node.service, node_id)
if depend then
-- 令牌桶流控
if depend == tl_ops_constant_limit.depend.token then
local token_result = tl_ops_limit_fuse_token_bucket.tl_ops_limit_token( node.service, node_id)
if not token_result or token_result == false then
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = "";
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "t-limit"
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Mode'] = balance_mode
ngx.exit(503)
end
end
-- 漏桶流控
if depend == tl_ops_constant_limit.depend.leak then
local leak_result = tl_ops_limit_fuse_leak_bucket.tl_ops_limit_leak( node.service, node_id)
if not leak_result or leak_result == false then
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = "";
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "l-limit"
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Mode'] = balance_mode
ngx.exit(503)
end
end
end
-- 節點下線
if not node_state or node_state == false then
-- incr failed count
local balance_req_fail_count_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_balance.cache_key.req_fail, node.service, node_id)
local failed_count = shared:get(balance_req_fail_count_key)
if not failed_count then
shared:set(balance_req_fail_count_key, 0);
end
shared:incr(balance_req_fail_count_key, 1)
local limit_req_fail_count_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_limit.fuse.cache_key.req_fail, node.service, node_id)
failed_count = shared:get(limit_req_fail_count_key)
if not failed_count then
shared:set(limit_req_fail_count_key, 0);
end
shared:incr(limit_req_fail_count_key, 1)
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = node['service'];
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Node'] = node['name'];
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "offline"
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Mode'] = balance_mode
ngx.exit(503)
end
-- 負載成功
local balance_req_succ_count_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_balance.cache_key.req_succ, node.service, node_id)
local success_count = shared:get(balance_req_succ_count_key)
if not success_count then
shared:set(balance_req_succ_count_key, 0);
end
shared:incr(balance_req_succ_count_key, 1)
local limit_req_succ_count_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_limit.fuse.cache_key.req_succ, node.service, node_id)
success_count = shared:get(limit_req_succ_count_key)
if not success_count then
shared:set(limit_req_succ_count_key, 0);
end
shared:incr(limit_req_succ_count_key, 1)
ngx.var.node = node['protocol'] .. node["ip"] .. ':' .. node["port"];
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = node['service'];
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Node'] = node['name'];
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "online"
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Mode'] = balance_mode
end
以上就是負載核心思路,下面我將對不同策略以及每種策略下的不同模式進行説明
API最長前綴匹配策略
全稱,api最長前綴匹配負載策略,通過請求的URI的最長前綴子串,再拿到所有API負載規則進行匹配,得到命中的API匹配規則,進而得到具體匹配的節點。
# 代碼位置 : balance/tl_ops_balance_core_api.lua
local tl_ops_balance_api_service_matcher = function(service_list_table)
local matcher = nil
local node = nil
-- 獲取當前url
local request_uri = tl_ops_utils_func:get_req_uri();
-- api路由策略
local api_rule, _ = cache_api:get(tl_ops_constant_api.cache_key.rule);
if not api_rule then
return nil, nil, nil, nil
end
-- api配置列表
local api_list, _ = cache_api:get(tl_ops_constant_api.cache_key.list);
if not api_list then
return nil, nil, nil, nil
end
local api_list_table = cjson.decode(api_list);
if not api_list_table then
return nil, nil, nil, nil
end
-- 根據路由當前策略進行路由, 返回正則命中的api
if api_rule == tl_ops_constant_api.rule.point then
matcher = tl_ops_utils_func:get_table_matcher_longer_str_for_api_list(
api_list_table, tl_ops_constant_api.rule.point, request_uri
);
elseif api_rule == tl_ops_constant_api.rule.random then
matcher = tl_ops_utils_func:get_table_matcher_longer_str_for_api_list(
api_list_table, tl_ops_constant_api.rule.random, request_uri
);
end
if not matcher or type(matcher) ~= 'table' then
return nil, nil, nil, nil
end
local service_list = service_list_table[matcher.service]
-- node balance
local node_id = matcher.node -- lua index start 1
if node_id then
node = service_list[tonumber(node_id) + 1]
else
-- random balance
math.randomseed(#request_uri)
node_id = tonumber(math.random(0,1) % #service_list_table[matcher.service]) + 1
node = service_list[node_id]
end
local host = matcher.host
if not host or host == nil then
host = ""
end
-- 獲取當前節點健康狀態
local key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.state, matcher.service, node_id)
local node_state , _ = shared:get(key)
return node, node_state, node_id, host
endCOOKIE精準匹配策略
這種策略是精準匹配,獲取請求內所有cookie後,再拿到所有cookie負載規則進行匹配,得到命中的cookie匹配規則,進而得到具體匹配的節點。
具體實現代碼類似 URI 匹配。
請求參數精準匹配策略
這種策略是精準匹配,獲取請求內所有請求參數後,再拿到所有請求參數負載規則進行匹配,得到命中的請求參數匹配規則,進而得到具體匹配的節點。
具體實現代碼類似 URI 匹配。
請求頭部精準匹配策略
這種策略是精準匹配,獲取請求內所有請求頭後,再拿到所有請求頭負載規則進行匹配,得到命中的請求頭匹配規則,進而得到具體匹配的節點。
具體實現代碼類似 URI 匹配。
路由統計
路由統計,是在負載均衡模塊上擴充的一種功能,在服務進行負載邏輯時,可能存在負載成功,或失敗,有些情況下可能需要統計負載情況進行展示。在此需求下,用定時任務實現了統計負載數據。
# 代碼位置 : conf/tl_ops_manage.conf
init_worker_by_lua_block {
...
-- 啓動路由統計
require("balance.tl_ops_balance_count"):init();
}我們可以看到主入口在 init_worker_by_lua_block 中調用了定時任務啓動器。
關於路由統計啓動器主要邏輯如下,大家可以看到這裏有加鎖操作,因為在啓動時存在多worker搶佔執行,而統計只需要一個worker執行即可。
獲取到鎖後,先獲取所有服務節點,對所有服務節點的負載成功次數,負載失敗次數,時間,進行記錄,放置在list中並持久化到store文件中(為避免過多內存暫用,之所以只用store持久即可)
# 代碼位置 : conf/tl_ops_manage.conf
-- 統計器 : 持久化數據
local tl_ops_balance_count = function()
-- 統計器加鎖
if not tl_ops_balance_count_lock() then
return
end
local service_list = nil
local service_list_str, _ = cache_service:get(tl_ops_constant_service.cache_key.service_list);
if not service_list_str then
-- use default
service_list = tl_ops_constant_service.list
else
service_list = cjson.decode(service_list_str);
end
-- 控制細度 ,以週期為分割,僅用store持久
local count_name = "tl-ops-balance-count-" .. tl_ops_constant_balance.count.interval;
local cache_balance_count = require("cache.tl_ops_cache"):new(count_name);
for service_name, nodes in pairs(service_list) do
...
for i = 1, #nodes do
local node_id = i-1
local cur_count_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_balance.cache_key.req_succ, service_name, node_id)
local cur_count = shared:get(cur_count_key)
if not cur_count then
cur_count = 0
shared:set(cur_count_key, cur_count)
end
-- push to list
local success_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_balance.cache_key.balance_5min_success, service_name, node_id)
local balance_5min_success = cache_balance_count:get001(success_key)
if not balance_5min_success then
balance_5min_success = {}
else
balance_5min_success = cjson.decode(balance_5min_success)
end
balance_5min_success[os.date("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", ngx.now())] = cur_count
local ok, _ = cache_balance_count:set001(success_key, cjson.encode(balance_5min_success))
...
end
end
end熔斷限流
熔斷限流,其實是服務自動化熔斷降級,服務限流兩種的組合。
為什麼稱其為自動化熔斷 ?
因為我們在判斷服務是否處於 `性能不佳` 狀態,而不能及時處理請求時,是需要依據一些服務本身的`健康狀態`或實際`負載率`來衡量是否將服務降級,但是我們在進行服務降級後,此服務恢復正常,那麼此時該服務應該被升級,用於處理更多請求。而此 ‘服務升級/降級’ 步驟應該實現系統自動化。
對於服務自動化熔斷來説,其應該是根據節點 ‘狀態’ 來進行一種服務降級的手段。在節點負載過高時,應該對節點減少流量的進入,在服務性能較優時,增加流量的進入,而控制流量的進入就需要用到一些流控手段。所以我將其組合設計。
對於這兩種服務治理手段,在各大框架中也有不少應用,如java的spring cloud Hystrix,其實現也是做到了自動化熔斷恢復。
自動化熔斷
假設某個服務在內存溢出時,不斷返回504(請求超時),那這個時候如果其他服務存在rpc一直調用此服務,會導致整個系統被拖垮。所以這個時候應該將此服務降級,讓其處理更少的請求或不處理請求。
下面我們看回tl-ops-manage實現自動化熔斷代碼,依然還是用定時任務來實現,主入口如下
# 代碼位置 : conf/tl_ops_manage.conf
init_worker_by_lua_block {
...
-- 啓動限流熔斷
require("limit.fuse.tl_ops_limit_fuse"):init();
...
}進入主入口後,我們可以看到代碼和健康檢查實現類似,都是啓動相應定時器,以及服務配置版本初始化,配置版本號的初始化主要是用於加載最新配置到定時任務中。也用於動態同步配置到worker中
# 代碼位置 : limit/fuse/tl_ops_limit_fuse.lua
function _M:init( )
-- 給定配置啓動限流熔斷檢查,支持動態加載已有服務變更配置
local limit_fuse = tl_ops_limit_fuse_check:new(
tl_ops_constant_limit.fuse.options, tl_ops_constant_limit.fuse.service
);
limit_fuse:tl_ops_limit_fuse_start();
-- 啓動動態新增配置檢測
tl_ops_limit_fuse_check_dynamic_conf.dynamic_conf_add_start()
-- 默認初始化一次version, 啓動時讀取最新數據
for i = 1, #tl_ops_constant_limit.fuse.options do
local option = tl_ops_constant_limit.fuse.options[i]
local service_name = option.service_name
if service_name then
tl_ops_limit_fuse_check_version.incr_service_version(service_name)
end
end
-- 啓動動態檢測配置版本
tl_ops_limit_fuse_check_version.incr_service_option_version()
end接着我們看回主邏輯 tl_ops_limit_fuse_start,這裏的主邏輯前部分和健康檢查類似,這裏直接講解定時器中的核心邏輯 tl_ops_limit_fuse_main,可以看到在鎖內執行了兩段邏輯,除了對服務進行降級升級操作外,多了一個自動恢復邏輯塊 tl_ops_limit_fuse_auto_recover,也就是靠這個邏輯來做到自動化熔斷恢復的。
# 代碼位置 : limit/fuse/tl_ops_limit_fuse_check.lua
tl_ops_limit_fuse_main = function( conf )
--同步配置
tl_ops_limit_fuse_check_dynamic_conf.dynamic_conf_change_start( conf )
-- 自動熔斷/恢復
if tl_ops_limit_fuse_get_lock( conf ) then
tl_ops_limit_fuse_auto_recover( conf )
tl_ops_limit_fuse_check_nodes( conf )
end
end我們先看主要的自檢邏輯tl_ops_limit_fuse_check_nodes,和健康檢查自檢不同,對於熔斷的自檢我用的是自檢週期內節點負載的失敗率來衡量節點處於何種狀態。
節點熔斷
我們可以看到在自檢時,是輪詢所有節點,獲取每個節點的成功負載次數,負載失敗次數,並根據得出的失敗率和用户設定的節點失敗率作對比,如果超過這個閾值,進行節點降級
,代碼裏面寫的是狀態升級,也就是從 0 [正常節點] -> 1 [節點半熔斷] -> 2 [節點全熔斷]。
# 代碼位置 : limit/fuse/tl_ops_limit_fuse_check.lua
tl_ops_limit_fuse_check_nodes = function ( conf )
...
-- node層級
for i = 1, #nodes do
local node_id = i-1
local success_count_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_limit.fuse.cache_key.req_succ, service_name, node_id)
local success_count = shared:get(success_count_key)
if not success_count then
success_count = 0
end
local failed_count_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_limit.fuse.cache_key.req_fail, service_name, node_id)
local failed_count = shared:get(failed_count_key)
if not failed_count then
failed_count = 0
end
local total_count = success_count + failed_count
if total_count == 0 then
total_count = -1 -- can not be 0
end
-- 超過閾值
if failed_count / total_count >= node_threshold then
upgrade_count = upgrade_count + 1
tl_ops_limit_fuse_node_upgrade( conf, node_id )
else
degrade_count = degrade_count + 1
tl_ops_limit_fuse_node_degrade( conf, node_id )
end
end
...
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_limit_fuse_check_nodes done")
end服務熔斷
在輪詢完所有節點後,得出每個節點的狀態,如果降級節點超過設定的服務閾值,那麼進行服務降級
,代碼裏面寫的是狀態升級,也就是從 0 [正常服務] -> 1 [服務半熔斷] -> 2 [服務全熔斷]。
# 代碼位置 : limit/fuse/tl_ops_limit_fuse_check.lua
tl_ops_limit_fuse_check_nodes = function ( conf )
...
-- service層級
local service_total_count = upgrade_count + degrade_count
if service_total_count == 0 then
service_total_count = -1 -- can not be 0
end
-- 節點狀態升級比率超過閾值,對服務進行狀態升級
if upgrade_count / service_total_count >= service_threshold then
tl_ops_limit_fuse_service_upgrade( conf )
else
tl_ops_limit_fuse_service_degrade( conf )
end
tlog:dbg("tl_ops_limit_fuse_check_nodes done")
end動態限流器
在處理完節點/服務的狀態時,會並行處理限流器的擴縮容。因為要想做到服務升降級,從而減少進入服務節點的流量,限流器是不可缺少的一部分。而要想要限流器做到隨着服務升降級而動態進行限流。就需要用到動態擴縮容的概念
在tl-ops-manage中,我提供了兩種限流算法,並整合了這兩種算法到熔斷邏輯中,我稱之為熔斷限流器,目前有 令牌桶限流器,漏桶限流器。下面我着重説明下兩種限流器的擴縮容實現和整合
令牌桶限流器
令牌桶擴容
我們知道令牌桶是一個容器,之所以它能實現限流,是因為他有最大最小邊界值,我們假設桶最大容量為capacity, 那麼令牌數量的範圍就是 [0, capacity],在某一時刻,這裏我們假定容量為 [0, capacity/2],也就是服務處理請求的能力將下降一半,發生擴容後,能夠存放令牌的數量將變為 [0, (capacity/2) * 擴容比例]
下面我們看具體實現代碼,可以看到首先從shared中拿出 capacity,判定是否在合法值內,如果是,再拿到擴容比例,將其擴容,
# 代碼位置 : limit/fuse/tl_ops_limit_fuse_token_bucket_.lua
-- 擴容 熔斷定時器中保證鎖,所以這裏不加鎖
local tl_ops_limit_token_expand = function( service_name, node_id )
local token_mode = tl_ops_limit_token_mode( service_name, node_id)
local capacity_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(token_mode.cache_key.capacity, service_name, node_id)
local capacity = shared:get(capacity_key)
if not capacity then
local res, _ = shared:set(capacity_key, token_mode.options.capacity)
if not res then
return false
end
capacity = token_mode.options.capacity
end
if capacity <= 1 then
return false
end
local expand_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(token_mode.cache_key.expand, service_name, node_id)
local expand = shared:get(expand_key)
if not expand then
local res, _ = shared:set(expand_key, token_mode.options.expand)
if not res then
return false
end
expand = token_mode.options.expand
end
-- 擴容量 = 當前桶容量 * 比例
local expand_capacity = capacity * expand
local capacity_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(token_mode.cache_key.capacity, service_name, node_id)
local res ,_ = shared:incr(capacity_key, expand_capacity)
if not res or res == false then
return false
end
return true
end令牌桶縮容
明白了,上面的的擴容,自然也就能明白縮容了,只是將擴容的值補充負號即可。部分代碼如下
# 代碼位置 : limit/fuse/tl_ops_limit_fuse_token_bucket_.lua
-- 縮容量 = -當前桶容量 * 比例
local shrink_capacity = capacity * shrink
local res ,_ = shared:incr(capacity_key, -shrink_capacity)
if not res or res == false then
return false
end漏桶限流器
漏桶擴容
漏桶的擴縮容也是類似於令牌桶,部分代碼如下
# 代碼位置 : limit/fuse/tl_ops_limit_fuse_leak_bucket_.lua
-- 擴容量 = 當前桶容量 * 比例
local expand_capacity = capacity * expand
local res ,_ = shared:incr(capacity_key, expand_capacity)
if not res or res == false then
return false
end漏桶縮容
# 代碼位置 : limit/fuse/tl_ops_limit_fuse_leak_bucket_.lua
-- 縮容量 = -當前桶容量 * 比例
local shrink_capacity = capacity * shrink
local res ,_ = shared:incr(capacity_key, -shrink_capacity)
if not res or res == false then
return false
end負載均衡流控
明白了上面的擴縮容,對於取用令牌桶的消費和漏桶的消費也是需要了解的。下面將對兩種情況分別介紹
我們可以看到流控接入負載均衡邏輯是在負載核心邏輯中,依賴配置的限流器,選擇對應的限流策略。
# 代碼位置 : balance/tl_ops_balance_core.lua
-- 流控介入
local depend = tl_ops_balance_core_get_limiter(node.service, node_id)
if depend then
-- 令牌桶流控
if depend == tl_ops_constant_limit.depend.token then
local token_result = tl_ops_limit_fuse_token_bucket.tl_ops_limit_token( node.service, node_id)
if not token_result or token_result == false then
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = "";
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "t-limit"
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Mode'] = balance_mode
ngx.exit(503)
end
end
-- 漏桶流控
if depend == tl_ops_constant_limit.depend.leak then
local leak_result = tl_ops_limit_fuse_leak_bucket.tl_ops_limit_leak( node.service, node_id)
if not leak_result or leak_result == false then
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Server'] = "";
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-State'] = "l-limit"
ngx.header['Tl-Proxy-Mode'] = balance_mode
ngx.exit(503)
end
end
end令牌桶流控
令牌桶的實現思路之前我額外寫過一些文章來講解,這裏就不細説了 具體可查看我的這篇文章 令牌桶的實現思路
這裏需要注意的是,實際令牌桶算法應該要在獲取令牌時加鎖,避免併發問題。tl-ops-manage 接入負載邏輯中的限流器,並未加鎖,所以是允許少量請求併發獲取的情況。如果對加鎖能接受,可以自行補充鎖即可。
# 代碼位置 : limit/fuse/tl_ops_limit_fuse_token_bucket.lua
-- block 取用令牌數量
local tl_ops_limit_token = function( service_name, node_id )
...
-- 取出令牌
if token_bucket > block then
local ok, _ = shared:incr(token_bucket_key, -block)
if not ok then
return false
end
return true
end
-- 距離上次填充時間差 * 生成速率 = 需要補充的令牌
ngx.update_time()
local cur_time = ngx.now()
local duration_token_bucket = (cur_time - pre_time) * rate
if duration_token_bucket <= 0 then
return false
end
local new_token_bucket = math.min(token_bucket + duration_token_bucket, capacity)
-- 令牌還是不夠
if new_token_bucket < block then
local ok, _ = shared:set(token_bucket_key, new_token_bucket)
if not ok then
return false
end
local ok, _ = shared:set(pre_time_key, cur_time)
if not ok then
return false
end
return false
end
-- 移除一個令牌
local ok, _ = shared:set(token_bucket_key, new_token_bucket - block)
if not ok then
return false
end
local ok, _ = shared:set(pre_time_key, cur_time)
if not ok then
return false
end
return true
end漏桶流控
和令牌桶不同,漏桶的實現是依靠向外流出令牌的方式,他們的區別可以大致這麼理解,令牌桶是從桶中拿令牌,拿到令牌後執行請求,漏桶是將請求當成令牌,一個一個放入桶。
同令牌桶一致,漏桶限流器也未加鎖。需要可自行補充
# 代碼位置 : limit/fuse/tl_ops_limit_fuse_leak_bucket.lua
-- block 取用漏桶數量
local tl_ops_limit_leak = function( service_name, node_id )
...
-- 當前堆積量
local leak_bucket_key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(leak_mode.cache_key.leak_bucket, service_name, node_id)
local leak_bucket, _ = shared:get(leak_bucket_key)
if not leak_bucket then
local res, _ = shared:set(leak_bucket_key, 0)
if not res then
return false
end
leak_bucket = 0
end
-- 漏桶當前可堆積請求量 = 當前堆積量 - (在此時間區間應該被漏出的請求量)
-- ==
-- 漏桶當前可堆積請求量 = 當前堆積量 - (距離上次時間差 * 漏出速率)
ngx.update_time()
local cur_time = ngx.now()
local lave_leak_bucket = math.max(leak_bucket - (cur_time - pre_time) * rate, 0)
-- 溢出
if lave_leak_bucket + block > capacity then
return false
end
local new_leak_bucket = math.min(capacity, lave_leak_bucket + block)
local ok, _ = shared:set(leak_bucket_key, new_leak_bucket)
if not ok then
return false
end
local ok, _ = shared:set(pre_time_key, cur_time)
if not ok then
return false
end
return true
end動態配置
在tl-ops-manage中。動態配置是一大特性,支持動態更新定時任務中的配置,無需重啓nginx或定時任務即可修改規則策略等。
依靠shared共享內存實現,多個worker中依賴一個公共的配置版本號,若有某個worker檢測到配置的新增或變動,自增版本號,其他worker執行定時任務前,與共享版本號對比自身配置版本號,若存在新增或變動,同步最新配置到worker內即可
以健康檢查配置同步為例,我們可以看到代碼如下,該文件提供兩個接口, tl_ops_health_check_version_incr_service_version,tl_ops_health_check_version_incr_service_option_version,一個用於控制服務節點的配置數據版本號,一個用於控制服務配置數據版本號。
服務節點配置數據版本號 :例如,某服務下新增一個節點,那麼此節點應該被自檢定時器所識別,並加入自檢列表中,這樣才能達到動態節點註冊的效果。
服務配置數據版本號 : 例如,健康檢查配置的某一項變動,如,心跳包狀態碼新增 203 也為成功,那麼這個改動應該同步到自檢中的定時器中,以達到動態修改的目的。
# 代碼位置 : health/tl_ops_health_check_version.lua
-- 更新當前service的狀態版本,用於通知其他worker進程同步最新conf
local tl_ops_health_check_version_incr_service_version = function( service_name )
if not service_name then
tlog:err(" service_name nil ")
return
end
local key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.service_version, service_name)
local service_version, _ = cache_dict:get(key)
if not service_version then
service_version, _ = cache_dict:add(key, 1);
if not service_version then
tlog:err(" failed to publish new service_version:" , _)
end
else
service_version, _ = cache_dict:incr(key, 1);
if not service_version then
tlog:err(" failed to publish new service_version:" , _)
end
end
return service_version
end
-- 對service_options_version更新,通知timer檢查是否有新增service
local tl_ops_health_check_version_incr_service_option_version = function( )
local res, _ = cache_dict:set(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.service_options_version, true)
if not res then
tlog:err(" set service_options_version err " , _)
end
end目前支持的配置同步為兩種,增量配置同步,修改配置同步。即將支持 刪除配置同步。對於增量配置同步和修改配置同步所用的定時器邏輯是不同的。因為增量配置同步需要啓動新的定時器,而修改配置是在定時器的基礎上去同步配置即可,無需新增定時器。
增量配置同步
代碼位置 : health/tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf.lua
- 獲取當前健康檢查的所有service,並對新增的service啓動定時器
local tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_add_core = function(options, services)
-- 暫時還有service的option未同步對應的,先不執行,等到option準備完畢再執行後續邏輯
local all_service_option_asynced = tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_all_service_option_asynced(options, services)
if not all_service_option_asynced then
return
end
-- 查看現在已有的service timer,如果沒有,説明首次啓動,為所有service啓動timer
local timers_str = shared:get(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.timers)
if not timers_str then
require("health.tl_ops_health_check"):new(options, services):tl_ops_health_check_start();
shared:set(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.service_options_version, nil)
return
end
-- 如果有,查看cache service中的所有服務是否都已啓動timer,如果沒有, 補充啓動相應service timer
local timers_list = cjson.decode(timers_str)
for service_name, nodes in pairs(services) do
local service_name_exist = false
for i = 1, #timers_list do
if service_name == timers_list[i] then
service_name_exist = true;
end
end
if service_name_exist == true then
tlog:dbg("[add-check] timer exist , service_name=",service_name)
else
local matcher_options = tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_get_option( options, service_name)
require("health.tl_ops_health_check"):new(matcher_options, services):tl_ops_health_check_start();
shared:set(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.service_options_version, nil)
end
end
end
-- 同步新增的service option
local tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_add_check = function()
local version, _ = shared:get(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.service_options_version)
if not version then
return
end
local options_str, _ = cache_health:get(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.options_list)
if not options_str then
tlog:dbg("[add-check] load dynamic options failed , options_str=",options_str)
return
end
local dynamic_options = cjson.decode(options_str)
local cache_service = require("cache.tl_ops_cache"):new("tl-ops-service");
local service_str, _ = cache_service:get(tl_ops_constant_service.cache_key.service_list)
if not service_str then
tlog:dbg("[add-check] load dynamic service failed , service_str=",service_str)
return
end
local dynamic_service = cjson.decode(service_str)
if dynamic_options and dynamic_service then
tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_add_core(dynamic_options, dynamic_service)
tlog:dbg("[add-check] async dynamic conf done")
end
end修改配置同步
代碼位置 : health/tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf.lua
-- 同步變更的service信息
local tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_change_core = function( conf, service_version )
-- 保證更新順序,service/options > service.nodes > node.state
tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_change_service_options_async(conf)
tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_change_service_node_async(conf)
tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_change_state_async(conf)
conf.service_version = service_version
end
-- 校驗是否需要同步conf變更
local tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_change_check = function( conf )
local key = tl_ops_utils_func:gen_node_key(tl_ops_constant_health.cache_key.service_version, conf.check_service_name)
local service_version, _ = shared:get(key)
if not service_version then
local ok ,_ = shared:add(key, 1)
if not ok then
tlog:err("[change-check] failed to init service_version key, " , _)
end
return
end
if service_version > conf.service_version then
tl_ops_health_check_dynamic_conf_change_core( conf, service_version )
end
end