前言
最近看vuePress源碼時發現在使用markdownLoader之餘使用了大量的 markdown-it 插件,除了社區插件(如高亮代碼、錨點、emoji識別等),同時也自行編寫了很多自定義插件(如內外鏈區分渲染等)。
文章結合源碼和自己之前寫過的插件來詳細解讀如何編寫一個 markdown-it 插件規則。
簡介
markdown-it 是一個輔助解析markdown的庫,可以完成從 # test 到 <h1>test</h1> 的轉換,渲染過程和babel類似為Parse -> Transform -> Generate。
Parse
source通過3個嵌套的規則鏈core、block、inline進行解析:
core
core.rule1 (normalize)
...
core.ruleX
block
block.rule1 (blockquote)
...
block.ruleX
inline (applied to each block token with "inline" type)
inline.rule1 (text)
...
inline.ruleX解析的結果是一個token列表,將傳遞給renderer以生成html內容。
如果要實現新的markdown語法,可以從Parse過程入手:
可以在 md.core.ruler、md.block.ruler、md.inline.ruler 中自定義規則,規則的定義方法有 before、after、at、disable、enable 等。
// @vuepress/markdown代碼片段
md.block.ruler.before('fence', 'snippet', function replace(state, startLine, endLine, silent) {
//...
});上述代碼在 md.block.ruler.fence 之前加入snippet規則,用作解析 <<< @/filepath 這樣的代碼,它會把其中的文件路徑拿出來和 root 路徑拼起來,然後讀取其中文件內容。
具體代碼就不詳細分析了,一般parse階段用到的情況比較少,感興趣的可以自行查看vuePress源碼。
Transform
Token
通過官方在線示例拿 # test 舉例,會得到如下結果:
[
{
"type": "heading_open",
"tag": "h1",
"attrs": null,
"map": [
0,
1
],
"nesting": 1,
"level": 0,
"children": null,
"content": "",
"markup": "#",
"info": "",
"meta": null,
"block": true,
"hidden": false
},
{
"type": "inline",
"tag": "",
"attrs": null,
"map": [
0,
1
],
"nesting": 0,
"level": 1,
"children": [
{
"type": "text",
"tag": "",
"attrs": null,
"map": null,
"nesting": 0,
"level": 0,
"children": null,
"content": "test",
"markup": "",
"info": "",
"meta": null,
"block": false,
"hidden": false
}
],
"content": "test",
"markup": "",
"info": "",
"meta": null,
"block": true,
"hidden": false
},
{
"type": "heading_close",
"tag": "h1",
"attrs": null,
"map": null,
"nesting": -1,
"level": 0,
"children": null,
"content": "",
"markup": "#",
"info": "",
"meta": null,
"block": true,
"hidden": false
}
]
使用更底層的數據表示Token,代替傳統的AST。區別很簡單:
- 是一個簡單的數組
- 開始和結束標籤是分開的
- 會有一些特殊token (type: "inline") 嵌套token,根據標記順序(bold, italic, text, ...)排序
更詳細的數據模型可以通過 Token類定義 查看。
Renderer
token生成後被傳遞給renderer,renderer會將所有token傳遞給每個與token類型相同的rule規則。
renderer的rule規則都定義在 md.renderer.rules[name],是參數相同的函數。
Rules
代表對token的渲染規則,可以被更新或擴展,後續的實例基本都會從這裏展開。
用法
基礎用法
const MarkdownIt = require('markdown-it');
const md = new MarkdownIt();
const result = md.render('# test');預設和選項
預設(preset)定義了激活的規則以及選項的組合。可以是 commonmark、zero、default。
- commonmark 嚴格的 CommonMark 模式
- default 默認的 GFM 模式, 沒有 html、 typographer、autolinker 選項
- zero 無任何規則
// commonmark 模式
const md = require('markdown-it')('commonmark');
// default 模式
const md = require('markdown-it')();
// 啓用所有
const md = require('markdown-it')({
html: true,
linkify: true,
typographer: true
});選項文檔:
| 參數 | 類型 | 默認值 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| html | Boolean | false |
在源碼中啓用 HTML 標籤 |
| xhtmlOut | Boolean | false |
使用 / 來閉合單標籤 (比如 <br />)
這個選項只對完全的 CommonMark 模式兼容 |
| breaks | Boolean | false |
轉換段落裏的 \n 到 <br /> |
| langPrefix | String | language- |
給圍欄代碼塊的 CSS 語言前綴
對於額外的高亮代碼非常有用 |
| linkify | Boolean | false |
將類似 URL 的文本自動轉換為鏈接 |
| typographer | Boolean | false |
啓用語言無關的替換
美化引號 |
| quotes | String \ Array | “”‘’ |
雙引號或單引號或智能引號替換對,當 typographer 啓用時 |
| highlight | Function | function (str, lang) { return ''; } |
高亮函數,會返回轉義的HTML或''
如果源字符串未更改,則應在外部進行轉義 如果結果以 <pre ... 開頭,內部包裝器則會跳過 |
實例
transform階段一般有兩種寫法
- 重寫 md.renderer.rules[name]
- require('markdown-it')().use(plugin1).use(plugin2, opts, ...)
在搭建組件庫文檔過程中,需要判斷是否為http開頭的外部鏈接,內鏈直接通過a標籤跳轉相對路由,外鏈則新開窗口打開。
代碼地址
const MarkdownIt = require('markdown-it');
const md = new MarkdownIt({
html: true,
highlight,
...options
});
const defaultRender = md.renderer.rules.link_open || function(tokens, idx, options, env, self) {
return self.renderToken(tokens, idx, options);
};
md.renderer.rules.link_open = function(tokens, idx, options, env, self) {
const hrefAttr = tokens[idx].attrGet('href');
if (/^https?/.test(hrefAttr)) {
tokens[idx].attrPush(['target', '_blank']); // add new attribute
}
return defaultRender(tokens, idx, options, env, self);
};plugin有 markdown-it-for-inline、markdown-it-anchor 等,以上例為例,如果你需要添加屬性,可以在沒有覆蓋規則的情況下做一些事情。
接下來用markdown-it-for-inline插件來完成上例一樣的功能。
const MarkdownIt = require('markdown-it');
const iterator = require('markdown-it-for-inline');
const md = new MarkdownIt({
html: true,
highlight,
...options
});
md.use(iterator, 'url_new_win', 'link_open', function (tokens, idx) {
const hrefAttr = tokens[idx].attrGet('href');
if (/^https?/.test(hrefAttr)) {
tokens[idx].attrPush(['target', '_blank']); // add new attribute
}
});這比直接渲染器覆蓋規則要慢,但寫法更簡單。
vuePress實例
如果上面我自己寫的例子還比較難懂的話,接下去就拿vue的官方實例來講解。
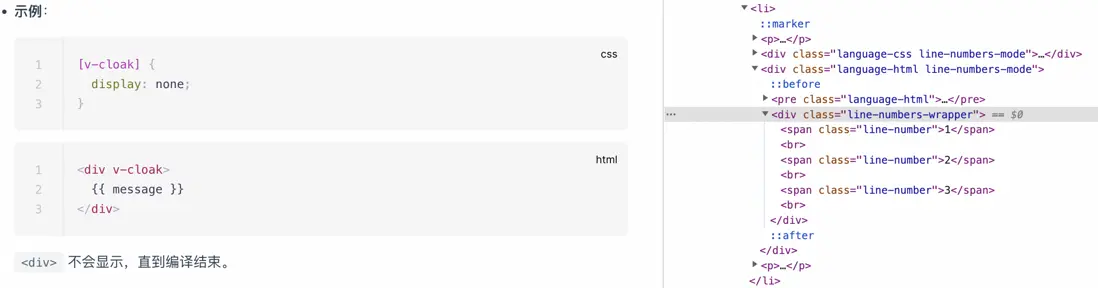
重寫 md.renderer.rules.fence 規則,通過換行符 \n 的數量來推算代碼行數,並生成帶有行號的代碼串,最後在外層包裹上一層絕對定位的樣式。
代碼地址
const fence = md.renderer.rules.fence
md.renderer.rules.fence = (...args) => {
const rawCode = fence(...args)
const code = rawCode.slice(
rawCode.indexOf('<code>'),
rawCode.indexOf('</code>')
)
const lines = code.split('\n')
const lineNumbersCode = [...Array(lines.length - 1)]
.map((line, index) => `<span class="line-number">${index + 1}</span><br>`).join('')
const lineNumbersWrapperCode =
`<div class="line-numbers-wrapper">${lineNumbersCode}</div>`
const finalCode = rawCode
.replace('<!--beforeend-->', `${lineNumbersWrapperCode}<!--beforeend-->`)
.replace('extra-class', 'line-numbers-mode')
return finalCode
}需要注意的是 <!--beforeend--> 註釋也是另一個內部插件 preWrapper 生成的,得到最終效果。
fence 這個規則用到的頻率比較高,可以直接處理具體的代碼塊,例如 ElementUI 組件庫中也有一段代碼,利用了 vue 組件插槽的特性,將同一段 markdown 代碼片段分別解析為代碼插槽和 html 代碼展示,非常精妙!
參考文檔
markdown-it design principles
markdown-it