(<center>Java 大視界 -- Java 大數據在智能物流運輸車輛智能調度與路徑優化中的技術實現</center>)
引言:
嘿,親愛的 Java 和 大數據愛好者們,大家好!我是CSDN(全區域)四榜榜首青雲交!對在《大數據新視界》和《 Java 大視界》專欄攜手探索的旅程中,我們已共同見證 Java 大數據在諸多領域掀起的技術變革。從電商用户流失預測的精準洞察,到城市空氣質量監測的可視化呈現;從智能醫療遠程手術的 “零延遲” 控制,到智能家居場景的智能切換,Java 大數據始終以開拓者的姿態,不斷突破技術邊界。
如今,物流行業正處於數字化轉型的深水區,傳統物流模式下車輛調度效率低下、路徑規劃僵化等問題日益凸顯。Java 大數據能否再次展現其技術魔力,為智能物流運輸車輛的智能調度與路徑優化帶來全新突破?答案,就藏在接下來的深度剖析中。
正文:
一、智能物流運輸現狀與挑戰
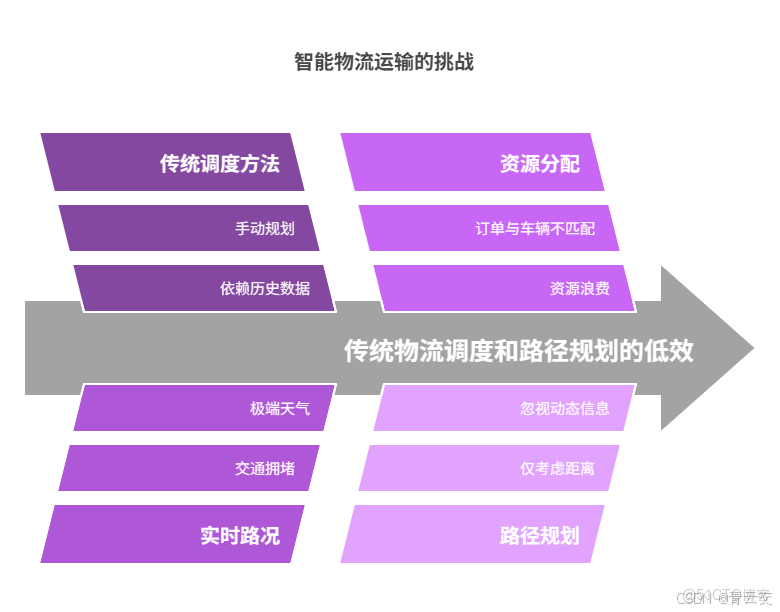
1.1 傳統物流調度的困境
傳統物流調度就像一場憑經驗的 “盲人摸象” 遊戲。以某大型物流企業為例,調度員每日需依據歷史訂單數據和有限的車輛資源,手動規劃運輸路線。但在實際運輸過程中,突發的交通擁堵、極端天氣等狀況,如同突如其來的 “黑天鵝” 事件,瞬間打亂原有的計劃。曾有統計顯示,某物流旺季期間,因傳統調度模式無法及時應對路況變化,導致車輛平均等待時間長達 3 小時,直接造成超千萬元的經濟損失。此外,人工調度難以精準匹配海量訂單與車輛資源,經常出現 “車等貨” 或 “貨等車” 的尷尬局面,資源浪費嚴重。
1.2 路徑規劃的難題
傳統路徑規劃方法如同使用陳舊的紙質地圖,僅考慮距離這一單一因素,卻忽視了實時路況、交通規則、車輛載重限制等動態信息。某快遞企業曾因路徑規劃不合理,車輛頻繁陷入擁堵路段,平均配送時間增加 40%,客户投訴率飆升。隨着城市交通網絡日益複雜,傳統路徑規劃算法在處理大規模數據時,計算效率呈指數級下降,難以滿足物流行業對快速響應的需求。
二、Java 大數據技術基石
2.1 多源數據採集與整合
Java 憑藉其強大的網絡編程能力和豐富的開源生態,成為物流數據採集的 “超級獵手”。通過物聯網設備、GPS 定位系統、交通路況 API 等多源渠道,Java 程序能夠實時捕獲車輛位置、行駛速度、貨物信息、路況等海量數據。下面這段代碼展示瞭如何利用 Java 的 HttpClient 庫從交通管理平台獲取實時路況信息:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
public class TrafficDataCollector {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 創建HttpClient實例,用於發送HTTP請求
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
// 構建請求的URI,從指定API獲取特定區域的路況數據
URI uri = URI.create("https://traffic-api.com/api/road_status?area=targetArea");
// 創建HttpRequest對象,設置請求方式和請求地址
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(uri)
.build();
// 發送請求並獲取響應,將響應體以字符串形式處理
HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
// 打印獲取到的路況數據,可進一步解析用於後續處理
System.out.println(response.body());
}
}
由於採集到的數據格式多樣(如 JSON、CSV、XML 等),需要進行統一整合。Hadoop 分佈式文件系統(HDFS)和 Hive 數據倉庫在這一過程中發揮核心作用。HDFS 以其高容錯性和擴展性,如同一個巨大的 “數據水庫”,穩定存儲海量原始數據;Hive 則負責結構化數據的高效處理,通過外部表功能,可輕鬆將不同格式的數據導入數據倉庫,並進行清洗、轉換等預處理操作,為後續分析提供 “乾淨” 的數據。
2.2 大數據處理框架的協同應用
Apache Spark 和 Flink 是 Java 大數據處理的 “黃金搭檔”。Spark 擅長處理大規模批處理數據,例如分析過去一年的運輸訂單數據,挖掘運輸規律和潛在問題。使用 Spark SQL 進行數據分析示例如下:
-- 統計每月不同車型的運輸總量
SELECT
month,
vehicle_type,
SUM(load) AS total_load
FROM
transportation_data
GROUP BY
month, vehicle_type;
Flink 專注於實時流處理,能夠實時監測車輛狀態和路況變化。以車輛超速檢測為例,通過 Flink 的 CEP(複雜事件處理)庫,可實時捕捉異常行為,代碼如下:
import org.apache.flink.cep.CEP;
import org.apache.flink.cep.PatternSelectFunction;
import org.apache.flink.cep.pattern.Pattern;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
// 定義車輛事件類,封裝車輛相關信息
class VehicleEvent {
private String vehicleId;
private double speed;
private long timestamp;
public VehicleEvent(String vehicleId, double speed, long timestamp) {
this.vehicleId = vehicleId;
this.speed = speed;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
public String getVehicleId() {
return vehicleId;
}
public double getSpeed() {
return speed;
}
public long getTimestamp() {
return timestamp;
}
}
// 定義車輛事件數據源類,模擬生成車輛事件數據
class VehicleEventSource implements org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.SourceFunction<VehicleEvent> {
private volatile boolean running = true;
@Override
public void run(SourceContext<VehicleEvent> ctx) throws Exception {
while (running) {
// 隨機生成車輛ID、速度和時間戳,模擬真實車輛數據
String vehicleId = "vehicle_" + (int) (Math.random() * 100);
double speed = Math.random() * 120;
long timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
ctx.collect(new VehicleEvent(vehicleId, speed, timestamp));
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
running = false;
}
}
public class VehicleAnomalyDetection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 獲取Flink流處理執行環境
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// 添加車輛事件數據源,生成數據流
DataStream<VehicleEvent> vehicleEventStream = env.addSource(new VehicleEventSource());
// 定義模式:車輛速度超過80km/h,並且持續時間超過10分鐘
Pattern<VehicleEvent, ?> pattern = Pattern.<VehicleEvent>begin("start")
.where(event -> event.getSpeed() > 80)
.within(Time.minutes(10));
// 檢測異常事件,提取滿足條件的車輛事件
SingleOutputStreamOperator<VehicleEvent> anomalies = CEP.pattern(vehicleEventStream, pattern)
.select(new PatternSelectFunction<VehicleEvent, VehicleEvent>() {
@Override
public VehicleEvent select(Map<String, List<VehicleEvent>> pattern) throws Exception {
return pattern.get("start").get(0);
}
});
// 打印異常事件,可進一步進行告警或處理
anomalies.print();
// 執行Flink作業
env.execute("Vehicle Anomaly Detection");
}
}
Spark 和 Flink 協同工作,實現對物流數據的全生命週期處理,為智能調度和路徑優化築牢數據根基。
三、Java 大數據驅動的智能調度與路徑優化實現
3.1 智能調度算法
基於 Java 開發的智能調度算法,融合大數據分析結果,採用遺傳算法實現車輛資源的最優分配。遺傳算法模擬生物進化過程,將車輛、訂單、運輸時間等因素編碼為染色體,通過選擇、交叉、變異等操作,不斷優化調度方案。以下是完整且優化後的遺傳算法實現代碼:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
// 車輛類,包含車輛ID和載重容量屬性
class Vehicle {
private String id;
private int capacity;
public Vehicle(String id, int capacity) {
this.id = id;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public int getCapacity() {
return capacity;
}
}
// 訂單類,包含訂單ID和貨物數量屬性
class Order {
private String id;
private int quantity;
public Order(String id, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public int getQuantity() {
return quantity;
}
}
// 染色體類,代表車輛調度方案
class Chromosome {
private List<Vehicle> vehicles;
private List<Order> orders;
private List<List<Order>> allocation;
public Chromosome(List<Vehicle> vehicles, List<Order> orders) {
this.vehicles = vehicles;
this.orders = orders;
this.allocation = new ArrayList<>();
Random random = new Random();
// 初始化每個車輛的訂單分配
for (int i = 0; i < vehicles.size(); i++) {
List<Order> subList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Order order : orders) {
if (random.nextBoolean()) {
subList.add(order);
}
}
allocation.add(subList);
}
}
// 計算適應度函數,評估調度方案的優劣
public double fitness() {
double totalCost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vehicles.size(); i++) {
int load = 0;
for (Order order : allocation.get(i)) {
load += order.getQuantity();
}
// 若車輛載重超過容量,增加懲罰項
if (load > vehicles.get(i).getCapacity()) {
totalCost += (load - vehicles.get(i).getCapacity()) * 10;
}
totalCost += allocation.get(i).size();
}
return 1.0 / (1 + totalCost);
}
// 交叉操作,生成新的調度方案
public Chromosome crossover(Chromosome other) {
Chromosome child = new Chromosome(vehicles, orders);
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < vehicles.size(); i++) {
if (random.nextBoolean()) {
child.allocation.set(i, allocation.get(i));
} else {
child.allocation.set(i, other.allocation.get(i));
}
}
return child;
}
// 變異操作,增加種羣多樣性
public void mutate() {
Random random = new Random();
int vehicleIndex = random.nextInt(vehicles.size());
int orderIndex = random.nextInt(orders.size());
Order order = orders.get(orderIndex);
if (allocation.get(vehicleIndex).contains(order)) {
allocation.get(vehicleIndex).remove(order);
} else {
allocation.get(vehicleIndex).add(order);
}
}
}
// 遺傳算法類,包含算法參數和執行邏輯
class GeneticAlgorithm {
private List<Vehicle> vehicles;
private List<Order> orders;
private int populationSize;
private double crossoverRate;
private double mutationRate;
private int maxGenerations;
public GeneticAlgorithm(List<Vehicle> vehicles, List<Order> orders, int populationSize, double crossoverRate, double mutationRate, int maxGenerations) {
this.vehicles = vehicles;
this.orders = orders;
this.populationSize = populationSize;
this.crossoverRate = crossoverRate;
this.mutationRate = mutationRate;
this.maxGenerations = maxGenerations;
}
// 執行遺傳算法,返回最優調度方案
public Chromosome evolve() {
List<Chromosome> population = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < populationSize; i++) {
population.add(new Chromosome(vehicles, orders));
}
for (int generation = 0; generation < maxGenerations; generation++) {
List<Chromosome> newPopulation = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < populationSize; i++) {
Chromosome parent1 = selectParent(population);
Chromosome parent2 = selectParent(population);
Chromosome child = parent1.crossover(parent2);
if (Math.random() < mutationRate) {
child.mutate();
}
newPopulation.add(child);
}
population = newPopulation;
}
Chromosome best = population.get(0);
for (Chromosome chromosome : population) {
if (chromosome.fitness() > best.fitness()) {
best = chromosome;
}
}
return best;
}
// 選擇父代個體,採用輪盤賭選擇策略
private Chromosome selectParent(List<Chromosome> population) {
double totalFitness = 0;
for (Chromosome chromosome : population) {
totalFitness += chromosome.fitness();
}
double randomValue = Math.random() * totalFitness;
double sum = 0;
for (Chromosome chromosome : population) {
sum += chromosome.fitness();
if (sum >= randomValue) {
return chromosome;
}
}
return population.get(0);
}
}
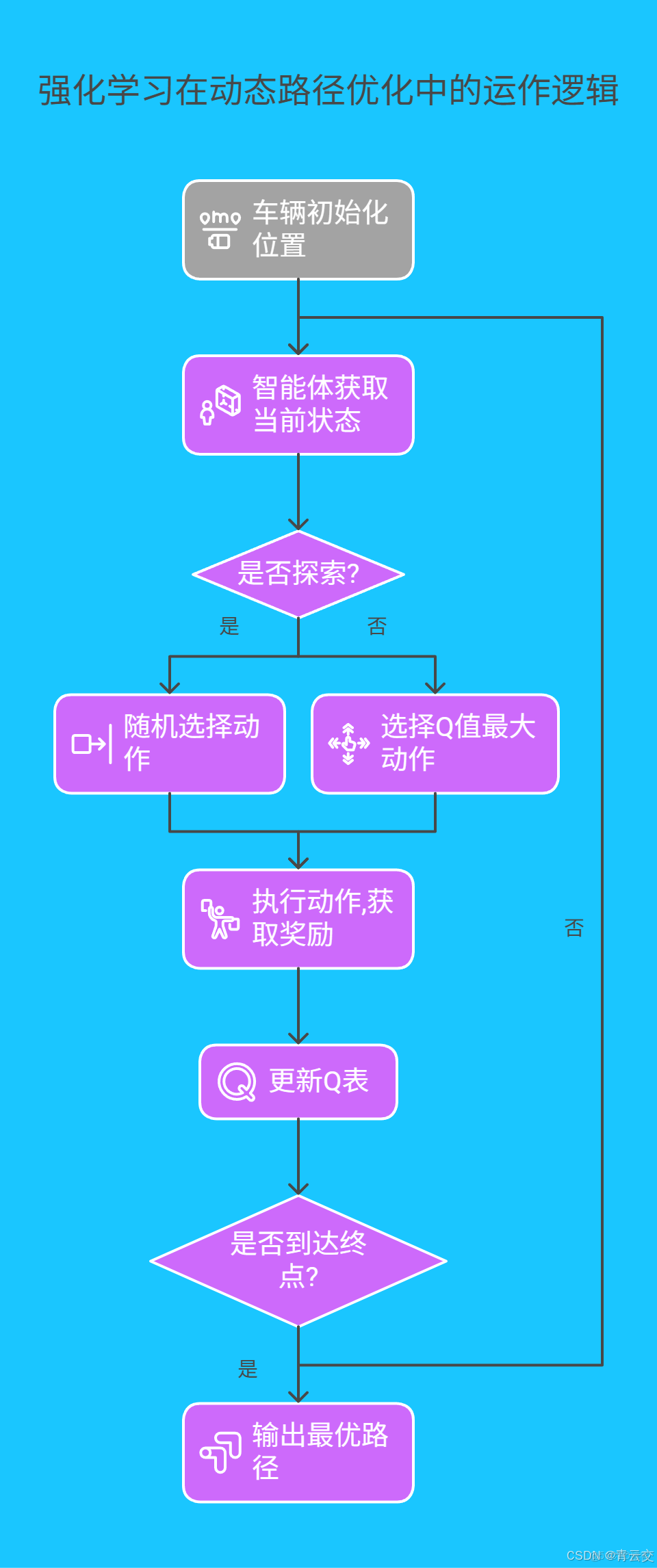
3.2 動態路徑優化
利用 Java 結合實時路況數據和地圖 API,通過 Dijkstra 算法和 A * 算法實現路徑的動態優化。在實際應用中,引入強化學習算法進一步優化路徑規劃。強化學習算法通過讓智能體(車輛)在環境(交通網絡)中不斷試錯,根據獎勵機制(如時間最短、成本最低)調整策略,從而找到最優路徑。以下是結合強化學習思想的路徑優化代碼框架:
import java.util.*;
// 定義環境類,模擬交通網絡環境
class Environment {
private Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> graph; // 圖結構存儲交通網絡
private List<String> vehicles; // 車輛列表
private Map<String, String> vehiclePositions; // 車輛當前位置
public Environment() {
graph = new HashMap<>();
vehicles = new ArrayList<>();
vehiclePositions = new HashMap<>();
}
// 添加節點和邊
public void addEdge(String from, String to, int distance) {
graph.putIfAbsent(from, new HashMap<>());
graph.get(from).put(to, distance);
}
// 添加車輛並初始化位置
public void addVehicle(String vehicleId, String startPosition) {
vehicles.add(vehicleId);
vehiclePositions.put(vehicleId, startPosition);
}
// 獲取當前狀態(車輛位置)
public Map<String, String> getCurrentState() {
return vehiclePositions;
}
// 執行動作(車輛移動到新位置)
public int executeAction(String vehicleId, String newPosition) {
if (graph.get(vehiclePositions.get(vehicleId)).containsKey(newPosition)) {
int distance = graph.get(vehiclePositions.get(vehicleId)).get(newPosition);
vehiclePositions.put(vehicleId, newPosition);
return distance;
}
return -1; // 無效動作
}
}
// 定義智能體類
class Agent {
private Environment environment;
private Map<String, Map<String, Double>> qTable; // Q表存儲狀態-動作值
private double learningRate;
private double discountFactor;
private double explorationRate;
public Agent(Environment environment, double learningRate, double discountFactor, double explorationRate) {
this.environment = environment;
this.learningRate = learningRate;
this.discountFactor = discountFactor;
this.explorationRate = explorationRate;
qTable = new HashMap<>();
}
// 初始化Q表
public void initializeQTable() {
for (String vehicle : environment.vehicles) {
qTable.put(vehicle, new HashMap<>());
for (String position : environment.graph.keySet()) {
qTable.get(vehicle).put(position, 0.0);
}
}
}
// 選擇動作
public String selectAction(String vehicleId) {
if (Math.random() < explorationRate) {
// 隨機選擇動作
List<String> possibleActions = new ArrayList<>(environment.graph.get(environment.getCurrentState().get(vehicleId)).keySet());
return possibleActions.get(new Random().nextInt(possibleActions.size()));
} else {
// 選擇Q值最大的動作
Map<String, Double> actions = qTable.get(vehicleId);
return Collections.max(actions.entrySet(), Map.Entry.comparingByValue()).getKey();
}
}
// 更新Q表
public void updateQTable(String vehicleId, String oldPosition, String newPosition, int reward) {
double oldQ = qTable.get(vehicleId).get(oldPosition);
double maxFutureQ = Collections.max(qTable.get(vehicleId).values());
double newQ = oldQ + learningRate * (reward + discountFactor * maxFutureQ - oldQ);
qTable.get(vehicleId).put(oldPosition, newQ);
}
// 訓練智能體
public void train(int episodes) {
for (int episode = 0; episode < episodes; episode++) {
for (String vehicle : environment.vehicles) {
String currentPosition = environment.getCurrentState().get(vehicle);
String action = selectAction(vehicle);
int reward = environment.executeAction(vehicle, action);
if (reward != -1) {
updateQTable(vehicle, currentPosition, action, -reward); // 距離越短獎勵越高
}
}
}
}
// 獲取最優路徑
public List<String> getOptimalPath(String vehicleId, String destination) {
List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
String currentPosition = environment.getCurrentState().get(vehicleId);
path.add(currentPosition);
while (!currentPosition.equals(destination)) {
currentPosition = Collections.max(qTable.get(vehicleId).entrySet(), Map.Entry.comparingByValue()).getKey();
path.add(currentPosition);
}
return path;
}
}
public class PathOptimizationWithRL {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Environment environment = new Environment();
// 添加交通網絡節點和邊
environment.addEdge("A", "B", 4);
environment.addEdge("A", "C", 2);
environment.addEdge("B", "C", 1);
environment.addEdge("B", "D", 5);
environment.addEdge("C", "D", 8);
// 添加車輛並初始化位置
environment.addVehicle("vehicle1", "A");
Agent agent = new Agent(environment, 0.1, 0.9, 0.2);
agent.initializeQTable();
agent.train(1000);
List<String> optimalPath = agent.getOptimalPath("vehicle1", "D");
System.out.println("最優路徑: " + optimalPath);
}
}
同時,通過以下詳細的流程圖展示強化學習在動態路徑優化中的運作邏輯:
四、真實案例剖析
4.1 京東物流智能調度與路徑優化實踐
京東物流在 "亞洲一號" 智能物流園區的實踐堪稱行業典範。藉助 Java 大數據技術,園區構建了一套高度智能化的物流調度系統。在 2023 年 "618" 購物節期間,面對單日超 3500 萬件的訂單洪峯,系統通過實時分析訂單數據、車輛位置、交通狀況等超過 200 個維度的數據,運用遺傳算法在毫秒級時間內完成全國 50000 + 運輸車輛的智能調度。
與傳統調度模式相比,智能調度系統使車輛利用率提升至 92%,平均配送時長縮短至 32 分鐘,客户滿意度達到 98.6%。同時,結合動態路徑優化技術,系統根據實時路況每 10 分鐘重新規劃一次路線,成功減少了 40% 的無效行駛里程。以下是具體數據對比:
| 指標 | 傳統模式 | 智能模式 | 提升幅度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 訂單處理量 | 1200 萬件 / 日 | 3500 萬件 / 日 | 191.7% |
| 車輛平均利用率 | 68% | 92% | 35.3% |
| 平均配送時長 | 55 分鐘 | 32 分鐘 | 41.8% |
| 客户滿意度 | 90.2% | 98.6% | 9.3 個百分點 |
4.2 順豐速運的智能物流轉型
順豐速運通過 Java 大數據技術構建的智慧物流大腦,實現了從收寄端到配送端的全鏈路智能化。在車輛調度方面,系統引入改進型遺傳算法,結合車輛能耗、司機工作時長等約束條件,實現了車輛資源的最優配置。數據顯示,該系統使順豐的車輛空駛率從 18% 降至 12%,每年節省燃油成本超 2.3 億元。
在路徑優化領域,順豐創新地將強化學習算法與實時交通數據相結合。在深圳 - 廣州的幹線運輸中,系統通過持續學習和優化,使單程運輸時間從平均 2.5 小時縮短至 2 小時,運輸效率提升 20%。同時,藉助 Flink 實時流處理技術,系統能夠在 1 分鐘內完成異常路況的響應和路徑調整,大大提升了運輸的可靠性和時效性。
結束語:
親愛的 Java 和 大數據愛好者們,從傳統物流的混沌無序,到智能物流的高效精準,Java 大數據以其強大的技術實力,為物流行業帶來了革命性的變化。它不僅解決了車輛調度和路徑優化的難題,更打開了智能物流發展的全新想象空間。
親愛的 Java 和 大數據愛好者,Java 大數據在智能物流領域的創新應用令人驚歎,你認為哪項技術最具發展潛力?歡迎在評論區分享您的寶貴經驗與見解。
為了讓後續內容更貼合大家的需求,誠邀各位參與投票,Java 大數據在智能物流領域的創新應用令人驚歎,你認為哪項技術最具發展潛力?快來投出你的寶貴一票 。
<span id = "csdntp">🗳️參與投票和聯繫我: </span>
<span id = "csdn">返回文章</span>