🧑💻 寫在開頭
點贊 + 收藏 === 學會🤣🤣🤣
我們知道,Next.js 最核心的特性便是 支持靜態生成(SSG)和服務端渲染(SSG),這也就意味着我們可以以部署 Node 服務的方式,將其部署在服務器上,用請求後端接口類似的形式來請求頁面文件。換句話説,我們其實可以直接把 Next.js 看成一個特殊的 Node 後端服務。
既然是在服務端進行運行,那麼它在數據庫的查詢方式上自然和一般的 SPA 客户端進行查詢有所區別。
我們先簡單分析一下一般 React SPA 項目的前後端交互:
- 前後端分離開發,後端無論用什麼語言編寫,最終只需要提供一個 API Endpoint(URL) 給前端。
- 前端二次封裝 axios,或者直接使用 fetch,自己手動封裝對應 URL 的異步請求函數,根據 API Endpoint 的不同依次進行封裝,並定義需要傳入的參數、方法等。
- 前端在需要調用接口的位置調用這些封裝好的接口函數獲取數據,展示頁面。
這樣是一套完整的前後端分離接口交互的編寫。很顯然,這樣的交互、從數據庫中拿數據的行為是以頁面為單位的,當用户重新在這個頁面上發生相同的交互行為時,對應的 HTTP 請求會 100%完整地復刻一遍。
而在 Next.js 中,基於其自身的特殊性,提供了一個與數據庫直接進行交互的特殊方式:Server Actions。
Server Actions 是?
Server Actions 直譯為 服務端行為,是 Next.js 中的一個特殊概念,用於在服務端直接進行數據庫查詢等操作,而不是在客户端進行異步請求。
下面貼一下官方的一些解釋:
React Server Actions allow you to run asynchronous code directly on the server. They eliminate the need to create API endpoints to mutate your data. Instead, you write asynchronous functions that execute on the server and can be invoked from your Client or Server Components.
React Server Actions 允許您直接在服務器上運行異步代碼。您無需創建 API 端點來更改數據。相反,您可以編寫在服務器上執行的異步函數,並可從客户端或服務器組件中調用。
Security is a top priority for web applications, as they can be vulnerable to various threats. This is where Server Actions come in. They offer an effective security solution, protecting against different types of attacks, securing your data, and ensuring authorized access. Server Actions achieve this through techniques like POST requests, encrypted closures, strict input checks, error message hashing, and host restrictions, all working together to significantly enhance your app's safety.
安全性是網絡應用程序的重中之重,因為它們很容易受到各種威脅。這就是服務器操作的用武之地。它們提供了一種有效的安全解決方案,可抵禦各種類型的攻擊、保護數據安全並確保授權訪問。Server Actions 通過 POST 請求、加密關閉、嚴格輸入檢查、錯誤信息散列和主機限制等技術來實現這一目標,所有這些技術共同作用,大大提高了應用程序的安全性。
因此簡單來説,所謂的 Server Actions 實際上就是一個在 Next.js 中的一個 普通異步函數,只不過這個異步函數可以直接操作數據庫而已。這個函數與 React Server Components 深度集成,可以看成是組件本身的一部分。
這個異步函數的執行單純在服務端進行,而 不以接口請求的形式獲取數據,因此 無法在網絡調試中看到接口的請求,可以理解為這個異步函數是在服務端直接執行的。
也正是因此,不將請求的數據暴露出來,能夠最大程度上保證數據的安全性。
Server Actions 還與 Next.js 緩存深度集成。通過其提交表單時,不僅可以使用該動作更改數據,還可以使用 revalidatePath 和 revalidateTag 等 Next API 刷新相關頁面的緩存,以確保在每次數據更新之後重新訪問該頁面時能夠獲取最新的數據。
與傳統 API 的比較
我們可以試着總結一下 Server Action 和傳統 API Endpoints 的優缺點:
Server Actions
優點:
-
簡化代碼結構
- 將處理邏輯和組件邏輯放在一起,減少代碼分散,提高可讀性。例如一般處理點擊按鈕觸發請求,我們可以直接往
onClick中傳遞 Server Action 異步函數即可,無需調用 API Endpoint。
- 將處理邏輯和組件邏輯放在一起,減少代碼分散,提高可讀性。例如一般處理點擊按鈕觸發請求,我們可以直接往
-
直接與組件交互
- Server Actions 直接在組件中調用,減少了不必要的中間層,簡化了數據流。
-
減少網絡請求
- 通過 Server Actions 直接在服務器上處理數據,不需要通過 HTTP 請求來獲取數據,減少了網絡延遲。
-
自動處理錯誤
- Server Actions 可以自動處理常見的錯誤,如網絡錯誤或數據庫連接錯誤,使得代碼更加健壯。
缺點:
-
難以複用
- 由於 Server Actions 緊密耦合在組件中,複用性較差,不如 API Endpoints 容易在多個組件或項目中共享。
-
測試難度大
- 測試 Server Actions 可能比測試 API Endpoints 更加複雜,因為它們嵌入在組件中,需要模擬更多的上下文。不過 Next 官方提供的 console 工具可以直接在 Chrome 的 Dev tool 裏面進行輸出。
-
可擴展性
- 當項目變大時,將所有邏輯放在組件中可能會導致代碼難以維護和擴展,需要提前組織好代碼的邏輯。
傳統 API Endpoints
優點:
-
鬆散耦合
- API Endpoints 將業務邏輯與前端組件分離,提高了代碼的模塊化和複用性。
-
易於測試
- API Endpoints 獨立於組件,便於進行單元測試和集成測試。可以與各類 API 測試工具相集成,適合前後端分離、大型團隊的合作開發。
-
靈活性
- 可以使用各種中間件和框架(如 Express, Koa 等)來擴展和處理複雜的邏輯。
-
可擴展性
- 更容易擴展和維護,適合大型應用程序的開發。
缺點:
-
額外的網絡開銷
- 每次數據請求都需要通過 HTTP 請求,增加了網絡延遲,尤其在高頻請求的情況下影響性能。需要使用防抖、節流等方式處理請求。
-
複雜性
- 需要額外的配置和設置來處理 API 請求和響應,增加了項目的複雜性。
-
代碼分散
- 數據處理邏輯與組件邏輯分開,可能導致代碼分散,降低可讀性。
適用場景
-
Server Actions
- 適合小型項目或簡單的數據交互場景。
- 當需要快速開發、減少代碼複雜性時,Server Actions 是一個不錯的選擇。
- 適用於處理簡單邏輯和不頻繁的數據操作。
-
API Endpoints
- 適合中大型項目或複雜的數據交互場景。
- 需要高複用性、易測試和可擴展性時,選擇 API Endpoints 更為合適。
- 適用於需要處理複雜業務邏輯、多端共享 API 的場景。
Server Action 實例
上面我們簡單討論了 Server Actions 的定義以及其與一般 API Endpoint 的區別,接下來我們看一個實際使用 Server Action 與數據庫進行交互的例子。
此處的例子來源於Next 官方教程,需要的同學可以去官網進行查閲。此處需要實現的目標是對數據庫 Invoices(發票)數據的 增、改、刪 ,也就是直接修改數據庫數據。
我們可以看一下具體的代碼,並對它進行解析:
"use server"; // Server Actions 只在服務端運行
import { z } from "zod";
import { sql } from "@vercel/postgres";
import { revalidatePath } from "next/cache";
import { redirect } from "next/navigation";
// zod 是一個用於驗證數據的庫,它可以幫助我們定義數據的結構,並驗證數據是否符合這個結構。
const FormSchema = z.object({
id: z.string(),
customerId: z.string(),
amount: z.coerce.number(), // coerce.number() 會將字符串轉換為數字
status: z.enum(["pending", "paid"]),
date: z.string(),
});
const CreateInvoice = FormSchema.omit({ id: true, date: true });
export async function createInvoice(formData: FormData) {
// CreateInvoice.parse 方法用於驗證 formData 中的數據是否符合 CreateInvoice 的結構
const { customerId, amount, status } = CreateInvoice.parse({
customerId: formData.get("customerId"),
amount: formData.get("amount"),
status: formData.get("status"),
});
const amountInCents = amount * 100;
const date = new Date().toISOString().split("T")[0]; // 獲取當前日期:YYYY-MM-DD
await sql`
INSERT INTO invoices (customer_id, amount, status, date)
VALUES (${customerId}, ${amountInCents}, ${status}, ${date})
`;
revalidatePath("/dashboard/invoices"); // revalidatePath 的作用是重新生成指定路由的頁面,以便在下次訪問時顯示最新數據
redirect("/dashboard/invoices"); // 重定向
}
const UpdateInvoice = FormSchema.omit({ id: true, date: true });
export const updateInvoice = async (id: string, formData: FormData) => {
const { customerId, amount, status } = UpdateInvoice.parse({
customerId: formData.get("customerId"),
amount: formData.get("amount"),
status: formData.get("status"),
});
const amountInCents = amount * 100; // 將金額轉換為分
await sql`
UPDATE invoices
SET customer_id = ${customerId}, amount = ${amountInCents}, status = ${status}
WHERE id = ${id}
`;
revalidatePath("/dashboard/invoices"); // 重新生成指定路由的頁面
redirect("/dashboard/invoices"); // 重定向
};
export const deleteInvoice = async (id: string) => {
await sql`DELETE FROM invoices WHERE id = ${id}`;
revalidatePath("/dashboard/invoices");
};
這段代碼是一個完整的 actions.ts 文件。對相同對象的數據庫操作可以用單獨的文件進行存放。
首先我們看一下導入。這裏使用了 zod 庫用於 TS 數據驗證,@vercel/postgres 用於數據庫操作,next/cache 和 next/navigation 用於緩存和導航控制。定義了一個 FormSchema 來驗證發票表單數據的結構。
const CreateInvoice = FormSchema.omit({ id: true, date: true });
CreateInvoice 是一個從 FormSchema 中去除 id 和 date 字段的驗證器,用於創建發票時的數據驗證。
export async function createInvoice(formData: FormData) {
// CreateInvoice.parse 方法用於驗證 formData 中的數據是否符合 CreateInvoice 的結構
const { customerId, amount, status } = CreateInvoice.parse({
customerId: formData.get("customerId"),
amount: formData.get("amount"),
status: formData.get("status"),
});
const amountInCents = amount * 100;
const date = new Date().toISOString().split("T")[0]; // 獲取當前日期:YYYY-MM-DD
await sql`
INSERT INTO invoices (customer_id, amount, status, date)
VALUES (${customerId}, ${amountInCents}, ${status}, ${date})
`;
revalidatePath("/dashboard/invoices"); // 重新生成指定路由的頁面
redirect("/dashboard/invoices"); // 重定向
}
createInvoice 函數處理髮票創建:
- 從
formData獲取並驗證數據。 - 將金額轉換為分(cents)。
- 獲取當前日期。
- 使用 SQL 插入語句將數據插入數據庫。
- 使用
revalidatePath重新生成/dashboard/invoices路由的頁面,以便顯示最新數據。 - 使用
redirect重定向到/dashboard/invoices。
其餘兩函數對 Invoice 的操作大同小異,三個函數分別實現了增、改、刪的操作。
那麼,對應具體該怎麼在組件中使用 Server Actions 呢?
我們對應的來看一下提交表單的內容:
import { CustomerField } from "@/app/lib/definitions";
import Link from "next/link";
import {
CheckIcon,
ClockIcon,
CurrencyDollarIcon,
UserCircleIcon,
} from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
import { Button } from "@/app/ui/button";
import { createInvoice } from "@/app/lib/actions";
export default function Form({ customers }: { customers: CustomerField[] }) {
return (
<form action={createInvoice}>
{/* ~此處省略表單的具體內容~ */}
<div className="mt-6 flex justify-end gap-4">
<Link
href="/dashboard/invoices"
className="flex h-10 items-center rounded-lg bg-gray-100 px-4 text-sm font-medium text-gray-600 transition-colors hover:bg-gray-200"
>
Cancel
</Link>
{/* 在 form 標籤內部,使用 type="submit" 的 button 標籤會觸發表單的提交事件。*/}
<Button type="submit">Create Invoice</Button>
</div>
</form>
);
}
此處的 createInvoice 函數就是上述分析過的函數。可以看到,此處的創建表單單純使用 <form> 元素配合 <button type="submit"> 進行表單提交,通過 action 屬性將表單數據傳給對應的位置。
但是我們知道,form 的 action 屬性一般只能接受一個 url 字符串表示傳給後端的地址,後端通過這個地址來接收表單數據進行相應的處理,而此處卻傳遞了一個函數。
在 Next.js 中,對 <form> 的 action 屬性進行了特殊處理,使其可以接受一個字符串或一個函數。如果使用純 React,action 一般只接受一個字符串,也就是提交表單的 URL。
在 Next.js 中,如果 action 被傳遞為一個函數,那麼這個函數可以自動接收 FormData 類型的對象並被調用,之後就自動的走 zod 驗證流程、提出數據,使用 SQL 插入到數據庫中。
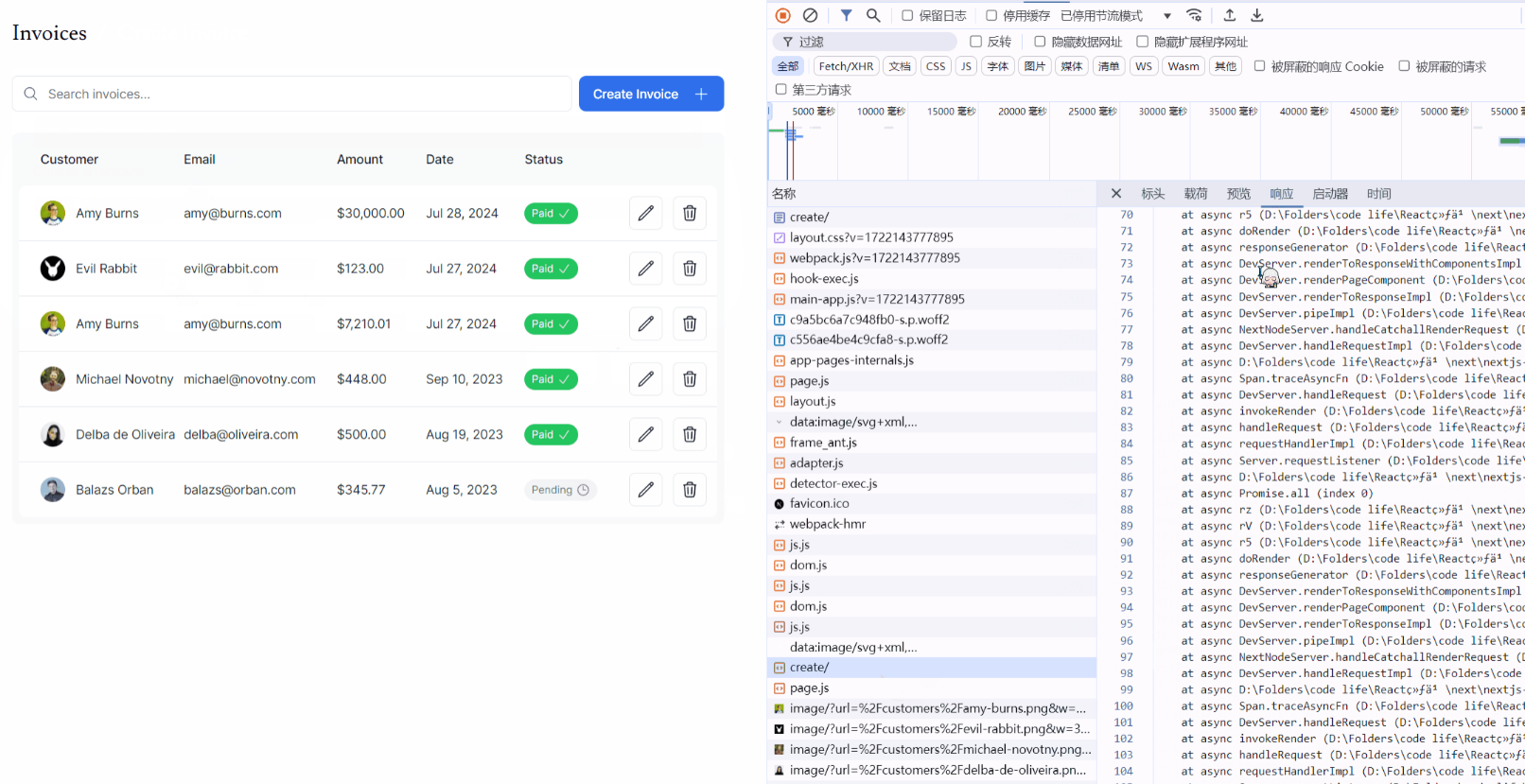
最終實現的請求效果如下圖所示:
可見,具體的請求、返回數據都和原本的 API 調用方法有所區別。
對應的,我們來看看更新 Invoice 的調用代碼:
"use client";
import { CustomerField, InvoiceForm } from "@/app/lib/definitions";
import {
CheckIcon,
ClockIcon,
CurrencyDollarIcon,
UserCircleIcon,
} from "@heroicons/react/24/outline";
import Link from "next/link";
import { Button } from "@/app/ui/button";
import { updateInvoice } from "@/app/lib/actions";
export default function EditInvoiceForm({
invoice,
customers,
}: {
invoice: InvoiceForm;
customers: CustomerField[];
}) {
const updateInvoiceWithId = updateInvoice.bind(null, invoice.id);
return (
<form action={updateInvoiceWithId}>
<div className="rounded-md bg-gray-50 p-4 md:p-6">
{/* Customer Name */}
<div className="mb-4">
<label htmlFor="customer" className="mb-2 block text-sm font-medium">
Choose customer
</label>
<div className="relative">
<select
id="customer"
name="customerId"
className="peer block w-full cursor-pointer rounded-md border border-gray-200 py-2 pl-10 text-sm outline-2 placeholder:text-gray-500"
defaultValue={invoice.customer_id}
>
<option value="" disabled>
Select a customer
</option>
{customers.map((customer) => (
<option key={customer.id} value={customer.id}>
{customer.name}
</option>
))}
</select>
<UserCircleIcon className="pointer-events-none absolute left-3 top-1/2 h-[18px] w-[18px] -translate-y-1/2 text-gray-500" />
</div>
</div>
{/* Invoice Amount */}
<div className="mb-4">
<label htmlFor="amount" className="mb-2 block text-sm font-medium">
Choose an amount
</label>
<div className="relative mt-2 rounded-md">
<div className="relative">
<input
id="amount"
name="amount"
type="number"
step="0.01"
defaultValue={invoice.amount}
placeholder="Enter USD amount"
className="peer block w-full rounded-md border border-gray-200 py-2 pl-10 text-sm outline-2 placeholder:text-gray-500"
/>
<CurrencyDollarIcon className="pointer-events-none absolute left-3 top-1/2 h-[18px] w-[18px] -translate-y-1/2 text-gray-500 peer-focus:text-gray-900" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
{/* Invoice Status */}
<fieldset>
<legend className="mb-2 block text-sm font-medium">
Set the invoice status
</legend>
<div className="rounded-md border border-gray-200 bg-white px-[14px] py-3">
<div className="flex gap-4">
<div className="flex items-center">
<input
id="pending"
name="status"
type="radio"
value="pending"
defaultChecked={invoice.status === "pending"}
className="h-4 w-4 cursor-pointer border-gray-300 bg-gray-100 text-gray-600 focus:ring-2"
/>
<label
htmlFor="pending"
className="ml-2 flex cursor-pointer items-center gap-1.5 rounded-full bg-gray-100 px-3 py-1.5 text-xs font-medium text-gray-600"
>
Pending <ClockIcon className="h-4 w-4" />
</label>
</div>
<div className="flex items-center">
<input
id="paid"
name="status"
type="radio"
value="paid"
defaultChecked={invoice.status === "paid"}
className="h-4 w-4 cursor-pointer border-gray-300 bg-gray-100 text-gray-600 focus:ring-2"
/>
<label
htmlFor="paid"
className="ml-2 flex cursor-pointer items-center gap-1.5 rounded-full bg-green-500 px-3 py-1.5 text-xs font-medium text-white"
>
Paid <CheckIcon className="h-4 w-4" />
</label>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</fieldset>
</div>
<div className="mt-6 flex justify-end gap-4">
<Link
href="/dashboard/invoices"
className="flex h-10 items-center rounded-lg bg-gray-100 px-4 text-sm font-medium text-gray-600 transition-colors hover:bg-gray-200"
>
Cancel
</Link>
<Button type="submit">Edit Invoice</Button>
</div>
</form>
);
}
可以看到,具體的邏輯和上面的例子幾乎一模一樣,主要的差別在於這個例子傳給 action 的函數是用原本的 updateInvoice 通過 bind() 方法重新創建的,並且附帶了一個初始參數:invoice.id 。
此處為什麼需要 bind?
上述我們已經分析過了,Next 對 <form> 的 action 屬性進行了特殊處理,使其能夠接收一個以 FormData 為類型的對象為入參的函數。FormData 的數據是通過解析 <form> 標籤內部的所有 <input>、<select>、<textarea> 等元素的值,通過 name 屬性來構建 FormData 對象。
但是我們查看上面表單的具體內容,發現只有三個屬性:customerId、amount、status,而如果需要更新 invoice,我們還需要傳遞一個其原本的 id。那麼這個時候,就可以通過 bind 來傳遞額外的參數,此處是將 invoice.id 當作第一個參數傳遞給 updateInvoice 函數,使其能夠正常接收。
總結一下?
此處只是單純的將 Server Actions 的使用以及本質稍微進行了解析,並附上使用場景。雖然它很有用,但是 個人認為,如果是想維護一個大型的、規範的、涉及到很多與數據庫複雜交互的應用時,還是採用 API Endpoints 更符合開發者的直覺。並且 API Endpoints 容易測試,使用 Server Actions 需要額外自己創建一個場景出來,自己實際進行操作才能夠進行測試與調試,相對比較繁瑣。