1. Polygon 是什麼?能用來幹嘛?
Polygon 是 ArkUI 圖形繪製能力裏的 多邊形繪製組件,可以在一個給定的矩形區域內,根據一組點座標,繪製任意多邊形輪廓,並支持:
- 填充顏色 / 透明度;
- 描邊顏色 / 粗細 / 虛線 / 拐角樣式;
- 抗鋸齒控制;
attributeModifier動態修改屬性(API 18+),updateConstructorParams(API 20+)。
典型使用場景:
- 自定義圖表元素(雷達圖、多邊形圖例、熱點區域);
- UI 裝飾圖形(角標、多邊形標籤、波浪塊、菱形背景);
- 遊戲 / 可視化裏簡單幾何圖形的快速繪製;
- 配合手勢實現自定義選區(多邊形區域選中高亮等)。
基礎信息:
- 組件名:
Polygon - 子組件:無(它只負責畫圖,不是容器)
-
支持版本:
- 從 API 7 開始支持;
- 卡片能力:API 9+;
- 元服務 API:API 11+;
PolygonOptions標準化:API 18+;AttributeUpdater.updateConstructorParams:API 20+。
2. 快速上手:三角形 / 矩形 / 五邊形
先用最短的代碼跑起來,感受一下 Polygon 的基本用法。
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct PolygonQuickStart {
build() {
Column({ space: 16 }) {
// 1. 在 100 * 100 的區域裏畫一個三角形
Polygon({ width: 100, height: 100 })
.points([[0, 0], [50, 100], [100, 0]])
.fill(Color.Green)
// 2. 只描邊的矩形(中間透明)
Polygon()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.points([[0, 0], [0, 100], [100, 100], [100, 0]])
.fillOpacity(0) // 填充透明
.strokeWidth(5)
.stroke(Color.Blue) // 只有邊框
// 3. 半透明填充的五邊形
Polygon({ width: 100, height: 100 })
.points([[50, 0], [0, 50], [20, 100], [80, 100], [100, 50]])
.fill(Color.Red)
.fillOpacity(0.6)
}
.width('100%')
.margin({ top: 16 })
}
}這裏你已經看到 Polygon 的幾個核心元素:
- 創建時可以給
width/height(也可以後面.width()/.height()設); - 用
points提供一組二維座標,系統會自動把最後一點和第一點連起來; - 用
fill/fillOpacity控制填充,用stroke相關屬性控制邊框。
3. 構造函數 & PolygonOptions
3.1 構造函數
Polygon(options?: PolygonOptions)options可以不傳:Polygon();- 傳的話一般用來給
width/height賦初值。
3.2 PolygonOptions 關鍵字段
從 API 18 開始,PolygonOptions 規範成對象形式,常用的就是這倆:
interface PolygonOptions {
width?: Length // ≥ 0,默認 0,單位 vp
height?: Length // ≥ 0,默認 0,單位 vp
}注意點:
- 默認
width = 0,height = 0→ 圖形是看不見的; -
Length既可以是number也可以是string或資源:100、'100'、$r('app.string.xxx')都可以;
- 異常值(
undefined/null/NaN/Infinity)會退回默認值 0。
小習慣:
一般我會直接寫Polygon({ width: 120, height: 80 }),
或者用.width('80%')這類相對佈局方式配合父容器控制。
4. 核心屬性速查
Polygon 支持通用屬性(寬高、對齊、偏移等),這裏重點説圖形相關的專有屬性。
4.1 points:頂點座標列表
.points(value: Array<any>)- 必填,用一個二維數組傳入;
- 每個子數組是一個點的
[x, y]座標; - 座標單位默認 vp,以 Polygon 自己的寬高為座標空間基準;
- 默認值是
[](空數組,啥都不畫)。
示例:
Polygon({ width: 100, height: 100 })
.points([[0, 0], [50, 100], [100, 0]]) // 三角形技巧:
- 不需要手動重複起點,系統會自動閉合最後一點和第一點;
- 點的順序決定多邊形的形狀,順時針 / 逆時針都可以,但亂序會畫出「自交」多邊形,看起來很怪。
4.2 fill / fillOpacity:填充顏色 & 透明度
.fill(value: ResourceColor)
.fillOpacity(value: number | string | Resource)-
fill:填充區域顏色- 默認:
Color.Black; - 異常值(
undefined/null/NaN/Infinity)回退到默認。
- 默認:
-
fillOpacity:填充透明度- 取值範圍
[0.0, 1.0]; - number/字符串/資源都可以;
- 默認:
1.0(不透明)。
- 取值範圍
數值處理規則:
< 0→ 0;> 1→ 1;NaN→ 0;undefined/null/Infinity→ 1。
注意:
同時設置了fill和通用屬性foregroundColor時,後設置的屬性生效。
4.3 stroke / strokeWidth / strokeOpacity:邊框樣式
.stroke(value: ResourceColor)
.strokeWidth(value: Length)
.strokeOpacity(value: number | string | Resource)- 不設置
stroke時,默認透明度為 0 → 看不到邊框; - 建議:只要想看見邊框,就顯式設置
stroke和strokeWidth。
要點:
-
strokeWidth:- 默認
1vp; - ≥ 0,異常值回退默認,
Infinity視為 0;
- 默認
-
strokeOpacity:- 範圍
[0.0, 1.0],同fillOpacity規則; - 默認繼承
stroke設置的透明度。
- 範圍
4.4 strokeDashArray / strokeDashOffset:虛線邊框
.strokeDashArray(value: Array<any>)
.strokeDashOffset(value: number | string)strokeDashArray定義虛線「線段長 / 間隙長」模式;- 單位是 vp;
- 默認
[]→ 實線。
數組規則:
- 空數組:實線;
-
偶數長度:按
[a, b, c, d]循環:- 線段 a → 間隙 b → 線段 c → 間隙 d → 再重複;
-
奇數長度:會自動拼接一次自己再按偶數規則:
[a, b, c]==[a, b, c, a, b, c]。
strokeDashOffset 用來指定「從哪裏開始畫這段虛線」,可以做滾動 / 動畫效果:
Polygon()
.strokeDashArray([10, 5])
.strokeDashOffset(5) // 起點向前偏移 5注意:
strokeDashOffset異常值按默認 0 處理;- 若為
NaN/Infinity,會導致strokeDashArray失效(退成實線)。
4.5 strokeLineCap / strokeLineJoin / strokeMiterLimit
.strokeLineCap(value: LineCapStyle)
.strokeLineJoin(value: LineJoinStyle)
.strokeMiterLimit(value: number | string)-
strokeLineCap:邊框端點樣式- 枚舉
LineCapStyle,常用Butt/Round/Square; - 默認:
LineCapStyle.Butt。
- 枚舉
-
strokeLineJoin:拐角的連接方式- 枚舉
LineJoinStyle,常用Miter/Round/Bevel; - 默認:
LineJoinStyle.Miter。
- 枚舉
-
strokeMiterLimit:- 用在
LineJoinStyle.Miter時,控制斜接長度和線寬的比值; - 合法值應 ≥ 1.0;
[0,1)按 1.0 處理;- 其他異常值按默認 4 處理;
Infinity會導致stroke失效。
- 用在
設計建議:
- UI 比較圓潤:可以用
strokeLineJoin(LineJoinStyle.Round); - 多邊形鋭角很多時,慎用無限制的
Miter,否則有長「尖刺」。
4.6 antiAlias:是否開啓抗鋸齒
.antiAlias(value: boolean)- 默認:
true(推薦保持開啓); - 關閉後繪製性能略好,但邊緣會有明顯鋸齒,一般不建議在 UI 場景關閉;
- 異常值按默認值處理。
5. 實戰示例:把 Polygon 用到真實界面裏
下面幾個例子會更貼近實際場景,而不是純幾何圖像。
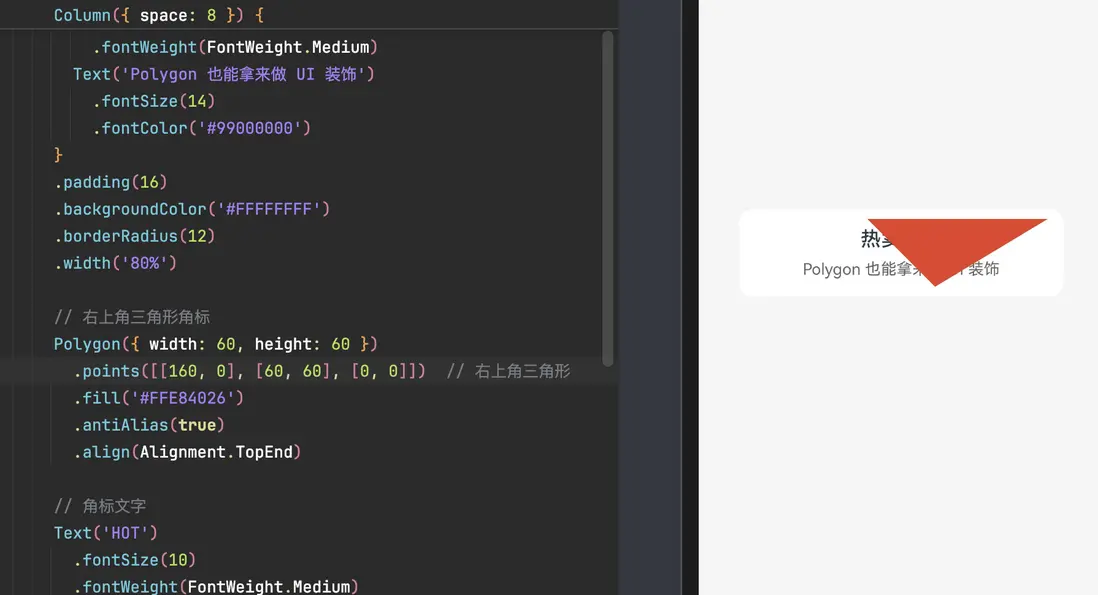
5.1 繪製一個角標 / Tag 多邊形
做一個右上角的「標籤」角標,用 Polygon 畫一個三角形疊在容器上。
@Entry
@Component
struct CornerTagExample {
build() {
Stack() {
// 主內容卡片
Column({ space: 8 }) {
Text('熱賣商品')
.fontSize(18)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
Text('Polygon 也能拿來做 UI 裝飾')
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor('#99000000')
}
.padding(16)
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFFFF')
.borderRadius(12)
.width('80%')
// 右上角三角形角標
Polygon({ width: 60, height: 60 })
.points([[60, 0], [60, 60], [0, 0]]) // 右上角三角形
.fill('#FFE84026')
.antiAlias(true)
.align(Alignment.TopEnd)
// 角標文字
Text('HOT')
.fontSize(10)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
.fontColor(Color.White)
.rotate({ angle: 45 }) // 簡單旋轉一點
.align(Alignment.TopEnd)
.margin({ top: 8, right: 4 })
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#FFF5F5F5')
.align(Alignment.Center)
}
}這個例子説明:
- Polygon 也可以作為 視覺元素 疊加在佈局之上;
- 配合
Stack和對齊屬性,很容易做角標 / 波浪背景 / 裁切效果。
5.2 不同類型 Length:number / string / Resource
@Entry
@Component
struct PolygonLengthTypeExample {
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
// 1. string 類型('100')
Polygon({ width: '100', height: '100' })
.points([[0, 0], [50, 100], [100, 0]])
.fill('#FF64BB5C')
// 2. number 類型(100)
Polygon({ width: 100, height: 100 })
.points([[0, 0], [0, 100], [100, 100], [100, 0]])
.fillOpacity(0)
.strokeWidth(5)
.stroke(Color.Blue)
// 3. Resource 類型(需自行在資源中定義寬高字符串)
Polygon({
width: $r('app.string.PolygonWidth'),
height: $r('app.string.PolygonHeight')
})
.points([[50, 0], [0, 50], [20, 100], [80, 100], [100, 50]])
.fill(Color.Red)
.fillOpacity(0.6)
}
.width('100%')
.margin({ top: 10 })
}
}如果你團隊習慣把尺寸統一放到資源配置,這種寫法就比較自然。
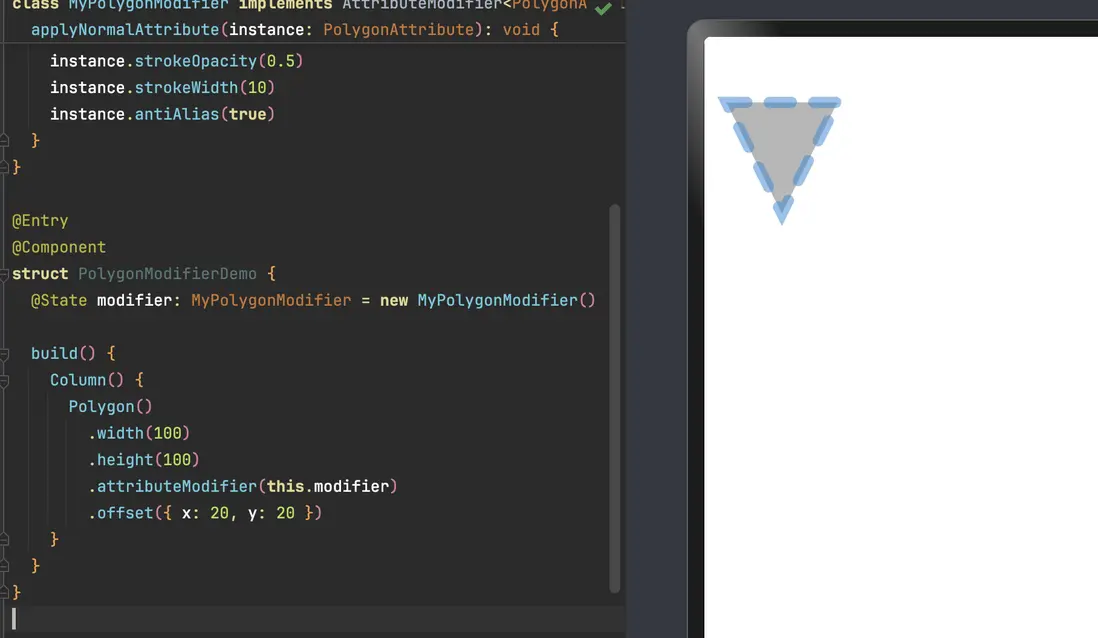
5.3 使用 attributeModifier 動態修改 Polygon 屬性(進階)
attributeModifier 可以一次性集中修改多個繪製屬性,在做主題切換 / 動畫時很好用。
// xxx.ets
class MyPolygonModifier implements AttributeModifier<PolygonAttribute> {
applyNormalAttribute(instance: PolygonAttribute): void {
// 這裏可以把所有「繪製相關」的邏輯集中起來
instance.points([[0, 0], [50, 100], [100, 0]])
instance.fill('#707070')
instance.fillOpacity(0.5)
instance.stroke('#2787D9')
instance.strokeDashArray([20])
instance.strokeDashOffset('15')
instance.strokeLineCap(LineCapStyle.Round)
instance.strokeLineJoin(LineJoinStyle.Miter)
instance.strokeMiterLimit(5)
instance.strokeOpacity(0.5)
instance.strokeWidth(10)
instance.antiAlias(true)
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct PolygonModifierDemo {
@State modifier: MyPolygonModifier = new MyPolygonModifier()
build() {
Column() {
Polygon()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.attributeModifier(this.modifier)
.offset({ x: 20, y: 20 })
}
}
}優勢:
- 把複雜的樣式組合統一收口到一個類裏,組件樹更乾淨;
- 後續如果要做按主題切換 / 配色調整,只需要換
modifier實例即可。
6. 常見坑 & 調試建議
-
width / height 默認為 0,看不到圖形
- 一旦忘了設置寬高,Polygon 就是「隱身」的;
- 建議統一在構造參數裏寫上寬高或使用百分比佈局。
-
points 為空或順序亂了
[]→ 不會畫任何東西;- 點的順序亂排會導致形狀自交,視覺上看起來像 bug。
-
fillOpacity / strokeOpacity 數值超範圍
<0會被夾到 0,>1會被夾到 1;- 配合設計稿調試時,不要驚訝「怎麼透明度調不動了」。
-
虛線設置失效
strokeDashArray中有非法值 /strokeDashOffset為NaN/Infinity時,會退成實線;- 調試時可以先只用
[10, 5]這類簡單數組確認虛線能否正常出現。
-
strokeMiterLimit 亂設
- 在拐角角度很尖的時候,如果
LineJoinStyle.Miter且strokeMiterLimit很大,會產生極長的尖角; - UI 上通常通過改成
Round或調小strokeWidth來避免。
- 在拐角角度很尖的時候,如果
-
抗鋸齒關閉導致邊緣很糙
- 一般情況下保持
.antiAlias(true)就好; - 真的性能吃緊再考慮關。
- 一般情況下保持
到這裏,你基本已經掌握了 Polygon 的「正確打開方式」。
後續可以考慮配合 Path、Polyline、Circle 等其它圖形組件,做一些更完整的自定義圖表 / 卡片背景 / 裝飾 UI,Polygon 在其中是非常好用的一塊「幾何積木」。