1. 前言
大家好,我是若川,歡迎關注我的公眾號:若川視野。我傾力持續組織了 3 年多每週大家一起學習 200 行左右的源碼共讀活動,感興趣的可以點此掃碼加我微信 ruochuan02 參與。另外,想學源碼,極力推薦關注我寫的專欄《學習源碼整體架構系列》,目前是掘金關注人數(6k+人)第一的專欄,寫有幾十篇源碼文章。
截至目前(2024-07-17),taro 正式版是 3.6.34,Taro 4.0 Beta 發佈:支持開發鴻蒙應用、小程序編譯模式、Vite 編譯等。文章提到將於 2024 年第二季度,發佈 4.x。目前已經發布 4.x。所以我們直接學習 main 分支最新版本是 4.0.2。
多編譯內核生態下的極速研發體驗 官方博客有如下圖。
計劃寫一個 Taro 源碼揭秘系列,博客地址:https://ruochuan12.github.io/taro 可以加入書籤,持續關注若川。
- [x] 1. 揭開整個架構的入口 CLI => taro init 初始化項目的秘密
- [x] 2. 揭開整個架構的插件系統的秘密
- [x] 3. 每次創建新的 taro 項目(taro init)的背後原理是什麼
- [x] 4. 每次 npm run dev:weapp 開發小程序,build 編譯打包是如何實現的?
- [x] 5. 高手都在用的發佈訂閲機制 Events 在 Taro 中是如何實現的?
- [x] 6. 為什麼通過 Taro.xxx 能調用各個小程序平台的 API,如何設計實現的?
- [x] 7. Taro.request 和請求響應攔截器是如何實現的
- [x] 8. Taro 是如何使用 webpack 打包構建小程序的?
- [x] 9. Taro 是如何生成 webpack 配置進行構建小程序的?
- [ ] 等等
學完本文,你將學到:
1. 學會通過兩種方式調試 taro 源碼
2. 學會入口 taro-cli 具體實現方式
3. 學會 cli init 命令實現原理,讀取用户項目配置文件和用户全局配置文件
4. 學會 taro-service kernal (內核)解耦實現
5. 初步學會 taro 插件架構,學會如何編寫一個 taro 插件2. 準備工作
# 克隆項目
git clone https://github.com/NervJS/taro.git
# 切換到分支 main
git checkout main
# 寫文章時,項目當前 hash
git checkout f53250b68f007310bf098e77c6113e2012983e82
# Merge branch 'main' into 4.x
# 寫文章時,當前版本
# 4.0.2看一個開源項目,第一步應該是先看 README.md 再看 貢獻文檔 和 package.json。
環境準備
需要安裝 Node.js 16(建議安裝 16.20.0 及以上版本)及 pnpm 7
我使用的環境:mac,當然 Windows 一樣可以。
一般用 nvm 管理 node 版本。
nvm install 18
nvm use 18
# 可以把 node 默認版本設置為 18,調試時會使用默認版本
nvm alias default 18
pnpm -v
# 9.1.1
node -v
# v18.20.2
cd taro
# 安裝依賴
pnpm i
# 如果網絡不好,一直安裝不上可以指定國內鏡像站,速度比較快
pnpm i --registry=https://registry.npmmirror.com
# 編譯構建
pnpm build# 刪除根目錄的 node_modules 和所有 workspace 裏的 node_modules
$ pnpm run clear-all
# 對應的是:rimraf **/node_modules
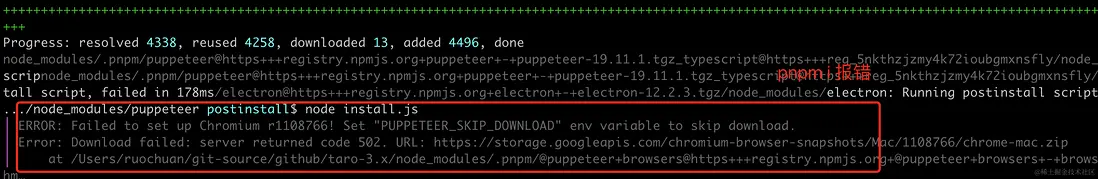
# mac 下可以用 rm -rf **/node_modules安裝依賴可能會報錯。
Failed to set up Chromium r1108766! Set "PUPPETEER_SKIP_DOWNLOAD" env variable to skip download.通過谷歌等搜索引擎可以找到解決方法。
stackoverflow
Mac : export PUPPETEER_SKIP_DOWNLOAD='true'
Windows: SET PUPPETEER_SKIP_DOWNLOAD='true'
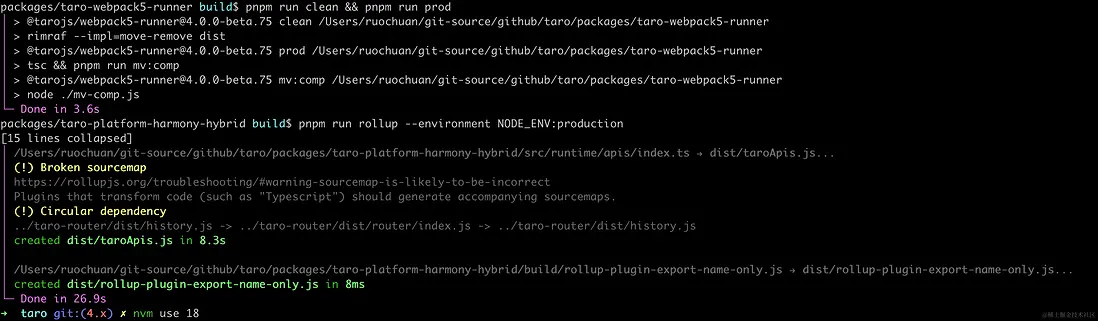
pnpm build 完成,如下圖所示:
3. 調試
package.json
// packages/taro-cli/package.json
{
"name": "@tarojs/cli",
"version": "4.0.0",
"description": "cli tool for taro",
"main": "index.js",
"types": "dist/index.d.ts",
"bin": {
"taro": "bin/taro"
}
}3.1 入口文件 packages/taro-cli/bin/taro
// packages/taro-cli/bin/taro
#! /usr/bin/env node
require("../dist/util").printPkgVersion();
const CLI = require("../dist/cli").default;
new CLI().run();3.2 調試方法 1 JavaScript Debug Terminal
可參考我的文章新手向:前端程序員必學基本技能——調試 JS 代碼,或者據説 90%的人不知道可以用測試用例(Vitest)調試開源項目(Vue3) 源碼
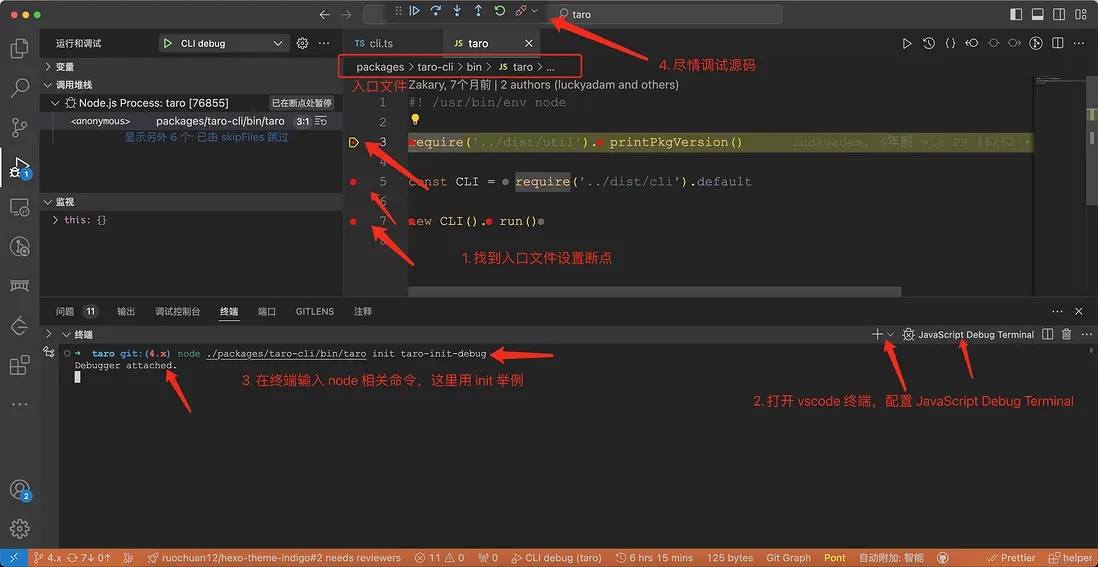
簡而言之就是以下步驟:
1. 找到入口文件設置斷點
2. ctrl + `\`` (反引號) 打開終端,配置`JavaScript調試終端`
3. 在終端輸入 `node` 相關命令,這裏用 `init` 舉例
4. 盡情調試源碼node ./packages/taro-cli/bin/taro init taro-init-debug本文將都是使用 init 命令作為示例。
如下圖所示:
也可以使用項目中提供的測試用例 packages/taro-cli/src/__tests__/cli.spec.ts 提前打斷點調試源碼。貢獻文檔-單元測試中有提到:
package.json中設置了test:ci命令的子包都配備了單元測試。
開發者在修改這些包後,請運行pnpm --filter [package-name] run test:ci,檢查測試用例是否都能通過。
# JavaScript Debug Terminal
pnpm --filter @tarojs/cli run test:ci調試和上圖類似,就不截調試圖了。
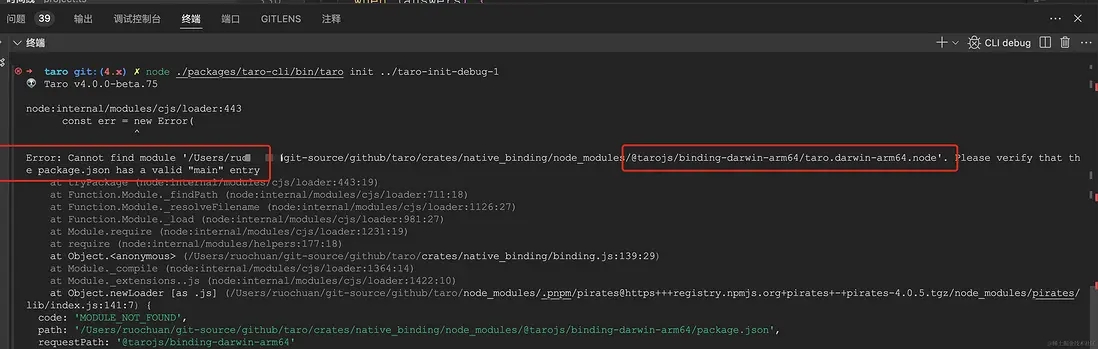
調試時應該會報錯 binding taro.[os-platform].node。如下圖所示:
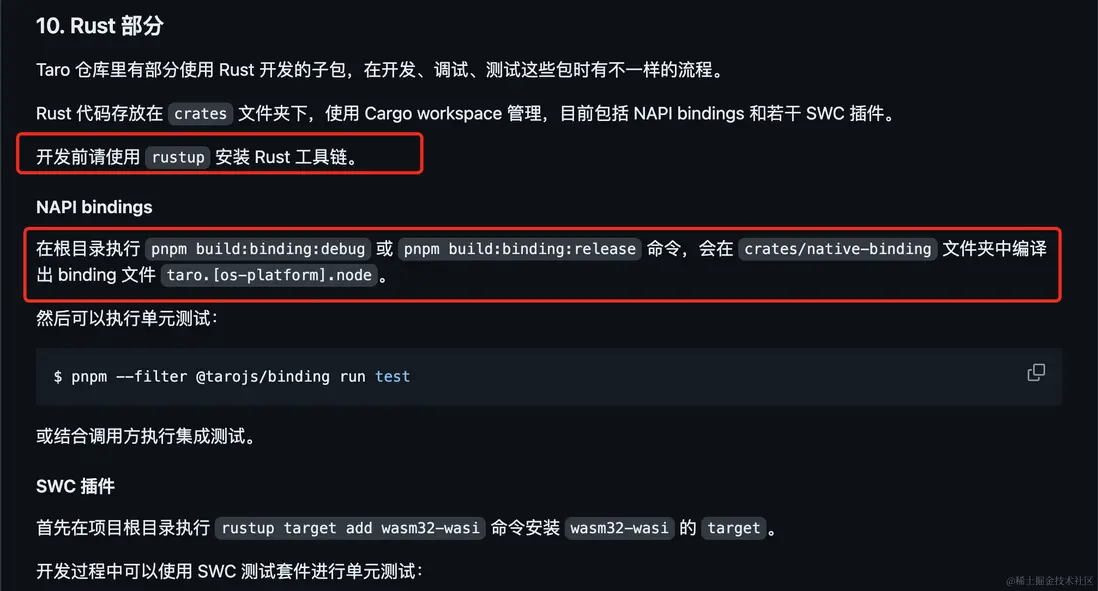
運行等過程報錯,不要慌。可能是我們遺漏了一些細節,貢獻文檔等應該會給出答案。所以再來看下 貢獻文檔-10-rust-部分
通過 rustup 找到安裝命令:
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh安裝完成後,執行 pnpm run build:binding:debug 或 pnpm run binding:release 編譯出文件:crates/native_binding/taro.darwin-arm64.node。
就完美解決了,調試時不會報錯了。
3.3 調試方式 2 配置 .vscode/launch.json
taro 文檔 - 單步調測配置
寫的挺好的,通過配置 launch.json 來調試,在此就不再贅述了。
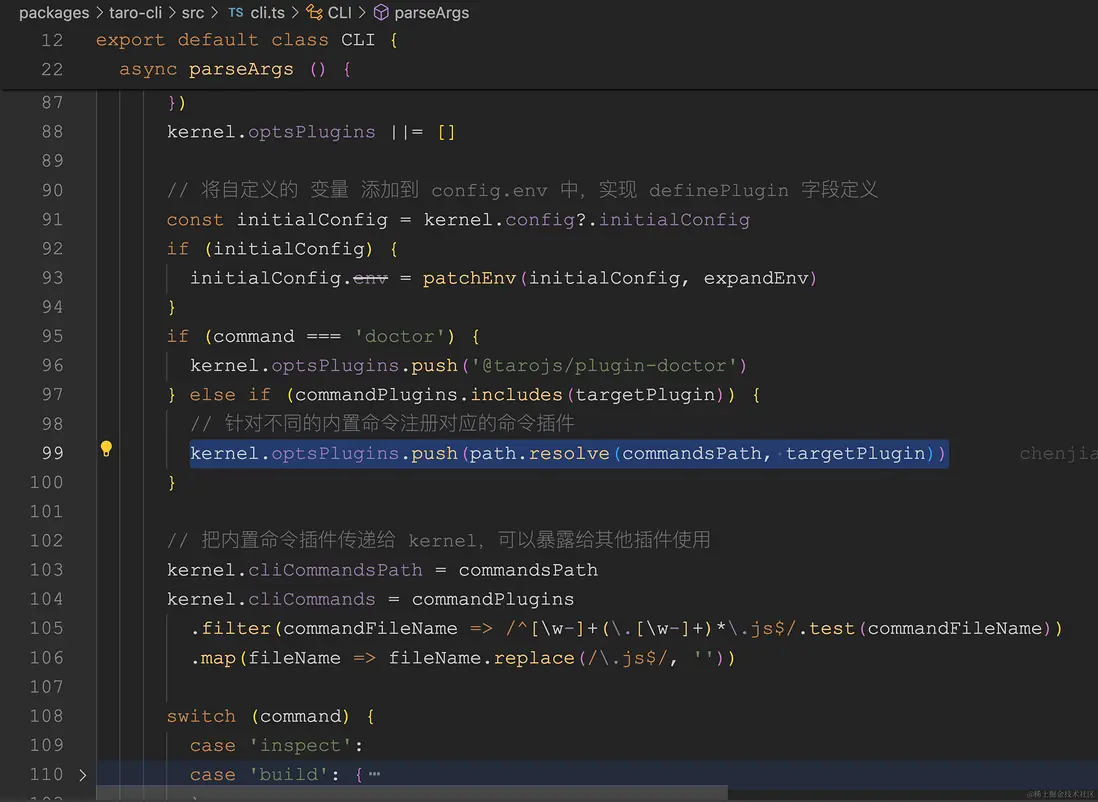
不過補充一條:launch.json 文件可以添加一條 "console": "integratedTerminal"(集成終端)配置,就可以在調試終端輸入內容。args 參數添加 init 和指定要初始化項目的文件夾。當然調試其他的時候也可以修改為其他參數。比如args: ["build", "--type", "weapp", "--watch"]。
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "node",
"request": "launch",
"name": "CLI debug",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/packages/taro-cli/bin/taro",
// "cwd": "${project absolute path}",
"args": [
"init",
"taro-init-debug",
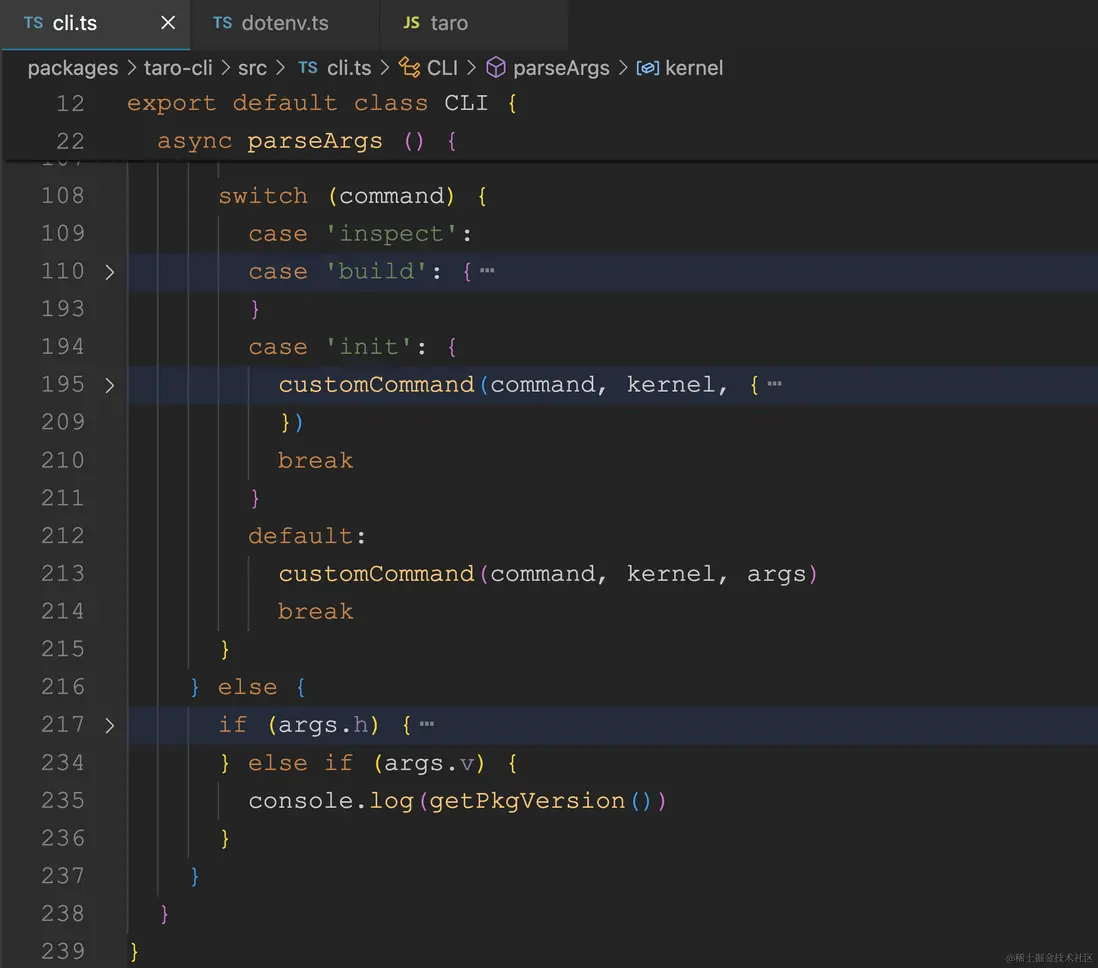
],
"skipFiles": ["<node_internals>/**"],
"console": "integratedTerminal"
}
]
}vscode nodejs 調試
console- 啓動程序的控制枱(internalConsole,integratedTerminal,externalTerminal)。
// packages/taro-cli/bin/taro
#! /usr/bin/env node
require("../dist/util").printPkgVersion();
const CLI = require("../dist/cli").default;
new CLI().run();我們跟着斷點進入,入口文件中的第一句require("../dist/util").printPkgVersion(); printPkgVersion 函數。
4. taro-cli/src/utils/index.ts
工具函數
// packages/taro-cli/src/util/index.ts
import * as path from "path";
export function getRootPath(): string {
return path.resolve(__dirname, "../../");
}
export function getPkgVersion(): string {
return require(path.join(getRootPath(), "package.json")).version;
}
export function printPkgVersion() {
console.log(`👽 Taro v${getPkgVersion()}`);
console.log();
}可以看出這句輸出的是 taro/packages/taro-cli/package.json 的版本號。
👽 Taro v4.0.0我們繼續跟着斷點,進入第二第三句,可以進入到 packages/taro-cli/src/cli.ts 這個文件。
5. CLI 整體結構
taro-cli 對應的文件路徑是:
packages/taro-cli/src/cli.ts
我們先來看下這個文件的整體結構。class CLI 一個 appPath 屬性(一般指 taro 工作目錄),兩個函數 run 和 parseArgs。
// packages/taro-cli/src/cli.ts
export default class CLI {
appPath: string;
constructor(appPath) {
this.appPath = appPath || process.cwd();
}
run() {
return this.parseArgs();
}
async parseArgs() {
const args = minimist(process.argv.slice(2), {
alias: {
// 省略一些別名設置 ...
},
boolean: ["version", "help", "disable-global-config"],
default: {
build: true,
},
});
const _ = args._;
// init、build 等
const command = _[0];
if (command) {
// 省略若干代碼
} else {
if (args.h) {
// 輸出幫助信息
// 省略代碼
} else if (args.v) {
// 輸出版本號
console.log(getPkgVersion());
}
}
}
}使用了minimist,參數解析工具。
同類工具還有:
commander,命令行工具。功能齊全的框架,提供類似 git 的子命令系統,自動生成幫助信息等。有很多知名的 cli 都是用的這個commander。比如:vue-cli、webpack-cli 和 create-react-app 用的是這個。
cac,類似 Commander.js 但更輕巧、現代,支持插件。也有很多使用這個cac npm,比如vite 使用的是這個。
yargs,交互式命令行工具。功能強大的框架,但顯得過於臃腫。
cli.run 函數最終調用的是 cli.parseArgs 函數。我們接着來看 parseArgs 函數。
6. cli parseArgs
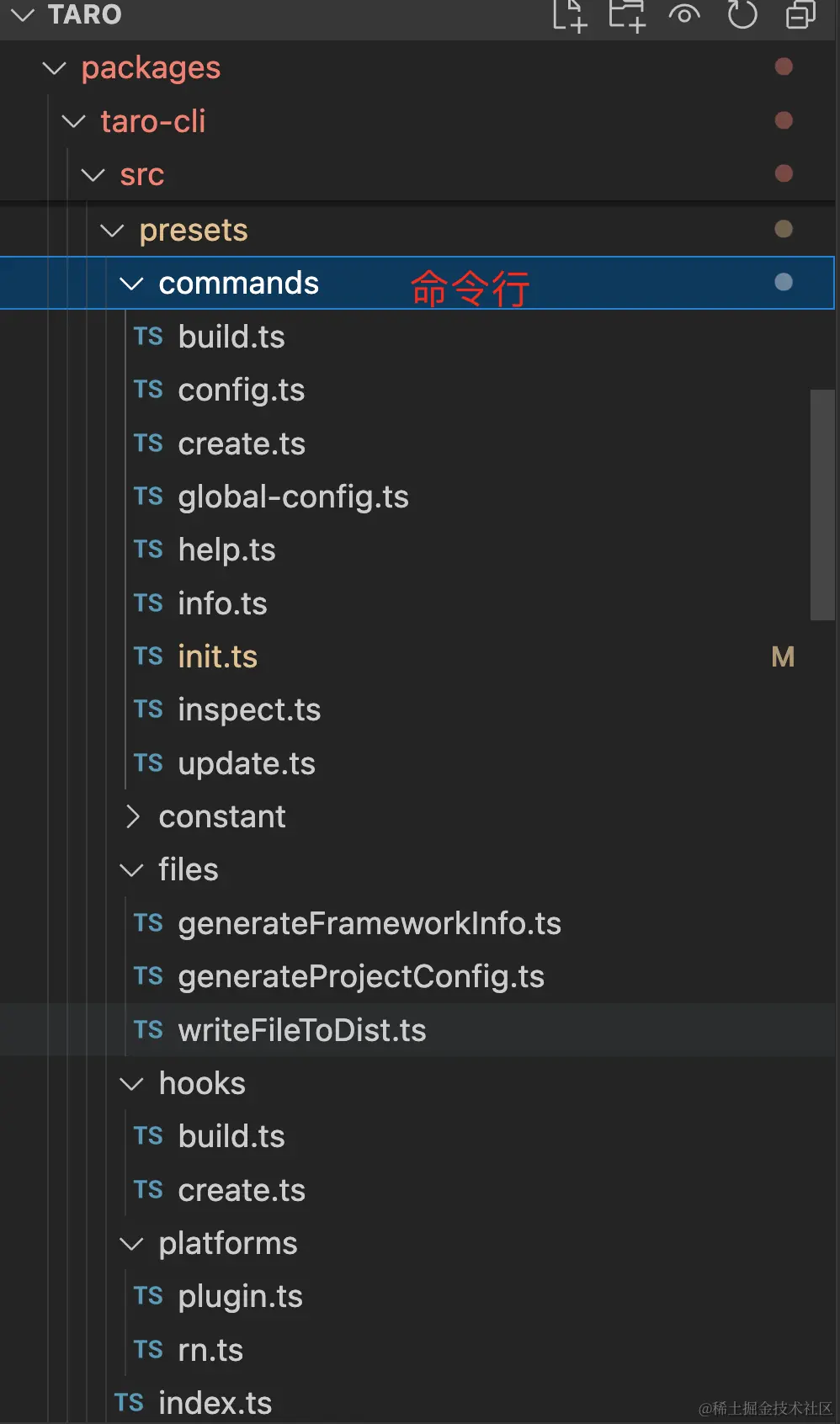
6.1 presets 預設插件集合
presets 對應的目錄結構如圖所示:
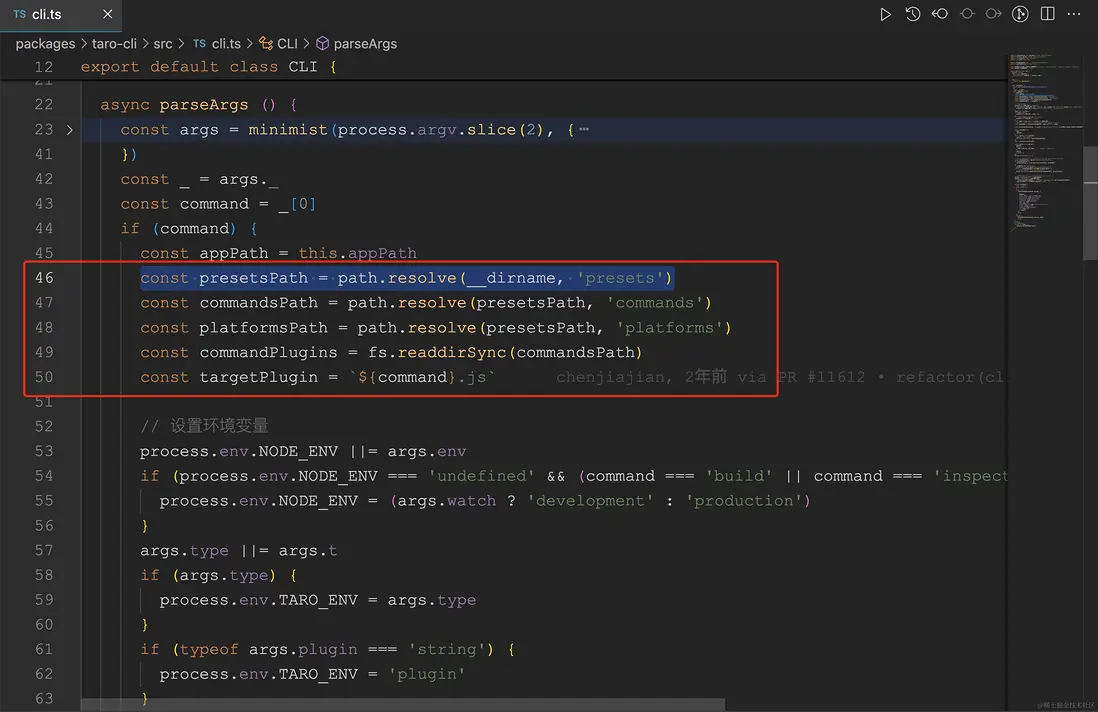
6.2 Config
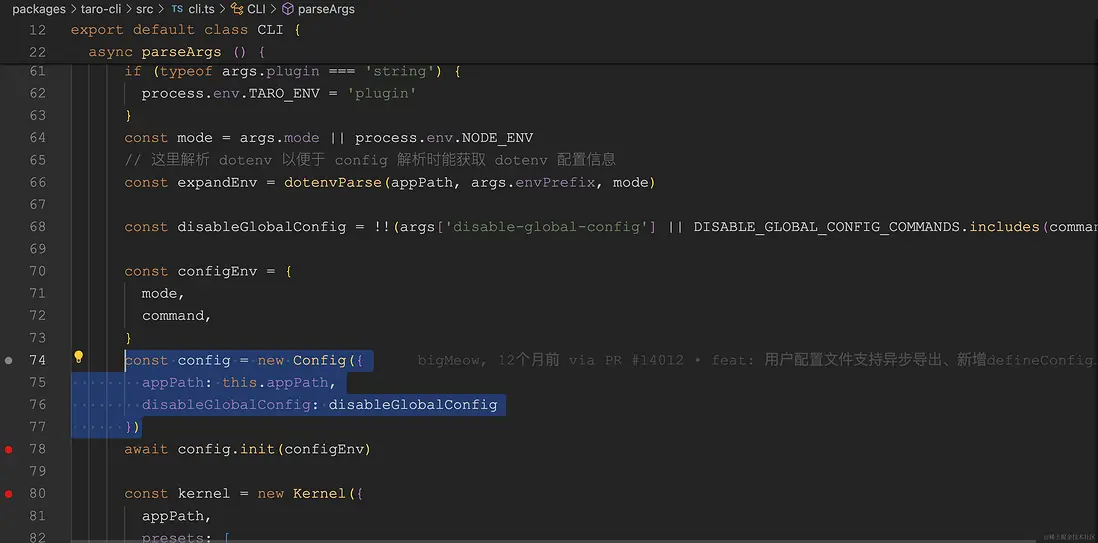
64-78 行代碼,代碼量相對較少,就截圖同時順便直接放代碼了。
// packages/taro-cli/src/cli.ts
// 這裏解析 dotenv 以便於 config 解析時能獲取 dotenv 配置信息
const expandEnv = dotenvParse(appPath, args.envPrefix, mode);
const disableGlobalConfig = !!(
args["disable-global-config"] ||
DISABLE_GLOBAL_CONFIG_COMMANDS.includes(command)
);
const configEnv = {
mode,
command,
};
const config = new Config({
appPath: this.appPath,
disableGlobalConfig: disableGlobalConfig,
});
await config.init(configEnv);dotenvParse 函數簡單來説就是通過 dotenv 和 dotenv-expand 解析 .env、.env.development、.env.production 等文件和變量的。
dotenv是一個零依賴模塊,可將.env文件中的環境變量加載到process.env中。
我之前寫過一篇 面試官:項目中常用的 .env 文件原理是什麼?如何實現?
接着我們來看 Config 類。
// packages/taro-service/src/Config.ts
export default class Config {
appPath: string;
configPath: string;
initialConfig: IProjectConfig;
initialGlobalConfig: IProjectConfig;
isInitSuccess: boolean;
disableGlobalConfig: boolean;
constructor(opts: IConfigOptions) {
this.appPath = opts.appPath;
this.disableGlobalConfig = !!opts?.disableGlobalConfig;
}
async init(configEnv: { mode: string; command: string }) {
// 代碼省略
}
initGlobalConfig() {
// 代碼省略
}
getConfigWithNamed(platform, configName) {
// 代碼省略
}
}Config 構造函數有兩個屬性。
appPath 是 taro 項目路徑。
disableGlobalConfig 是禁用全局配置。
接着我們來看 Config 類的實例上的 init 方法。
6.2.1 config.init 初始化配置
讀取的是 config/index .ts 或者 .js 後綴。
判斷是否禁用 disableGlobalConfig 全局配置。不禁用則讀取全局配置 ~/.taro-global-config/index.json。
async init (configEnv: {
mode: string
command: string
}) {
this.initialConfig = {}
this.initialGlobalConfig = {}
this.isInitSuccess = false
this.configPath = resolveScriptPath(path.join(this.appPath, CONFIG_DIR_NAME, DEFAULT_CONFIG_FILE))
if (!fs.existsSync(this.configPath)) {
if (this.disableGlobalConfig) return
this.initGlobalConfig()
} else {
createSwcRegister({
only: [
filePath => filePath.indexOf(path.join(this.appPath, CONFIG_DIR_NAME)) >= 0
]
})
try {
const userExport = getModuleDefaultExport(require(this.configPath))
this.initialConfig = typeof userExport === 'function' ? await userExport(merge, configEnv) : userExport
this.isInitSuccess = true
} catch (err) {
console.log(err)
}
}
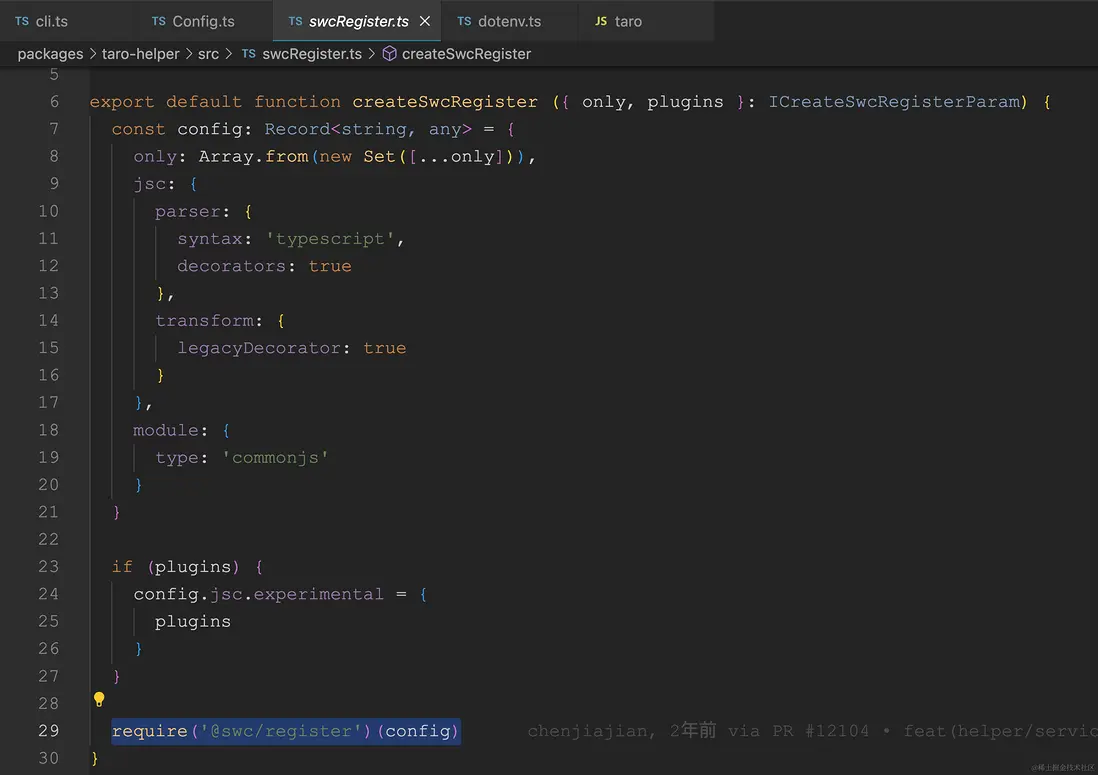
}值得一提的是:
createSwcRegister 使用了 @swc/register 來編譯 ts 等轉換成 commonjs。可以直接用 require。
使用 swc 的方法之一是通過require鈎子。require鈎子會將自身綁定到node的require並自動動態編譯文件。不過現在更推薦 @swc-node/register。
export const getModuleDefaultExport = (exports) =>
exports.__esModule ? exports.default : exports;this.initialConfig = typeof userExport === 'function' ? await userExport(merge, configEnv) : userExport。這句就是 config/index.ts 支持函數也支持對象的實現。
接着我們來看 Config 類的實例上的 initGlobalConfig 方法。
6.2.2 config.initGlobalConfig 初始化全局配置
讀取配置 ~/.taro-global-config/index.json。
{
"plugins": [],
"presets": []
}initGlobalConfig () {
const homedir = getUserHomeDir()
if (!homedir) return console.error('獲取不到用户 home 路徑')
const globalPluginConfigPath = path.join(getUserHomeDir(), TARO_GLOBAL_CONFIG_DIR, TARO_GLOBAL_CONFIG_FILE)
if (!fs.existsSync(globalPluginConfigPath)) return
const spinner = ora(`開始獲取 taro 全局配置文件: ${globalPluginConfigPath}`).start()
try {
this.initialGlobalConfig = fs.readJSONSync(globalPluginConfigPath) || {}
spinner.succeed('獲取 taro 全局配置成功')
} catch (e) {
spinner.stop()
console.warn(`獲取全局配置失敗,如果需要啓用全局插件請查看配置文件: ${globalPluginConfigPath} `)
}
}getUserHomeDir 函數主要是獲取用户的主頁路徑。比如 mac 中是 /Users/用户名/。
如果支持 os.homedir() 直接獲取返回,如果不支持則根據各種操作系統和環境變量判斷獲取。
ora 是控制枱的 loading 小動畫。
優雅的終端旋轉器
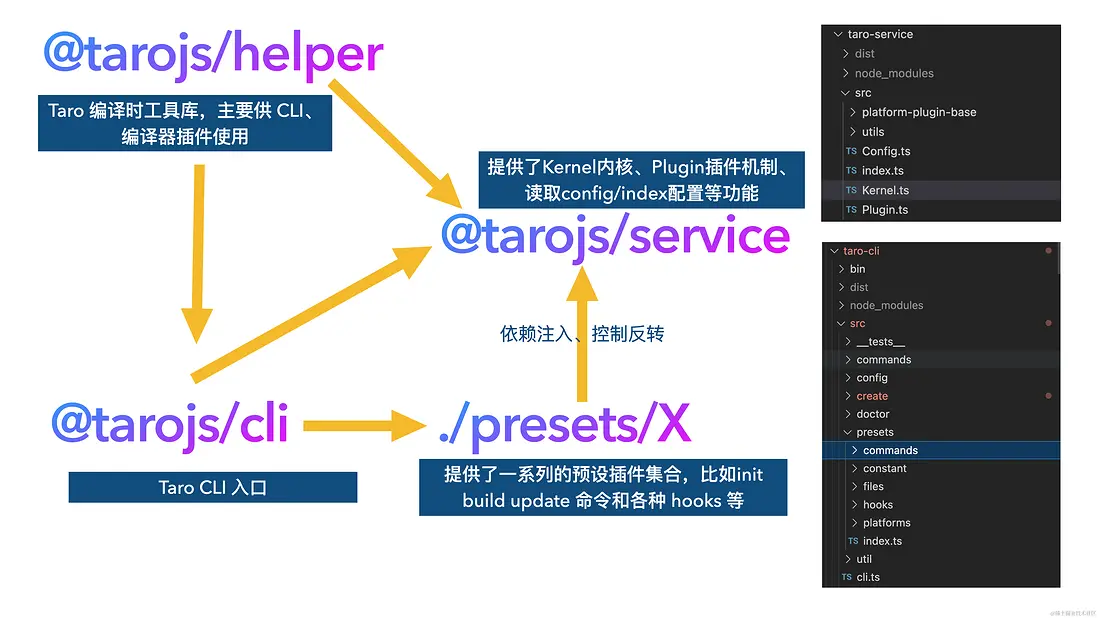
這裏的是 fs 是 @tarojs/helper 。
Taro 編譯時工具庫,主要供 CLI、編譯器插件使用。
導出的 fs-extra。
fs-extra 添加本機模塊中未包含的文件系統方法 fs,併為這些方法添加承諾支持 fs。它還用於 graceful-fs 防止 EMFILE 錯誤。它應該是 的替代品 fs。
使用 fs.readJSONSync 同步讀取 json 的方法。
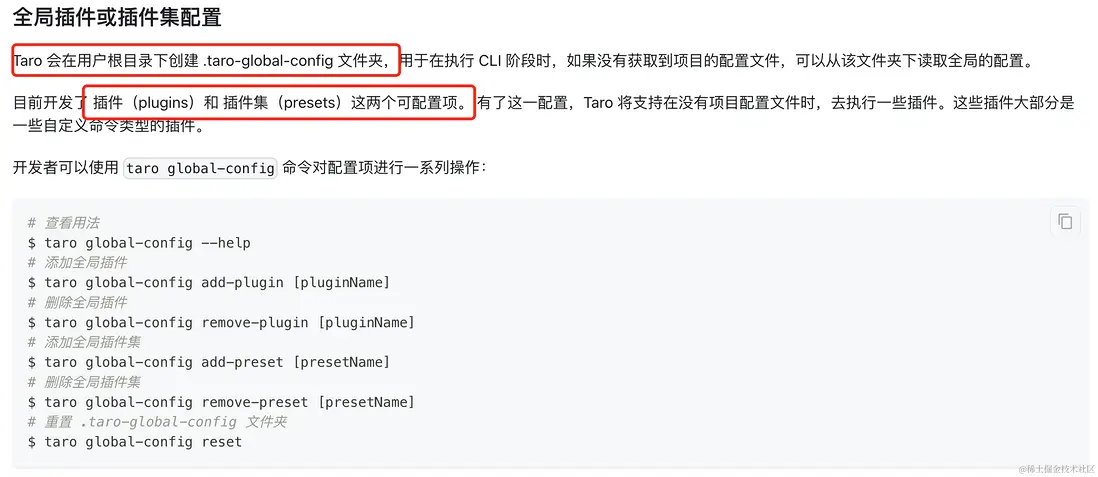
文檔中也有對這個全局參數的描述。
全局插件或插件集配置
Config 部分我們基本分析完成,接下來我們學習 Kernel (內核)部分。
7. Kernel (內核)
// packages/taro-cli/src/cli.ts
// 省略若干代碼
const kernel = new Kernel({
appPath,
presets: [path.resolve(__dirname, ".", "presets", "index.js")],
config,
plugins: [],
});
kernel.optsPlugins ||= [];接着我們來看 Kernel 類, Kernel 類繼承自 Nodejs 的事件模塊EventEmitter。
// packages/taro-service/src/Kernel.ts
export default class Kernel extends EventEmitter {
constructor(options: IKernelOptions) {
super();
this.debugger =
process.env.DEBUG === "Taro:Kernel"
? helper.createDebug("Taro:Kernel")
: function () {};
// taro 項目路徑
this.appPath = options.appPath || process.cwd();
// 預設插件集合
this.optsPresets = options.presets;
// 插件
this.optsPlugins = options.plugins;
// 配置
this.config = options.config;
// 鈎子,Map 存儲
this.hooks = new Map();
// 存儲方法
this.methods = new Map();
// 存儲命令
this.commands = new Map();
// 存儲平台
this.platforms = new Map();
this.initHelper();
this.initConfig();
this.initPaths();
this.initRunnerUtils();
}
}// packages/taro-helper/src/index.ts
export const createDebug = (id: string) => require("debug")(id);this.debugger 當沒有配置 DEBUG 環境變量時,則 debugger 是空函數。配置了 process.env.DEBUG === "Taro:Kernel" 為則調用的 npm 包 debug。
一個仿照Node.js核心調試技術的微型JavaScript調試實用程序。適用於Node.js和Web瀏覽器。
我們接着看構造器函數裏調用的幾個初始化函數,基本都是顧名知義。
// packages/taro-service/src/Kernel.ts
initConfig () {
this.initialConfig = this.config.initialConfig
this.initialGlobalConfig = this.config.initialGlobalConfig
this.debugger('initConfig', this.initialConfig)
}
initHelper () {
this.helper = helper
this.debugger('initHelper')
}
initRunnerUtils () {
this.runnerUtils = runnerUtils
this.debugger('initRunnerUtils')
}// packages/taro-service/src/Kernel.ts
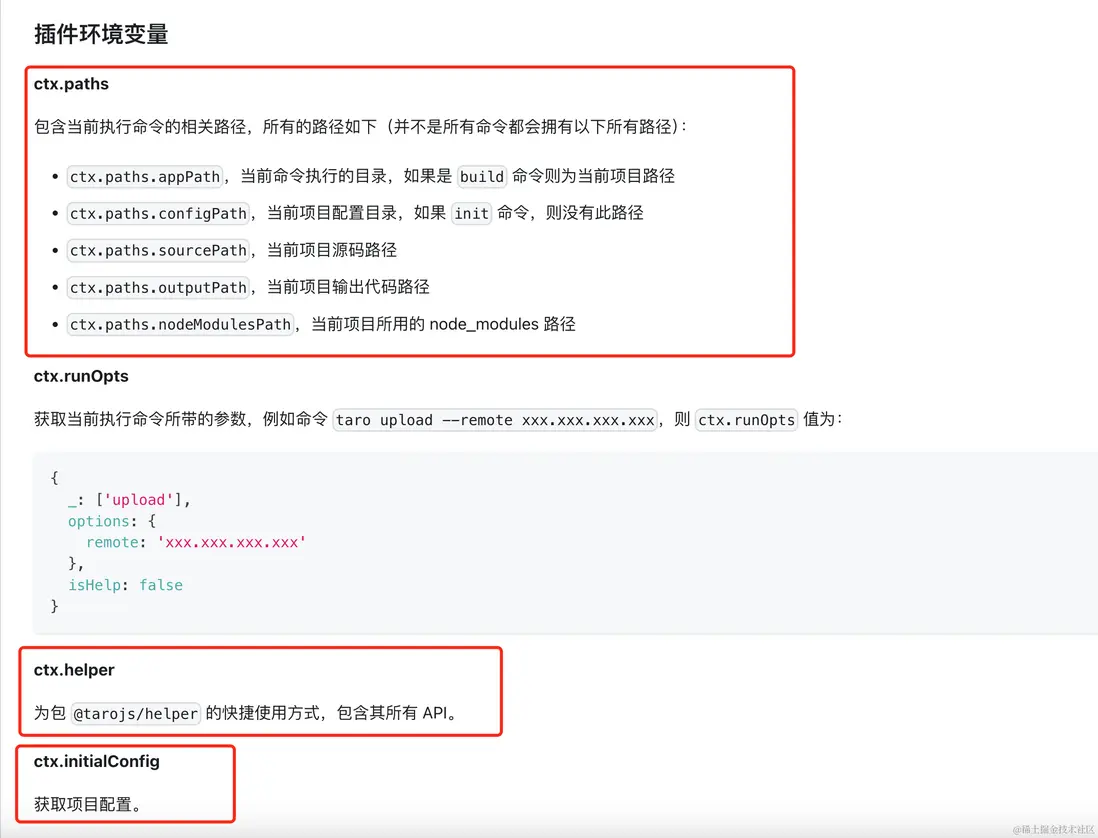
initPaths () {
this.paths = {
appPath: this.appPath,
nodeModulesPath: helper.recursiveFindNodeModules(path.join(this.appPath, helper.NODE_MODULES))
} as IPaths
if (this.config.isInitSuccess) {
Object.assign(this.paths, {
configPath: this.config.configPath,
sourcePath: path.join(this.appPath, this.initialConfig.sourceRoot as string),
outputPath: path.resolve(this.appPath, this.initialConfig.outputRoot as string)
})
}
this.debugger(`initPaths:${JSON.stringify(this.paths, null, 2)}`)
}初始化後的參數,如 taro 官方文檔 - 編寫插件 api中所示。
7.1 cli kernel.optsPlugins 等
我們接下來看,customCommand 函數。
7.2 cli customCommand 函數
我們可以看到最終調用的是 customCommand 函數
// packages/taro-cli/src/commands/customCommand.ts
import { Kernel } from "@tarojs/service";
export default function customCommand(
command: string,
kernel: Kernel,
args: { _: string[]; [key: string]: any }
) {
if (typeof command === "string") {
const options: any = {};
const excludeKeys = [
"_",
"version",
"v",
"help",
"h",
"disable-global-config",
];
Object.keys(args).forEach((key) => {
if (!excludeKeys.includes(key)) {
options[key] = args[key];
}
});
kernel.run({
name: command,
opts: {
_: args._,
options,
isHelp: args.h,
},
});
}
}customCommand 函數移除一些 run 函數不需要的參數,最終調用的是 kernal.run 函數。
接下來,我們來看 kernal.run 函數的具體實現。
8. kernal.run 執行函數
// packages/taro-service/src/Kernel.ts
async run (args: string | { name: string, opts?: any }) {
// 上半部分
let name
let opts
if (typeof args === 'string') {
name = args
} else {
name = args.name
opts = args.opts
}
this.debugger('command:run')
this.debugger(`command:run:name:${name}`)
this.debugger('command:runOpts')
this.debugger(`command:runOpts:${JSON.stringify(opts, null, 2)}`)
this.setRunOpts(opts)
// 拆解下半部分
}run 函數中,開頭主要是兼容兩種參數傳遞。
9. kernal.setRunOpts
把參數先存起來。便於給插件使用。
// packages/taro-service/src/Kernel.ts
setRunOpts (opts) {
this.runOpts = opts
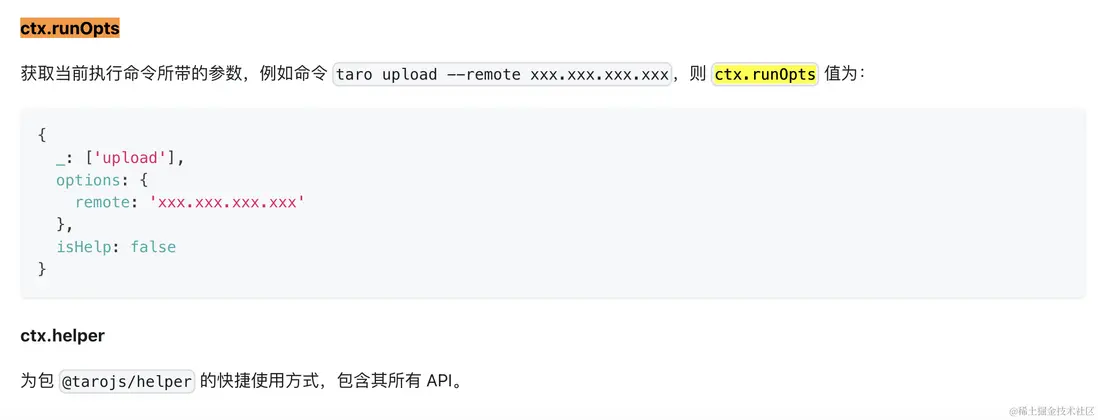
}Taro 文檔 - 編寫插件 - ctx.runOpts
我們接着來看,run 函數的下半部分。
// packages/taro-service/src/Kernel.ts
async run (args: string | { name: string, opts?: any }) {
// 下半部分
this.debugger('initPresetsAndPlugins')
this.initPresetsAndPlugins()
await this.applyPlugins('onReady')
this.debugger('command:onStart')
await this.applyPlugins('onStart')
if (!this.commands.has(name)) {
throw new Error(`${name} 命令不存在`)
}
if (opts?.isHelp) {
return this.runHelp(name)
}
if (opts?.options?.platform) {
opts.config = this.runWithPlatform(opts.options.platform)
await this.applyPlugins({
name: 'modifyRunnerOpts',
opts: {
opts: opts?.config
}
})
}
await this.applyPlugins({
name,
opts
})
}run 函數下半部分主要有三個函數:
1. this.initPresetsAndPlugins() 函數,顧名知義。初始化預設插件集合和插件。
2. this.applyPlugins() 執行插件
3. this.runHelp() 執行 命令行的幫助信息,例:taro init --help我們分開敍述
this.initPresetsAndPlugins()函數,因為此處涉及到的代碼相對較多,容易影響主線流程。所以本文在此先不展開深入學習了。將放在下一篇文章中詳細講述。
執行 this.initPresetsAndPlugins() 函數之後。我們完全可以在調試時把 kernal 實例對象打印出來。
我們來看插件的註冊。
10. kernal ctx.registerCommand 註冊 init 命令
// packages/taro-cli/src/presets/commands/init.ts
import type { IPluginContext } from "@tarojs/service";
export default (ctx: IPluginContext) => {
ctx.registerCommand({
name: "init",
optionsMap: {
"--name [name]": "項目名稱",
"--description [description]": "項目介紹",
"--typescript": "使用TypeScript",
"--npm [npm]": "包管理工具",
"--template-source [templateSource]": "項目模板源",
"--clone [clone]": "拉取遠程模板時使用git clone",
"--template [template]": "項目模板",
"--css [css]": "CSS預處理器(sass/less/stylus/none)",
"-h, --help": "output usage information",
},
async fn(opts) {
// init project
const { appPath } = ctx.paths;
const { options } = opts;
const {
// 省略若干參數
} = options;
const Project = require("../../create/project").default;
console.log(Project, "Project");
const project = new Project({
projectName,
projectDir: appPath,
// 省略若干參數
});
project.create();
},
});
};通過 ctx.registerCommand 註冊了一個 name 為 init 的命令,會存入到內核 Kernal 實例對象的 hooks 屬性中,其中 ctx 就是 Kernal 的實例對象。具體實現是 fn 函數。
11. kernal.applyPlugins 觸發插件
// packages/taro-service/src/Kernel.ts
async applyPlugins (args: string | { name: string, initialVal?: any, opts?: any }) {
// 上半部分
let name
let initialVal
let opts
if (typeof args === 'string') {
name = args
} else {
name = args.name
initialVal = args.initialVal
opts = args.opts
}
this.debugger('applyPlugins')
this.debugger(`applyPlugins:name:${name}`)
this.debugger(`applyPlugins:initialVal:${initialVal}`)
this.debugger(`applyPlugins:opts:${opts}`)
if (typeof name !== 'string') {
throw new Error('調用失敗,未傳入正確的名稱!')
}
// 拆解到下半部分
}上半部分,主要是適配兩種傳參的方式。
// packages/taro-service/src/Kernel.ts
async applyPlugins (args: string | { name: string, initialVal?: any, opts?: any }) {
// 下半部分
const hooks = this.hooks.get(name) || []
if (!hooks.length) {
return await initialVal
}
const waterfall = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['arg'])
if (hooks.length) {
const resArr: any[] = []
for (const hook of hooks) {
waterfall.tapPromise({
name: hook.plugin!,
stage: hook.stage || 0,
// @ts-ignore
before: hook.before
}, async arg => {
const res = await hook.fn(opts, arg)
if (IS_MODIFY_HOOK.test(name) && IS_EVENT_HOOK.test(name)) {
return res
}
if (IS_ADD_HOOK.test(name)) {
resArr.push(res)
return resArr
}
return null
})
}
}
return await waterfall.promise(initialVal)
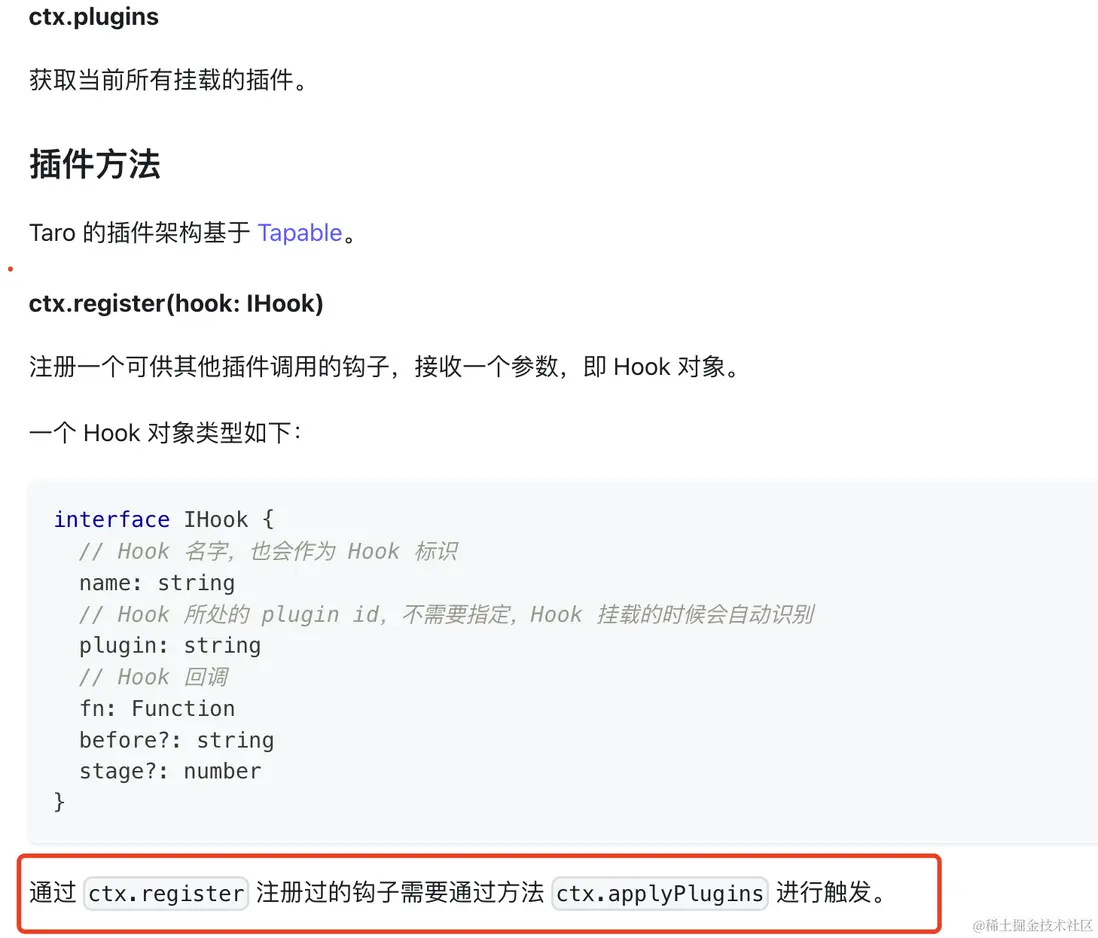
}Taro 的插件架構基於 Tapable。
這裏使用了這個函數:AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook。
The hook type is reflected in its class name. E.g., AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook allows asynchronous functions and runs them in series, passing each function’s return value into the next function.
簡言之就是異步或者同步方法串聯起來,上一個函數的結果作為下一個函數的參數依次執行。依次執行。
這時讓我想起一句小虎隊的愛的歌詞。
喔,把你的心我的心串一串,串一株幸運草串一個同心圓...
舉個例子用户寫的插件中有多個鈎子函數。比如 onReday 等可以有多個。
applyPlugins 根據執行的命令 init 從 hooks 取出,串起來,然後依次執行插件的 fn 方法。
我們順便來看一下,kernal.runHelp 的實現。
12. kernal.runHelp 命令幫助信息
在 kernal.run 函數中,有一個 opts.isHelp 的判斷,執行 kernal.runHelp 方法。
// packages/taro-service/src/Kernel.ts
// run 函數
if (opts?.isHelp) {
return this.runHelp(name);
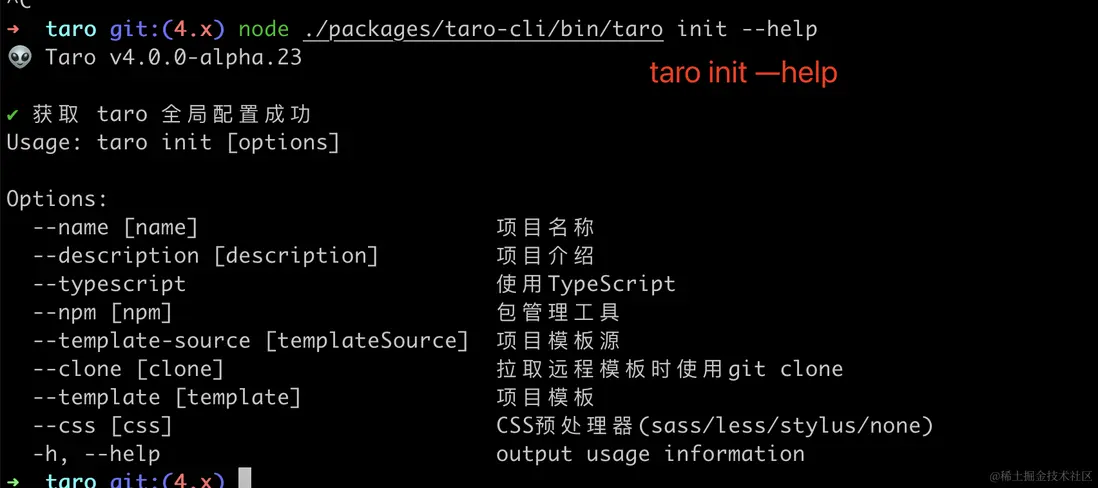
}以 taro init --help 為例。輸出結果如下圖所示:
具體實現代碼如下:
// packages/taro-service/src/Kernel.ts
runHelp (name: string) {
const command = this.commands.get(name)
const defaultOptionsMap = new Map()
defaultOptionsMap.set('-h, --help', 'output usage information')
let customOptionsMap = new Map()
if (command?.optionsMap) {
customOptionsMap = new Map(Object.entries(command?.optionsMap))
}
const optionsMap = new Map([...customOptionsMap, ...defaultOptionsMap])
printHelpLog(name, optionsMap, command?.synopsisList ? new Set(command?.synopsisList) : new Set())
}根據 name 從 this.commands Map 中獲取到命令,輸出對應的 optionsMap 和 synopsisList。
13. 總結
我們主要學了
- 學會通過兩種方式調試 taro 源碼
- 學會入口 taro-cli 具體實現方式
- 學會 cli init 命令實現原理,讀取用户項目配置文件和用户全局配置文件
- 學會 taro-service kernal (內核)解耦實現
- 初步學會 taro 插件架構,學會了如何編寫一個 taro 插件
taro-cli 使用了minimist,命令行參數解析工具。
使用了 @swc/register 讀取 config/index .js 或者 .ts 配置文件和用 fs-extra fs.readJSONSync 全局配置文件。
CLI 部分有各種預設插件集合 presets。
taro 單獨抽離了一個 tarojs/service (packages/taro-service) 模塊,包含 Kernal 內核、Config、Plugin 等。
taro 的基於 Tapable 的 AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook (把函數組合在一起串行) 實現的插件機制。各個插件可以分開在各個地方,達到解耦效果。非常值得我們學習。
簡單做了一個本文的總結圖。
如果看完有收穫,歡迎點贊、評論、分享、收藏支持。你的支持和肯定,是我寫作的動力。
作者:常以若川為名混跡於江湖。所知甚少,唯善學。若川的博客,github blog,可以點個 star 鼓勵下持續創作。
最後可以持續關注我@若川,歡迎關注我的公眾號:若川視野。我傾力持續組織了 3 年多每週大家一起學習 200 行左右的源碼共讀活動,感興趣的可以點此掃碼加我微信 ruochuan02 參與。另外,想學源碼,極力推薦關注我寫的專欄《學習源碼整體架構系列》,目前是掘金關注人數(6k+人)第一的專欄,寫有幾十篇源碼文章。