1. 目標
探索 Node.js 的 require 方法是如何實現的。準備兩個文件
// test.js
const str = require('./testa');
console.log(str)// testa.js
module.exports = 'abc'2. 調試方法
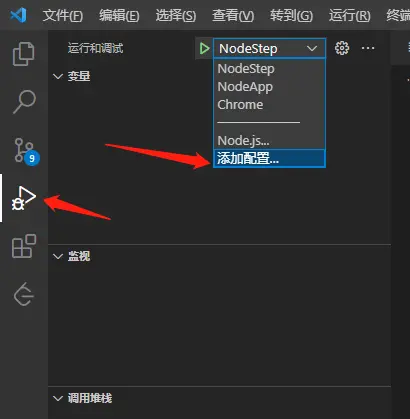
2.1 點擊添加配置
2.2 配置相關信息
這裏需要注意的是,把 skipFiles 需要把 <node_internals>/** 註釋掉,這樣才能夠 debug Node 的源碼。
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "NodeStep", //單獨調試js,即可以直接運行js
"type": "node",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${file}", //
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"skipFiles": [
// "<node_internals>/**"
]
}
]
}3. require執行的過程是怎樣的
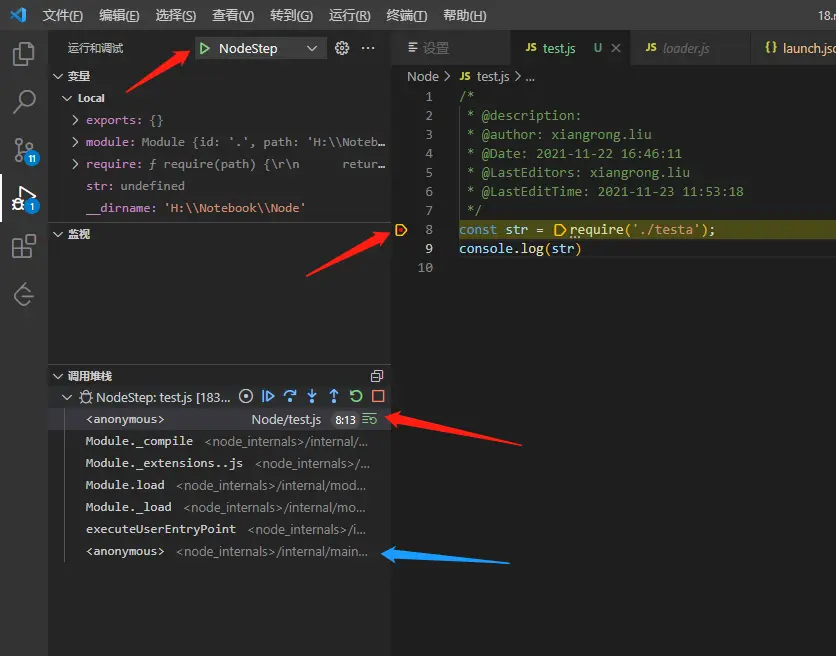
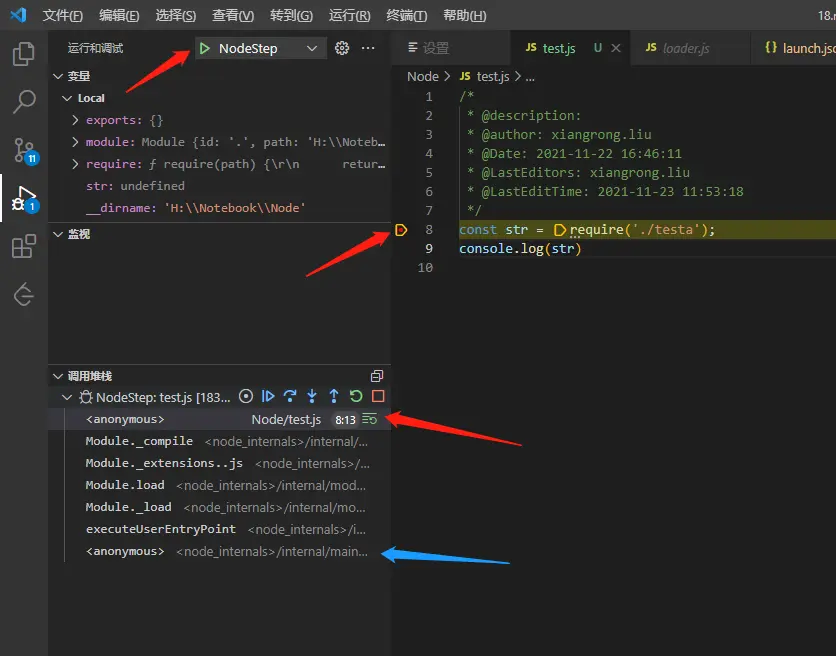
在第八行打斷點,之後就可以點擊debug按鈕了,我們可以看到調用堆棧中,目前停止執行的函數。單步調試。
可以看到是調用了一個工具函數,最終調用了 mod.require 方法。繼續單步調用。
上面的 mod.require 調用的是 loader.js 的 Module.prototype.require 方法,然後調用 Module._load 靜態方法。繼續單步調用。
//lib\internal\modules\cjs\loader.js
// Check the cache for the requested file.
// 1. If a module already exists in the cache: return its exports object.
// 2. If the module is native: call
// `NativeModule.prototype.compileForPublicLoader()` and return the exports.
// 3. Otherwise, create a new module for the file and save it to the cache.
// Then have it load the file contents before returning its exports
// object.
// request 是請求模塊的路徑,這裏對應着 './testa'
// parent 是父模塊test的信息
// isMain 是否主文件(入口文件),這裏是false
Module._load = function(request, parent, isMain) {
let relResolveCacheIdentifier;
// 如果有父模塊,則查詢是否已經緩存請求模塊。如果已緩存,則更新對應的模塊並且返回緩存的模塊
if (parent) {
debug('Module._load REQUEST %s parent: %s', request, parent.id);
// Fast path for (lazy loaded) modules in the same directory. The indirect
// caching is required to allow cache invalidation without changing the old
// cache key names.
relResolveCacheIdentifier = `${parent.path}\x00${request}`;
const filename = relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier];
if (filename !== undefined) {
const cachedModule = Module._cache[filename];
if (cachedModule !== undefined) {
updateChildren(parent, cachedModule, true);
return cachedModule.exports;
}
delete relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier];
}
}
// 得到請求模塊的絕對路徑
const filename = Module._resolveFilename(request, parent, isMain);
// 查詢緩存,如果已緩存,則更新對應的模塊並且返回緩存的模塊
const cachedModule = Module._cache[filename];
if (cachedModule !== undefined) {
updateChildren(parent, cachedModule, true);
return cachedModule.exports;
}
// 如果加載的是原生模塊(c++模塊),則判斷canBeRequiredByUsers然後返回對應的模塊
const mod = loadNativeModule(filename, request);
if (mod && mod.canBeRequiredByUsers) return mod.exports;
// 否則,新建Module實例,構造函數本身已經調用了updateChildren,這裏不需要再調用
// Don't call updateChildren(), Module constructor already does.
const module = new Module(filename, parent);
if (isMain) {
process.mainModule = module;
module.id = '.';
}
// 建立緩存
Module._cache[filename] = module;
if (parent !== undefined) {
relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier] = filename;
}
let threw = true;
try {
// Intercept exceptions that occur during the first tick and rekey them
// on error instance rather than module instance (which will immediately be
// garbage collected).
if (enableSourceMaps) {
try {
module.load(filename);
} catch (err) {
rekeySourceMap(Module._cache[filename], err);
throw err; /* node-do-not-add-exception-line */
}
} else {
// 執行load方法
module.load(filename);
}
threw = false;
} finally {
if (threw) {
delete Module._cache[filename];
if (parent !== undefined) {
delete relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier];
const children = parent && parent.children;
if (ArrayIsArray(children)) {
const index = children.indexOf(module);
if (index !== -1) {
children.splice(index, 1);
}
}
}
}
}
// 最後返回module.exports
return module.exports;
};Module._load 主要是做了以下三件事:
- 如果模塊已經在緩存中,則直接返回緩存的對象
- 如果模塊是原生模塊(c++模塊),則返回對應的模塊
- 否則,創建一個
Module實例,然後保存到緩存中,執行實例方法load,最後返回實例屬性exports
接下來我們看看 module.load 做了什麼。
// lib\internal\modules\cjs\loader.js
// Given a file name, pass it to the proper extension handler.
Module.prototype.load = function(filename) {
debug('load %j for module %j', filename, this.id);
assert(!this.loaded);
this.filename = filename;
// 獲得node_modules的路徑
this.paths = Module._nodeModulePaths(path.dirname(filename));
// 這裏的extension是js
const extension = findLongestRegisteredExtension(filename);
// allow .mjs to be overridden
if (filename.endsWith('.mjs') && !Module._extensions['.mjs']) {
throw new ERR_REQUIRE_ESM(filename);
}
// 這裏做了什麼?
Module._extensions[extension](this, filename);
this.loaded = true;
// 下面是cjs兼容esm的操作,這次先不分析
const ESMLoader = asyncESM.ESMLoader;
const url = `${pathToFileURL(filename)}`;
const module = ESMLoader.moduleMap.get(url);
// Create module entry at load time to snapshot exports correctly
const exports = this.exports;
// Called from cjs translator
if (module !== undefined && module.module !== undefined) {
if (module.module.getStatus() >= kInstantiated)
module.module.setExport('default', exports);
} else {
// Preemptively cache
// We use a function to defer promise creation for async hooks.
ESMLoader.moduleMap.set(
url,
// Module job creation will start promises.
// We make it a function to lazily trigger those promises
// for async hooks compatibility.
() => new ModuleJob(ESMLoader, url, () =>
new ModuleWrap(url, undefined, ['default'], function() {
this.setExport('default', exports);
})
, false /* isMain */, false /* inspectBrk */)
);
}
};Module.prototype.load 做了以下這些事:
- 調用
Module._extensions[extension](this, filename)方法 - 標記已加載模塊
- cjs兼容esm
接下來看看 Module._extensions[extension](this, filename) 做了什麼
// lib\internal\modules\cjs\loader.js
// Native extension for .js
Module._extensions['.js'] = function(module, filename) {
if (filename.endsWith('.js')) {
const pkg = readPackageScope(filename);
// Function require shouldn't be used in ES modules.
if (pkg && pkg.data && pkg.data.type === 'module') {
const parentPath = module.parent && module.parent.filename;
const packageJsonPath = path.resolve(pkg.path, 'package.json');
throw new ERR_REQUIRE_ESM(filename, parentPath, packageJsonPath);
}
}
// 以utf8格式讀取文件
const content = fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf8');
// 編譯
module._compile(content, filename);
};Module.prototype.load 做了以下這些事:
- 以utf8格式讀取模塊文件,得到字符串
- 編譯
下面看看 module._compile(content, filename) 是如何編譯的
// lib\internal\modules\cjs\loader.js
// Run the file contents in the correct scope or sandbox. Expose
// the correct helper variables (require, module, exports) to
// the file.
// Returns exception, if any.
Module.prototype._compile = function(content, filename) {
let moduleURL;
let redirects;
if (manifest) {
moduleURL = pathToFileURL(filename);
redirects = manifest.getRedirector(moduleURL);
manifest.assertIntegrity(moduleURL, content);
}
maybeCacheSourceMap(filename, content, this);
// 見下文,得到一個組裝好的函數
/*
function (exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname) {
// 模塊代碼
module.exports = 'abc'
}
*/
const compiledWrapper = wrapSafe(filename, content, this);
var inspectorWrapper = null;
if (getOptionValue('--inspect-brk') && process._eval == null) {
if (!resolvedArgv) {
// We enter the repl if we're not given a filename argument.
if (process.argv[1]) {
try {
resolvedArgv = Module._resolveFilename(process.argv[1], null, false);
} catch {
// We only expect this codepath to be reached in the case of a
// preloaded module (it will fail earlier with the main entry)
assert(ArrayIsArray(getOptionValue('--require')));
}
} else {
resolvedArgv = 'repl';
}
}
// Set breakpoint on module start
if (resolvedArgv && !hasPausedEntry && filename === resolvedArgv) {
hasPausedEntry = true;
inspectorWrapper = internalBinding('inspector').callAndPauseOnStart;
}
}
const dirname = path.dirname(filename);
const require = makeRequireFunction(this, redirects);
let result;
const exports = this.exports;
const thisValue = exports;
const module = this;
if (requireDepth === 0) statCache = new Map();
if (inspectorWrapper) {
result = inspectorWrapper(compiledWrapper, thisValue, exports,
require, module, filename, dirname);
} else {
/* 執行組裝好的函數
call方法的this,指向exports。所以在cjs模塊裏直接console.log(this)結果是{},而非global對象
exports,指向module實例的exports屬性,值為{}
require,就是加載模塊的方法本身
module,module = this,this是module實例對象,包括模塊的一些信息
__filename,其實就是模塊的絕對路徑
__dirname,其實就是調用path.dirname獲取該模塊的文件夾路徑
*/
result = compiledWrapper.call(thisValue, exports, require, module,
filename, dirname);
}
hasLoadedAnyUserCJSModule = true;
if (requireDepth === 0) statCache = null;
// 返回執行結果
return result;
};// lib\internal\modules\cjs\loader.js
let wrap = function(script) {
return Module.wrapper[0] + script + Module.wrapper[1];
};
const wrapper = [
'(function (exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname) { ',
'\n});',
];
function wrapSafe(filename, content, cjsModuleInstance) {
// 補丁方法
if (patched) {
/* 組裝函數,效果如下:
(function (exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname) {
// 模塊代碼
module.exports = 'abc'
});
*/
const wrapper = Module.wrap(content);
// 使用node虛擬機的沙箱方法,返回組裝好的函數
return vm.runInThisContext(wrapper, {
filename,
lineOffset: 0,
displayErrors: true,
importModuleDynamically: async (specifier) => {
const loader = asyncESM.ESMLoader;
return loader.import(specifier, normalizeReferrerURL(filename));
},
});
}
// 下面是使用了c++的內部方法compileFunction,效果同上,就不分析了
let compiled;
try {
compiled = compileFunction(
content,
filename,
0,
0,
undefined,
false,
undefined,
[],
[
'exports',
'require',
'module',
'__filename',
'__dirname',
]
);
} catch (err) {
if (process.mainModule === cjsModuleInstance)
enrichCJSError(err);
throw err;
}
const { callbackMap } = internalBinding('module_wrap');
callbackMap.set(compiled.cacheKey, {
importModuleDynamically: async (specifier) => {
const loader = asyncESM.ESMLoader;
return loader.import(specifier, normalizeReferrerURL(filename));
}
});
return compiled.function;
}module._compile 做了以下這些事:
-
結合模塊讀出來的文本內容,組裝模塊成為這樣的字符串
(function (exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname) { // 模塊代碼 module.exports = 'abc' }); - 通過
vm.runInThisContext虛擬機沙箱返回函數 - 執行函數,並且注入變量
3. 入口模塊是如何加載的
其實在一開始斷點的時候已經揭示了。我們可以看到 調用堆棧 ,其實就是我們上面分析的過程。只不過這裏是直接調用 Module._load 來加載模塊,而子模塊是調用工具方法封裝好的 makeRequireFunction 方法來調用。
4. 總結
4.1 require的執行主要過程
- 如果模塊已經在緩存中,則直接返回緩存的對象
- 如果模塊是原生模塊(c++模塊),則返回對應的模塊
- 否則,創建一個
Module實例,然後保存到緩存中 - 以
utf8格式讀取模塊內容 -
組裝函數字符串
(function (exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname) { // 模塊代碼 module.exports = 'abc' }); - 通過
vm.runInThisContext虛擬機沙箱返回函數 - 執行函數,並且注入變量
- cjs兼容esm
- 返回實例屬性
module.exports
4.2 從源碼中揭示了哪些現象
- 在cjs模塊裏直接
console.log(this)結果是{},而非global對象。因為cjs模塊本質是一個封裝好的函數,而且執行的時候使用call綁定了this為module實例的屬性exports,其值為{} -
在cjs模塊中,初始化之後,
this === module.exports === exports,都是指向module實例的屬性exports的默認值{}// testa.js console.log(module.exports) // {} console.log(exports) // {} console.log(exports === this) // true console.log(this === module.exports) // true console.log(exports === module.exports) // true module.exports = 'abc' console.log(module.exports) // 'abc' console.log(exports) // {} console.log(exports === this) // true console.log(this === module.exports) // false console.log(exports === module.exports) //false我們重新來看變量注入的過程
const exports = this.exports; // module實例對象的exports屬性,默認值為{} const thisValue = exports; const module = this; compiledWrapper.call(thisValue, exports, require, module, filename, dirname); }改造一下就變成
const exports = module.exports = {}exports、module.exports都指向默認值
{}的內存地址。
所以,以下的寫法是成立的:exports.a = 'abc' // {a: 'abc'} module.exports.a = 'abc' // {a: 'abc'} module.exports = 'abc' // 'abc'以下寫法是不成立的,雖然不會報錯,但是不會返回模塊的內容,因為在
Module._load方法的最後是return module.exportsexports = 'abc' - nodejs文檔中説
exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname都不是全局對象,其實是注入的變量 - 多次
equire同一個模塊,只會執行一次,因為做了緩存,第二次require的時候直接返回module.exports的內容