OpenEuler 中安裝配置 MySQL 與其他系統有所不同, 需要一些手動的配置. 這裏整理了在這個過程中涉及的一些 Linux 基礎知識
- 只想看結果
-
正文開始
- 修改配置文件:
sed指令 - 暫時禁用安全策略:SELinux
- MySQL 服務的本質:Linux Run Level 及其控制 與 自啓動
- 修改配置文件:
只想看結果 👇
已驗證的方法: OpenEuler上MySQL的部署與使用_albert-rabbit的博客-CSDN博客
正文開始 👇
推薦先了解完整的安裝過程,再看下面的內容。因為具體步驟將不會詳細説明。
修改配置文件: sed 指令
在安裝 MySQL 之前需要禁用 SELinux。SELinux 是 Linux 內核的安全策略, 如不禁用可能因為會訪問權限的限制導致最後初始化時如下錯誤:
[root@host-x-x init.d]# mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf –initialize
2021-08-10T07:08:26.745109Z 0 [System] [MY-010116] [Server] /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld (mysqld 8.0.22) starting as process 2916
2021-08-10T07:08:26.798812Z 1 [ERROR] [MY-011011] [Server] Failed to find valid data directory.
2021-08-10T07:08:26.798989Z 0 [ERROR] [MY-010020] [Server] Data Dictionary initialization failed.
2021-08-10T07:08:26.799066Z 0 [ERROR] [MY-010119] [Server] Aborting
2021-08-10T07:08:26.799407Z 0 [System] [MY-010910] [Server] /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld: Shutdown complete (mysqld 8.0.22) Source distribution.方法為:
sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/sysconfig/selinuxsed 用於對輸入到該指令的文件進行處理並輸出, 因此 sed 的參數字符串都是為了描述如何處理傳入的文件
要理解 sed 指令, 需要知道, sed 指令的使用包括兩個部分:參數 flag 和 動作
參考:Linux sed 命令
-
參數 flag:
-e或-f之後的內容為 描述如何處理文件的字符串. 不同的是使用-f時, 傳入的是文件。處理後會輸出到終端,一般會使用輸出重定向的寫入到一個文件裏-i直接對文件本身進行修改
-
動作: 文件處理方法字符串的語法, (和 vim 的語法很像?
-
a :新增, a 的後面可以接字串,而這些字串會在新的一行出現(目前的下一行)
$ sed -e 4a\newline testfile #使用sed 在第四行後添加新字符串 -
c :取代, c 的後面可以接字串,這些字串可以取代 n1,n2 之間的行!
[root@www ~]# nl /etc/passwd | sed '2,5c No 2-5 number' 1 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash No 2-5 number 6 sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync .....(後面省略)..... -
d :刪除
[root@www ~]# nl /etc/passwd | sed '2,5d' 1 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash 6 sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync 7 shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown .....(後面省略)..... - i :插入, i 的後面可以接字串,而這些字串會在新的一行出現(目前的上一行);
-
p :打印,亦即將某個選擇的數據印出。通常 p 會與參數 sed -n 一起運行~
nl /etc/passwd | sed '/root/p' # 搜索'root'並展示 1 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash 1 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash 2 daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/bin/sh 3 bin:x:2:2:bin:/bin:/bin/sh 4 sys:x:3:3:sys:/dev:/bin/sh 5 sync:x:4:65534:sync:/bin:/bin/sync ....下面忽略 -
s :取代,可以直接進行取代的工作哩!通常這個 s 的動作可以搭配正規表示法!例如 1,20s/old/new/g 就是啦!
sed 's/要被取代的字串/新的字串/g'
-
暫時禁用安全策略:SELinux
參考:理解Linux下的SELinux
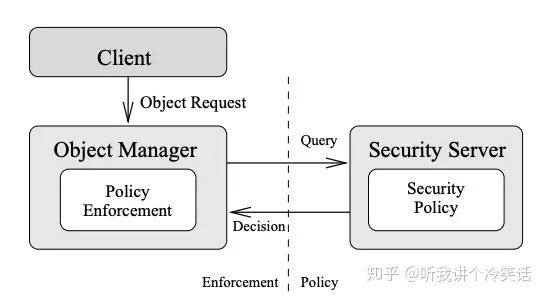
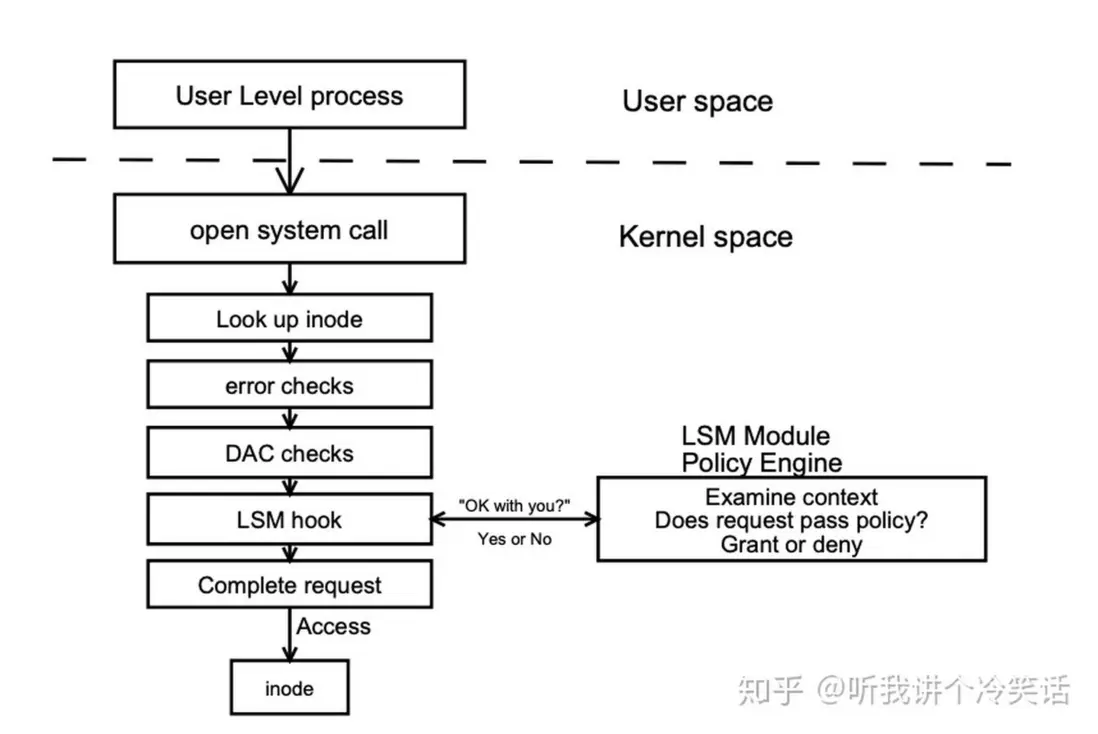
簡而言之, SELinux 是 一個 Mandatory Access Control (MAC) 的實現, 建立在 LSM (Linux Security Module) 基礎上, 參考了 Flask 的架構設計.
- MAC: 進程的權限控制並不是簡單的 誰可以做什麼, 而是檢查 進程 和 其請求的資源 的 context , 進而給出相應的安全策略.
- Flask是一種靈活的操作系統安全架構,並且在Fluke research operating system中得到了實現。Flask的主要特點是把安全策略執行代碼和安全策略決策代碼,劃分成了兩個組件。
- LSM 在內核數據結構中增加了安全字段,並且在重要的內核代碼(系統調用)中增加了hook。可以在hook中註冊回調函數對安全字段進行管理,以及執行接入控制。
SELinux 有 三個運行狀態:
- Disable: 禁用SELinux,不會給任何新資源打Label,如果重新啓用的話,將會給資源重新打上Lable,過程會比較緩慢。
- Permissive:如果違反安全策略,並不會真正的執行拒絕操作,替代的方式是記錄一條log信息。
- Enforcing: 默認模式,SELinux的正常狀態,會實際禁用違反策略的操作
分別使用 getenforce 和 setenforce [0|1] 可以查看和設置 SeLinux 的運行狀態.
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# setenforce 0
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# getenforce
Permissive
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# setenforce 1
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# getenforce
Enforcing
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# setenforce --help
usage: setenforce [ Enforcing | Permissive | 1 | 0 ]MySQL 服務的本質:Linux Run Level 及其控制 與 自啓動
MySQL 最終將作為一個 "服務" 在系統中運行, 並在 開機後 自動啓動, 那麼什麼是 linux 中的 服務? 如何實現自啓動?
參考
在 Linux 中, /etc/init.d/ (或 /etc/rc.d/init.d) 目錄下有啓動腳本, 一般稱之為 服務.
另一方面, Linux 將系統的運行生命週期抽象為 7 個狀態:
- 0 – System halt i.e the system can be safely powered off with no activity.
- 1 – Single user mode.
- 2 – Multiple user mode with no NFS(network file system).
- 3 – Multiple user mode under the command line interface and not under the graphical user interface.
- 4 – User-definable.
- 5 – Multiple user mode under GUI (graphical user interface) and this is the standard runlevel for most of the LINUX based systems.
- 6 – Reboot which is used to restart the system.
在 /etc/rc.d 下有7個名為 rcN.d 的目錄,對應系統的7個運行級別,其中存儲的是一些指向鏈接文件(類似 windows 中的快捷方式)
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# ls /etc/rc.d
init.d rc0.d rc1.d rc2.d rc3.d rc4.d rc5.d rc6.d rc.local
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# ls /etc/rc.d/rc2.d
S64mysql
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# ls /etc/rc.d/rc4.d
S64mysql
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# ls /etc/rc.d/rc5.d
S64mysql
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# ls /etc/rc.d/rc6.d
K36mysql
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# ls /etc/rc.d/rc0.d
K36mysql
[root@host-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]# ls /etc/rc.d/rc1.d
K36mysql文件的命名方式為:[K|S]+[優先權重]+[服務名], 其中 K 標誌終結服務, S 表示開始服務. 這裏意為在 2, 3, 4, 5 狀態時開啓 MySQL 服務, 其他狀態關閉