遍歷二叉樹一共有四種方式:前序遍歷,中序遍歷,後序遍歷,層序遍歷(廣度優先)
準備
先定義一個結點類(後續代碼需要使用)
public class Node<V> {
public V value;
public Node<V> left;
public Node<V> right;
public Node(V value) {
this.value = value;
}
}前序遍歷
操作步驟如下:
- 訪問根結點
- 遞歸遍歷左子樹
- 遞歸遍歷右子樹
假設一個二叉樹的結構如下圖所示: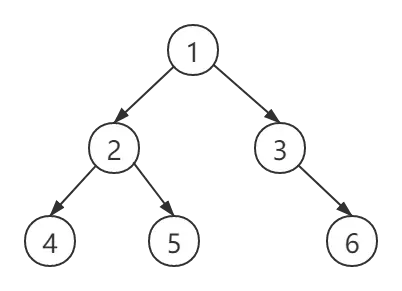
則遍歷結果為:1 2 4 5 3 6
實現方式:
- 遞歸方式
public class PreOrderRecursivelyVisitor {
public <V> void visit(Node<V> root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println(node.value + " ");
visit(root.left, output);
visit(root.right, output);
}
}- 非遞歸方式
藉助棧(先進後出)來實現
代碼如下:
public class PreOrderVisitor {
public <V> void visit(Node<V> root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node<V>> help = new Stack<>();
// 1. 根結點入棧
help.push(root);
while (!help.isEmpty()) {
// 2. 棧頂結點出棧
Node<V> node = help.pop();
// 3. 訪問出棧結點
System.out.println(node.value + " ");
// 4. 依次將該結點的右,左孩子入棧
if (node.right != null) {
help.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
help.push(node.left);
}
}
}
}中序遍歷
操作步驟如下:
- 遞歸遍歷左子樹
- 訪問根結點
- 遞歸遍歷右子樹
假設一個二叉樹的結構如下圖所示: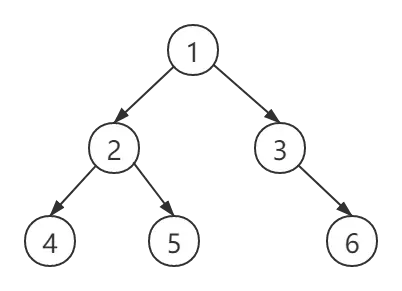
則遍歷結果為:4 2 5 1 3 6
實現方式:
- 遞歸方式
public class InOrderRecursivelyVisitor {
public <V> void visit(Node<V> root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
visit(root.left, output);
System.out.println(node.value + " ");
visit(root.right, output);
}
}- 非遞歸方式
public class InOrderVisitor {
public <V> void visit(Node<V> root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node<V>> help = new Stack<>();
// 定義一個當前結點遍歷並指向根結點
Node<V> current = root;
while (current != null || !help.isEmpty()) {
if (current != null) {
// 若當前結點不為空,則入棧
help.push(current);
// 將當前結點指向該結點的左孩子
current = current.left;
} else {
// 若當前結點為空(即當前已經沒有可訪問的左子樹了),則出棧
current = help.pop();
// 訪問出棧結點
System.out.println(current.value + " ");
// 將當前結點指向出棧結點的右孩子
current = current.right;
// (若該結點存在,則重複執行上面的if分支將該結點的左子樹依次入棧)
}
}
}
}
後序遍歷
操作步驟如下:
- 遞歸遍歷左子樹
- 遞歸遍歷右子樹
- 訪問根結點
假設一個二叉樹的結構如下圖所示: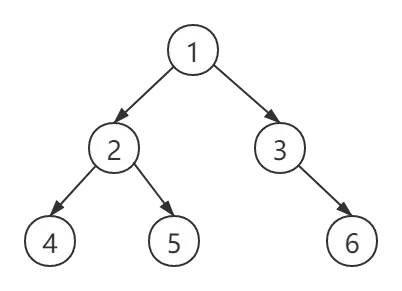
則遍歷結果為:4 5 2 6 3 1
實現方式:
- 遞歸方式
public class PostOrderRecursivelyVisitor {
public <V> void visit(Node<V> root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
visit(root.left, output);
visit(root.right, output);
System.out.println(node.value + " ");
}
}- 非遞歸方式
這種方式稍微複雜一點,因為要先遍歷完左右子樹,再訪問根結點,所以需要知道左右子樹的訪問狀態。
public class PostOrderVisitor {
public <V> void visit(Node<V> root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node<V>> help = new Stack<>();
// 根結點入棧
help.push(root);
// top指向棧頂元素
Node<V> top = null;
// visited表示剛剛訪問過的結點(初始指向根結點)
Node<V> visited = root;
while (!help.isEmpty()) {
// 獲取棧頂元素,但是不進行出棧操作
top = help.peek();
if (top.left != null && top.left != visited && top.right != visited) {
// 若棧頂元素的左孩子結點存在,且左右孩子都未被訪問過,則左孩子入棧
help.push(top.left);
} else if (top.right != null && top.right != visited) {
// 若棧頂元素的右孩子結點存在,且右孩子未被訪問過,則右孩子入棧
help.push(top.right);
} else {
// 棧頂元素出棧,並訪問該結點
System.out.println(help.pop().value + " ");
// 記錄已訪問過的結點
visited = top;
}
}
}
}層序遍歷
也可稱為廣度優先遍歷
操作步驟如下:
從上往下,從左至右依次訪問每層的結點
假設一個二叉樹的結構如下圖所示: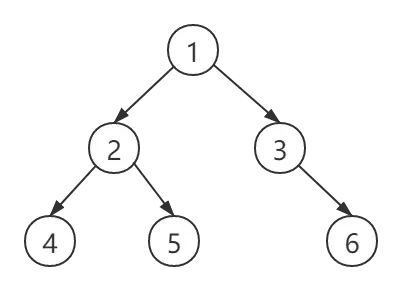
則遍歷結果為:1 2 3 4 5 6
實現方式:
藉助隊列(先進先出)來實現
代碼如下:
public class LevelOrderVisitor {
public <V> void visit(Node<V> root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Queue<Node<V>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 根結點進入隊尾
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 出隊列
Node<V> node = queue.poll();
// 訪問該結點
System.out.println(node.value + " ");
// 依次將該結點的左右孩子入隊列
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
}
以上就是遍歷二叉樹的幾種方式,完整代碼可查看二叉樹的遍歷。如有錯誤,請指正,謝謝。

