博主介紹:✌全網粉絲22W+,博客專家、Java領域優質創作者,華為雲/阿里雲/等平台優質作者、專注於Java技術領域✌
技術範圍:SpringBoot、SpringCloud、Vue、SSM、HTML、Nodejs、Python、MySQL、PostgreSQL、大數據、物聯網、機器學習等設計與開發。
感興趣的可以先關注收藏起來,在工作中、生活上等遇到相關問題都可以給我留言諮詢,希望幫助更多的人。
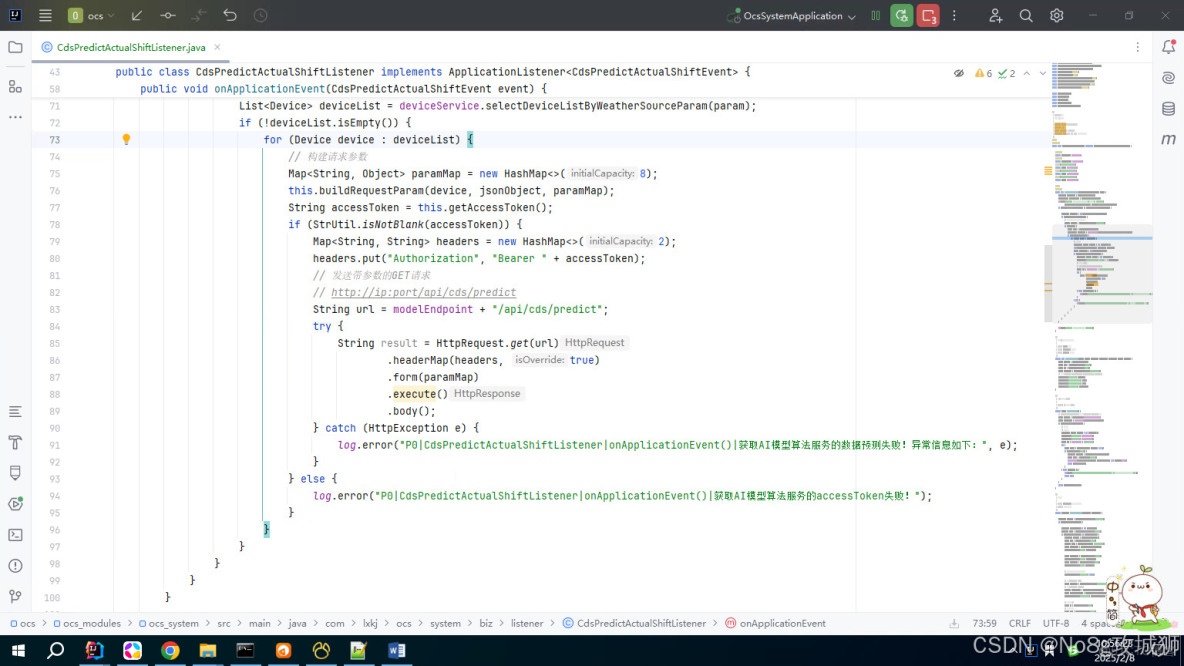
在idea中提示 hutool 提示 HttpResponse used withoud try-with-resources statement
- 一、try-with-resources介紹
- 二、try-with-resources優點
- 三、如何修改為 try-with-resources 結構
- 四、使用 try-with-resources 的示例
- 4.1 示例 1:讀取文件
- 4.2 示例 2:寫入文件
- 4.3 多個資源的管理
- 4.4 自定義資源類
- 4.5 異常處理
- 五、注意事項
- 六、總結
如下圖所示,在idea中提示 hutool 提示 HttpResponse used withoud try-with-resources statement 的內容:
一、try-with-resources介紹
在 Java 開發中,使用 try-with-resources 語句是一種推薦的做法,因為它可以確保在語句結束時自動釋放資源,比如關閉文件、數據庫連接等。對於 hutool 庫中的 HttpResponse 對象,如果你在使用它時沒有遵循這種模式,IDEA(或其他IDE)會提示你這樣做。
try-with-resources 是 Java 7 引入的一種語法結構,用於自動管理資源(如文件流、數據庫連接、網絡連接等)。它可以確保在 try 塊執行完畢後,資源會被自動關閉,無需手動調用 close() 方法,從而避免資源泄漏。
二、try-with-resources優點
為什麼需要使用 try-with-resources?
- 自動資源管理:確保每次使用完資源後都能正確關閉,防止資源泄露。
- 代碼簡潔:減少顯式的關閉代碼,使代碼更簡潔易讀。
- 異常處理:自動處理資源關閉過程中可能出現的異常。
如何修改代碼以使用 try-with-resources?
三、如何修改為 try-with-resources 結構
try-with-resources 的語法如下:
try (ResourceType resource = new ResourceType()) {
// 使用資源的代碼
} catch (Exception e) {
// 異常處理
}
ResourceType: 必須實現java.lang.AutoCloseable接口(或java.io.Closeable,它是AutoCloseable的子接口)。resource: 在 try 塊中聲明的資源對象。自動關閉: 無論 try 塊是否正常執行完畢,或者是否拋出異常,資源都會在 try 塊結束後自動關閉。
如何使用?假設你有以下使用 hutool 的 HttpResponse 的代碼:
HttpResponse response = HttpRequest.get("http://example.com")
.execute();你可以改寫為使用 try-with-resources 的形式:
try (HttpResponse response = HttpRequest.get("http://example.com").execute()) {
// 在這裏處理你的響應
} catch (IOException e) {
// 處理異常
e.printStackTrace();
}解釋:
try:開始一個try-with-resources塊。HttpResponse response = ...:聲明並初始化資源,放在括號內,這樣在 try 塊結束時會自動調用 response.close()(如果該方法存在)。try 塊內的代碼:執行你的邏輯,比如讀取響應內容。catch 塊:捕獲並處理可能發生的 IOException。
四、使用 try-with-resources 的示例
4.1 示例 1:讀取文件
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TryWithResourcesExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "example.txt";
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath))) {
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("讀取文件時發生錯誤: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}説明:
BufferedReader和FileReader都實現了AutoCloseable接口。- 在 try 塊結束後,
BufferedReader和FileReader會自動關閉,無需手動調用close()方法。
4.2 示例 2:寫入文件
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TryWithResourcesExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "output.txt";
try (BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath))) {
bw.write("Hello, try-with-resources!");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("This is a test.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("寫入文件時發生錯誤: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}説明:
BufferedWriter和FileWriter都實現了AutoCloseable接口。- 在 try 塊結束後,
BufferedWriter和FileWriter會自動關閉。
4.3 多個資源的管理
try-with-resources 支持同時管理多個資源,多個資源之間用分號 ; 分隔。
示例:同時讀取和寫入文件
import java.io.*;
public class TryWithResourcesExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String inputFilePath = "input.txt";
String outputFilePath = "output.txt";
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(inputFilePath));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(outputFilePath))) {
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("文件操作時發生錯誤: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}説明:
- 同時管理
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter兩個資源。 - 資源會按照聲明的相反順序關閉(即先關閉
BufferedWriter,再關閉BufferedReader)。
4.4 自定義資源類
如果你有自定義的資源類,需要實現 AutoCloseable 接口,並重寫 close() 方法。
示例:自定義資源類
public class CustomResource implements AutoCloseable {
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("執行某些操作...");
}
@Override
public void close() {
System.out.println("資源已關閉!");
}
}
public class TryWithResourcesExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (CustomResource resource = new CustomResource()) {
resource.doSomething();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("發生異常: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}輸出內容:
執行某些操作...
資源已關閉!説明:
CustomResource實現了AutoCloseable接口,並重寫了close()方法。- 在 try 塊結束後,
close()方法會被自動調用。
4.5 異常處理
try-with-resources 中的異常處理與普通 try-catch 類似。如果在 try 塊和 close() 方法中都拋出了異常,try 塊中的異常會被拋出,而 close() 方法中的異常會被抑制(可以通過 Throwable.getSuppressed() 獲取被抑制的異常)。
示例:異常處理
public class CustomResource implements AutoCloseable {
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
throw new Exception("關閉資源時發生異常!");
}
}
public class TryWithResourcesExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (CustomResource resource = new CustomResource()) {
throw new Exception("執行操作時發生異常!");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("捕獲異常: " + e.getMessage());
for (Throwable suppressed : e.getSuppressed()) {
System.err.println("被抑制的異常: " + suppressed.getMessage());
}
}
}
}輸出內容:
捕獲異常: 執行操作時發生異常!
被抑制的異常: 關閉資源時發生異常!五、注意事項
確保 HttpResponse 類實現了 AutoCloseable 接口或者在內部使用了可以自動關閉的資源。如果不是,你可能需要手動管理資源的關閉,例如通過調用 response.close()。
如果 HttpResponse 沒有實現 AutoCloseable 或類似的接口,你可以考慮在 finally 塊中手動關閉它:
HttpResponse response = HttpRequest.get("http://example.com").execute();
try {
// 使用 response
} finally {
if (response != null) {
response.close(); // 確保關閉資源
}
}六、總結
總之,使用 try-with-resources 是更好的實踐,因為它可以自動管理資源,減少代碼冗餘並提高代碼的健壯性。如果庫的類不提供自動關閉的支持,你應該確保在 finally 塊中手動關閉資源。
- 優點:
- 自動管理資源,避免資源泄漏。
- 代碼簡潔,減少手動關閉資源的繁瑣操作。
- 支持多個資源的管理。
- 適用場景:
- 文件 I/O 操作。
- 數據庫連接。
- 網絡連接。
- 任何實現了 AutoCloseable 接口的資源類。
通過正確使用 try-with-resources,可以顯著提高代碼的健壯性和可讀性,同時避免資源泄漏問題。
好了,今天分享到這裏。希望你喜歡這次的探索之旅!不要忘記 “點贊” 和 “關注” 哦,我們下次見!🎈
本文完結!