一、開篇
本篇是《Spring OAuth2 開發指南》系列文章的第二篇,通過代碼實例詳細介紹 OAuth2 密碼模式的開發細節。網絡上關於 OAuth2 開發的代碼示範十分多而且雜亂,基本上都是官方手冊的摘錄搬運,或者過多地受制於框架本身如 Spring Security,約束太多,缺乏系統性,容易造成同學們雲裏霧裏,以至於生搬硬套。
本人主張在開發落地過程中,既不能完全自己造輪子,也不應完全依賴輪子,應該從本質出發,在理清技術原理和細節的條件下,選擇適合的方法。從這個原則出發,本文將根據“密碼模式的典型架構層次和主要流程”(見《Spring OAuth2 開發指南(一)》)中描述的流程節點,展示其代碼實現。另外,文章的要點在於後半部分,提出了資源服務器端鑑權/權限控制,和授權服務器端鑑權/權限控制兩種實現方法。
需要注意的是 password 模式由於 OAuth2.1 不推薦使用所以只提供舊的組件代碼版本,具體請參見 https://datatracker.ietf.org/...
二、 演示案例
我們繼續用相冊預覽系統(PAPS,Photo Album Preview System)作為演示案例。
PAPS 是一個社交平台的子系統,與 IBCS 類似,採用 RESTful API 對外交互,主要功能是允許用户預覽自己的相冊,以下是 PAPS 演示項目的必要服務:
服務名 | 類別 | 描述 | 技術選型
-
photo-service 內部服務 資源服務器角色,相冊預覽服務 Spring Boot 開發的 RESTful 服務 idp 內部服務 授權服務器角色,具體指負責認證、授權和鑑權 Spring Boot 開發 demo-h5 外部應用 demo 應用的前端 使用 Postman 代替
為此,我們將搭建兩個工程項目:photo-service 和 idp,客户端用 Postman 代替。
三、 工程結構
接下來演示兩個工程項目的框架代碼,這部分代碼包含工程的框架結構、Spring Security 和 OAuth2 的基礎配置,儘量採用最精簡的方式書寫。其他項目可以 copy 這部分代碼作為基礎模板使用。
photo-service 相冊服務
- 基礎工程結構
src/main
java
com.example.demophoto
config
oauth2
CheckTokenAuthentication.java
CheckTokenFilter.java
CustomPermissionEvaluator.java
CustomRemoteTokenServices.java
ResourceServerConfigurer.java
service
PermisionEvaluatingService.java
web
PhotoController.java
DemoPhotoApplication.java
resources
applicaton.yaml- pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>oauth2-demo-1a-photo-service</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>oauth2-demo-1a-photo-service</name>
<description>oauth2-demo-1a-photo-service</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.security.oauth.boot/spring-security-oauth2-autoconfigure -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security.oauth.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>- applicaton.yaml
server:
port: 8010
security:
oauth2:
client:
clientId: client2
clientSecret: client2p
resource:
tokenInfoUri: http://127.0.0.1:8000/oauth/check_token- ResourceServerConfigurer.java
package com.example.demophoto.config.oauth2;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableResourceServer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer;
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfigurer extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* spring-security-oauth2 組件一般性配置
*
* @param resources
*/
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) {
resources.resourceId("demo-1");
}
/**
* spring-security-oauth2 組件一般性配置
*
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}idp 授權服務
- 基礎工程結構
src/main
java
com.example.demoidp
config
oauth2
AuthorizationServerConfigurer.java
CheckTokenInterceptor.java
WebSecurityConfig.java
service
業務邏輯,如鑑權邏輯
DemoIdpApplication.java
resources
applicaton.yaml- pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>oauth2-demo-1a-idp</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>oauth2-demo-1a-idp</name>
<description>oauth2-demo-1a-idp</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.security.oauth/spring-security-oauth2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security.oauth</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2</artifactId>
<version>2.3.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>- applicaton.yaml
server:
port: 8000- AuthorizationServerConfigurer.java
package com.example.demoidp.config.oauth2;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.factory.PasswordEncoderFactories;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableAuthorizationServer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer;
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class AuthorizationServerConfigurer extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
/**
* spring-security-oauth2 組件一般性配置
*
* @param authenticationManager
*/
@Autowired
public AuthorizationServerConfigurer(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {
this.authenticationManager = authenticationManager;
}
/**
* 配置密碼加密方法
*/
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
/**
* spring-security-oauth2 組件一般性配置
*
* @param endpoints
*/
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) {
endpoints.authenticationManager(authenticationManager);
}
/**
* spring-security-oauth2 組件一般性配置
*
* @param security
*/
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) {
security
// /oauth/check_token 請求放行
.checkTokenAccess("permitAll()")
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
}- WebSecurityConfig.java
package com.example.demoidp.config.oauth2;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* spring-security-oauth2 組件一般性配置
*
* @return AuthenticationManager
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
}四、 代碼實現
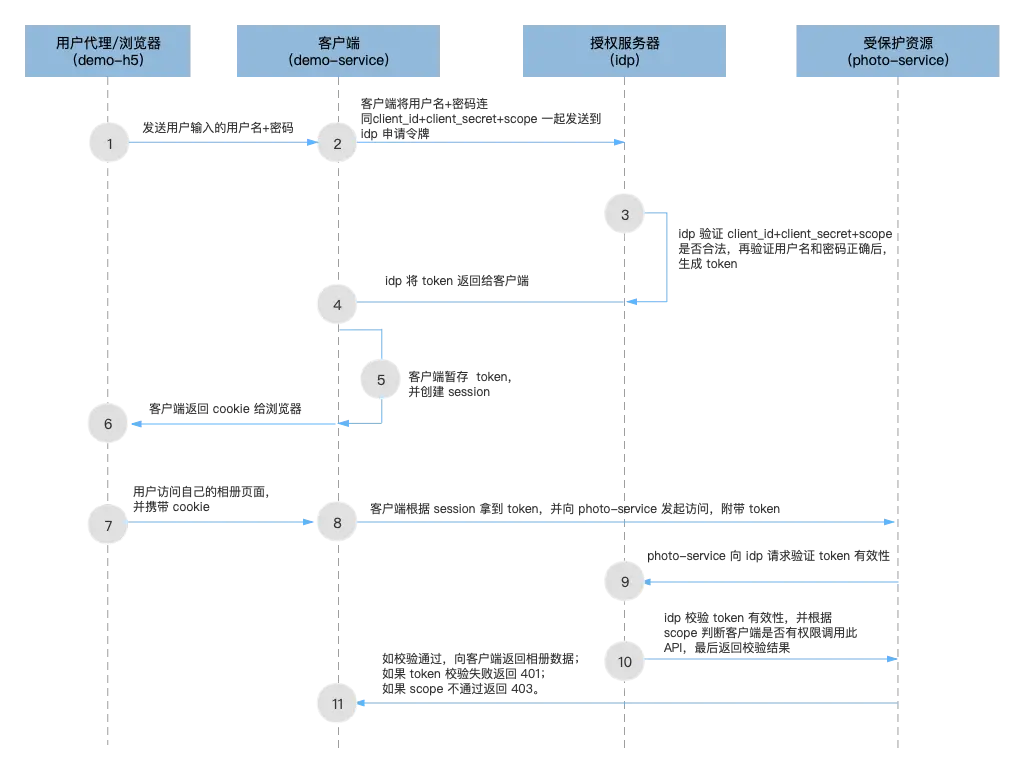
如圖所示,是密碼模式的最精簡架構層次和主要流程。下面我們逐步實現該流程:
一)第一階段:認證授權階段
1)用户代理(demo-h5)將用户輸入的用户名和密碼,發送給客户端(demo-service)
此步驟我們使用 Postman 執行,這裏不展開介紹。
2)客户端(demo-service)將用户輸入的用户名和密碼,連同 client_id + client_secret (由 idp 分配)一起發送到 idp 以請求令牌,如果 idp 約定了 scope 則還需要帶上 scope 參數
此步驟我們使用 Postman 執行,這裏不展開介紹。需要注意的是,Postman 在這裏仍然是一個 client 角色,client_id 代表的是它自己。請求的 URL 為:
POST http://127.0.0.1:8000/oauth/token3)idp 首先驗證 client_id + client_secret 的合法性,再檢查 scope 是否無誤,最後驗證用户名和密碼是否正確,正確則生成 token。這一步也叫“認證”
為了實現這個步驟,我們在 idp 工程的 AuthorizationServerConfigurer 類中加入以下代碼:
- 首先是 client_id + client_secret + scope 的校驗
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class AuthorizationServerConfigurer extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
...
/**
* 3. [密碼模式的典型架構層次和主要流程] 中的第 3 步:
* idp 首先驗證 client_id + client_secret 的合法性,再檢查 scope 是否無誤
*
* PS: 這裏為演示方便,就地創建了賬號,生產環境應自行替換成數據庫查詢等方式
*/
private class MockJDBCClientDetailsService implements ClientDetailsService {
@Override
public ClientDetails loadClientByClientId(String clientId) throws ClientRegistrationException {
/**
* GrantedAuthority 與 hasAuthority() 關聯
*/
Set<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new HashSet<>();
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("READ"));
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("WRITE"));
BaseClientDetails details1 = new BaseClientDetails();
details1.setClientId("client1");
details1.setClientSecret(passwordEncoder().encode("client1p"));
details1.setAuthorizedGrantTypes(Arrays.asList("password"));
details1.setScope(Arrays.asList("resource:write", "resource:read"));
details1.setResourceIds(Arrays.asList("demo-1"));
details1.setAuthorities(authorities);
BaseClientDetails details2 = new BaseClientDetails();
details2.setClientId("client2");
details2.setClientSecret(passwordEncoder().encode("client2p"));
details2.setAuthorizedGrantTypes(Arrays.asList("client_credentials"));
details2.setScope(Arrays.asList("resource:write", "resource:read"));
details2.setResourceIds(Arrays.asList("demo-1"));
details2.setAuthorities(authorities);
BaseClientDetails details3 = new BaseClientDetails();
details3.setClientId("client3");
details3.setClientSecret(passwordEncoder().encode("client3p"));
details3.setAuthorizedGrantTypes(Arrays.asList("password"));
details3.setScope(Arrays.asList("resource:write", "resource:read"));
details3.setResourceIds(Arrays.asList("demo-1"));
details3.setAuthorities(authorities);
Map<String, ClientDetails> clients = new HashMap<>();
clients.put("client1", details1);
clients.put("client2", details2);
clients.put("client3", details3);
if (!clients.containsKey(clientId)) {
throw new ClientRegistrationException("Client not found");
}
return clients.get(clientId);
}
}
/**
* spring-security-oauth2 組件一般性配置
* 配置自定義 ClientDetails
*
* @param clients
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.withClientDetails(new MockJDBCClientDetailsService());
}
...
}- 然後是用户名和密碼的校驗
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* 3. [密碼模式的典型架構層次和主要流程] 中的第 3 步:
* 驗證用户名和密碼是否正確,正確則生成 token
*
* PS: 這裏為演示方便,就地創建了賬號,生產環境應自行替換成數據庫查詢等方式
*/
private class MockJDBCUserDeatilsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
Map<String, String> users = new HashMap<>();
users.put("user1", "pwd1");
users.put("user2", "pwd2");
if (!users.containsKey(username)) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User not found");
}
return User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username(username)
.password(users.get(username))
.roles("USER")
.build();
}
}
@Bean
@Override
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
return new MockJDBCUserDeatilsService();
}
}當 client_id + client_secret + scope,以及用户名和密碼都校驗通過後,spring-security-oauth2 會調用合適的 tokenServices 生成 token。有興趣的同學可以自行查閲源代碼追蹤整個過程,這裏介紹源碼追蹤的入口方法:
我們知道 demo-h5 客户端(Postman)首先向 http://127.0.0.1:8000/oauth/t... 發起請求,因此我們找到 spring-security-oauth2 組件源碼中的 /oauth/token 端點,具體路徑為:
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.endpoint.TokenEndpoint.postAccessToken()4)idp 返回認證結果給客户端,認證通過返回 token,認證失敗返回 401。如果認證成功則此步驟也叫“授權”
這一步 spring-security-oauth2 已經為我們處理好了,不需要額外處理。想要追蹤源碼過程的同學,可參考上一步驟介紹的入口方法。
5)客户端收到 token 後進行暫存,並創建對應的 session
這個步驟通過 Postman 演示(直接複製返回的 token 字符串即可),這裏不展開介紹。
6)客户端頒發 cookie 給用户代理/瀏覽器
這個步驟通過 Postman 演示,這裏不展開介紹。
二)第二階段:授權後請求資源階段
7)用户通過用户代理(demo-h5)訪問“我的相冊”頁面,用户代理攜帶 cookie 向客户端(demo—service)發起請求
此步驟使用 Postman 執行,不展開敍述。
8)客户端通過 session 找到對應的 token,攜帶此 token 向資源服務器(photo-service)發起請求
此步驟使用 Postman 執行,我們將第 5) 步獲取的 token 作為 Bearer Token,向 photo-service 發起請求,請求的 URL 為:
GET http://127.0.0.1:8010/api/photo
該請求只需要攜帶 token 即可,不需要其他參數9)資源服務器(photo-service)向 idp 請求驗證 token 有效性
在介紹如何處理請求前,我們先在 photo-service 工程中新增相關代碼:
- PhotoController.java
package com.example.demophoto.web;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/")
public class PhotoController {
@GetMapping("/photo")
public String fetchPhoto() {
return "GET photo";
}
}
此外,還有幾個關鍵配置:
- ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter.configure(HttpSecurity http) 方法配置了 http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated() 使得所有請求都要先鑑權;
- application.yaml 中配置了 client_id、client_secret 和 resource.tokenInfoUri,當資源服務接受到請求時,會攜帶 token 向 tokenInfoUri 指定的地址發起鑑權請求。
默認情況下,當 demo-h5 向 photo-service 發起資源訪問的請求時,photo-service 會將獲取的 token 發到 idp 進行校驗,在這個過程中 spring-security-oauth2 不會對 scope 做任何處理。我們知道 scope 是用來約束 client 的權限範圍的,因此 scope 權限檢查(也視為鑑權的工作之一)這個工作需要自己編碼實現。
通常來説,scope 權限檢查的業務邏輯可以靈活設定,甚至可以忽略它。本文介紹兩種 scope 檢查的實現方法:
- 資源服務器端檢查;
- 授權服務器端檢查。
接下來的第 10) 步將拆分成兩種方式,分別對此進行介紹。
10)【方式一:資源服務器端 scope 檢查】 idp 校驗 token 有效性,資源服務器校驗 scope
idp 校驗 token 有效性,通過則返回 client 相關信息(包含 scope )給 photo-service,photo-service 再根據 scope 判斷客户端(demo-h5)是否有權限調用此 API,如通過檢查則繼續下一步驟,否則返回 403 錯誤給 demo-h5。這一步也叫“鑑權”
我們在 photo-service 工程中添加以下代碼:
- ResourceServerConfigurer.java
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfigurer extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
...
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/photo/**").access("#oauth2.hasScope('resource:read')")
.antMatchers("/api/photo2/**").access("#oauth2.hasScope('resource:read')")
.antMatchers("/api/photo3/**").access("#oauth2.hasScope('resource:write')")
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
...
}通過 access("#oauth2.hasScope('resource:write')") 方法可以實現資源服務器端的 scope 檢查。其主要流程為:
- photo-service 收到客户端請求後,將獲取到的 token 發往 idp 校驗;
- idp 校驗通過後,將 clientDetails 信息返回給 photo-service,其中就包括 scope 參數;
- photo-service 拿到 scope 後,根據 access("#oauth2.hasScope('resource:write')") 判斷該請求是否在 scope 範圍內。
10)【方式二:idp 端 scope 檢查】 idp 校驗 token + scope 有效性
idp 校驗 token 有效性,再根據 scope 判斷客户端(demo-h5)是否有權限調用此 API,最後返回校驗結果給資源服務器。由於 spring-security-oauth2 本身沒有處理 scope 檢查,且默認情況下,photo-service 向 idp 請求 token 鑑權時,並未攜帶任何其他請求信息,因此 idp 無法知道本次請求的細節,因此無法執行 socpe 檢查。
所以重點有兩個:一是 photo-service 向 idp 請求 token 鑑權的同時如何攜帶請求的細節(比如訪問的是什麼資源?請求的是哪個API?);二是如何攔截 token 鑑權過程使得 scope 校驗失敗是返回 403 錯誤?
當然實現這個目的,有很多方法,本文采用了比較直觀的方法:利用 Filter。
我們在 photo-service 工程中添加以下代碼:
- ResourceServerConfigurer.java
package com.example.demophoto.config.oauth2;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.ResourceServerProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableResourceServer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.preauth.AbstractPreAuthenticatedProcessingFilter;
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfigurer extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
private final ResourceServerProperties resource;
@Autowired
protected ResourceServerConfigurer(ResourceServerProperties resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
/**
* 自定義 RemoteTokenServices 以取代資源服務器默認使用的
* RemoteTokenServices 向 IDP 發起 /oauth/check_token 鑑權請求
*
* @return
*/
public CustomRemoteTokenServices customRemoteTokenServices() {
CustomRemoteTokenServices services = new CustomRemoteTokenServices();
services.setCheckTokenEndpointUrl(this.resource.getTokenInfoUri());
services.setClientId(this.resource.getClientId());
services.setClientSecret(this.resource.getClientSecret());
return services;
}
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) {
resources.resourceId("demo-1")
.tokenServices(customRemoteTokenServices());
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.addFilterBefore(new CheckTokenFilter(), AbstractPreAuthenticatedProcessingFilter.class);
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/photo/**").access("#oauth2.hasScope('resource:read')")
.antMatchers("/api/photo2/**").access("#oauth2.hasScope('resource:read')")
.antMatchers("/api/photo3/**").access("#oauth2.hasScope('resource:write')")
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}- CheckTokenFilter.java
package com.example.demophoto.config.oauth2;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 在向 IDP 發起 /oauth/check_token 請求前,將請求細節存儲到 SecurityContext 中,
* 以便 CustomRemoteTokenServices.loadAuthentication() 可以獲取到該請求細節
*/
public class CheckTokenFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException,
ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
String method = request.getMethod();
/**
* 僅處理 /api/**
*/
if (!uri.startsWith("/api/")) {
chain.doFilter(req, res);
return;
}
SecurityContext sc = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
CheckTokenAuthentication authentication = (CheckTokenAuthentication) sc.getAuthentication();
if (authentication == null) {
authentication = new CheckTokenAuthentication(null);
}
/**
* 將用户代理或其他服務請求訪問本資源服務器的細節(此處為 HTTP-Method + URI)
* 存儲到 SecurityContext 的 authentication 對象中
*/
Map<String, Object> details = new HashMap<>();
details.put("uri", uri);
details.put("method", method);
authentication.setDetails(details);
sc.setAuthentication(authentication);
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
}- CustomRemoteTokenServices.java
package com.example.demophoto.config.oauth2;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.http.*;
import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.codec.Base64;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.resource.OAuth2AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.OAuth2AccessToken;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.exceptions.InvalidTokenException;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.OAuth2Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.AccessTokenConverter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.DefaultAccessTokenConverter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.ResourceServerTokenServices;
import org.springframework.util.LinkedMultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.web.client.DefaultResponseErrorHandler;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestOperations;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 以 RemoteTokenServices 為模板
* 基本思路是在向 IDP 發起 /oauth/check_token 的請求中,
* 添加用户代理或其他服務請求訪問本資源服務器的 API 的細節,
* 以便 IDP 可以判斷該用户代理或其他服務(即 client)是否可以調用此 API
* <p>
* (PS:也可以由 IDP 返回 ClientDetails 給資源服務,由資源服務處理放行邏輯)
*/
public class CustomRemoteTokenServices implements ResourceServerTokenServices {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private RestOperations restTemplate;
private String checkTokenEndpointUrl;
private String clientId;
private String clientSecret;
private String tokenName = "token";
/**
* 與 IDP 約定的存儲 API 請求細節的參數
*/
private String reqPayload = "payload";
private AccessTokenConverter tokenConverter = new DefaultAccessTokenConverter();
public CustomRemoteTokenServices() {
restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
((RestTemplate) restTemplate).setErrorHandler(new DefaultResponseErrorHandler() {
@Override
// Ignore 400
public void handleError(ClientHttpResponse response) throws IOException {
Integer statusCode = response.getRawStatusCode();
if (statusCode != 400) {
if (statusCode == 401 || statusCode == 403) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.resolve(statusCode);
throw new AccessDeniedException(status.toString());
}
super.handleError(response);
}
}
});
}
public void setRestTemplate(RestOperations restTemplate) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
}
public void setCheckTokenEndpointUrl(String checkTokenEndpointUrl) {
this.checkTokenEndpointUrl = checkTokenEndpointUrl;
}
public void setClientId(String clientId) {
this.clientId = clientId;
}
public void setClientSecret(String clientSecret) {
this.clientSecret = clientSecret;
}
public void setAccessTokenConverter(AccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter) {
this.tokenConverter = accessTokenConverter;
}
public void setTokenName(String tokenName) {
this.tokenName = tokenName;
}
/**
* 當使用自定義的 tokenServices 替換默認的 tokenServices 後,
* 原來流程中的第 9 步就變成由該方法執行。
*
* 9. [密碼模式的典型架構層次和主要流程] 中的第 9 步:
* 資源服務器(photo-service)向 idp 請求驗證 token 有效性
*
* @param accessToken
* @return
* @throws AuthenticationException
* @throws InvalidTokenException
*/
@Override
public OAuth2Authentication loadAuthentication(String accessToken) throws AuthenticationException, InvalidTokenException {
Map<String, Object> authDetails = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 取得在 CheckTokenFilter 過濾器中置入的 API 請求細節
*/
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication != null) {
authDetails = (Map<String, Object>) authentication.getDetails();
}
MultiValueMap<String, String> formData = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
formData.add(tokenName, accessToken);
if (!authDetails.isEmpty()) {
formData.add(reqPayload, authDetails.get("method") + " " + authDetails.get("uri"));
}
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.set("Authorization", getAuthorizationHeader(clientId, clientSecret));
Map<String, Object> map = postForMap(checkTokenEndpointUrl, formData, headers);
/**
* 11. [密碼模式的典型架構層次和主要流程] 中的第 11 步:
* 如果 token 校驗失敗則返回 401 給客户端,如果 scope 檢查不通過則返回 403
*/
if (map.containsKey("error")) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("check_token returned error: " + map.get("error"));
}
if (map.containsKey("status")) {
if ("403".equals(map.get("status").toString())) {
throw new OAuth2AccessDeniedException(map.get("error").toString());
}
}
throw new InvalidTokenException(accessToken);
}
// gh-838
if (map.containsKey("active") && !"true".equals(String.valueOf(map.get("active")))) {
logger.debug("check_token returned active attribute: " + map.get("active"));
throw new InvalidTokenException(accessToken);
}
return tokenConverter.extractAuthentication(map);
}
@Override
public OAuth2AccessToken readAccessToken(String accessToken) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported: read access token");
}
private String getAuthorizationHeader(String clientId, String clientSecret) {
if (clientId == null || clientSecret == null) {
logger.warn("Null Client ID or Client Secret detected. Endpoint that requires authentication will reject request with 401 error.");
}
String creds = String.format("%s:%s", clientId, clientSecret);
try {
return "Basic " + new String(Base64.encode(creds.getBytes("UTF-8")));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not convert String");
}
}
private Map<String, Object> postForMap(String path, MultiValueMap<String, String> formData, HttpHeaders headers) {
if (headers.getContentType() == null) {
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED);
}
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
try {
Map map = restTemplate.exchange(path, HttpMethod.POST,
new HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, String>>(formData, headers), Map.class).getBody();
result = map;
}
catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage());
}
return result;
}
}- CheckTokenAuthentication.java
package com.example.demophoto.config.oauth2;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AbstractAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CheckTokenAuthentication extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
/**
* Creates a token with the supplied array of authorities.
*
* @param authorities the collection of <tt>GrantedAuthority</tt>s for the principal
* represented by this authentication object.
*/
public CheckTokenAuthentication(Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object getPrincipal() {
return null;
}
}接着在 idp 工程中添加以下代碼:
- AuthorizationServerConfigurer.java
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class AuthorizationServerConfigurer extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
...
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) {
endpoints.authenticationManager(authenticationManager)
// 通過插入 interceptor 來實現自定義的鑑權方法
.addInterceptor(new CheckTokenInterceptor(endpoints.getTokenStore()));
}
...
}- CheckTokenInterceptor.java
package com.example.demoidp.config.oauth2;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.OAuth2Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.OAuth2Request;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.TokenStore;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* /oauth/check_token 校驗 token 請求攔截器
*/
public class CheckTokenInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private String TOKEN_NAME = "token";
private final String TOKEN_INFO_URI = "/oauth/check_token";
private TokenStore tokenStore;
public CheckTokenInterceptor(TokenStore tokenStore) {
this.tokenStore = tokenStore;
}
// for test only
private final Map<String, String> clientScopes = new HashMap<String, String>() {
{
put("client1[resource:read]", "GET /api/photo");
put("client1[resource:write]", "POST /api/photo");
put("client2[resource:read]", "GET /api/photo2");
put("client2[resource:write]", "POST /api/photo2");
put("client3[resource:read]", "GET /api/photo3");
put("client3[resource:write]", "POST /api/photo3");
}
};
/**
* 10. [密碼模式的典型架構層次和主要流程] 中的第 10 步:
* idp 校驗 token 有效性和 scope 權限
* <p>
* 即 IDP 根據 scope 判斷客户端(demo-service)
* 是否有權限調用此 API,最後返回校驗結果給資源服務器
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
/**
* 僅攔截 /oauth/check_token
*/
if (!TOKEN_INFO_URI.equals(uri)) {
return true;
}
/**
* payload 是 IDP 和資源服務器角色約定的傳參格式
* 即 client 請求訪問資源服務器的 API 的細節
* 可要求必須攜帶 payload
*
* 此部分可根據業務邏輯自行處理
*/
String paylad = request.getParameter("payload");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(paylad)) {
throw new AccessDeniedException("insufficient_payload");
}
if ("GET /error".equals(paylad)) {
return true;
}
/**
* 10. [密碼模式的典型架構層次和主要流程] 中的第 10 步:
* 【方式二:idp 端 scope 檢查】 idp 校驗 token + scope 有效性
*
* 根據 token 查得 clientId,再根據 scope 檢查該 client 是否有權限調用此 API
* 此部分可根據業務邏輯自行處理,比如從數據庫中查詢 client、API 和 scope 的關係
*/
String token = request.getParameter(TOKEN_NAME);
OAuth2Authentication oAuth2Authentication = tokenStore.readAuthentication(token);
OAuth2Request oAuth2Request = oAuth2Authentication.getOAuth2Request();
String scopeKey = oAuth2Request.getClientId() + oAuth2Request.getScope();
if (clientScopes.containsKey(scopeKey)) {
if (!clientScopes.get(scopeKey).equals(paylad)) {
throw new AccessDeniedException("insufficient_scope");
}
}
return true;
}
}idp 端的 scope 檢查實現起來稍微麻煩點,其主要思路是:
- 在 photo-service 向 idp 發起 /oauth/check_oauth 鑑權請求前,添加過濾器,將客户端的請求細節保存到某個全局對象中;
- 替換 photo-service 默認的 tokenServices,在向 idp 發起 /oauth/check_oauth 鑑權請求的過程中,將請求細節附加到請求中;
- idp 在 AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer 中添加自定義 Interceptor,在每次 check token 前先執行 自定義 Interceptor;
- idp 在自定義 Interceptor 中取出請求細節,根據請求細節和 clientDetails 信息(scope),執行 scope 檢查。
以上方法,雖然實現麻煩,但是定製性和靈活性很強,不受框架約束,可以適應各種複雜的業務邏輯。
11)資源服務器根據 idp 檢驗結果(true/false 或其他等效手段)決定是否返回用户相冊數據給客户端。如果 token 校驗失敗則返回 401 給客户端,如果 scope 檢查不通過則返回 403。這一步也叫“權限控制”
與鑑權工作中的 scope 範圍檢查類似,實現權限控制的方法也有兩種:
- 授權服務器端的權限控制,屬於集中式權限控制;
- 資源服務器端的權限控制,屬於分散型權限控制。
其中,授權服務器端的權限控制比較簡單,在 idp 工程的 CheckTokenInterceptor.preHandle() 方法中添加權限控制的業務代碼即可:
- CheckTokenInterceptor.java
public class CheckTokenInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
...
/**
* 11. [密碼模式的典型架構層次和主要流程] 中的第 11 步:
* 授權服務器短的權限控制,即集中式權限控制
*
* 實現更細粒度的權限控制,從某種程度上來説,這個過程也可以稱作鑑權
*/
// 授權服務器端鑑權/權限控制業務的邏輯
return true;
}
}最後來看資源服務器端的權限控制。我們使用 spring-secutity 提供的標準方法來實現:
- 資源服務器端 PreAuthorize hasRole/hasAuthority
- 資源服務器端 PreAuthorize 自定義實現 hasPermission
以上説法在某種程度上也可以理解為鑑權。
首先,我們添加或修改 photo-service 工程的相關代碼:
- PhotoController.java
package com.example.demophoto.web;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* 1、 權限控制的兩種類型:資源服務端權限控制、授權服務器端權限控制
* 2、 權限控制的三種方法:
* A、 資源服務器端 PreAuthorize hasRole/hasAuthority
* B、 資源服務器端 HttpSecurity access 自定義實現 hasPermission
* D、 授權服務器端 HandlerInterceptor
* 以上説法在某種程度上也可以理解為鑑權。
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/")
public class PhotoController {
@GetMapping("/photo")
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('USER') and hasAuthority('WRITE')")
public String fetchPhoto() {
return "GET photo";
}
@GetMapping("/photo2")
public String fetchPhoto2() {
return "GET photo 2";
}
@GetMapping("/photo3")
@PreAuthorize("hasPermission('PhotoController', 'read')")
public String fetchPhoto3() {
return "GET photo 3";
}
}- ResourceServerConfigurer.java
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfigurer extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
...
/**
* 舊版本的 spring-security-oauth2 還需要將執行 resources.expressionHandler(oAuth2WebSecurityExpressionHandler)
* 以注入自定義的 expressionHandler,當前及以後版本不需要了
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public OAuth2WebSecurityExpressionHandler oAuth2WebSecurityExpressionHandler() {
OAuth2WebSecurityExpressionHandler oAuth2WebSecurityExpressionHandler = new OAuth2WebSecurityExpressionHandler();
// 在新版本的 spring-security-oauth2 中,這行代碼可以不用,
// 框架會自動注入 customPermissionEvaluator 替換默認的 DenyAllPermissionEvaluator
// oAuth2WebSecurityExpressionHandler.setPermissionEvaluator(customPermissionEvaluator);
return oAuth2WebSecurityExpressionHandler;
}
...
}- CustomPermissionEvaluator.java
package com.example.demophoto.config.oauth2;
import com.example.demophoto.service.PermisionEvaluatingService;
import org.springframework.security.access.PermissionEvaluator;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Component
public class CustomPermissionEvaluator implements PermissionEvaluator {
private PermisionEvaluatingService permisionEvaluatingService = new PermisionEvaluatingService();
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(Authentication authentication, Object targetDomainObject, Object permission) {
return permisionEvaluatingService.hasPermission(authentication, targetDomainObject, permission);
}
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(Authentication authentication, Serializable targetId, String targetType, Object permission) {
return permisionEvaluatingService.hasPermission(authentication, targetId, targetType, permission);
}
}- PermisionEvaluatingService.java
package com.example.demophoto.service;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class PermisionEvaluatingService {
public boolean hasPermission(Authentication authentication, Object targetDomainObject, Object permission) {
// 業務邏輯
return true;
}
public boolean hasPermission(Authentication authentication, Serializable targetId, String targetType, Object permission) {
// 業務邏輯
return true;
}
}- DemoPhotoApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) // 開啓 hasRole/hasAuthority/hasPermission 支持
public class DemoPhotoApplication {
...
}經過以上配置,當客户端向 photo-service 發起 GET /api/photo3 請求時,將會進入 CustomPermissionEvaluator.hasPermission() 方法進行判斷,因此可以實現非常靈活的資源服務器端權限控制。