Source
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/datetime.html
Mysql 官方文檔解釋
The DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP types are related.
DATE"、"DATETIME "和 "TIMESTAMP "類型是相關的。
This section describes their characteristics, how they are similar, and how they differ. MySQL recognizes DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP values in several formats, described in Section 9.1.3, “Date and Time Literals”.
本節將介紹它們的特點、相似之處和不同之處。MySQL以幾種格式識別DATE、DATETIME和TIMESTAMP值,在第9.1.3節,"日期和時間字面"中描述。
For the DATE and DATETIME range descriptions, “supported” means that although earlier values might work, there is no guarantee.
對於 DATE 和 DATETIME 範圍描述,"支持 "表示雖然早期值可能有效,但不能保證。
The DATE type is used for values with a date part but no time part. MySQL retrieves and displays DATE values in '_`YYYY-MM-DD`_' format. The supported range is '1000-01-01' to '9999-12-31'.
Date "類型用於包含日期部分但不包含時間部分的值。MySQL 以 '_`YYY-MM-DD`_' 格式檢索和顯示 DATE 值。支持的範圍是1000-01-01 至 9999-12-31。
The DATETIME type is used for values that contain both date and time parts.
DATETIME "類型用於包含日期和時間部分的值。
MySQL retrieves and displays DATETIME values in '_`YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss`_' format.
MySQL 以YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss格式檢索和顯示DATETIME值。
The supported range is '1000-01-01 00:00:00' to '9999-12-31 23:59:59'.
支持的範圍是'1000-01-01 00:00:00' 至'9999-12-31 23:59:59'。
The TIMESTAMP data type is used for values that contain both date and time parts. TIMESTAMP has a range of '1970-01-01 00:00:01' UTC to '2038-01-19 03:14:07' UTC.
“TIMESTAMP”數據類型用於包含日期和時間部分的值。 “TIMESTAMP”的範圍為“1970-01-01 00:00:01”UTC 到“2038-01-19 03:14:07”UTC。
A DATETIME or TIMESTAMP value can include a trailing fractional seconds part in up to microseconds (6 digits) precision.
數據時間 "或 "時間戳 "值可包括尾部小數秒部分,精度可達微秒(6 位)。
In particular, any fractional part in a value inserted into a DATETIME or TIMESTAMP column is stored rather than discarded.
特別是,插入DATETIME或TIMESTAMP列的值中的任何小數部分都會被存儲而不是被丟棄。
With the fractional part included, the format for these values is '_`YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss`_[._`fraction`_]', the range for DATETIME values is '1000-01-01 00:00:00.000000' to '9999-12-31 23:59:59.499999', and the range for TIMESTAMP values is '1970-01-01 00:00:01.000000' to '2038-01-19 03:14:07.499999'.
如果包含小數部分,這些值的格式是 '_`YYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss`_[._`fraction`_]',
DATETIME值的範圍是`'1000-01-01 00:00:00. 000000'到'9999-12-31 23:59:59.499999'TIMESTAMP值的範圍是'1970-01-01 00:00:01.000000'到'2038-01-19 03:14:07.499999'。
The fractional part should always be separated from the rest of the time by a decimal point; no other fractional seconds delimiter is recognized.
For information about fractional seconds support in MySQL, see Section 11.2.6, “Fractional Seconds in Time Values”.
The TIMESTAMP and DATETIME data types offer automatic initialization and updating to the current date and time. For more information, see Section 11.2.5, “Automatic Initialization and Updating for TIMESTAMP and DATETIME”.
小數部分應始終用小數點與時間的其餘部分分隔;不識別其他小數秒分隔符。有關 MySQL 支持小數秒的信息,請參閲 第 11.2.6 節,"時間值中的小數秒"。
MySQL converts TIMESTAMP values from the current time zone to UTC for storage, and back from UTC to the current time zone for retrieval.
MySQL 將 TIMESTAMP 值從當前時區轉換到 UTC 以進行存儲,並從 UTC 返回到當前時區以進行檢索。
(This does not occur for other types such as DATETIME.)
(這不會發生在其他類型,如 DATETIME)。
By default, the current time zone for each connection is the server's time.
默認情況下,每個連接的當前時區是服務器時間。
The time zone can be set on a per-connection basis.
時區可按每個連接設置。
As long as the time zone setting remains constant, you get back the same value you store.
只要時區設置保持不變,就會返回存儲的相同值。
If you store a TIMESTAMP value, and then change the time zone and retrieve the value, the retrieved value is different from the value you stored.
如果存儲了一個 TIMESTAMP 值,然後更改時區並檢索該值,檢索到的值將與存儲的值不同。
This occurs because the same time zone was not used for conversion in both directions.
出現這種情況是因為在兩個方向的轉換中沒有使用相同的時區。
The current time zone is available as the value of the time_zone system variable. For more information, see Section 5.1.15, “MySQL Server Time Zone Support”.
當前時區可作為 time_zone 系統變量的值。更多信息,請參閲第 5.1.15 節,"MySQL 服務器時區支持"。
In MySQL 8.0.19 and later, you can specify a time zone offset when inserting a TIMESTAMP or DATETIME value into a table. See Section 9.1.3, “Date and Time Literals”, for more information and examples.
在 MySQL 8.0.19 及更高版本中,在表中插入 TIMESTAMP 或 DATETIME 值時,可以指定時區偏移。更多信息和示例請參閲 第 9.1.3 節 "日期和時間字串"。
Invalid DATE, DATETIME, or TIMESTAMP values are converted to the “zero” value of the appropriate type ('0000-00-00' or '0000-00-00 00:00:00'), if the SQL mode permits this conversion.
如果 SQL 模式允許轉換,無效的 DATE、DATETIME 或 TIMESTAMP 值會被轉換為相應類型的 "零 "值('0000-00-00' 或 '0000-00-00 00:00:00')。
The precise behavior depends on which if any of strict SQL mode and the NO_ZERO_DATE SQL mode are enabled; see Section 5.1.11, “Server SQL Modes”.
確切的行為取決於啓用了嚴格 SQL 模式和 NO_ZERO_DATE SQL 模式中的哪一種;請參閲 5.1.11 節,"服務器 SQL 模式"。
In MySQL 8.0.22 and later, you can convert TIMESTAMP values to UTC DATETIME values when retrieving them using CAST() with the AT TIME ZONE operator, as shown here:
在 MySQL 8.0.22 及更高版本中,使用帶有 AT TIME ZONE 操作符的 CAST()檢索時,可以將 TIMESTAMP 值轉換為 UTC DATETIME 值,如下所示:
mysql> SELECT col,
> CAST(col AT TIME ZONE INTERVAL '+00:00' AS DATETIME) AS ut
> FROM ts ORDER BY id;
+---------------------+---------------------+
| col | ut |
+---------------------+---------------------+
| 2020-01-01 10:10:10 | 2020-01-01 15:10:10 |
| 2019-12-31 23:40:10 | 2020-01-01 04:40:10 |
| 2020-01-01 13:10:10 | 2020-01-01 18:10:10 |
| 2020-01-01 10:10:10 | 2020-01-01 15:10:10 |
| 2020-01-01 04:40:10 | 2020-01-01 09:40:10 |
| 2020-01-01 18:10:10 | 2020-01-01 23:10:10 |
+---------------------+---------------------+For complete information regarding syntax and additional examples, see the description of the CAST() function.
有關語法和其他示例的完整信息,請參閲 CAST() 函數的説明。
Be aware of certain properties of date value interpretation in MySQL:
注意 MySQL 中日期值解釋的某些屬性:
MySQL permits a “relaxed” format for values specified as strings, in which any punctuation character may be used as the delimiter between date parts or time parts.
對於指定為字符串的值,MySQL 允許使用一種 "寬鬆 "格式,其中日期部分或時間部分之間可以使用任何標點符號作為分隔符。
In some cases, this syntax can be deceiving.
在某些情況下,這種語法可能具有欺騙性。
For example, a value such as '10:11:12' might look like a time value because of the :, but is interpreted as the year '2010-11-12' if used in date context.
例如,"'10:11:12'"這樣的值可能因為": "而看起來像一個時間值,但如果在日期上下文中使用,則會被解釋為 年份"'2010-11-12'"。
The value '10:45:15' is converted to '0000-00-00' because '45' is not a valid month.
值'10:45:15'被轉換為'0000-00-00',因為'45'不是有效的月份。
The only delimiter recognized between a date and time part and a fractional seconds part is the decimal point.
日期和時間部分與小數秒鐘部分之間的唯一分隔符是小數點。
The server requires that month and day values be valid, and not merely in the range 1 to 12 and 1 to 31, respectively.
服務器要求月份和日期值必須有效,包括但不限於 1 至 12 和 1 至 31 的範圍內。
With strict mode disabled, invalid dates such as '2004-04-31' are converted to '0000-00-00' and a warning is generated.
服務器要求月份和日期值必須有效,包括但不限於 1 至 12 和 1 至 31 的範圍內。
With strict mode enabled, invalid dates generate an error.
啓用嚴格模式後,存儲無效日期會產生錯誤。
To permit such dates, enable ALLOW_INVALID_DATES.
要允許此類日期,請啓用 ALLOW_INVALID_DATES。
ALLOW_INVALID_DATES
Do not perform full checking of dates. Check only that the month is in the range from 1 to 12 and the day is in the range from 1 to 31. This may be useful for Web applications that obtain year, month, and day in three different fields and store exactly what the user inserted, without date validation. This mode applies to [`DATE`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/datetime.html "11.2.2 The DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP Types") and [`DATETIME`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/datetime.html "11.2.2 The DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP Types") columns. It does not apply to [`TIMESTAMP`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/datetime.html "11.2.2 The DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP Types") columns, which always require a valid date.
如果啓用 [`ALLOW_INVALID_DATES`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/sql-mode.html#sqlmode_allow_invalid_dates),則不會對日期進行嚴格檢查。
非嚴格模式只檢查**月是否在 1 至 12 的範圍內,日是否在 1 至 31 的範圍內**。這對於在三個不同字段中獲取年、月、日,並準確存儲用户插入的內容而不進行日期驗證的網絡應用程序可能很有用。這種模式適用於 [`DATE`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/datetime.html "11.2.2 日期、數據時間和 TIMESTAMP 類型") 和 [`DATETIME`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/datetime.html "11.2.2 日期、數據時間和 TIMESTAMP 類型") 列。它不適用於 [`TIMESTAMP`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/datetime.html "11.2.2 DATE、DATETIME 和 TIMESTAMP 類型") 列,這些列**始終需要有效日期**。
With [`ALLOW_INVALID_DATES`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/sql-mode.html#sqlmode_allow_invalid_dates) disabled, the server requires that month and day values be legal, and not merely in the range 1 to 12 and 1 to 31, respectively. With strict mode disabled, invalid dates such as `'2004-04-31'` are converted to `'0000-00-00'` and a warning is generated. With strict mode enabled, invalid dates generate an error. To permit such dates, enable [`ALLOW_INVALID_DATES`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/sql-mode.html#sqlmode_allow_invalid_dates).
如果禁用 [`ALLOW_INVALID_DATES`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/sql-mode.html#sqlmode_allow_invalid_dates),服務器會要求月和日的值必須是合法的,而不只是分別在 1 至 12 和 1 至 31 的範圍內。禁用嚴格模式後,**諸如`'2004-04-31'`之類的無效日期會被轉換為`'0000-00-00'`**,併產生警告。啓用嚴格模式後,無效日期會產生錯誤。
要允許使用此類日期,請啓用 [`ALLOW_INVALID_DATES`](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/sql-mode.html#sqlmode_allow_invalid_dates)。
See Section 5.1.11, “Server SQL Modes”, for more information.
更多信息,請參見第 Section 5.1.11, “Server SQL Modes”。
- MySQL does not accept
TIMESTAMPvalues that include a zero in the day or month column or values that are not a valid date.
MySQL 不接受在日或月列中包含零的 TIMESTAMP 值,也不接受不是有效日期的值。
The sole exception to this rule is the special “zero” value '0000-00-00 00:00:00', if the SQL mode permits this value.
這一規則的唯一例外是特殊的 "零 "值'0000-00-00 00:00:00',如果 SQL 模式允許該值的話。
The precise behavior depends on which if any of strict SQL mode and the NO_ZERO_DATE SQL mode are enabled; see Section 5.1.11, “Server SQL Modes”.
具體行為取決於是否啓用了嚴格 SQL 模式和 NO_ZERO_DATE SQL 模式;請參閲 5.1.11 節,"服務器 SQL 模式"。
Dates containing 2-digit year values are ambiguous because the century is unknown. MySQL interprets 2-digit year values using these rules:
包含 2 位數年份值的日期是模糊的,因為世紀不明。MySQL 使用這些規則解釋兩位數的年份值:
Year values in the range 00-69 become 2000-2069
00-69 "範圍內的年份值變為 "2000-2069"。
Year values in the range 70-99 become 1970-1999.
年份範圍70-99中的數值變為1970-1999。
See also Section 11.2.9, “2-Digit Years in Dates”.
另請參見 第 11.2.9 節,"日期中的兩位數年份"。
Linux系統如何查看設置所在的時區?
下面是查看設置所在時區的方法:
date -R[root@localhost alexxander]# date -R
Fri, 21 Jul 2023 16:29:07 -0400可以看到這裏使用的是美國的時區,個人安裝Linux系統的時候選擇的時區未做修改就會出現這樣的情況。
-0400 就是西四區。
那麼我們應該如何設置Linux的所在時區?
方法一:使用tzselect設置時區
[root@localhost conf]# tzselect
Please identify a location so that time zone rules can be set correctly.
Please select a continent or ocean.
1) Africa
2) Americas
3) Antarctica
4) Arctic Ocean
5) Asia
6) Atlantic Ocean
7) Australia
8) Europe
9) Indian Ocean
10) Pacific Ocean
11) none - I want to specify the time zone using the Posix TZ format.
#? 5
Please select a country.
1) Afghanistan 18) Israel 35) Palestine
2) Armenia 19) Japan 36) Philippines
3) Azerbaijan 20) Jordan 37) Qatar
4) Bahrain 21) Kazakhstan 38) Russia
5) Bangladesh 22) Korea (North) 39) Saudi Arabia
6) Bhutan 23) Korea (South) 40) Singapore
7) Brunei 24) Kuwait 41) Sri Lanka
8) Cambodia 25) Kyrgyzstan 42) Syria
9) China 26) Laos 43) Taiwan
10) Cyprus 27) Lebanon 44) Tajikistan
11) East Timor 28) Macau 45) Thailand
12) Georgia 29) Malaysia 46) Turkmenistan
13) Hong Kong 30) Mongolia 47) United Arab Emirates
14) India 31) Myanmar (Burma) 48) Uzbekistan
15) Indonesia 32) Nepal 49) Vietnam
16) Iran 33) Oman 50) Yemen
17) Iraq 34) Pakistan
#? 9
Please select one of the following time zone regions.
1) Beijing Time
2) Xinjiang Time
#? 1
The following information has been given:
China
Beijing Time
Therefore TZ='Asia/Shanghai' will be used.
Local time is now: Sat Jul 22 05:28:59 CST 2023.
Universal Time is now: Fri Jul 21 21:28:59 UTC 2023.
Is the above information OK?
1) Yes
2) No
#? yes
Please enter 1 for Yes, or 2 for No.
#? 1
You can make this change permanent for yourself by appending the line
TZ='Asia/Shanghai'; export TZ
to the file '.profile' in your home directory; then log out and log in again.
Here is that TZ value again, this time on standard output so that you
can use the /usr/bin/tzselect command in shell scripts:
Asia/Shanghai
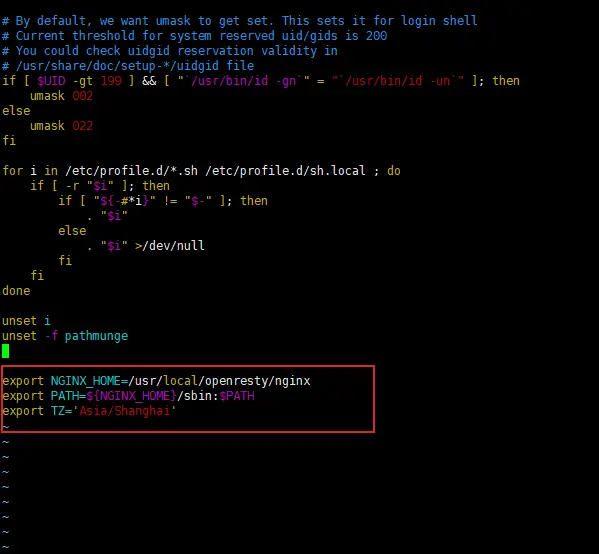
tzselect命令只告訴你選擇的時區的寫法,並不會生效,我們可以在各種諸如.profile、.bash_profile或者/etc/profile中設置正確的TZ環境變量並導出,例如在/etc/profile裏面設置 TZ='Asia/Shanghai':
修改完成之後,我們執行source /etc/profile讓配置生效,並且使用date -R查看當前時間:
[root@localhost conf]# date -R
Sat, 22 Jul 2023 05:34:56 +0800
這裏發現時間還是存在偏差問題,現在我們要讓docker中的Mysql實時同步當前硬件的 clock時間,需要注意的是設置系統時間需要root的權限。
hwclock命令用於訪問服務器的硬件CMOS時間,無論讀取還是設置都需要root權限,例如:
# 獲取系統硬件時間
$ sudo hwclock
Fri 23 Jan 2015 03:33:17 PM CST -0.567492 seconds
# 設置操作系統的軟件時間,與系統硬件時間同步
$ sudo hwclock -s
# 設置系統硬件時間,與操作系統的軟件時間同步
$ sudo hwclock -w通過執行hwclock -s,我們可以將Linux設置為一個“近似當前時間”的時間,Linux操作系統維護的軟件時間隨着服務器的長時間運行會出現漂移,最終會越來越不準確。
方法2:複製相應的時區文件,替換系統時區文件;或者創建鏈接文件
在/usr/share/zoneinfo/下面有很多時區文件,可以複製這些時區文件覆蓋/etc/localtime文件,或修改符號鏈接/etc/locatime對應的文件。
cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtimeCST/UTC/GMT 是什麼?
CST:中國標準時間(China Standard Time),這個解釋可能是針對RedHat Linux。
UTC:協調世界時,又稱世界標準時間,簡稱UTC,從英文國際時間/法文協調時間”Universal Time/Temps Cordonné”而來。中國大陸、香港、澳門、台灣、蒙古國、新加坡、馬來西亞、菲律賓、澳洲西部的時間與UTC的時差均為+8,也就是UTC+8。
GMT:格林尼治標準時間(舊譯格林威治平均時間或格林威治標準時間;英語:Greenwich Mean Time,GMT)是指位於英國倫敦郊區的皇家格林尼治天文台的標準時間,因為本初子午線被定義在通過那裏的經線。
個人驗證1:timestamp 是如何工作的
注意下面的所有實驗均在控制枱進行,請不要使用Navicat進行測試,看到的結果和控制枱結果存在差異。
MySQL converts TIMESTAMP values from the current time zone to UTC for storage, and back from UTC to the current time zone for retrieval.
MySQL 將 TIMESTAMP 值從當前時區轉換到 UTC 以進行存儲,並從 UTC 返回到當前時區以進行檢索。
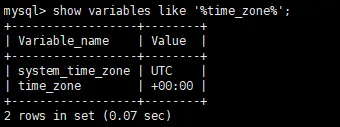
在Mysql中可以通過下的語句查看當前的時區信息:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%time_zone%'這裏解釋下UTC以及SYSTEM的含義:
system_time_zone:表明使用系統時間。time_zone:相對於 UTC 時間的偏移,比如 '+08:00' 或者 '-6:00'。
全局參數 system_time_zone
系統時區,在MySQL啓動時,會檢查當前系統的時區,根據系統時區設置全局參數system_time_zone的值。
The system time zone. When the server starts, it attempts to determine the time zone of the host machine automatically and uses it to set the
system_time_zonesystem variable. The value does not change thereafter.系統時區。服務器啓動時,會嘗試自動確定主機的時區,並以此設置
system_time_zone系統變量。此後,該值不會改變。
注意,system_time_zone 變量只有全局值沒有會話值,不能動態修改,MySQL 啓動時,將嘗試自動確定服務器的時區,並使用它來設置 system_time_zone 系統變量。
全局參數 time_zone
用來設置每個連接會話的時區,默認為system時,使用全局參數system_time_zone的值。
The current time zone. This variable is used to initialize the time zone for each client that connects. By default, the initial value of this is 'SYSTEM' (which means, “use the value of system_time_zone”).
當前時區。該變量用於為每個連接的客户端初始化時區。默認情況下,初始值為 "SYSTEM"(即 "使用 system_time_zone 的值")。
需要注意,在一些系統中,system_time_zone的值是CST,中國標準時間=CST(China Standard Time) UT+8:00 ,mysql的時區=system_time_zone+time_zone。
下面是在Session當中通過更改時區對應timestamp的影響。
-- 時間戳測試表和數據
CREATE TABLE `timestamp_test` (
`id` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '主鍵',
`time` timestamp NULL COMMENT '時間戳',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
-- 存入 + 8 時區
INSERT INTO `timestamp_test` (`id`, `time`) VALUES ('1', '2023-10-17 13:48:55');
INSERT INTO `timestamp_test` (`id`, `time`) VALUES ('2', '2023-10-17 13:10:55');
INSERT INTO `timestamp_test` (`id`, `time`) VALUES ('3', '2023-10-17 13:22:55');
-- 查看時區
show variables like '%time_zone%';
-- system_time_zone UTC
-- time_zone SYSTEM
-- 更改時區
set session time_zone = '+8:00';
-- 查看時間
select id,`time` from timestamp_test;
-- 1 2023-10-17 13:48:55
-- 2 2023-10-17 13:10:55
-- 3 2023-10-17 13:22:55
set session time_zone = '+2:00';
-- 查看時間
select id,`time` from timestamp_test;
-- +----+---------------------+
-- | id | time |
-- +----+---------------------+
-- | 1 | 2023-10-17 15:48:55 |
-- | 2 | 2023-10-17 15:10:55 |
-- | 3 | 2023-10-17 15:22:55 |
-- +----+---------------------+
在當前session修改時區之後,對應的timestamp讀取時間也出現變化。
個人驗證2:時區設置影響
參考:https://opensource.actionsky.com/20211214-time_zone/
1.NOW() 和 CURTIME() 系統函數的返回值受當前 session 的時區影響
select now(),包括insert .. values(now())、以及字段的 DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP 屬性也受此影響。這裏依舊使用上面的案例:
-- 時間戳測試表和數據
CREATE TABLE `timestamp_test` (
`id` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '主鍵',
`time` timestamp NULL COMMENT '時間戳',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
-- 存入 + 8 時區
INSERT INTO `timestamp_test` (`id`, `time`) VALUES ('1', '2023-10-17 13:48:55');
INSERT INTO `timestamp_test` (`id`, `time`) VALUES ('2', '2023-10-17 13:10:55');
INSERT INTO `timestamp_test` (`id`, `time`) VALUES ('3', '2023-10-17 13:22:55');
更改數據庫時區為+02:00之後,對應結果如下:
mysql> show variables like '%time_zone%';
+------------------+--------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------+--------+
| system_time_zone | UTC |
| time_zone | +02:00 |
+------------------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> select now();
+---------------------+
| now() |
+---------------------+
| 2023-07-21 21:51:48 |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
可以看到,修改time_zone會對函數的結果產生影響。
2.timestamp 數據類型字段存儲的數據受時區影響
根據Mysql文檔的描述,timestamp 數據類型會存儲當前session的時區信息,讀取時會根據當前 session 的時區進行轉換,而date和datetime則不會因為時區的變更而出現數據變更。
國內安裝Mysql的時區問題避坑
1.明確指定時區
在 my.cnf 寫入 default-time-zone='+08:00',其他地區和開發確認取對應時區即可。
至於為什麼要明確指明時區,一方面是Mysql 在很多沒有DBA的公司都是全部由運維負責,運維如果沒有設置時區,在數據庫遷移到海外服務器的時候可能會出現時區變更的各種問題,另一方面是這樣明確的設置可以減少系統計算的開銷,如果系統大量使用timestamp的數據類型,這也是一個不小的優化點。
2.JAVA應用讀取到的時間和北京時間差了14個小時,為什麼?怎麼解決?
基於mysql-connector-java-8.0.19 進行分析,使用 com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver,在獲取java.sql.Connection的過程會確定時區,調用如下方法。
com.mysql.cj.protocol.a.NativeProtocol#configureTimezone
/**
* Configures the client's timezone if required.
*
* @throws CJException
* if the timezone the server is configured to use can't be
* mapped to a Java timezone.
*/
public void configureTimezone() {
String configuredTimeZoneOnServer = this.serverSession.getServerVariable("time_zone");
if ("SYSTEM".equalsIgnoreCase(configuredTimeZoneOnServer)) {
configuredTimeZoneOnServer = this.serverSession.getServerVariable("system_time_zone");
}
String canonicalTimezone = getPropertySet().getStringProperty(PropertyKey.serverTimezone).getValue();
if (configuredTimeZoneOnServer != null) {
// user can override this with driver properties, so don't detect if that's the case
if (canonicalTimezone == null || StringUtils.isEmptyOrWhitespaceOnly(canonicalTimezone)) {
try {
canonicalTimezone = TimeUtil.getCanonicalTimezone(configuredTimeZoneOnServer, getExceptionInterceptor());
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
throw ExceptionFactory.createException(WrongArgumentException.class, iae.getMessage(), getExceptionInterceptor());
}
}
}
if (canonicalTimezone != null && canonicalTimezone.length() > 0) {
this.serverSession.setServerTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone(canonicalTimezone));
//
// The Calendar class has the behavior of mapping unknown timezones to 'GMT' instead of throwing an exception, so we must check for this...
//
if (!canonicalTimezone.equalsIgnoreCase("GMT") && this.serverSession.getServerTimeZone().getID().equals("GMT")) {
throw ExceptionFactory.createException(WrongArgumentException.class, Messages.getString("Connection.9", new Object[] { canonicalTimezone }),
getExceptionInterceptor());
}
}
this.serverSession.setDefaultTimeZone(this.serverSession.getServerTimeZone());
}
上面的代碼大致邏輯如下:
- 從mysql的
time_zone讀取值。 - 如果值是
SYSTEM則使用system_time_zone的值. - 如果
jdbc url配置了時區則使用url裏的,如jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai,則最優先使用URL設置的時區。
那麼為什麼JAVA應用讀取到的時間和北京時間差了14個小時?通常是因為沒有在URL裏面設置時區屬性,某些系統下,MySQL默認使用的是系統時區CST(CST 在 RedHat 上是 +08:00 時區),而應用和MySQL 建立的連接的session time_zone為CST。
實際上,CST 一共能代表4個時區:
Central Standard Time (USA) UT-6:00美國標準時間Central Standard Time (Australia) UT+9:30澳大利亞標準時間China Standard Time UT+8:00中國標準時間Cuba Standard Time UT-4:00古巴標準時間
雖然Mysql正確認識了CST是中國標準時間,但是JDBC卻沒有認識這個時間,JDBC在解析CST時使用了美國標準時間,這就會導致時區錯誤。
具體可以看下面的代碼:
public class TimeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 這裏的CST指的是美國中部時間,
TimeZone tz = TimeZone.getTimeZone("CST");
System.out.println("tz => "+ tz);// 可以看到偏移量是offset=-21600000,-21600000微秒=-6小時,所以這裏的CST指美國
// 建議創建 TimeZone 用 ZoneId,因為ZoneId 不允許 CST、JST 這種簡稱,能提前預防進坑,如下
// ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("CST");// 拋異常
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("GMT+8");// 明確指定,是OK的,或者 "區域/城市" 的寫法如 Asia/Shanghai TimeZone tz1 = TimeZone.getTimeZone(zoneId);
System.out.println("tz1 => "+ tz1);
}/**運行結果:
tz => sun.util.calendar.ZoneInfo[id="CST",offset=-21600000,dstSavings=3600000,useDaylight=true,transitions=235,lastRule=java.util.SimpleTimeZone[id=CST,offset=-21600000,dstSavings=3600000,useDaylight=true,startYear=0,startMode=3,startMonth=2,startDay=8,startDayOfWeek=1,startTime=7200000,startTimeMode=0,endMode=3,endMonth=10,endDay=1,endDayOfWeek=1,endTime=7200000,endTimeMode=0]]
tz1 => sun.util.calendar.ZoneInfo[id="GMT+08:00",offset=28800000,dstSavings=0,useDaylight=false,transitions=0,lastRule=null] */}3.修改MySQL的時區會影響已經存儲的時間類型數據嗎?
答案是只會影響對 timestamp 數據類型的讀取。
4.遷移數據時會有導致時間類型數據時區錯誤的可能嗎?
這一點依然是針對 timestamp 數據類型,比如使用 mysqldump 導出 csv 格式的數據,默認這種導出方式會使用 UTC 時區讀取 timestamp 類型數據,這意味導入時必須手工設置 session.time_zone=’+00:00’才能保證時間準確。
--將 test.t 導出成 csv
mysqldump -S /data/mysql/data/3306/mysqld.sock --single-transaction \
--master-data=2 -t -T /data/backup/test3 --fields-terminated-by=',' test t
--查看導出數據
cat /data/backup/test3/t.txt
2021-12-02 08:45:39,2021-12-02 16:45:39為了避免這些繁瑣的操作,mysqldump 也提供了一個參數 --skip-tz-utc,意思就是導出數據的那個連接不設置 UTC 時區,使用 MySQL 的 gloobal time_zone 系統變量值。
當然這個設置也算是告訴我們,mysqldump 導出默認也是使用 UTC 時區,為了確保導出和導入的時區正確,會在導出的 sql 文件頭部帶有 session time_zone 信息。
需要注意--compact參數會去掉 sql 文件的所有頭信息,所以--compact參數得和--skip-tz-utc一起使用。
為什麼mysql有system_time_zone和time_zone兩個?
見 https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/time-zone-support.html
- Mysql 服務的時候會讀取Linux宿主機所在的時區,固定值之後這個值不再改變。(簡單説
system_time_zone是Mysql系統算出來的值)。 - 默認情況
time_zone值為 SYSTEM,也就是説它跟隨system_time_zone的值。 - 注意
system_time_zone的值固定下來後,數據庫宿主機的時區再改變,time_zone的值都是不變的,因為它是跟隨system_time_zone變量的,不是實時跟隨操作系統的,如果想要讓他跟隨操作系統,最簡單的方法就是重啓Mysql。 - 有時候我們會發現,Linux時區是對的,但是mysql的時區是錯,這時候我們把Linux的時區改對,但是發現Mysql還是錯的,原因是Linux時區改對之後沒有重啓Mysql服務器重新讀取Linux系統時區。