由於圖片和格式解析問題,可前往 閲讀原文
從本篇文章開始講解node中最為出色的框架——NestJS,為什麼説它出色,想必市面上已經議論紛紛了吧。如果你熟悉Spring框架那nest也會讓你輕而易舉的理解,基於typescript裝飾器結合IOC讓nest的框架設計更加清晰明瞭
NestJS 是一個基於 Node.js 平台的現代化 Web 框架,它結合了 TypeScript、面向對象編程的思想和函數式編程的思想,提供了一種高效、可擴展的方式來構建可維護的 Node.js 應用程序,相比express、koa、egg等幾種框架nest更有出色的架構能力
Nest中使用了大量的IOC設計模式,它將控制權(即對象的創建、依賴關係的管理等)從應用程序代碼中轉移出去,交由容器來管理。這樣做可以降低應用程序代碼的複雜度,提高代碼的可維護性和可重用性。在IOC模式中,容器通過控制反轉(即控制權從應用程序代碼中反轉過來)來管理對象的創建和依賴關係。這樣做有利於解耦應用程序中的各個組件,提高代碼的可維護性和可重用性。而依賴注入(Dependency Injection,DI)則是IOC模式的一種實現方式,它可以幫助將對象之間的依賴關係自動注入到類中,使得代碼更加簡潔、可讀性更高。在傳統的編程模型中,對象之間的依賴關係是在代碼中直接編寫的。例如,一個類可能需要創建其他類的實例,或者需要依賴其他類的實例來完成某些操作。這樣做會導致代碼之間的耦合度很高,難以進行單元測試和代碼重用
Nest真正的實現了架構的能力,以至於現在它可以變成出色的框架得到業界的重視。內部提供了中間件、攔截器、過濾器、異常、管道、鑑權設計理念,都非常值得我們思考和學習。學習nest最重要的就是它的設計思想,如:基本的架構設計、控制反轉原理等等,從本篇開始講nest的基本使用、實踐、原理等等
安裝
# 1. git clone
➜ git clone https://github.com/nestjs/typescript-starter.git nestjs-starter
# 2. nest cli
➜ npm i -g @nestjs/cli
➜ nest new nestjs-template程序入口
// main.ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
// 返回應用實例 INestApplication
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();nest可以與任何的HTTP框架對接,這裏有兩個開箱即用的HTTP框架:express、fastify,通常使用大家熟悉的express。這裏可以傳入express類型:
import type { NestExpressApplication } from '@nestjs/platform-express';
const app = await NestFactory.create<NestExpressApplication>(AppModule);Module
模塊是nest應用程序的起點,至少都會有一個module;通過module來給應用程序提供元數據,通常根據功能來劃分不同的模塊
module中有4個屬性他們都有自己的作用:
- controllers:提供當前模塊的控制器來定義路由處理HTTP請求
- providers:給當前module提供可注入的數據,如相關的service
- imports:引入其他依賴或模塊,如引入子模塊、第三方模塊等等
- exports:暴露當前模塊中的部分內容,以便其他引用了當前模塊的模塊可以使用當前暴露出的內容
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppController } from './app.controller';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
@Module({
exports: [AppService],
imports: [MockModule],
controllers: [AppController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule {}controllers
controllers用來給當前模塊提供路由控制器類,這類類都會被@Controller裝飾器進行裝飾,用來處理HTTP請求,控制器類並不直接參與業務,通常和業務分開
定義一個控制器類:
@Controller('cat') // 統一前綴
export class CatController {
@Get() // GET: cat
findAll() {}
}存放到當前模塊的的controllers中
@Module({ controllers: [CatController] })
export class CatModule {}這樣cat module就擁有了Cat控制器中的路由 GET: /cat,後面會詳細對Controller展開講解,你可以點擊這裏跳轉閲讀
providers
providers用來給當前模塊提供可注入的元數據,通過提供可注入的標識,在當前模塊內部就可以注入使用被提供的內容。這些元數據可以是類、函數、值類型,通常類都會使用@Injectable進行裝飾來標識當前類可以被注入,被@Injectable裝飾器進行裝飾的元數據不需要使用@Inject顯式注入,而沒有使用@Injectable裝飾器的元數據需要顯式注入
通常provider被縮寫成數組形式[AClass, BClass]這樣的,其本質還是 { provide: name, useClass: value }這種形式,前面説了值支持多種類型,不同類型會使用不同的值字段,其中包括:useValue(值)、useClass(類)、useFactory(函數),可以根據這些類型自定義prividers
-
useValue:用來直接提供值類型的元數據
@Module({ controllers: [MockController], providers: [ // 定義string類型的值 { provide: 'APP_NAME', useValue: 'nestjs-template', }, // 定義數組類型 { provide: 'APP_VERSIONS', useValue: [1, 2, 3], }, ], }) export class MockModule {} // 在當前模塊的controller中使用inject注入使用 @Controller('mock') export class MockController { constructor( @Inject('APP_NAME') // 顯式注入 private readonly APP_NAME: string, @Inject('APP_VERSIONS') private readonly APP_VERSIONS: string[], ) { console.log(this.APP_NAME, this.APP_VERSIONS); } } -
useClass:用來提供類類型的元數據,可以是可注入的類或者直接類的實例
// 1. 定義可注入的類 Test @Injectable() export class Test { log() { console.log('test'); } } // 2. 提供元數據 @Module({ controllers: [MockController], providers: [Test], // 直接寫成數據形式或者下面方式 // providers: [ // { provider: Test, useClass: Test } // ] }) export class MockModule {} // 3. controller中使用 @Controller('mock') export class MockController { constructor( private readonly testIns: Test, // 內部會查找當前模塊所提供的providers標識進行注入 ) {} }除此之外還可以使用類的實例:
// Test類也不需要 @Injectable 進行裝飾,其餘使用方法一致 @Module({ controllers: [MockController], providers: [ { provide: Test, useValue: new Test(), // 提供實例 }, ], }) export class MockModule {} -
useFactory:值可以使用函數,這樣也方便動態控制值;初次之外還可以注入其他類作為函數的參數使用
@Module({ controllers: [MockController], providers: [ { provide: 'FUNC_PROVIDER', useFactory: () => 'func_provider', // 函數provider }, ], }) export class MockModule {} // 在當前模塊的controller中使用inject注入使用 @Controller('mock') export class MockController { constructor( @Inject('FUNC_PROVIDER') // 顯式注入 private readonly FUNC_PROVIDER: string, ) { console.log(this.FUNC_PROVIDER); } }除此之外還支持異步函數、函數傳參
@Injectable() class XXX { create() { console.log('xxx create'); return ['create']; } } @Module({ controllers: [MockController], providers: [ { provide: 'FUNC_PROVIDER', useFactory: () => 'func_provider', scope: 'x' }, ], }) export class MockModule {}
provider還支持生命週期的定義,默認情況下提供的元數據的生命週期是全局跟着整個應用程序實例化一次,其支持的生命週期範圍有:DEFAULT、TRANSIENT、REQUEST
@Module({
controllers: [MockController],
providers: [
{
provide: 'USER_LIST',
useFactory: (xxx: XXX) => xxx.create(),
inject: [XXX], // 注入XXX 類,作為函數的參數
scope: Scope.DEFAULT
},
{
provide: "xxx",
useFactory: async() => return Promise.resolve(), // 異步provider
scope: Scope.REQUEST
}
],
})
export class MockModule {}三者區別:
| 生命週期 | 作用範圍 | |
|---|---|---|
| DEFAULT | 整個應用程序 | 全局共享一個實例 |
| TRANSIENT | 整個應用程序 | 每個注入一個實例 |
| REQUEST | 請求瞬間 | 每個請求一個實例 |
imports
用來導入其他的模塊,以便使用其他模塊的服務和依賴。通常可以按功能劃分模塊或路由
import { UserModule } from './user/user.module';
@Module({
imports: [UserModule], // 導入User模塊
})
export class AppModule {}exports
導出當前模塊的依賴以便其他模塊可以使用
@Module({
providers: [ Test ],
exports: [Test], // 這裏導出Test provider
})
export class MockModule {}
@Module({
imports: [MockModule],
})
export class AppModule {
// 這裏可以直接注入Test,而不需要定義 providers
constructor(private readonly testIns: Test) {
this.testIns.log();
}
}動態模塊
使用動態模塊可以在不同的模塊之間共享配置,共享模塊是一種用於組織和重用代碼的機制。共享模塊可以定義一組公共的、可重用的服務、控制器、管道、攔截器等,這些組件可以被其他模塊引用和使用
-
創建共享模塊
@Module({}) export class ShareModule { // 提供register方法,並返回固定格式 static register(opts: { name: string }) { return { module: ShareModule, providers: [ { provide: 'SHAREMODULE', // useValue: 'xxx', useValue: () => xxx(opts) } ] } } } -
使用共享模塊
@Module({ imports: [ // 註冊模塊 ShareModule.register({ name: "Jack" }) ] }) export class AppModule {}
Controller
控制器用來接受具體的路由,可以通過路徑前綴、域名來區分具體的路由
可以手動創建controller文件,對於初學者也可以使用nestjs的cli命令創建:
# 創建名為 cat 的controller
➜ nest n controller cat路由分組
-
路由前綴控制
類型定義:
declare function Controller(prefix: string | string[]): ClassDecorator;例子:
import { Controller } from '@nestjs/common'; // 以cats開頭的路徑會走這裏,如:/cats/all @Controller("cats") export class AppController {} @Controller(["cats", "dogs"]) export class AppController {} -
域名控制
類型定義:
interface ControllerOptions { path?: string | string[]; host?: string | RegExp | Array<string | RegExp>; }例子:
import { Controller } from '@nestjs/common'; @Controller({ host: "https://blog.usword.cn" }) export class AppController {} @Controller({ host: "https://blog.usword.cn", path: "/frontend" }) export class AppController {}
路由定義
在控制器中定義具體的路由,如查詢所有的貓咪,GET /cat/all;nestjs中內置了HTTP規範的請求方法裝飾器,可以在具體的路由方法中輕鬆使用請求方式
import { Controller, Get, Post } from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller({ path: 'cat' })
export class AppController {
// get請求 /cats/all
@Get('/all')
getAllCats() {
return [];
}
// post請求 /cat 新增一個貓
@Post()
createCat() {
return true;
}
// 動態路由
// get /cat/1
@Get(':id')
getCatById() {
return { id: 1, name: '小白' };
}
// 通配符匹配
// get /cat/ab_cd
@Get('ab*cd')
getOne() {
return { id: 1, name: '小白' };
}
}除了get、post請求外,還有header、delete、options、patch等常見的http請求
參數處理
通常http請求時前端都會攜帶或多或少的數據傳遞給服務端,通過nestjs可以很好的拿到params、query、data等數據
-
處理param
import { Controller, Get, Param } from '@nestjs/common'; @Controller({ path: 'cat' }) export class AppController { @Get(':id') getCatById(@Param() params: any) { // 拿到整個params {id: xxx} console.log(params); return { id: 1, name: '小白' }; } @Get(':id') getCatById(@Param('id') id: number) { // 只獲取id console.log(id); return { id: 1, name: '小白' }; } } -
處理query
import { Controller, Get, Query } from '@nestjs/common'; @Controller({ path: 'cat' }) export class AppController { @Get(':id') getCatById(@Query() query: any) { // 拿到整個query console.log(query); return { id: 1, name: '小白' }; } @Get(':id') getCatById(@Query('id') id: number) { // 只獲取query中的id console.log(id); return { id: 1, name: '小白' }; } } -
處理body
import { Controller, Get, Body } from '@nestjs/common'; @Controller({ path: 'cat' }) export class AppController { @Post(':id') getCatById(@Body() body: any) { // 整個body對象 console.log(body); return { id: 1, name: '小白' }; } @Post(':id') getCatById(@Body("name") name: string) { // 獲取body的name屬性 console.log(name); return { id: 1, name: '小白' }; } } -
處理表單數據(目前沒有看到其它處理formdata的方法)
import { Controller, Get, Body, UseInterceptors } from '@nestjs/common'; import { FileInterceptor } from '@nestjs/platform-express'; @Controller({ path: 'cat' }) export class AppController { @Post(':id') @UseInterceptors(FileInterceptor('')) // 使用表單攔截器對數據進行表單轉換,會得到json數據 getCatById(@Body("name") name: string) { // 獲取body的name屬性 console.log(name); return { id: 1, name: '小白' }; } }
請求對象
在nestjs中一般不用獲取原始的請求對象(request、response),使用nestjs提供工具就夠用瞭如@Param、@Body等等;<u>在使用了原始的請求對象後就會脱離nestjs的本身,如果注入了Res那麼必須手動執行res原始的響應,不然nest將會被掛起</u>
import { Controller, Post, Req, Res } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request, Response } from 'express';
@Controller({ path: 'cat' })
export class AppController {
@Post(':id')
// 注入 req,res
getCatById(@Req() req: Request, @Res() res: Response) {
console.log(req.query);
// 使用原始的res進行數據響應
res.status(200).json({ code: 200, msg: '原始請求對象響應數據...' });
}
}狀態碼
declare function HttpCode(statusCode: number): MethodDecorator;例子:
import { Controller, Get, HttpCode, HttpStatus } from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('user')
export class UserController {
@Get()
@HttpCode(HttpStatus.OK)
getUser() {
return []
}
}頭信息
declare function Header(name: string, value: string): MethodDecorator;例子:
import { Controller, Get, Header } from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('user')
export class UserController {
@Get()
@Header('Cache-Control', 'none') // 設置cache-control頭信息
getUser() {
return [];
}
}也可以使用底層庫相應對象進行處理
重定向
declare function Redirect(url?: string, statusCode?: number): MethodDecorator;例子:
import { Controller, Get, HttpStatus, Redirect } from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('user')
export class UserController {
@Get()
@Redirect('https://blog.usword.cn', HttpStatus.MOVED_PERMANENTLY)
getUser() {
return [];
}
}
子域路由
import { Controller, Get, HostParam } from '@nestjs/common';
// host設置動態值 :host
@Controller({ host: ':host.usword.cn', path: 'cat' })
export class AppController {
@Get() // hostparam獲取域名的host值
findCats(@HostParam('host') host: string) {
console.log(host);
return true;
}
}自定義裝飾器
nestjs中除了提供一些常用的裝飾器,難免會不滿足業務中的使用,它也提供了自定義裝飾器的功能,只要遵循一定的原則就可以實現自己的裝飾器,本質底層還是裝飾器和Reflect兩者結合的結果
import { ExecutionContext, createParamDecorator } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request } from 'express';
// 獲取http協議的參數裝飾器
export const Protocol = createParamDecorator(
(defaultValue: string, ctx: ExecutionContext) => {
if (defaultValue) return defaultValue;
const request = ctx.switchToHttp();
return request.getRequest<Request>().protocol;
},
);
// 使用
import { Controller, Get } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Protocol } from 'src/common/decorator';
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
@Get()
async getList(@Protocol() protocol: string) { // 自定義參數裝飾器
console.log(protocol);
return protocol;
}
}Scope作用域
controller也支持provider的作用域生命週期,其內部含義和provide類似
生命週期
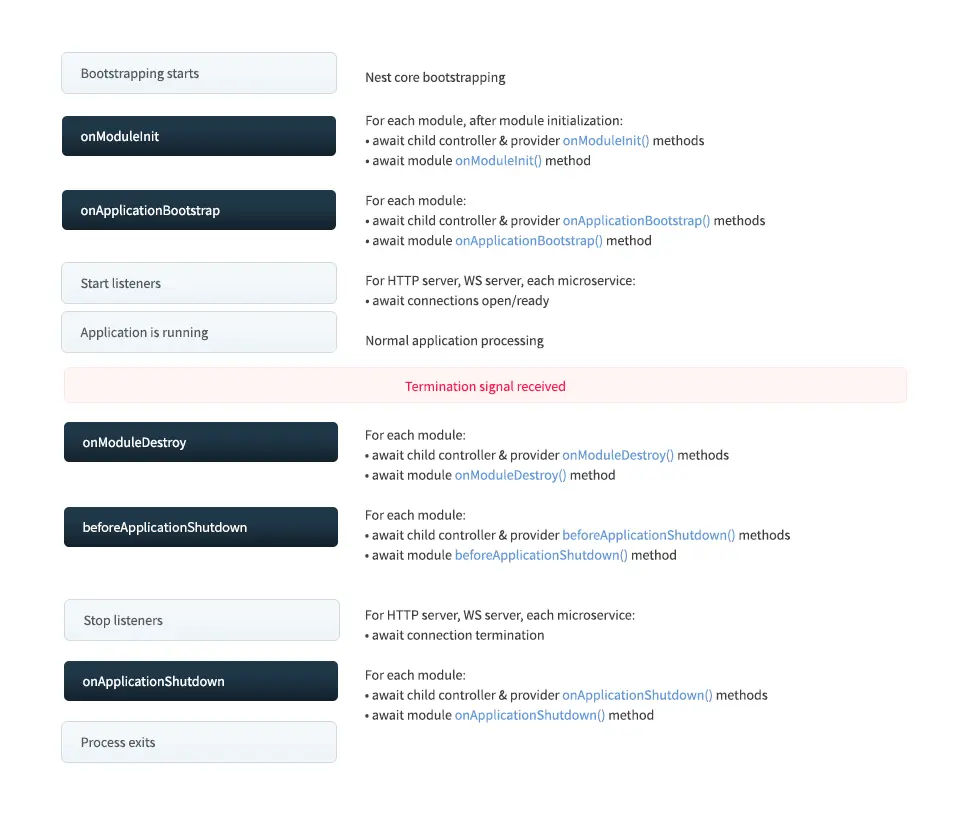
nest在module、controller和injectable的模塊代碼提供了生命週期鈎子事件
| Lifecycle hook method | Lifecycle event triggering the hook method call |
|---|---|
onModuleInit() |
Called once the host module's dependencies have been resolved. |
onApplicationBootstrap() |
Called once all modules have been initialized, but before listening for connections. |
onModuleDestroy()* |
Called after a termination signal (e.g., SIGTERM) has been received. |
beforeApplicationShutdown()* |
Called after all onModuleDestroy() handlers have completed (Promises resolved or rejected); once complete (Promises resolved or rejected), all existing connections will be closed (app.close() called). |
onApplicationShutdown()* |
Called after connections close (app.close() resolves). |
Service
service通常都用來處理具體的業務,給應用程序提供數據,通過數據庫增刪改查然後返回給控制器
service通常是個被@Injectable裝飾的類,提供給模塊的providers做為源數據的標識,這樣注入service就可以使用
service例子:
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
@Injectable()
export class AppService {
getHello(): string {
return 'Hello World!';
}
}
@Module({
imports: [],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule {}依賴注入
nestjs中使用了大量了依賴注入,使用@Injectable裝飾的類表示可被注入,@Inject用來注入可注入的依賴。通常使用@Injectable裝飾的類不需要顯式的使用Inject進行注入,內部會自動進行注入。所有注入的依賴都比在當前模塊的providers中提供注入的標識,更多類型的依賴可以查看providers
使用
// 定義可注入的類
@Injectable()
export class Test {
log() {
console.log('test');
}
}
// 提供注入的標識 provider
@Module({
controllers: [MockController],
providers: [
Test,
// 非class的依賴
{
provide: 'APP_NAME',
useValue: 'nestjs-template',
},
],
})
export class MockModule {}
// 注入依賴
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
constructor(
// 不需要Inject顯式注入,內部自動注入
private readonly testIns: Test,
@Inject('APP_NAME') // 顯式注入
private readonly APP_NAME: string,
) {}
}作用域
Injectable支持三種類型的作用域:DEFAULT、TRANSIENT、REQUEST
可選項 Optional
如果程序中注入了某個依賴,而該模塊沒有提供當前依賴,那麼就會報錯,使用可選注入可以解決報錯
// 注入依賴
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
constructor(
@Optional()
@Inject('APP_NAME') // 模塊沒有注入不會報錯
private readonly APP_NAME: string,
) {}
}應用配置
應用程序需要不同的配置文件分別在不同的環境進行運行,nestjs提供了@nestjs/config包來方便應用程序配置
在此包中包含了ConfigModule、ConfigService、registerAs等幾種工具方法,每個方法都有自己的作用
ConfigModule
ConfigModule用來加載配置文件,其包含forRoot、forFeature兩個方法,前者為全局作用域,後者為當前面模塊作用域
forRoot數據結構如下:
{
envFilePath: string | string[]; // 定義env配置文件路徑;默認加載根路徑下的 .env
ignoreEnvFile: boolean; // 是否忽略env文件
isGlobal: boolean; // 是否為全局
validationSchema: any; // 驗證配置
load: Array<ConfigFactory>; // 加載自定義的配置文件
// ...
}使用:
@Module({
controllers: [MockController],
// 引入模塊,這是必須的
imports: [
ConfigModule.forRoot({
envFilePath: resolve(__dirname, '../../.env'),
}),
],
})
export class MockModule {}ConfigService
加載好了配置後使用configService來獲取配置
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
constructor(
// 注入ConfigService
readonly configService: ConfigService<{ PORT: number }>,
) {
const port = this.configService.get('PORT', 5000, { infer: true });
console.log(port);
}
}通過將ConfigService注入到程序中,使用其提供的get方法獲取變量,get的類型定義如下:
// 這裏只舉一個重載
get(key, defaultValue, options: { infer: boolean; /*類型推斷*/ })自定義配置
使用load加載自定義的配置:
// 可以將配置放到一個配置文件合理處理後導出
export const Configuration = () => ({
PORT: process.env.PORT || 5000
});
@Module({
controllers: [MockController],
imports: [
ConfigModule.forRoot({
load: [Configuration], // 引入自定義配置
}),
],
})
export class MockModule {}registerAs 命名空間
對於前者的配置方案如果有嵌套的配置對於類型提示非常不友好(沒嵌套也沒類型推斷),而且不同方面的配置冗餘在一起對於後續維護不夠友好,nest中提供了registerAs來定義命名空間
// 定義 db 命名空間
export const DatabaseConfiguration = registerAs('db', () => ({
host: process.env.DB_HOST || 'localhost',
}));
@Module({
controllers: [MockController],
imports: [ConfigModule.forFeature(DatabaseConfiguration)], // 這裏註冊命名空間變量
})
export class MockModule {}
// 使用
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
constructor(
@Inject(DatabaseConfiguration.KEY) // 顯式注入配置的KEY,這是必須的
readonly dbConfiguration: ConfigType<typeof DatabaseConfiguration>,
) {
console.log(this.dbConfiguration.host);
}
}校驗
nestjs中可以使用joi對一些環境變量進行類型校驗和定義檢查,不合法就報錯提示
安裝相關依賴:
➜ yarn add joi配置:
import * as Joi from 'joi';
@Module({
controllers: [MockController],
imports: [
ConfigModule.forRoot({
load: [Configuration, DatabaseConfiguration],
validationSchema: Joi.object({
PORT: Joi.number(), // 必須是number
NODE_ENV: Joi.string().valid('development', 'production', 'testing'), // 必填且必須是這幾個值中的一個
}),
}),
],
})
export class MockModule {}更多相關驗證使用方式請訪問文檔
異步:forRootAsync({ useFactory: () => ({}) })
Middleware
middleware作用於應用路由,其生命週期為Request-Response,在middleware中必須調用next,不然程序請求將會掛起,內部基於koa的洋葱模型
使用middleware可以很輕鬆的創建通用的日誌中間件
創建日誌中間件,middleware需滿足以下幾點規則:
- 使用
@Injectable裝飾作為提供者 - 實現
NestMiddleware類中的use方法 - 必須調用
next方法
創建配置
創建middleware:
# 1. 使用cli生成
➜ nest g middleware log --no-spec
# 2. 或者自己創建配置middleware:這裏實現在每次HTTP請求時打印請求日誌,包括請求方法、地址、時間、耗時
// common/middleware/log.middleware.ts
import { Injectable, NestMiddleware } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request, Response } from 'express';
import { formatDate } from 'src/utils';
// 1. 可注入的
@Injectable()
export class LoggerMiddleware implements NestMiddleware {
// 2. 實現NestMiddleware中use方法
async use(req: Request, res: Response, next: (error?: any) => void) {
const startTime = new Date();
const method = req.method;
const url = req.originalUrl;
// 響應結束時打印相關耗時
res.on('finish', () => {
console.log(
`${method?.toUpperCase()}: ${url}\t\t\t 時間: ${formatDate(
startTime,
)}\t 耗時: ${((+new Date() - +new Date(startTime)) / 1000)?.toFixed(
3,
)}s`,
);
});
// 3. 必須調用next
next();
}
}註冊
middleware的註冊可以針對不同的範圍,你可以選擇對所有的路由生效,或者只針對某個路由,也可以針對某個請求方法等等,註冊非常靈活,有關更多註冊方式你可以點擊這裏參考文檔
@Module({
controllers: [AppController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule implements NestModule {
// 全局配置中間件 需要實現 NestModule中configure方法
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer) {
consumer.apply(LoggerMiddleware).forRoutes('*'); // 針對所有路由
// consumer
// .apply(LoggerMiddleware)
// .forRoutes({ path: 'mock', method: RequestMethod.GET });
// consumer
// .apply(LoggerMiddleware)
// .exclude('user')
// .forRoutes({ path: 'mock*', method: RequestMethod.ALL });
}
}Exception Filter
nest內置異常層來捕獲程序中沒有處理的錯誤,如果程序中沒有捕獲錯誤將會在異常層被捕獲。同時也提供了更加優化的異常使用如:HTTPException
nest中的filter、pipe、guard、interceptor可以在nest上下文以外、上下文中的module、controller、method以及param的位置使用,其中僅pipe支持在param位置使用
基本使用
import {
Controller,
Get,
HttpException,
HttpStatus,
} from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
@Get()
async getList() {
// 主動拋出 500 異常
throw new HttpException(
'主動拋出友好的500錯誤',
HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,
);
}
}
// 當請求時返回一下結果
{
"statusCode": 500,
"message": "主動拋出友好的500錯誤"
}HTTPException的類型定義如下:
constructor(response: string | Record<string, any>, status: number, options?: HttpExceptionOptions);內置filter
除了通用的HTTPException外,還包含了HTTP的所有狀態碼類型的異常,這樣就可以直接使用不同狀態的異常不需要再指定具體的狀態碼了
BadRequestExceptionUnauthorizedExceptionNotFoundException
示例:
// 404
new NotFoundException('頁面不見了');自定義filter catch
異常捕獲層默認會有固定的錯誤格式返回客户端,我們也可以根據自己的需求控制錯誤的格式。要實現自定義錯誤格式需要實現ExceptipnFilter類中的catch方法,並使用@Catch裝飾器裝飾
# 使用cli生成filter
➜ nest g filter HttpFilter --no-spec這裏做一個HTTP錯誤捕獲處理格式:
import {
ArgumentsHost,
Catch,
ExceptionFilter,
HttpException,
HttpStatus,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request, Response } from 'express';
@Catch()
export class HttpFilter implements ExceptionFilter {
// 實現catch方法
catch(exception: HttpException, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<Response>();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
const code =
exception instanceof HttpException
? exception.getStatus()
: HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
const errorException =
exception instanceof HttpException
? exception?.getResponse?.()
: exception;
// 定義錯誤格式
const error = {
code,
message:
typeof errorException === 'string'
? errorException
: (errorException as any)?.message || errorException,
error: (errorException as any)?.error,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
};
console.error(`【HTTP_FILTER】`, exception);
// 訪問的是頁面時渲染錯誤頁面 (這裏定義以api開始的代表接口數據)
const isAccessPage = !/^\/(api|.*-api).*/i.test(request.originalUrl);
if (isAccessPage) {
// 渲染錯誤頁面,對於頁面模板的使用請查看後續的mvc文章
return response.render('exception/index', {
code,
message: error.message || error.error,
});
}
try {
response.status(200).json({ ...error });
} catch (error) {
response.end();
}
}
}綁定filter
在定義好HTTPException Filter後還需要綁定到應用程序中,前面説了filter、pipe、guard、interceptor可以在nest上下文以外、上下文中的module、controller、method以及param的位置使用,其中僅pipe支持在param位置使用。filter支持除param以外的位置綁定
-
上下文以外
// main.ts import { HttpFilter } from './common/filter/http.filter'; function bootstrap() { // 省略其他... app.useGlobalFilters(new HttpFilter()); } -
module
import { APP_FILTER } from '@nestjs/core'; import { HttpFilter } from './common/filter/http.filter'; @Module({ providers: [ { provide: APP_FILTER, useClass: HttpFilter, }, ], })} export class AppModule {} -
controller
import { Get, HttpException, HttpStatus, UseFilters } from '@nestjs/common'; import { HttpFilter } from 'src/common/filter/http.filter'; @UseFilters(HttpFilter) // 使用 UseFilters裝飾器綁定 filter @Controller('mock') export class MockController { @Get() async getList() { throw new HttpException( '主動拋出友好的500錯誤', HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, ); } } -
method
import { Get, HttpException, HttpStatus, UseFilters } from '@nestjs/common'; import { HttpFilter } from 'src/common/filter/http.filter'; @Controller('mock') export class MockController { @UseFilters(HttpFilter) // 使用 UseFilters裝飾器綁定 filter @Get() async getList() { throw new HttpException( '主動拋出友好的500錯誤', HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, ); } }
以上不同的綁定方式作用的返回也不一樣,應以實際的情況進行綁定,一般綁定到全局即可
當再次訪問路由後,將會變成我們自定義的錯誤格式:
{
"code": 500,
"message": "主動拋出友好的500錯誤",
"timestamp": "2020-07-22T06:24:49.140Z"
}Pipe
pipe是nestjs中的管道技術主要用來對請求的數據進行轉換和類型驗證
基本使用
import {
Controller,
Get,
ParseIntPipe,
Query,
} from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
@Get()
async getList(
// @Query('id', ParseIntPipe)
@Query('id', new ParseIntPipe({ optional: true })) // id可選,如果不傳id不會報錯
id: number,
) {
console.log(typeof id); // number
return id;
}
}
綁定pipe
以上pipe綁定到了參數上,除了參數外,還支持nestjs上下文以外、module、controller、method
-
nestjs上下文以外
app.useGlobalPipes( // 類型轉換和驗證pipe(常用) new ValidationPipe({ // 刪除發送過來的不存在的屬性 whitelist: true, // 將傳過來的類型轉換為定義的類型,轉換為 string、number、boolean和自定義類型 transform: true, transformOptions: { enableImplicitConversion: true, // 隱式轉換 }, }), ); -
module
import { Module, ValidationPipe } from '@nestjs/common'; import { APP_PIPE } from '@nestjs/core'; @Module({ providers: [ { provide: APP_PIPE, useValue: new ValidationPipe({ // 刪除前端發送過來的不存在的屬性 whitelist: true, // 將傳過來的類型轉換為定義的類型,轉換為 string、number、boolean和自定義類型 transform: false, transformOptions: { enableImplicitConversion: true, // 隱式轉換 }, }), }, ], }) export class CommonModule {} -
controller
import { Controller, UsePipes, ValidationPipe } from '@nestjs/common'; @UsePipes(new ValidationPipe({}), ParseIntPipe /* ... */) @Controller('mock') export class MockController {}controller、method都使用
@UsePipes裝飾器進行包裝 -
method
import { Controller, UsePipes, ValidationPipe } from '@nestjs/common'; @Controller('mock') export class MockController { @UsePipes(new ValidationPipe({}), ParseIntPipe /* ... */) @Get(':id') async getOne(@Param('id') id: number) { return id; } } -
param
import { Controller, Get, Param, Body } from '@nestjs/common'; @Controller('mock') export class MockController { @Get(':id') async getOne( @Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number, // 轉換為 number @Body(new ParseArrayPipe({ optional: true })) users: string[], // 轉換為string[] ) { cosnole.log(id, users); return id; } }
內置pipe
ValidationPipeParseIntPipeParseFloatPipeParseBoolPipe- 更多點擊查看...
自定義pipe
除了內置的pipe外,nestjs中還支持自定義pipe,要實現自定義pipe需要實現PipeTransform類中的transform方法
# 使用cli生成pipe
➜ nest g pipe RequireId --no-spec一個需要ID參數的Pipe:
import {
ArgumentMetadata,
HttpException,
HttpStatus,
Injectable,
PipeTransform,
} from '@nestjs/common';
@Injectable()
export class RequiredId implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: any, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) {
const id = typeof value === 'object' ? value?.id : value;
if (isNaN(parseInt(id))) {
// 錯誤的客户端請求
throw new HttpException('Id must be number', HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
return parseInt(id);
}
}使用:
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
@Delete(':id')
async deleteOne(@Query(RequiredId) id: any) {
console.log(id, typeof id);
return true;
}
}Class-transformer、class-validator
nest中可以使用class-transformer、class-validator結合ValidationPipe進行數據格式轉換和驗證。更多使用詳情查看這裏以及響應序列化
創建數據模型:
// dto/pagination.dto.ts
import { Transform, Type } from 'class-transformer';
import { IsNumber, IsOptional, IsPositive } from 'class-validator';
export class PaginationQueryDto {
@IsOptional() // 可選
@Transform((val) => parseInt(val.value || 10)) // 對傳入的值進行轉換,轉換失敗默認10
@IsPositive() // 大於0 // 判斷必須大於0
@Type(() => Number) // 類型為number
@IsNumber() // number
readonly limit: number = 10;
@IsOptional()
@Transform((val) => parseInt(val.value || 1))
@IsPositive() // 大於0
@Type(() => Number)
@IsNumber()
readonly offset: number = 1;
}配置validationPipe:
import { Module, ValidationPipe } from '@nestjs/common';
import { APP_PIPE } from '@nestjs/core';
@Module({
providers: [
{
provide: APP_PIPE,
useValue: new ValidationPipe({
// 刪除發送過來的不存在的屬性
whitelist: true,
// 將傳過來的類型轉換為定義的類型,轉換為 string、number、boolean和自定義類型
transform: false,
transformOptions: {
enableImplicitConversion: true, // 隱式轉換,'1' ===> 1
},
}),
},
],
})
export class CommonModule {}在路由中使用:
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
@Get()
// 請求時會對query的數據進行驗證,如果不符合 PaginationQueryDto 將會報異常
async getList(@Query() query: PaginationQueryDto) {
console.log(query);
return query;
}
}這樣對於請求時不合法的數據類型將會自動返回錯誤,如傳入-1時:
{
"code": 400,
"message": [
"limit must be a positive number" // 必須是個正整數
],
"error": "Bad Request",
"timestamp": "2020-07-22T07:50:32.472Z"
}Guard
guard是nestjs提供給應用程序進行鑑權守衞的手段,取代傳統的middleware鑑權處理。<u>guard在所有的middleware後執行,但會在所有pipe、interceptor前執行</u>
基本使用
一個guard需要實現CanActivate類的canActivate方法,當返回結果為true時表示有權限,反之沒權限
# 使用ci生成guard
➜ nest g guard Authentication --no-spec定義路由鑑權守衞:
import { CanActivate, ExecutionContext, Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Reflector } from '@nestjs/core';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
import { AuthenticationRouteKey } from '../decorator';
import { Request } from 'express';
/**
* 控制某個路由守衞
*/
@Injectable()
export class AuthenticationRouteGuard implements CanActivate {
// 獲取元數據
constructor(private readonly reflector: Reflector) {}
// 實現 canActivate 方法
canActivate(
context: ExecutionContext,
): boolean | Promise<boolean> | Observable<boolean> {
// 這裏獲取定義的元數據,因為這裏的guard是針對某個路由的,元數據是在method上的,所以使用 getHandler 方法
const isRouteAuthenrication = this.reflector.get(
AuthenticationRouteKey,
context.getHandler(),
);
// 判斷當前請求路由不需要鑑權直接放行
if (!isRouteAuthenrication) return true;
// TODO: 需要鑑權的這裏簡單的使用 authorization 頭值是否等於route進行判斷
// 通常獲取用户信息進行鑑權
const ctx = context.switchToHttp();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
const key = request.headers.authorization;
return key === 'route';
}
}使用守衞:
import { Controller, Get, Param, UseGuards } from '@nestjs/common';
import { RegisterAuthenticationRoute } from 'src/common/decorator';
import { AuthenticationRouteGuard } from 'src/common/guard/authentication-route.guard';
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
@RegisterAuthenticationRoute() // 設置元數據
@UseGuards(AuthenticationRouteGuard) // 設置路由守衞
@Get('user/:id')
getUserInfo(@Param('id') userId: string) {
console.log(userId);
return {
name: 'Jack',
age: 10,
sex: 1,
};
}
}
// 設置元數據 RegisterAuthenticationRoute
export const AuthenticationRouteKey = 'Authentication-route-register';
export const RegisterAuthenticationRoute = () =>
SetMetadata(AuthenticationRouteKey, true); // 主要是使用setMetadata方法
關於setMetadata的使用點擊這裏查看文檔瞭解更多
綁定guard
上面使用@UseGuards在方法上進行了綁定,除此之外可以在Controller、module、上下文以外進行綁定,這裏不再演示了
Interceptor
interceptor是nestjs提供的攔截器,通常用來對請求和響應數據進行攔截改造,很常見的axios對響應數據進行攔截處理,這裏也通常對響應數據做一次包裝進行返回,這樣就可以形成統一的格式
# 使用cli生成interceptor
➜ nest g interceptor beauty-response --no-spec自定義interceptor
自定以interceptor需要實現NestInterceptor類的intercept方法,該方法返回一個Observable類型數據,關於更多RxJS的使用,請查看相關文檔
定義一個包裝響應數據格式的攔截器:
import {
CallHandler,
ExecutionContext,
Injectable,
NestInterceptor,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { Response } from 'express';
import { Observable, map } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable()
export class BeautyResponseInterceptor implements NestInterceptor {
intercept(context: ExecutionContext, next: CallHandler): Observable<any> {
const ctx = context.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<Response>();
const contentType = response.getHeader('Content-Type');
const isAttachment = response.getHeader('Content-Disposition');
const isJSON = /(text|json)/i.test(contentType as string);
// 流內容直接返回
if ((contentType && !isJSON) || isAttachment) {
return next.handle();
} else {
return next.handle().pipe(
// 這裏響應內容包裹了一層
map(data => ({
code: 200,
data,
})),
);
}
}
}綁定interceptor
interceptor也是支持nestjs上下文外全局綁定、module、controller、method等幾種方式綁定,這裏簡單演示module綁定
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { APP_INTERCEPTOR } from '@nestjs/core';
import { BeautyResponseInterceptor } from 'src/common/interceptor/beauty-response.interceptor';
@Module({
privoders: [
{
provide: APP_INTERCEPTOR,
useClass: BeautyResponseInterceptor,
},
]
})
export class CommonModule {}
@Controller('api')
class TestController {
@Get('users')
getUsers() {
return [1, 2, 3]; // 返回數據
}
}現在當訪問GET: /api/users時會以我們定義的格式返回:
{
"code": 200,
"data": [1, 2, 3]
}是不是體會到了NestJS的強大了
Logger
logger的使用這裏不做解釋,比較簡單可以自行翻閲文檔
版本控制
有時候需要兩種版本api同時存在,這時候可以使用版本來標識不同的路由。nest提供瞭解決不同版本的方案
:::warning 温馨提示
對於前端來講這種api版本場景可能很難遇到,此功能瞭解使用即可
:::
啓用版本控制:
// main.ts
// 版本控制
app.enableVersioning({
type: VersioningType.URI, // 使用URL版本控制 v1、v2、v3
});版本控制支持多種形式的版本設置:url、header、media、自定義等等,這裏使用URL來控制
基本使用
這裏定義兩個版本的方法來模擬不同版本
import { Controller, Version, Get } from '@nestjs/common';
// @Version('2') // 也可以對controller進行版本區分
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
// 版本控制
@Version('1') // path: /v1/mock/version
@Get('version')
getVersion1() {
return 'version1';
}
@Version('2') // path: /v2/mock/version
@Get('version')
getVersion2() {
return 'version2';
}
}打開終端分別訪問接口:
➜ ~ curl http://localhost:3000/v1/mock/version
{"code":200,"data":"version1"}
➜ ~ curl http://localhost:3000/v2/mock/version
{"code":200,"data":"version2"}自定義版本
自定義版本就是獲取版本的邏輯是如何的,以下是官方通過custom-versioning-field頭信息獲取版本的自定義版本提取器
const extractor = (request: FastifyRequest): string | string[] =>
[request.headers['custom-versioning-field'] ?? '']
.flatMap(v => v.split(','))
.filter(v => !!v)
.sort()
.reverse();
app.enableVersioning({
type: VersioningType.CUSTOM,
extractor, // 自定義提取器
});任務調度
nest中提供了任務調度系統允許我們在固定的時間或時間間隔執行任務方法,任務調度可以很好解決一些需要定時執行的任務
安裝
➜ yarn add @nestjs/schedule
➜ yarn add @types/cron -D模塊註冊
要使用任務調度需要導入任務調度模塊
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { TaskScheduleController } from './task-schedule.controller';
import { ScheduleModule } from '@nestjs/schedule';
@Module({
imports: [ScheduleModule.forRoot()], // 導入 ScheduleModule
controllers: [TaskScheduleController],
})
export class TaskScheduleModule {}註冊調度任務
調度系統支持:Cron具體時間、Interval間隔時間、Timeout延時時間幾種調度任務,其中cron更常用
-
cron任務
import { Controller } from '@nestjs/common'; import { Cron } from '@nestjs/schedule'; @Controller('schedule') export class TaskScheduleController { // 週一到週五早上11:30執行 @Cron('0 30 11 * * 1-5', { name: 'cronTime', // 名字 timeZone: 'Asia/Shanghai', // 時區 }) handleCron() { console.log('cron called...'); } }Cron的時間是cron表達式
* * * * * * | | | | | | | | | | | day of week | | | | months | | | day of month | | hours | minutes seconds (optional) -
Interval間隔任務
interval間隔任務其實就是使用setInterval定義的任務
import { Controller } from '@nestjs/common'; import { Interval } from '@nestjs/schedule'; @Controller('schedule') export class TaskScheduleController { @Interval('interval', 1000 * 60 * 5) // 間隔5分鐘執行一次 handleInterval() { console.log('interval called'); } } -
Timeout延時任務
timeout延時任務本質也是使用setTimeout定義的任務
import { Controller } from '@nestjs/common'; import { Timeout } from '@nestjs/schedule'; @Controller('schedule') export class TaskScheduleController { @Timeout('timeout', 1000 * 60) // 60s 後執行 handleTimeout() { console.log('timeout called'); } }
動態調度
任務調度系統同時也提供了動態操作任務的功能,通常的業務中我們也會對的某個任務進行動態執行和註冊,如請求某個接口新建一個任務或立即執行
任務調度的動態操作需要通過SchedulerRegistry進行,若要在controller中使用需要在構造器中注入
import { Controller, Get, Post } from '@nestjs/common';
import { SchedulerRegistry } from '@nestjs/schedule';
@Controller('mock')
export class MockController {
// 注入 SchedulerRegistry
constructor(private readonly scheduleRegistry: SchedulerRegistry) {}
}-
動態處理cron任務
@Controller('mock') export class MockController { // 注入 SchedulerRegistry constructor(private readonly scheduleRegistry: SchedulerRegistry) {} // 獲取調度任務 @Get('schedule/cron') handleScheduleCron() { // 獲取指定的cron,並停止 const job = this.scheduleRegistry.getCronJob('cronTime'); job.stop(); console.log('handleSchedule'); } // 添加調度任務 @Post('schedule/cron') handleAddScheduleCron() { const job = new CronJob('* * * * * *', () => console.log('新增的調度任務執行。。。'), ); this.scheduleRegistry.addCronJob('addCron', job); job.start(); // 5s 後停止並刪除添加的任務 setTimeout(() => { job.stop(); this.scheduleRegistry.deleteCronJob('addCron'); }, 5000); } } -
動態處理Interval任務
@Controller('mock') export class MockController { // 注入 SchedulerRegistry constructor(private readonly scheduleRegistry: SchedulerRegistry) {} // 獲取間隔任務 並取消 @Get('schedule/interval') handleScheduleInterval() { // 獲取指定的cron,並停止 const job = this.scheduleRegistry.getInterval('interval'); clearInterval(job); } // 添加間隔任務 @Post('schedule/interval') handleAddScheduleInterval() { const cb = () => console.log('新增的間隔任務...'); const interval = setInterval(cb, 1000); this.scheduleRegistry.addInterval('addInterval', interval); const intervalId = this.scheduleRegistry.getInterval('addInterval'); // 5s後取消並刪除 setTimeout(() => { clearInterval(intervalId); this.scheduleRegistry.deleteInterval('addInterval'); }, 5000); } } -
動態處理Timeout任務
@Controller('mock') export class MockController { // 注入 SchedulerRegistry constructor(private readonly scheduleRegistry: SchedulerRegistry) {} // 獲取延時任務 並取消 @Get('schedule/timeout') handleScheduleTimeout() { // 獲取指定的cron,並停止 const job = this.scheduleRegistry.getTimeout('timeout'); clearTimeout(job); } // 添加延時任務 @Post('schedule/timeout') handleAddScheduleTimeout() { const cb = () => console.log('新增的延時任務...'); const timeout = setTimeout(cb, 2000); this.scheduleRegistry.addTimeout('addTimeout', timeout); const timeoutId = this.scheduleRegistry.getTimeout('addTimeout'); setTimeout(() => clearTimeout(timeoutId), 5000); } }
總結
NestJS 是一個基於 Node.js 平台的現代化 Web 框架,它結合了 TypeScript、面向對象編程的思想和函數式編程的思想,提供了一種高效、可擴展的方式來構建可維護的 Node.js 應用程序
由於圖片和格式解析問題,可前往 閲讀原文